
MOBILE E-LEARNING
Support Services Case Study
Catarina Maximiano
Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Department of Computer Science, School of Technology and Management, Leiria, Portugal
Vitor Basto Fernandes
Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Research Center for Informatics and Communications (RCIC), Leiria, Portugal
Keywords: LMS, Mobile Device, e-Learning, m-Learning, Mobile Technologies.
Abstract: Currently mobile devices and wireless communications are present in the daily tasks of our lives.
m-Learning extends the e-Learning concept by the use of mobile computation and communication
technological resources. Mobile computing focuses the paradigm of "anytime, anywhere access" that offers
resources for distance education via mobile devices. This paradigm, allow that information is made
available to users with greater flexibility and diversity, supporting learning in non conventional places and
time schedules. The need for learning throughout life and flexibility of education profiles requires the
support and development of new approaches in the educational context and tools to support learning.
This paper presents a distance learning case study at Polytechnic Institute of Leiria. The main objective is
the utilization of mobile devices as support tools for course information/contents resources access available
in Learning Management Systems (in the presented case study - Moodle).
1 INTRODUCTION
The increasing of the computing power for mobile
devices such as PDAs and mobile phones, mobile
learning (m-Learning) be presented as supporting
tools in teaching process. m-Learning complements
the benefits of e-Learning in terms of access to
information anytime anywhere - "anytime anywhere
learning" (Perry2001). It allows for students new
freedom, which comes with a choice of where and
how they want to access the information.
The main function of mobile devices is to
provide immediate communication. In this
perspective, the present work represents one
contribution for the problematic regarding the
availability of contents from the LMS (Learning
Management Systems) in mobile devices. The main
goal consists in the definition of an architecture
using mobile devices to access both administrative
information associated to the courses and
collaboration/communication information. An
implementation of the prototype mBoard according
to the architecture defined was implemented and
presented in this paper.
mboard acceptance tests were performed by the
students of Institute Polytechnic of Leiria (IPLeiria)
- Informatics Engineering Department (DEI).
This paper is organized as follows. In section 2
we present an overview of applications using mobile
devices in the educational area. Section 3 describes
the supporting architecture for IPLeiria m-Learning
case study. mboard prototype and acceptance tests
results are presented in section 4 and 5 respectively.
Finally, conclusions and future work directions are
presented.
2 STATE OF THE ART
There are many researches regarding the
applicability of the mobile devices as supporting
tools in the educational scope. In this context, it will
be presented some of those studies.
Applications to Perform Knowledge Tests.
(Ally2007) uses the mobile devices in teaching
English as a second language for adults. The
contents used in the learning process are interactive,
106
Maximiano C. and Basto Fernandes V. (2010).
MOBILE E-LEARNING - Support Services Case Study.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Software Agents and Internet Computing, pages 106-113
DOI: 10.5220/0002946301060113
Copyright
c
SciTePress

allowing students to practice using different types of
questions. Indeed, four different types of questions
were used in the creation of more interactive
grammar exercises. They were easily accessible on
mobile devices to test the ability of students. The
type of questions were true/false, multiple choice,
ordering and correspondence. (Matthee2007) has
conducted the study on the use of mobile devices
applied to the teaching of mathematics in South
Africa. In this country there are low PC penetrations
in the country, but that is about three million young
people with mobile phones with Java. The MOBI
client application is developed in tests on
mathematics through mobile devices.
Games as Study Objects. (Liao2008) has
developed the mini-My-Pet game that is inserted
into the theme of creation/education of animals for
PDA. It was developed as having three components:
emotional bonding, controlled learning and
exposure. The project Programming Mobile Games
for Learners (MobiGP) was developed in order to
teach the programming language object-oriented
C++ to students through mobile games
(Hamid2007). The project originated three games to
test student’s knowledge in C++: SpaceOut, Doggy
and Snail. The Wireless Crossword Fan-Tan Game
(WiCFG) was designed has an attempt to increase
the vocabulary of English students (Lin2008). The
game WiCFG represents a type of competition
between groups through co-operation between the
members of groups.
Learning a Language and also Foreign Language.
The Mobile Adaptive CALL (MAC) application -
(Uther2005), was designed to help the Japanese
people to distinguish phonetic contrasts in the
English language through audio. In this application
students have to select the correct word from a
presented list, and the next word is selected, based
on the error rate of the student. Another system was
developed for oral practice and assessment of
English for students to be used with mobile devices
with wireless in the classroom (Yang2005). Another
study was presented by (Joseph2005) and describes
the photoStudy that serves to support students in
learning new words through pictures and
collaboration among students. Other example is the
PALLAS system (Petersen2008), which is based on
real life scenarios and provides access to
personalized and contextualized data associated with
the teaching of languages through mobile devices.
Mobile Applications Adapted from Desktop/Web
Application. (Kainulainen2004) has developed an
extension of the application Problem Processing
Assistant (PPA) which is a web tool for learning.
This tool combines the features of digital portfolios
with the functionality of problem. The adaptation of
this tool for web access via mobile devices was
implemented in two phases, where not all features
were included. At first it only took into account the
adaptation of digital portfolios and the second phase,
was focused on the pre-research of contents.
Another example is the study of (Marcelino2008),
who had developed the H-SICAS application
(Handheld - SICAS) which is the adaptation of
SICAS application for mobile devices. The H-
SICAS has all the features of the parent application,
which is the creation and simulation of algorithms.
The application also allows for the creation of the
solution by the algorithm flowchart and automatic
generation of pseudo-code. It also permits to run the
solution in order to validate the correct definition of
the algorithm.
These studies differ in technologies and approach to
the use of wireless networks, mobile technologies,
equipment integrated into devices (camera and
video, mp3 players, calendar, browser, etc.). While
some choose to create their own resources for
learning, others are concerned about the reuse of
existing content. Others are theoretical, with
emphasis on educational research by the use of
mobile devices as a tool to support learning.
While most m-Learning approaches presented
are focused on the learning process and resources,
the approach presented in this paper is specially
focused on academic community communication
and interaction processes (professors, students,
school coordination, direction boards, etc.).
3 ACHITECTURE
This study is centred in the use of mobile devices as
tools to support the education process, specially –
availability of administrative information of the
courses. Analysis of the overall information related
to courses and the learning supporting process lead
us to conclude for the need of a specific tool to
manage the diversity of information and interactions
involved in university level learning. The mobile
devices are used as tools for easy obtaining of
information about the existing courses without the
need of accessing the LMS.
MOBILE E-LEARNING - Support Services Case Study
107
3.1 Considerations
Before the definition of the architecture has been
done, the following considerations for the mBoard
application were assessed:
Platform: the objective is the use of application
to be adopted by the greatest number of students.
Therefore, we choose to implement the application
in Java ME;
Get Information: Web Services are used for
communication between the application and the
LMS;
Contextualized and Personalized Access:
Users should be able to set the terms for the
application to use, ensuring an application for
adjustment of terms used by the LMS platform and
also the ability to configure what types of content
should be displayed;
LMS: the architecture should not depend on any
data model of a specific LMS.
The contents to be displayed by the mBoard
application are events; news since the last access;
grade notes (marks); new posts in forums and blogs;
new messages and activity reports.
3.2 Steps in Designing the Architecture
The definition of technical functional and non
functional requirements for the mBoard system were
done using UML (Unified Modelling Language)
notation. For the sake of simplicity only a few
diagrams of structural level and representative
features are presented. Class Diagram is presented in
Figure 1, Authentication and data retrieval functions
are implemented by the use of Web Services
provided by the LMS system and are depicted in the
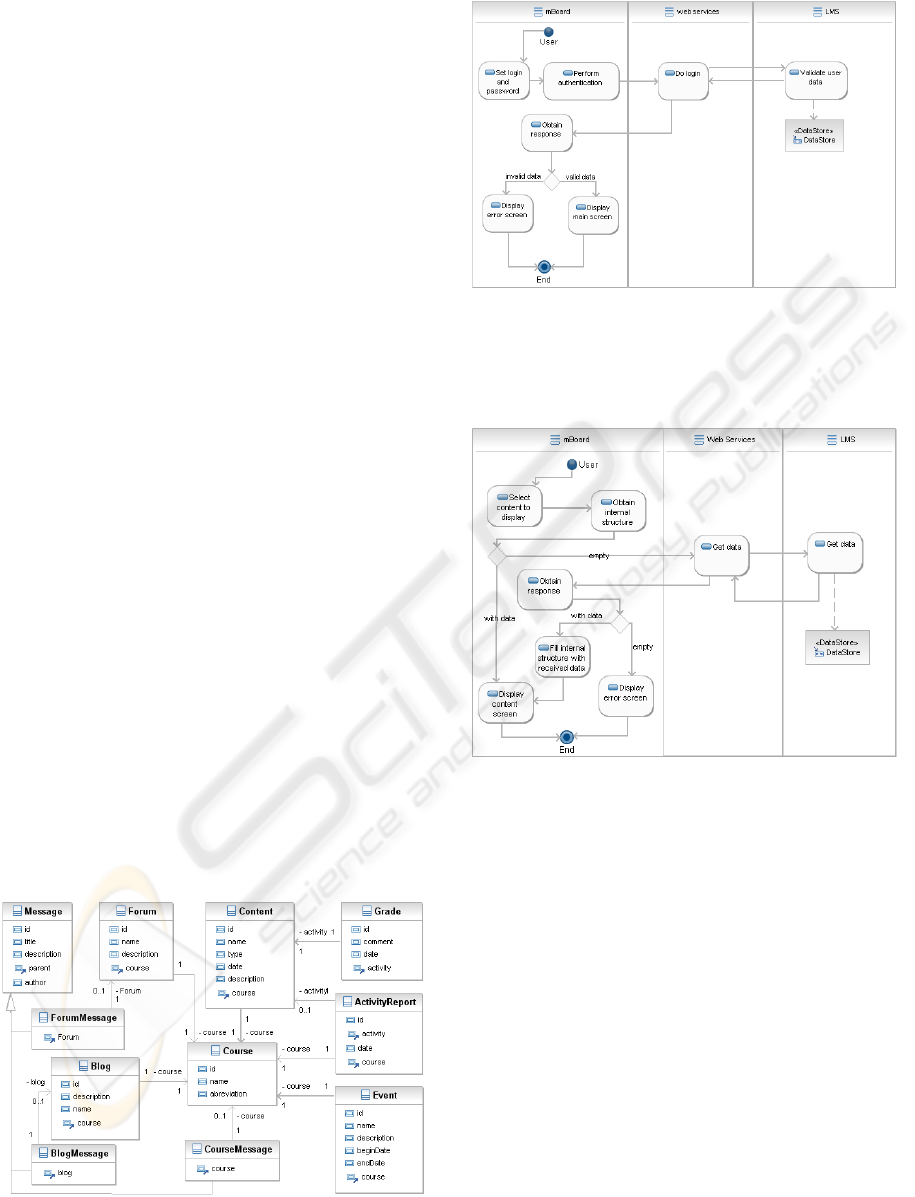
Activity Diagrams of Figure 2 and Figure 3
respectively.
Figure 1: Class diagram of mBoard architecture.
Figure 2: Authentication activity diagram.
The users to authenticate on the mBoard application
must provide the same authentication data they use
to login in the LMS.
Figure 3: Data retrieval from LMS activity diagram.
The architecture we propose is derived from a key
generic reference architecture defined by
(Trifonova2003). In our proposal, we are going to
improve some aspects that were not very well
defined in the generic architecture. The architecture
presented in the above study consisted in delegate to
the mobile device the responsibility of the
adaptation/conversion of the information to be
displayed. Due to the limited processing power and
memory of mobile devices, it was chosen to not
include the adaptation/conversion of the LMS data
in the application. Instead, it was included in the
services that the LMS should provide. A new
module was introduced for this specific purpose,
consisting in preferences configuration by the user.
The architecture, shown in
Figure 4, contains
three layers: the upper layer - represents the client
mobile application; the intermediate layer - is
composed by the web services need for the mBoard
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
108
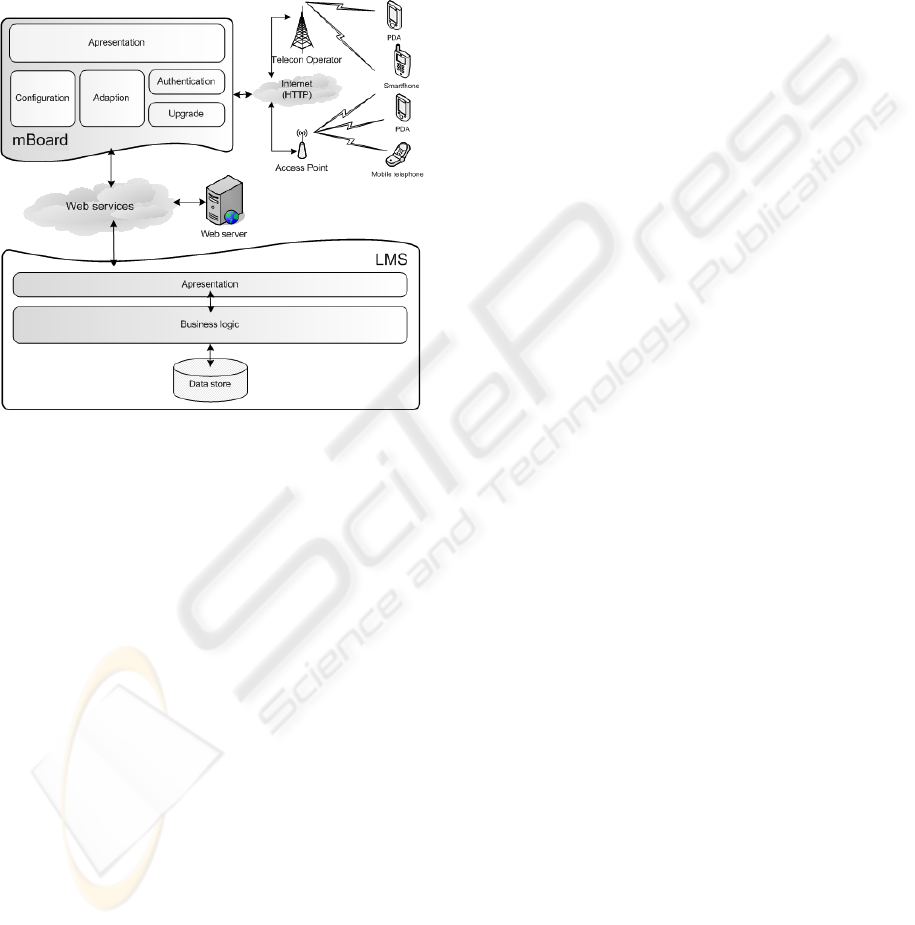
application; and the lower layer - represents the
LMS, that is going to contain all the information
need by the application, corresponding to the logical
layer of the architecture.
The most important advantage of this
architecture is that by isolating the implementation
of the Web Services need for mboard application, it
enables the use of different types of LMS, not
requiring the adoption of any specific LMS.
Figure 4: Architecture of mBoard system.
3.3 Upper Layer
In this architecture, the upper layer is the application
mBoard, which will be installed in the mobile
devices.
The application contains five modules:
Authentication Module: for mboard end user
identification in the LMS, using the same
authentication data used in the LMS.
Configuration Module: is constituted by two types
of configurations. One consists in the definition of
the connection to the LMS, i.e the address of the
Web Services provided by the LMS. The other is
related to the customization of the application, like
the terms used and types of contents that must be
displayed in the mBoard application.
Module for the Adaption: is responsible for the
adaptation of contents in HTML format to text
format. When it is detected that some attribute of the
received content is in HTML, this module is
responsible for its transformation into text.
Module for the Presentation of the Information:
is the main module of mBoard, it is responsible for
the information retrieval from LMS and let it
available for mboard users. This module invokes the
Web Services provided by the LMS and presents it
to the users.
Upgrade Module: is responsible to ensure
automatic upgrades for the mBoard application, i.e.
this module minimizes user interactions in mboard
versioning and configuring tasks.
3.4 Intermediate Layer
This layer represents how mBoard application is
going to obtain the contents existing in the LMS and
how contents will be then displayed to the users,
through Web Services. It is also constituted by a
Web Server responsible to provide data about
existing versions of mBoard and to perform
upgrades.
3.5 Lower Layer
The lower layer represents the LMS. This layer is
responsible by the creation and maintenance of all
the necessary information for the application
mBoard, acting as a provider for the application.
4 MBOARD SYSTEM
4.1 Used Technologies
For the mboard core application development, Java
ME framework was chosen, because of its wide
adoption by mobile devices suppliers and users.
Therefore, our application can be used by a high
share of mobile device users.
For the designing of the user interface,
Lightweight UI Toolkit – LWUIT was used. This
toolkit makes very easy the process of creating and
compelling UI's that will look and behave the same
on all devices using a programming paradigm
similar to Java Swing. To invoke the Web Services
we used the KSOAP package.
4.2 Implementation
Before moving into the application programming, it
was necessary to create a draft of the screens to be
implemented in the mBoard application.
In the development of the draft we took into
consideration some rules related to the orientation of
the interfaces for mobile applications (Keogh2003,
Gong2004): simplification of the interface; use of
MOBILE E-LEARNING - Support Services Case Study
109
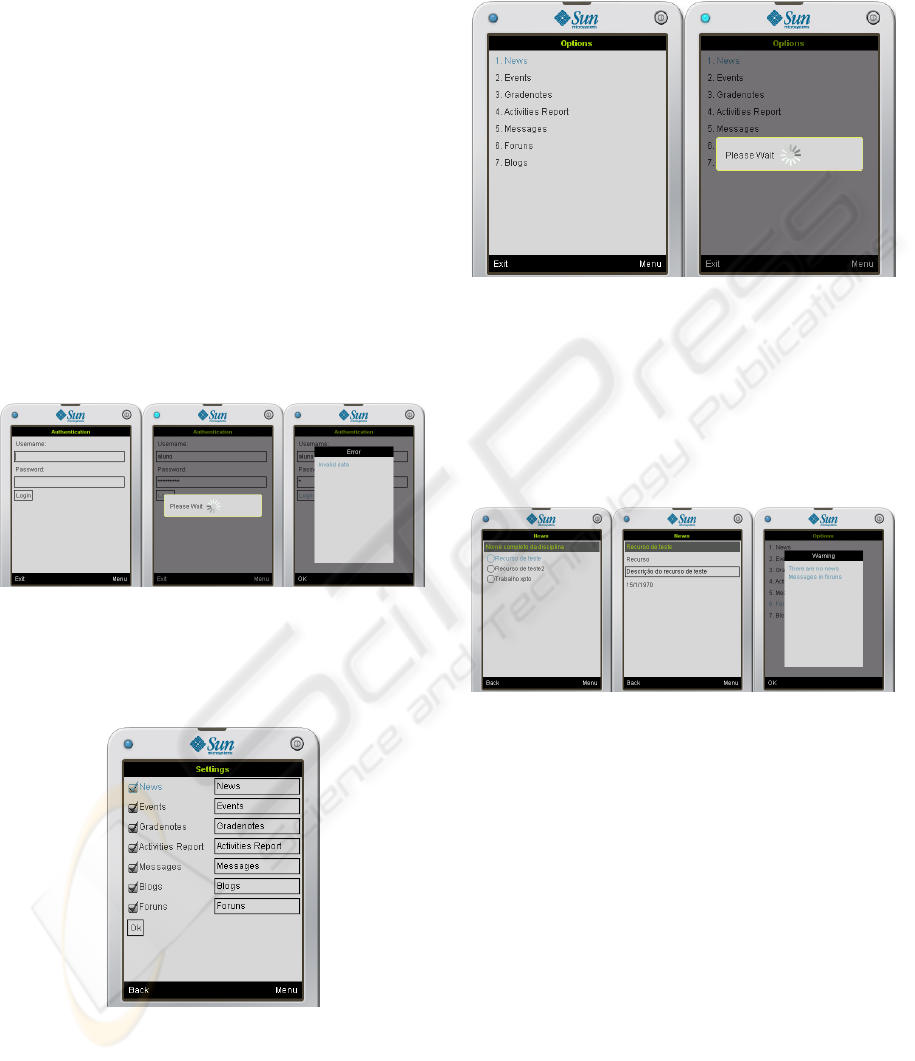
diverse screens and each should only present
relevant information (
Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and
Figure 8); always provide feedback to the user
(middle screen of
Figure 5 and right screen of Figure
7), because the mobile user is more impatient with
the mobile than the user of a desktop application;
consistency: in the "look and feel" uniformity in all
of the screens in all of the elements of the interface
(ex. names, plan of colors, appearance of the boxes),
create methodologies of input/output independent of
the device and reuse the same components used in
several screens (e.g. commands).
In the login screen, it is displayed the menu option.
However, the menu only allows the configuration of
the address of the Web Services provided by the
LMS, because the authentication involve the LMS
through the Web Services. The first time the user
accesses the application he must configure this
address, otherwise it will not have access to the
information.
Figure 5: Authentication screens.
In the setting setup screen, users can select which
type of contents they want to be available, as well as
defining the term to be displayed.
Figure 6: configuration screen.
On the main menu screen, users can choose the
information they want to see. A process bar was
added as feedback for the user when the application
is performing some processing (e.g., invocation of
Web Services). With this feedback the user gets to
know that the application is running and not
blocked.
Figure 7: Menu screens.
For the screens presenting the contents of the
courses associated to an user, two screens are
required: one with the resume of all new information
about the type of selected content by the user and the
other with the details of the content. The right screen
displays a warning message when there is no new
information available about the selected content.
Figure 8: Contents screens.
4.3 Tests
This chapter discusses the several tests performed to
validate the prototype implementation/functionality.
4.3.1 Tests in the Emulators
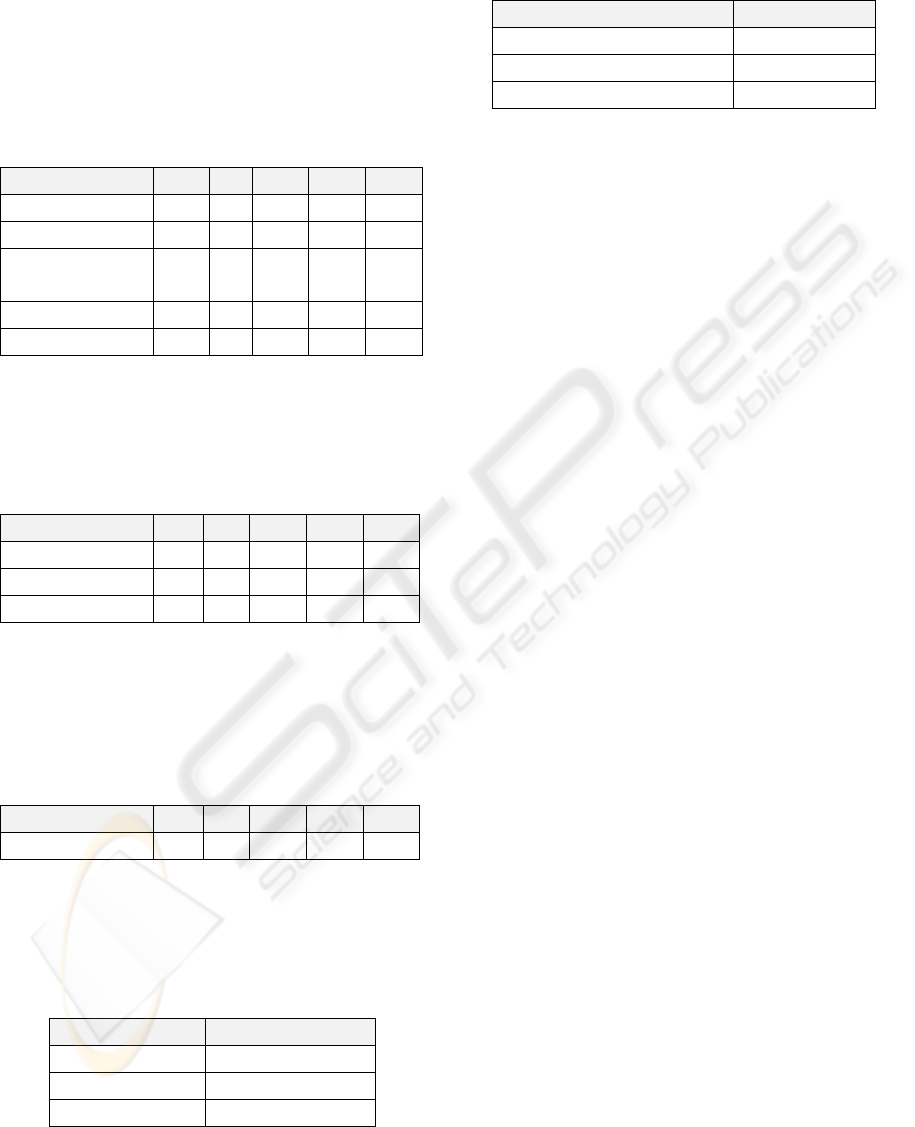
Several tests were performed in different emulators
available from several suppliers. Table 1 presents a
summary of those tests.
4.3.2 Acceptance Tests
To validate the prototype, a group of undergraduate
Computer Science students at IPLeiria were chosen
to perform the first mboard assessment and
acceptance tests.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
110
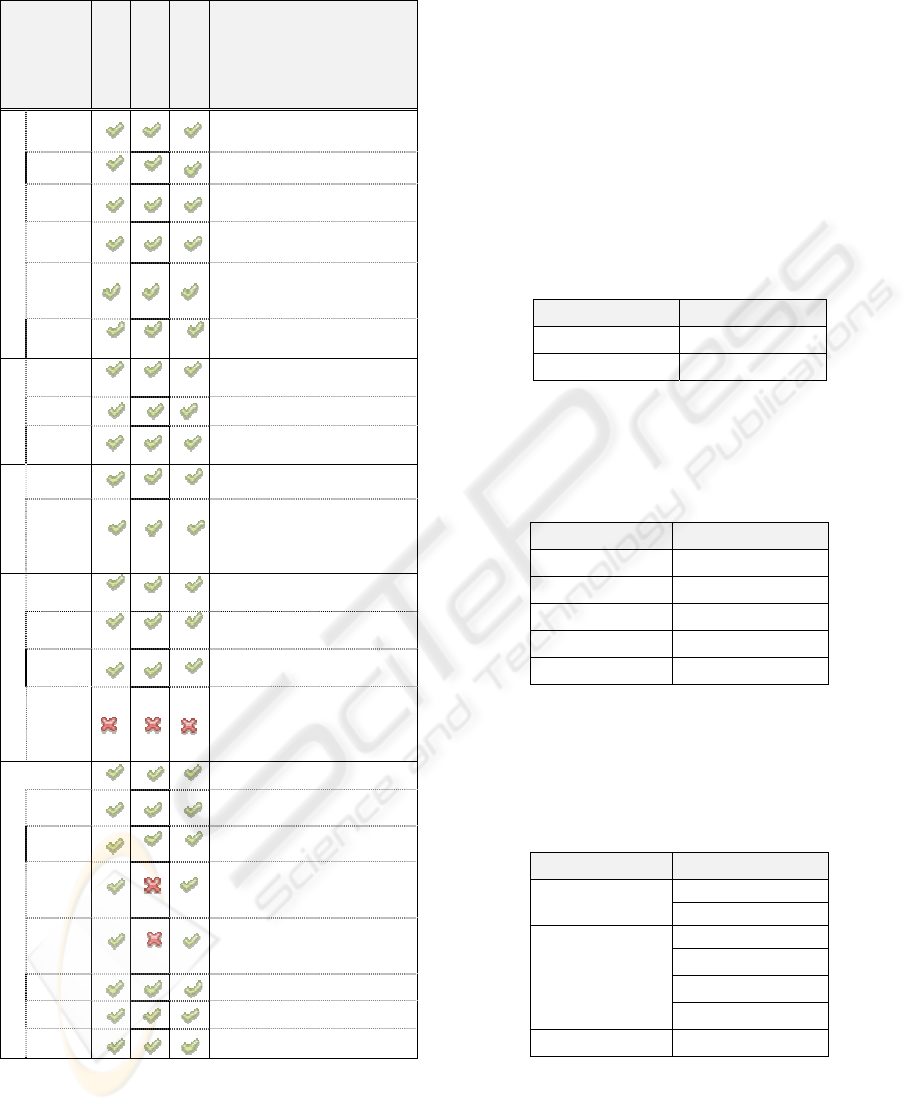
Table 1: Resume of tests performed with emulators.
Brands/
Model
Autentication
Settings
Contens
Comments
Samsung
SGH-
B2700
F480
SGH-
E250
SGH-
J800
SGH-
M880
0
SGH -
F700
LG
GD90
0
BL20
LX60
0
Nokia
N97
S40
5rd
editio
n
Motorola
Qwert
y
Candy
bar
G24 -
JHMI
Touch
Only has the virtual
keyboard and I could not
access it, so it was possible
to test the application
Sonny Ericsson
K750
W200
W700
W950
I could not access the menu,
in order to perform the
settings
M600
I could not access the menu,
in order to perform the
settings
V800
Z550
Z800
In order to gather necessary data to evaluate the
mBoard prototype developed, it was created an
inquiry composed by 14 questions, organised in
three sections: the first section was essentially
concerned with the installation of the application on
the mobile device, the second on the usability and
functionality of the application and the last section
on the motivation for the use of such a mobile
application.
The grades (marks) of the students were published in
the LMS and made available only by the mBoard
application. In a 93 potential users (students) group
15 answers were obtained for analysis. The
statistical analysis of the data collected follows.
In Table 2 is presented the success rate obtained
about the application installation in mobile devices.
Table 2: Answers percentage of question if application
was successeful installed.
Answer Response (%)
Yes 53.33
No 46.67
In Table 3 is indentified the mobile device suppliers
where the application was installed.
Table 3: Answers percentage of question to identity the
mobile devise.
Brand Response (%)
LG 6.67
HTC 13.33
Nokia 46.67
Sony-Ericsson 33.33
Other 6.67
Due to a high rate of application setup failures, a
more detailed analysis was made by mobile device
models (Table 4).
Table 4: Mobile devices witch student could not install
application.
Brand Model
HTC
TYTN II
P3600i
Nokia
9130
E66
E51
5610
Sony-Ericsson W880I
The technical requirements for each of these mobile
devices were checked and the analysis confirmed
that all devices had the necessary requirements.
However, it was noticed that all devices supported
applications with the MIDP 2.0 version of Java, and
the required information about the application was
MOBILE E-LEARNING - Support Services Case Study
111
defined the version 2.1 for MIDP. This definition in
fact was the cause of installation failures.
The results of users classification for application
usability (in 1 to 5 scale, where 1 is bad and 5 very
Good) are listed in Table 5.
Table 5: Answers percentage of question to classify the
application in terms of application usability.
Item 1 2 3 4 5
Authentication 0 0 25 25 50
Navigation 0 0 12.5 75 12.5
Information
visualization
12.5 0 75 12.5 0
Usability 0 0 12.5 75 12.5
Screens 0 0 50 37.5 12.5
The results of user classification for application
feedback (in 1 to 5 scale, where 1 is bad and 5 very
Good) are listed in Table 6.
Table 6: Answers percentage of question to classify the
application in terms of application feedback.
Item 1 2 3 4 5
Progress messages 0 0 25 50 25
Error messages 25 62.5 12.5
Response time 12.5 25 62.5
For the question “How do you classify the
application functionalities? (in 1 to 5 scale, where 1
is bad and 5 very Good)” the answers are present in
Table 7.
Table 7: Answers percentage of question to classify the
application in global.
Item 1 2 3 4 5
Functionality 0 0 25 50 25
Table 8 presents the answers for the question “Do
you think that is beneficial to access information
present in LMS via mobile devices?”
Table 8: Answers percentage of question about the
beneficial of use this kind of application.
Answer Response (%)
Yes 93.33
No 0
Without opinion 1 6.67
The answers for the “Identify the main cause to not
use the application” question are listed in Table 9.
Table 9: Answers percentage of question to identify the
main cause to not use the application.
Answer Response (%)
Price 80
Device limitation 13.33
Limited information visualization 6.67
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we presented a new method to make
traditional e-Learning content available to mobile
devices users, with no need to extra work of content
adaption from LMS in mobile devices.
In the case study, we observed a good acceptance
of students to this new approach for educational
information access. According to the preliminary
results from the acceptance tests we also conclude
that mobile devices configuration and versioning
management is one of the critical success factors for
m-Learning applications deployment. In addition to
configuration and versioning management
improvements we also need to assess the core
functions of m-Learning applications from the point
of view of professors, student and staff. Other future
working directions related to communication
models, economical cost analysis, etc. were
identified.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The resources required for the release of the
application and Moodle instance were provided by
the Unit of Distance Education (UED) at
Polytechnic Institute of Leiria.
REFERENCES
Ally, M., Schafer, S., Cheung, B., McGreal, R. & Tin, T.,
2007. Use of Mobile Learning Technology to Train
ESL Adults. In mLearn 2007 - 6th Annual
International Conference on Mobile Learning: Making
the connections.
Gong, J. & Tarasewich, P.,2004. Guidelines for handheld
mobile device interface design. In Proceedings of the
2004 DSI Annual Meeting.
Hamid, S.H.A. & Fung, L.Y., 2007. Learn Programming
by Using Mobile Edutainment Game Approach. In
IEEE International Workshop on Digital Game and
Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning (DIGITEL'07).
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
112

Joseph, S., Binsted, K. & Suthers, D., 2005. PhotoStudy:
Vocabulary Learning and Collaboration on Fixed &
Mobile Devices. In IEEE International Workshop on
Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education.
Kainulainen, V., Suhonen, J., Sutinen, E., Goh, T. &
Kinshuk, 2004. Mobile Digital Portfolio Extension. In
IEEE International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile
Technologies in Education.
Keogh, J., 2003. J2ME: The Complete Reference
McGraw Hill. New York, 1
nd
edition
Liao, C.C., Chen, Z.-H. & Chan, T.-W., 2008. My-Mini-
Pet: The Design of Pet-nurturing Handheld Game. In
IEEE International Conference on Digital Games and
Intelligent Toys Based Education.
Lin, C.-P., Young, S.S.-C. & Hung, H.-C., 2008. The
Game-based Constructive Learning Environment to
Increase English Vocabulary Acquisition:
Implementing a Wireless Crossword Fan-Tan Game
(WiCFG) as an example. In IEEE International
Conference on Wireless, Mobile, and Ubiquitous
Technology in Education.
Marcelino, M., Mihaylov, T. & Mendes, A., 2008. H-
SICAS, a Handheld Algorithm Animation And
Simulation Tool To Support Initial Programming
Learning. In ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education
Conference.
Matthee, M. & Liebenberg, J., 2007. Mathematics on the
Move: Supporting Mathematics Learners Trough
Mobile Technology in South Africa. In mLearn 2007 -
6th Annual International Conference on Mobile
Learning: Making the connections.
Perry, M., O’Hara, K., Abigail Sellen, B.B. & Harper, R.,
2001. Dealing with Mobility: Understanding access
anytime, anywhere. In ACM Transaction on
Computer-Human Interaction.
Petersen, S.A. & Markiewicz, J.-K., 2008. PALLAS:
Personalised Language Learning on Mobile Devices.
In IEEE International Conference on Wireless,
Mobile, and Ubiquitous Technology in Education.
Uther, M., Zipitria, I., Uther, J. & Singh, P., 2005. Mobile
Adaptive CALL (MAC): A case-study in developing a
mobile learning application for speech/audio language
training. In IEEE International Workshop on Wireless
and Mobile Technologies in Education.
Yang, J.C., Lai, C.H. & Chu, Y.M., 2005. Integrating
Speech Technologies into a One-on-one Digital
English Classroom. In IEEE International Workshop
on Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education
(WMTE’05).
MOBILE E-LEARNING - Support Services Case Study
113
