
A SUBOPTIMAL FAULT-TOLERANT DUAL CONTROLLER IN
MULTIPLE MODEL FRAMEWORK
Ivo Punˇcoch´aˇr and Miroslav
ˇ
Simandl
Faculty of Applied Sciences, University of West Bohemia, Univerzitn´ı 8, Plzeˇn, Czech Republic
Keywords:
Fault-tolerant control, Fault detection, Optimal control, Dual control, Stochastic systems.
Abstract:
The paper focuses on the design of a suboptimal fault-tolerant dual controller for stochastic discrete-time
systems. Firstly a general formulation of the active fault detection and control problem that covers several
special cases is presented. One of the special cases, a dual control problem, is then considered throughout
the rest of the paper. It is stressed that the designed dual controller can be regarded as a fault-tolerant dual
controller in the context of fault detection. Due to infeasibility of the optimal fault-tolerant dual controller for
general non-linear system, a suboptimal fault-tolerant dual controller based on rolling horizon technique for
jump Markov linear Gaussian system is proposed and illustrated by means of a numerical example.
1 INTRODUCTION
Fault detection is an important part of many auto-
matic control systems and it has attracted a lot of at-
tention during recent years because of increasing re-
quirements on safety, reliability and low maintenance
costs. An elementary aim of fault detection is early
recognition of faults, e.i. undesirable behaviors of an
observed system.
The very earliest fault detection methods use ad-
ditional sensors for detecting faults. These meth-
ods are simple and still used in safety-critical sys-
tems. A slightly better fault detection methods uti-
lize some basic assumptions on measured signals and
therefore they are usually called signal based meth-
ods (Isermann, 2005). To further improve fault detec-
tion, more complex methods called model based were
developed (Basseville and Nikiforov, 1993).
Except for a few situations were the primary ob-
jective is the fault detection itself, it usually comple-
ments a control system where the quality of control is
of main concern. This fact has stimulated research in
area of so called fault-tolerant control. Fault-tolerant
control methods can be divided into two basic group:
passive fault-tolerant control and active fault-tolerant
control methods (Blanke et al., 2003). Passive fault-
tolerant control methods design a controller that is ro-
bust with respect to considered faults and thus an ac-
ceptable deterioration of control quality is caused by
the considered faults. On the other hand, active fault-
tolerant control methods try to estimate faults and re-
configure a controller in order to retain desired closed
loop behavior of a system.
The mentioned fault detection methods and fault-
tolerant approaches usually use available measure-
ments passively as shown at the top of Fig. 1, where a
passive detector uses inputs u
k
and measurements y
k
for generating decisions d
k
. In the case of stochastic
systems further improvement can be obtained by ap-
plying a suitable input signal, see e.g. (Mehra, 1974)
for application in parameter estimation problem. This
idea leads to so-called active fault detection which is
depicted at the bottom of Fig. 1. The active detector
and controller generates, in addition to a decision d
k
,
an input signal u
k
that controls and simultaneously ex-
cites the system and thus improves fault detection and
control quality. Note, that the terms passive and ac-
tive have different meaning than in the fault-tolerant
control literature.
The active fault detection is a developing area.
The first attempt to formulate and solve the active
fault detection problem can be found in (Zhang,
1989), where the sequential probability ratio test was
used for determining a valid model and an auxiliary
input signal was designed to minimize average num-
ber of samples. More general formulation of active
fault detection was proposed in (Kerestecio˘glu, 1993).
An active fault detection for systems with determinis-
tic bounded disturbances was introduced in (Camp-
bell and Nikoukhah, 2004). A unified formulation of
active fault detection and control for stochastic sys-
tems that covers several special cases was proposed
93
Pun
ˇ
cochá
ˇ
r I. and Šimandl M. (2010).
A SUBOPTIMAL FAULT-TOLERANT DUAL CONTROLLER IN MULTIPLE MODEL FRAMEWORK.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 93-98
DOI: 10.5220/0002935300930098
Copyright
c
SciTePress

in (
ˇ
Simandl and Punˇcoch´aˇr, 2009). One of these spe-
cial cases is the optimal dual control problem that has
not been elaborated in the context of that general for-
mulation, yet.
Therefore, the aim of this paper is to examine the
dual control problem in the context of fault detection
problem. The general formulation for the optimal
dual control problem is adopted from (
ˇ
Simandl and
Punˇcoch´aˇr, 2009) and an optimal fault-tolerant con-
troller that uses idea of active probing for improving
the quality of control is designed. Because of infeasi-
bility of the optimal fault-tolerant dual controller for a
general nonlinear stochastic system, the systems that
can be described using jump linear Gaussian multiple
models are considered and the rolling horizon tech-
nique is used for obtaining an approximate solution.
The paper is organized as follows. A general for-
mulation of active fault detection and control is given
in Section 2 and the design of a fault-tolerant dual
controller is introduced as a special case of the gen-
eral formulation. The optimal fault-tolerant dual con-
troller obtained using the closed loop information pro-
cessing strategy is presented in Section 3. Section 4
is devoted to the description of a system using mul-
tiple models and the relations for state estimation are
given. Finally, a suboptimal fault-tolerant dual con-
troller based on rolling horizon technique is presented
in Section 5.
System
Active detector
and
controller
y
d
u
System
Passive
detector
y
d
u
Controller
A) Passive detection and control system
B) Active detection and control system
k
k
k
k
k
k
Figure 1: Block diagrams of the passive detection and con-
trol system and the active detection and control system.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
In this section a general formulation of the active fault
detection and control problem is adopted and then a
fault-tolerant dual control problem is specified as a
special case of the general formulation.
2.1 System
The problem is considered on the finite horizon F. Let
an observed system be described at each time k ∈ T =
{0,...,F} by the state space discrete-time nonlinear
stochastic model
x
k+1
= f
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,u
k
,w
k
), (1)
µ
k+1
= g
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,u
k
,e
k
), (2)
y
k
= h
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,v
k
), (3)
where nonlinear vector functions f
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,u
k
,w
k
),
g
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,u
k
,e
k
) and h
k
(x
k
,µ
k
,v
k
) are known. The
input and output of the system are denoted as u
k
∈
U
k
⊆ R
n
u
and y
k
∈ R
n
y
, respectively. The subset
U
k
can be continuous or discrete and it determines
admissible values of the input u
k
. The unmeasured
state
¯
x
k
=
x
T
k
,µ
T
k
T
consists of variables x
k
∈ R
n
x
and µ
k
∈ M ⊆ R
n
µ
. The variable x
k
is the part of
the state that should be driven by the input u
k
to a de-
sirable value or region. The variable µ
k
carries infor-
mation about faults. The variable µ
k
can be a vector
representing fault signals or a scalar that determines
the mode of system behavior. The initial state
¯
x
0
is
described by the known probability density function
(pdf) p(
¯
x
0
) = p(x
0
) p(µ
0
). The pdfs p(w
k
), p(e
k
)
and p(v
k
) of the white noise sequences {w
k
}, {e
k
}
and {v
k
} are known. The initial state
¯
x
0
and the noise
sequences {w
k
}, {e
k
}, {v
k
} are mutually indepen-
dent.
2.2 Active Fault Detector and
Controller
In the general formulation, the goal is to design a dy-
namic causal deterministic system that uses complete
available information to generate a decision about
faults and an input to the observed system. Such a
system can be described at each time step k ∈ T by
the following relation
d
k
u
k
=
σ
k
I
k
0
γ
k
I
k
0
= ρ
k
I
k
0
, (4)
where σ
k
I
k
0
and γ
k
I
k
0
are some unknown vec-
tor functions which should be designed to obtain an
active fault detector and controller. The complete
available information, which has been received up to
the time k, is stored in the information vector I
k
0
=
h
y
k
0
T
,u
k−1
0
T
,d
k−1
0
T
i
T
. The notation y
j
i
represents a
sequence of the variables y
k
from the time step i up to
the time step j. If i > j then the sequence y
j
i
is empty
and the corresponding variable is simply left out from
an expression. According to this rule, the information
vector for time k = 0 is defined as I
0
0
= I
0
= y
0
.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
94

2.3 Criterion
Analogously to the optimal stochastic control prob-
lem (Bar-Shalomand Tse, 1974), the design of the op-
timal active detector and controller is based on mini-
mization of a criterion. A general criterion that penal-
izes wrong decisions d
k
and deviations of variables x
k
and u
k
from desired values over the finite horizon is
the following
J
ρ
F
0
= E
L
x
F
0
,µ
F
0
,u
F
0
,d
F
0
, (5)
where E{·} is the expectation operator with respect to
all included random variables and L
x
F
0
,µ
F
0
,u
F
0
,d
F
0
is a non-negative real-valued cost function. Due to
practical reasons, the cost function is considered in
the following additive form
L
x
F
0
,µ
F
0
,u
F
0
,d
F
0
=
F
∑
k=0
α
k
L
d
k
(d
k
,µ
k
) + (1− α
k
)L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
),
(6)
where L
d
k
(µ
k
,d
k
) is a non-negative real-valued cost
function representing the detection aim, the non-
negative real-valued cost function L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) ex-
presses the control aim, and the coefficient α
k
belong-
ing to the closed interval [0,1] weights between these
two aims. In order to regard the function L
d
k
(µ
k
,d
k
)
as a meaningful cost function, it should satisfy the
inequality L
d
k
(µ
k
,µ
k
) ≤ L
d
k
(µ
k
,d
k
) for all µ
k
∈ M ,
d
k
∈ M , d
k
6= µ
k
at each time step k ∈ T , and the
strict inequality has to hold at least at one time step.
The sequence of the functions ρ
F∗
0
= [ρ
∗
0
,ρ
∗
1
,...,ρ
∗
F
]
given by minimization of (5) specifies the optimal ac-
tive detector and controller. The minimization of the
criterion (5) can be solved by using three different in-
formation processing strategies (IPS’s) (
ˇ
Simandl and
Punˇcoch´aˇr, 2009), but only the closed loop (CL) IPS
is considered in this paper because of its superiority.
2.4 Fault-tolerant Dual Controller
The introduced general formulation covers several
special cases that can be simply derived by choos-
ing a particular weighting coefficient α
k
and fixing
the function σ
k
I
k
0
or the function γ
k
I
k
0
in advance.
This paper is focused on the special case where only
control aim is considered, i.e. the coefficient α
k
is set
to zero for all k ∈ T and none of the functions σ
k
I
k
0
and γ
k
I
k
0
are specified in advance. The cost function
L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) is considered to be a quadratic cost func-
tion
L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) = [x
k
− r
k
]
T
Q
k
[x
k
− r
k
] + u
T
k
R
k
u
k
, (7)
where Q
k
is a symmetric positive semidefinite matrix,
R
k
is a symmetric positive definite matrix, and r
k
is a
reference signal. It is considered that the reference
signal r
k
is known for the whole horizon in advance.
Since decisions are no longer penalized in the cri-
terion, the function σ
k
I
k
0
can not be determined by
the minimization and the aim is to find only functions
γ
k
I
k
0
for all k. The resulting controller will steer the
system in such a way that the criterion is minimized
regardless the faults µ
k
. Moreover the controller can
exhibit the dual property because the CL IPS is used.
Due to these two facts the controller can be denoted
as the fault-tolerant dual controller.
3 DESIGN OF FAULT-TOLERANT
DUAL CONTROLLER
This section is devoted to the optimal fault-tolerant
dual controller design. The minimization of the cri-
terion (5) using the CL IPS can be solved by the dy-
namic programming where the minimization is solved
backward in time (Bertsekas, 1995).
The optimal fault-tolerant dual controller is ob-
tained by solving the following backward recursive
equation for time steps k = F,F − 1,...,0
V
∗
k
y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
=
min
u
k
∈U
k
E
n
L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) +V
∗
k+1
y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
y
k
0
,u
k
0
o
,
(8)
where E{·|·} stands for the conditional expectation
operator and the Bellman function V
∗
k
y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
is
the estimate of the minimal cost incurred from time
step k up to the final time step F given the input-
output data
y
k
0
,u
k
0
. The initial condition for the
backward recursiveequation (8) isV
∗
F+1
= 0 and it can
be shown that the optimal value of the criterion (5) is
J
∗
= J
ρ
F∗
0
= E
V
∗
0
(y
0
)
. Obviously, the optimal
input signal u
∗
k
is given as
u
∗
k
= γ
∗
k
y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
= arg
min
u
k
∈U
k
E
n
L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) +V
∗
k+1
y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
y
k
0
,u
k
0
o
,
(9)
where the function γ
∗
k
(I
k
0
) represents the optimal fault-
tolerant dual controller. The pdf’s p(
¯
x
k
|I
k
0
,u
k
,d
k
)
and p(y
k+1
|I
k
0
,u
k
,d
k
) needed for the evaluation of the
conditional expectation can be obtained using nonlin-
ear filtering methods. Note that there isn’t any closed
form solution to equations (8) and (9). Therefore ap-
proximate techniques have to be used to get at least
a suboptimal solution. The selection of a suitable ap-
proximation depends on a particular system descrip-
tion and estimation method.
A SUBOPTIMAL FAULT-TOLERANT DUAL CONTROLLER IN MULTIPLE MODEL FRAMEWORK
95

4 MULTIMODEL APPROACH
In the case of a general nonlinear system the state esti-
mation pose a complex functional problem that has to
be solved using approximate techniques. One of the
attractive method is based on the assumption that the
system exhibits distinct modes of behavior. Such sys-
tems can be encountered in various field of interests
including maneuvering target tracking (Bar-Shalom
et al., 2001), abrupt fault detection (Zhang, 1989) and
adaptive control (Athans et al., 2006). In this paper,
the multimodel approach is used as one step towards
the design of feasible fault-tolerant dual controller.
Henceforth, it is assumed that the variable µ
k
is a scalar index from the finite discrete set M =
{1,2, . . . , N} that determines the model valid at time
step k. If the exact behavior modes of the system are
not known, the set M can be determined by using ex-
isting techniques, see e.g. (Athans et al., 2006).
It is considered that the system can be described
at each time k ∈ T as
x
k+1
=A
µ
k
x
k
+ B
µ
k
u
k
+ G
µ
k
w
k
,
y
k
=C
µ
k
x
k
+ H
µ
k
v
k
(10)
where the meaning of the variables x
k
, y
k
, u
k
, w
k
and
v
k
is the same as in (1) to (3). The set U
k
is consid-
ered to be discrete. The pdf’s of the noises w
k
and
v
k
are Gaussian with zero-mean and unit variance.
The scalar random variable µ
k
∈ M denotes the in-
dex of the correct model at time k. Random model
switching from model i to model j is described by
the knownconditionaltransition probability P(µ
k+1
=
j|µ
k
= i) = P
ij
. Obviously, the decision d
k
∈ M is
now scalar too. Known matrices A
µ
k
, B
µ
k
, G
µ
k
, C
µ
k
,
and H
µ
k
have appropriate dimensions.
The conditional pdf of the state x
k
is a weighted
sum of Gaussian distributions
p
x
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
=
∑
µ
k
0
p
x
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
,µ
k
0
P
µ
k
0
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
,
(11)
where Gaussian conditional pdf p(x
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
,µ
k
0
) can
be computed using a Kalman filter that correspondsto
the model sequence µ
k
0
. The pdf P(µ
k
0
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
) can be
obtained recursively as
P
µ
k
0
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
=
p
y
k
|y
k−1
0
,u
k−1
0
,µ
k
0
c
× P(µ
k
|µ
k−1
)P
µ
k−1
0
|y
k−1
0
,u
k−2
0
,
(12)
where c is a normalization constant. The computation
of probability of the terminal model P(µ
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
)
and the predictive conditional pdf p(y
k+1
|y
k
0
,u
k
0
) is
straightforward.
Unfortunately, as the number of model sequences
exponentially increases with time, memory and com-
putational demands become unmanageable. To over-
come this problem several techniques based on prun-
ing or merging of Gaussian sum have been proposed.
A technique that merges model sequences with the
same terminal sequence µ
k
k−l
is used here. The prob-
ability of the terminal sequence of models µ
k
k−l
is
P
µ
k
k−l
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
=
∑
µ
k−l−1
0
P
µ
k
0
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
(13)
and the filtering density that has the form of a Gaus-
sian sum
p
x
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
,µ
k
k−l
=
∑
µ
k−l−1
0
P
µ
k
0
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
P
µ
k
k−l
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
× p
x
k
|y
k
0
,u
k−1
0
,µ
k
0
(14)
is replaced by a Gaussian distribution in such a way
that the first two moments, i.e. mean value and co-
variance matrix, of the variable x
k
remain unchanged.
5 FEASIBLE ALGORITHM
BASED ON ROLLING
HORIZON
Even if the state and output pdfs are known, the
backward recursive relation (8) can not be solved an-
alytically because of intractable integrals. A sys-
tematic approach to forward solution of the back-
ward recursive relation (8) based on the stochastic
approximation method is presented e.g. in (Bayard,
1991). A simple alternative approach is represented
by the rolling horizon technique, where the optimiza-
tion horizon is truncated and terminal cost-to-go of
such truncated optimization horizon is replaced by
zero. The length F
o
> 0 of truncated horizon should
be as short as possible to save computational demands
but on other hand it has to preserve dependence of
value of the minimized criterion on the input signal
u
k
. In this paper the optimization horizon F
o
= 3 will
be considered to simplify computations. The cost-
to-go function V
∗
k+3
y
k+3
0
,u
k+2
0
is replaced by zero
value. Then the input u
a
k+2
= 0 and the cost-to-go
function V
a
k+2
y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
is
V
a
k+2
y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
= (15)
E
n
[x
k+2
− r
k+2
]
T
Q
k+2
[x
k+2
− r
k+2
]|y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
o
.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
96

The input u
k+2
is zero because it can not influ-
ence the value of the criterion on the optimiza-
tion horizon and the matrix R
k+2
is positive defi-
nite. Note, that the value of the cost-to-go func-
tion V
a
k+2
y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
can be computed analytically
based on the first two moments of the state x
k+2
given by the pdf p
x
k+2
|y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
. The input
u
a
k+1
= −W
−1
D and the cost-to-go function at time
step k + 1 is
V
a
k+1
y
k+1
0
,u
k+1
0
=
E
n
[x
k+1
− r
k+1
]
T
Q
k+1
[x
k+1
− r
k+1
]|y
k+2
0
,u
k+1
0
o
+ K − D
T
W
−1
D, (16)
where
W = R
k+1
+
∑
µ
k+1
B
T
µ
k+1
Q
k+2
B
µ
k+1
P
µ
k+1
|y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
,
(17)
D =
∑
µ
k+1
B
T
µ
k+1
Q
k+2
A
µ
k+1
ˆ
x
k+1
(µ
k+1
) − r
k+2
×P
µ
k+1
|y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
,
(18)
K =
∑
µ
k+1
(
A
µ
k+1
ˆ
x
k+1
(µ
k+1
) − r
k+2
T
Q
k+2
×
A
µ
k+1
ˆ
x
k+1
(µ
k+1
) − r
k+2
+ Tr
Q
k+2
(A
µ
k+1
P
k+1
(µ
k+1
)A
T
µ
k+1
+ G
µ
k+1
G
T
µ
k+1
)
)
× P
µ
k+1
|y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
. (19)
The mean
ˆ
x
k+1
(µ
k+1
) = E
n
x
k+1
|y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
,µ
k+1
o
and
the corresponding covariance matrix P
k+1
(µ
k+1
) can
be obtained from estimation algorithm. If the input
u
k+1
was used at time step k + 1 the resulting con-
troller would be cautious because it would respect un-
certainty. The input at time step k is given as
u
a
k
= min
u
k
∈U
k
E
n
L
c
k
(x
k
,u
k
) +V
a
k+1
y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
y
k
0
,u
k
0
o
.
The expectation of the cost function V
a
k+1
y
k+1
0
,u
k
0
with respect to y
k+1
seems to be computationally in-
tractable. Therefore the expectation and subsequent
minimization over discrete set U
k
are performed nu-
merically.
6 NUMERICAL EXAMPLE
The proposed fault-tolerant dual controller is com-
pared with a cautious (CA) controller and a heuris-
tic certainty equivalence (HCE) controller. The CA
controller is obtained when just one-step look ahead
policy is used and it takes uncertainties into account
but lacks probing. The HCE controller is based on
the assumption that the certainty equivalence princi-
ple holds even it is not true and inputs are determined
as solutions to the problem where all uncertain quan-
tities were fixed at some typical values.
Although the relative performance of three subop-
timal controllers can differ in dependence on a par-
ticular system, the dual controller should outperform
HCE and CA controllers in problems where uncer-
tainty plays a major role. This numerical example il-
lustrates a well known issue of pure CA controllers
called ’turn-off’ phenomenon, where the CA con-
troller refuses to control a system because of large
uncertainty. The initial uncertainty is quite high, but
once it is reduced through measurements the problem
becomes almost certainty equivalent. It is the reason
why the HCE controller performs quite well in this
particular example.
The quality of control is evaluated by M Monte
Carlo runs. The value of the cost L for particular
Monte Carlo simulation is denoted L
i
and the value of
the criterion J is estimated as
ˆ
J = 1/M
∑
M
i=1
L
i
. Vari-
ability among Monte Carlo simulations is expressed
by var{L} = 1/(M − 1)
∑
i=1
(L
i
−
ˆ
J)
2
and the qual-
ity of the criterion estimate
ˆ
J is expressed by var{
ˆ
J}
which is computed using bootstrap technique.
The detection horizon F = 30 is considered and
the parameters of a single input single output scalar
system are given in Table 1. The initial probabilities
are P(µ
0
= 1) = P(µ
0
= 2) = 0.5, the transition prob-
abilities are P
1,1
= P
2,2
= 0.9, P
1,2
= P
2,1
= 0.1, and
parameters of Gaussian distribution are ˆx
′
0
= 1 and
P
′
x,0
= 0.01. The discrete set of admissible values of
input u
k
is chosen to be U
k
= {−3,−2.9,...,2.9,3}
for all k ∈ T . The reference signal is the square wave
with peaks of ±0.4 and the period 13 steps and the
weighting matrices in the cost function are chosen to
be Q
k
= 1 and R
k
= 0.001 for all time steps.
Table 1: Parameters of the controlled system.
µ
k
a
k
(µ
k
) b
k
(µ
k
) g
k
(µ
k
) c
k
(µ
k
) h
k
(µ
k
)
1 0.9 0.1 0.01 1 0.05
2 0.9 -0.098 0.01 1 0.05
An example of the typical state trajectories for all
three controllers is given in Fig. 2. It can be seen that
the CA controller does not control the system at the
beginning of the control horizon at all. The crite-
rion value estimates
ˆ
J, the accuracies of these esti-
mates var{
ˆ
J}, and the variability of Monte Carlo sim-
ulations var{L}, that were computed using M = 200
Monte Carlo simulations, are given in Table 2. In
A SUBOPTIMAL FAULT-TOLERANT DUAL CONTROLLER IN MULTIPLE MODEL FRAMEWORK
97
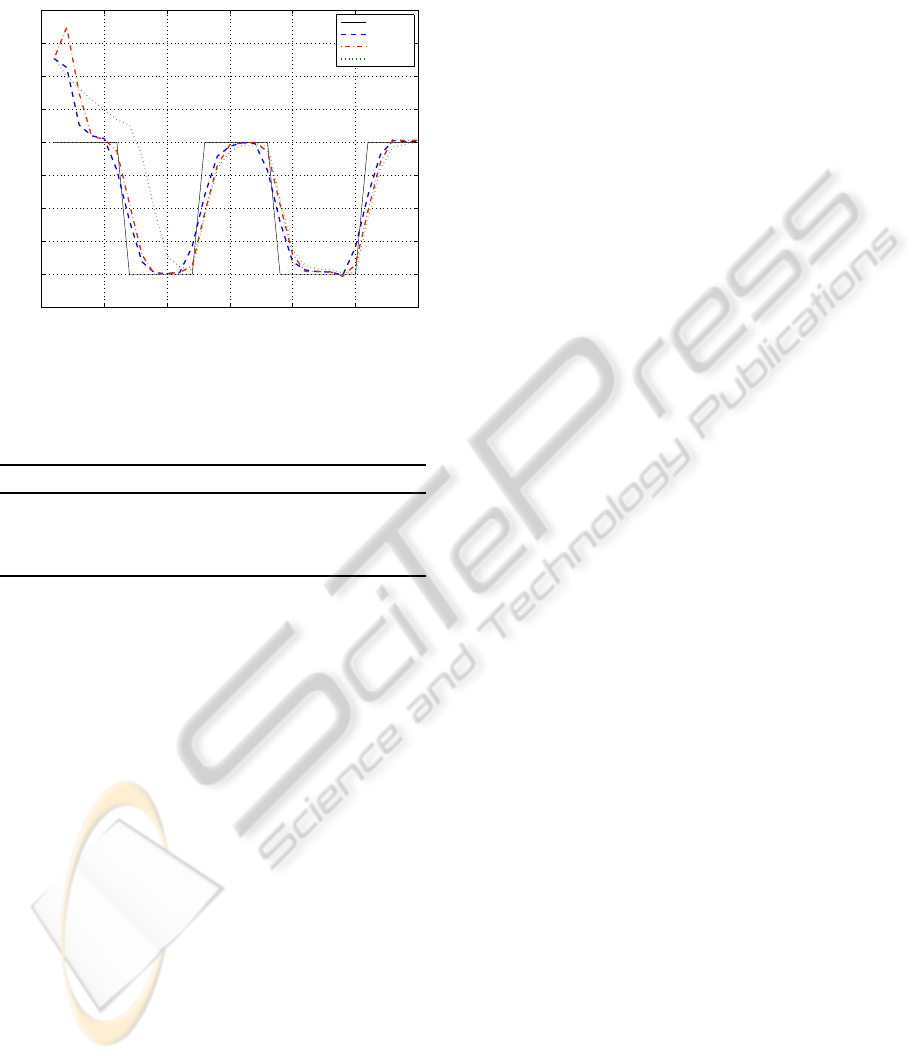
comparison with the CA controller,the quality of con-
trol is improved by 55% in the case of the HCE con-
troller and by 68% in the case of the dual controller.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
−0.6
−0.4
−0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Step k
State x
k
reference
DC
HCEC
CAC
Figure 2: State trajectories for dual controller (DC), heuris-
tic certainty equivalence controller (HCEC) and cautious
controller (CAC).
Table 2: Criterion value estimates for particular controllers.
Controller
ˆ
J var{
ˆ
J} var{L}
HCEC 3.2126 0.0164 3.2885
CAC 7.2186 0.0068 1.3194
DC 2.3131 0.0109 2.0889
7 CONCLUSIONS
The optimal fault-tolerant dual controller has been
obtained as a special case of the general formula-
tion. Since the optimal fault-tolerant controller is
computationally infeasible the multimodel approach
and rolling horizon techniques were used to obtain a
suboptimal fault-tolerant dual controller. The perfor-
mance of the proposed controller was compared with
a heuristic certainty equivalence controller and cau-
tious controller in a numerical example. Although all
controllerswere able to control the system even a fault
occurred, the fault-tolerant dual controller exhibits the
best performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Ministry of Educa-
tion, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic, project
No. 1M0572, and by the Czech Science Foundation,
project No. GA102/08/0442.
REFERENCES
Athans, M., Fekri, S., and Pascoal, A. (2006). Issues on
robust adaptive feedback control. In Proceedings of
the 16
th
IFAC World Congress, Oxford, UK.
Bar-Shalom, Y., Li, X. R., and Kirubarajan, T. (2001). Esti-
mation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation.
Wiley-Interscience, New York, USA.
Bar-Shalom, Y. and Tse, E. (1974). Dual effects, certainty
equivalence and separation in stochastic control. IEEE
Transactions on Automatic Control, 19:494–500.
Basseville, M. and Nikiforov, I. V. (1993). Detection of
abrupt changes – Theory and application. Prentice
Hall, New Jersey, USA.
Bayard, D. S. (1991). A forward method for optimal
stochastic nonlinear and adaptive control. IEEE
Transactions on Automatic Control, 36(9):1046–
1053.
Bertsekas, D. P. (1995). Dynamic programming and optimal
control: Volume I. Athena Scientific, Massachusetts,
USA.
Blanke, M., Kinnaert, M., Staroswiecki, M., and Lunze,
J. (2003). Diagnosis and Fault-tolerant Control.
Springer Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Campbell, S. L. and Nikoukhah, R. (2004). Auxiliary sig-
nal design for failure detection. Princeton University
Press, New Jersey, USA.
Isermann, R. (2005). Fault-Diagnosis Systems: An In-
troduction from Fault Detection to Fault Tolerance.
Springer.
Kerestecio˘glu, F. (1993). Change Detection and Input De-
sign in Dynamical Systems. Research Studies Press,
Taunton, England.
Mehra, R. K. (1974). Optimal input signals for parame-
ter estimation in dynamic systems – Survey and new
results. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,
19(6):753–768.
ˇ
Simandl, M. and Punˇcoch´aˇr, I. (2009). Active fault detec-
tion and control: Unified formulation and optimal de-
sign. Automatica, 45(9):2052–2059.
Zhang, X. J. (1989). Auxiliary Signal Design in Fault De-
tection and Diagnosis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Ger-
many.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
98
