
BIDM
The Business Intelligence Development Model
Catalina Sacu and Marco Spruit
Institute of Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University, 3508 TC, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Keywords: Business Intelligence, Maturity Modelling.
Abstract: Business Intelligence (BI) has been a very dynamic and popular field of research in the last few years as it
helps organizations in making better decisions and increasing their profitability. This paper aims at creating
some structure in the BI field of research by creating a BI development model that relates the current BI
development stages and their main characteristics. This framework can be used by organizations to identify
their current BI stage and provide insight into how to improve their BI function.
1 INTRODUCTION
In nowadays economy, organizations have a lot of
information to gather and process in order to be able
to take the best decisions as fast as possible (Misner
et al., 2002). One of the solutions that can improve
the decision making process is (BI).
According to (Gray & Negash, 2003), BI systems
“combine data gathering, data storage, and knowledge
management with analytical tools to present complex
and competitive information to planners and decision
makers”. Another interesting definition is the one
given by (Eckerson, 2007) who believes that BI
represents “the tools, technologies and processes
required to turn data into information and information
into knowledge and plans that optimize business
actions.” We can see in both definitions that BI helps
the decision making process by transforming data into
knowledge by using different analytical tools. But,
throughout time, BI has evolved from rather simple,
fixed reports to real-time analysis. However, even if
BI seems to play an important part in the present
economy, scientific research in this field is limited,
though research possibilities are many (Gray &
Negash, 2003). Some literature about BI in general
can be found, but there is not much scientific research
done regarding the evolution of BI and each of its
development stages. Moreover, there are lots of
redundant information, concepts and perspectives on
BI, but there is not too much structure among them
and not many articles give an overall insight into the
BI field and its development. This is the gap that our
paper is trying to narrow down by developing a model
that structures the most important stages of BI
maturity and their most representative characteristics.
A starting point for our framework is represented
by maturity models. Essentially, they describe the
development of an entity over time, where the entity
can be anything of interest: a human being, an
organizational function, an organization, etc.
(Klimko, 2001). Maturity models are characterized
by a number of sequentially ordered levels with
certain requirements that the entity has to achieve on
that level. Moreover, two models that can be a
starting point in assessing the BI maturity in a
company would be the BI Maturity Model developed
by (Chamoni & Gluchowski, 2004) and the Data
Warehousing Institute’s BI Maturity Model (2009).
More details about them will be given in section 2.
Hence, this paper tries to develop a framework
that presents different BI development stages and
their characteristics that will make it possible for a
company to assess its current BI maturity and see the
next steps it has to take in order to become an
intelligent organization. In order to develop our
framework, this paper will address and try to answer
the following research question: What Business
Intelligence development stages have been defined in
literature until now and how are they related?
Our BI development model will be created using
a design research approach (Vaishnavi & Kuechler,
2007). Hence, our research is structured into the
following steps: awareness of the problem,
suggestions for the problem solution, development
of an artifact – a problem’s solution, evaluation and
288
Sacu C. and Spruit M. (2010).
BIDM - The Business Intelligence Development Model.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Databases and Information Systems Integration, pages
288-293
DOI: 10.5220/0002967402880293
Copyright
c
SciTePress

conclusion. The first step was accomplished by
doing a thorough BI literature research and
examining professional magazines and websites.
Based on this review, we realized that the BI field is
very broad and it involves constant evolution, but
many organizations are not aware of all the
advantages that BI provides. In order to solve this
problem, we developed a BI Development Model
(BIDM). Its stages and characteristics will be
described in section 2. The evaluation step will be
done in future research case studies within several
organizations. Finally, section 3 contains
conclusions regarding our model and future research.
A preliminary version of this research has been
published in (Sacu & Spruit,2010).
2 THE BI DEVELOPMENT
MODEL (BIDM)
Even though the available literature on BI is very
broad, there are not many papers that deal with
developing a BI maturity model. One of the most
representative ones is (Chamoni & Gluchowski,
2004), but it is in German. It considers five BI
maturity stages and analyzes them from three
perspectives: business content, technologies and
organization. The basic idea for our framework is
inspired by (Chamoni & Gluchowski, 2004) and by
the BI maturity model developed by The Data
Warehousing Institute (TDWI, 2009). The latter six-
stage model shows the trajectory that most
organizations follow when evolving their BI
infrastructure (i.e: prenatal, infant, child, teenager,
adult and sage). However, the TDWI model presents
different perspectives of BI adoption by drawing
several graphs and providing concepts that are not
clearly explained and cannot be easily depicted from
the model. For each of the stages, there is interesting
information provided such as necessary architecture,
scope, system type, analytics, users, BI focus and
executive perception about the role of BI. Moreover,
there are more characteristics that could be
determined in order to create a better insight on the
BI field. This is what our model tries to do. It
involves six stages (i.e: predefined reporting, data
marts, enterprise-wide data warehouse, predictive
analytics, operational BI, business performance
management) with several characteristics categories.
Each characteristic can be assigned to one or more
stages depending on the maturity of a certain stage.
In this way, a company can assess its BI maturity as
some characteristics are typical for lower maturity
stages, whereas others are met only in very mature
BI infrastructures. The BIDM is shown in figure 1
and will be discussed in the remainder of this paper.
2.1 BI Maturity Stages
The BI maturity stages and their most representative
characteristics were derived from the literature
study. In this way we decided that the BIDM should
comprise of the following maturity stages:
predefined reporting, data marts, enterprise-wide
data warehouse, predictive analytics, operational BI
and business performance management (BPM). Each
of the stages will be described and analyzed further
in this paper.
2.1.1 Predefined Reporting
A few years ago before the development of data
warehouses, predefined reporting was the only way a
company analyzed their financial results and their
general development. At first, reports were only on
paper, but then different software programs were
developed for creating them. However, even if
nowadays most companies create the reports on
computers, the majority of users are casual or
without experience and prefer this type of reporting.
The Data Warehousing Institute and (Chamoni &
Gluchowski, 2004) have similar stages. We decided
to choose this name for our first stage of the BI
maturity model as it is very representative for its
characteristics: static deductive reports that present
rigid evaluations of business facts, with common
semantics, usually restricted to certain departments
or transactions and visualized by casual users. These
reports are quite rudimentary, containing redundant
information and they offer rather limited capability
to analyze data or change information.
2.1.2 Data Marts (Departmental Data
Warehouse)
The next BI maturity stage is represented by the
development of data marts or departmental data
warehouses. A data mart contains a subset of the
data volume from the whole organization specific to
a group of users or department, also called specific
subject areas. There is an argument in the IT
community whether it is better to build more data
marts instead of a unified data warehouse (Inmon,
2002).
Even if it is usually easier and cheaper to build a
data mart rather than a data warehouse, from a long-
term perspective, the former is never a substitute for
the latter. The structure of the data found in a data
BIDM - The Business Intelligence Development Model
289
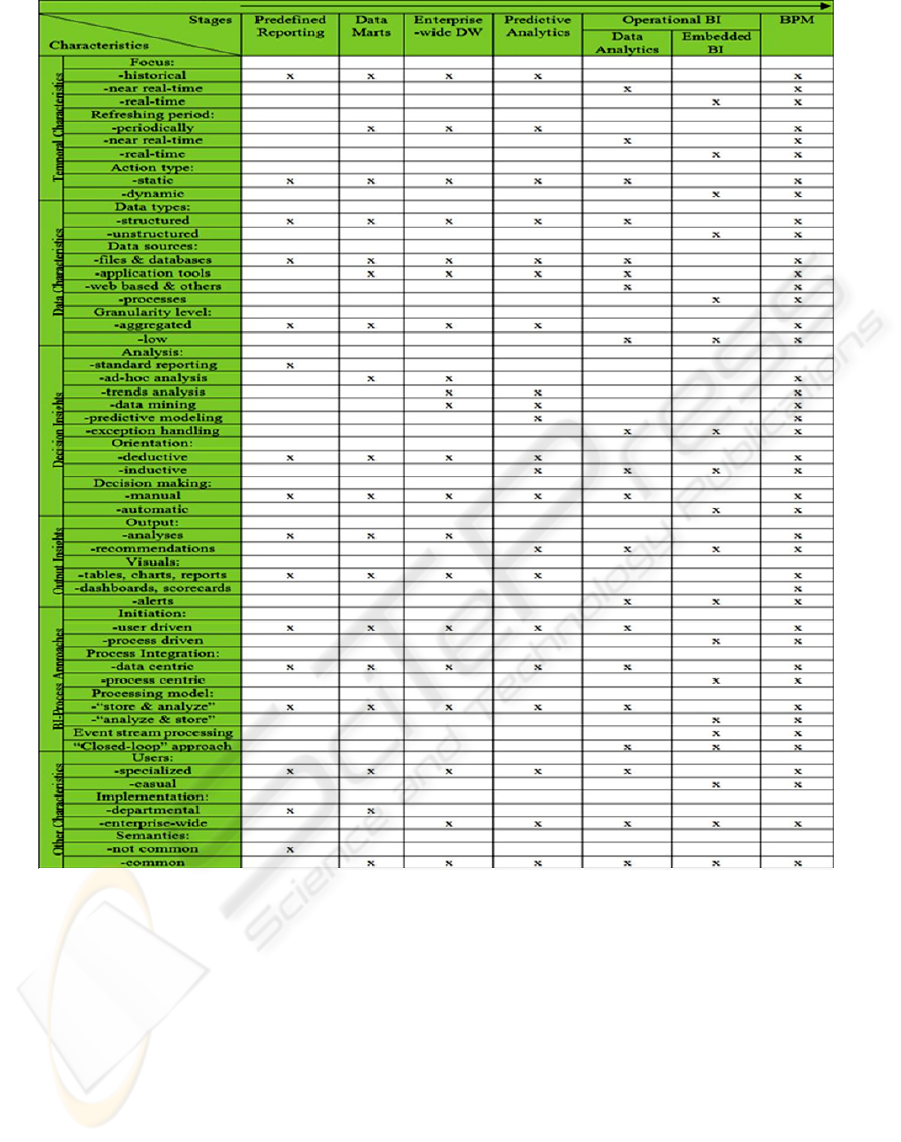
Figure 1: The Business Intelligence Development Model (BIDM).
mart is shaped by the particular requirements of the
department, making it difficult to build a data
warehouse from more data marts.But, this stage
offers some advantages. Even if valid only for
departments, these local data silos have a multi-
dimensional data structure supported by multi-
dimensional databases that make navigation and
visualization easy for the user. This enforces clear
commitment to a common semantic for the
department and the possibility of accessing ad-hoc
reports anytime a user requires one by using online
analytical processing (OLAP) technology that
automates the updates of the data cubes and makes
possible different operations (Inmon, 2002). The
same stage exists in (Chamoni & Gluchowski, 2004)
under a different name.
2.1.3 Enterprise-wide Data Warehouse
The third stage from our BI maturity model involves
the development of an enterprise-wide data
warehouse with high availability and integration,
common standards and an overall semantic.It
collects information about all the subject areas
involved in the whole organization. Even if the
volume of data is large and the costs and time for
modelling and development are higher than in the
case of data marts, an enterprise-wide data
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
290

warehouse could accomplish various useful
objectives (Airinei, 2002): access historical,
summarized and consolidated organizational data; a
single version of truth because the data from a data
warehouse are consistent as they have been
previously cleaned, transformed and integrated;
combined summarized/detailed access to data –
OLAP technology and other front end tools such as
query tools, report writers and analysis tools offer
the possibility of visualizing the information at
different hierarchical levels through operations like
roll-up, drill-down, slice, dice and pivot; separation
of the operational and decisional or analytical
processing as they have a very different architecture;
monitor and administer the warehousing system; and
store and manage metadata.
In addition to the main warehouse, there may
also be several data marts. However, contrary to the
previous stage described in 2.1.2, the warehouse is
created first for the whole organization and then, the
data marts are developed which makes a shared data
infrastructure possible. This stage also exists in
(Chamoni & Gluchowski, 2004). We decided to
choose the name enterprise-wide data warehouse in
order to differentiate it from the previous stage to a
greater extent.
2.1.4 Predictive Analytics
The fourth stage of our BI maturity model is called
predictive analytics and it involves more advanced
methods for data analysis which include discovering
different patterns in data. Predictive analytics has
been around for a long time, but it has commonly
been referred to as data mining or knowledge
discovery. Vendors and consultants have recently
started using other names such as predictive
analytics, advanced analytics or just analytics to
describe the nature of the tools or services they offer
(Eckerson, 2007).
However, there are some differences between the
names. Data mining is defined by (Holshemier &
Siebes, 1994) as being “the search for relationships
and global patterns that exist in large databases, but
are ‘hidden’ among the vast amount of data”; these
relationships can then offer valuable knowledge.
But, some researchers such as (Fayyad et al., 1996)
consider that actually knowledge discovery refers to
the overall process of discovering useful knowledge
from data by identifying valid, novel, potentially
understandable patterns in data; whereas data mining
refers to a particular step in this process (Fayyad et
al., 1996).
Note that unlike other BI technologies, such as
different reporting tools or OLAP, that are deductive
in nature as they examine what happened in the past,
predictive analytics is inductive as it employs
statistics, machine learning, neural computing,
robotics, computational mathematics and artificial
intelligence techniques to explore all the data,
instead of a narrow subset of it, and to ferret out
meaningful relationships and patterns.
2.1.5 Operational BI
The previous stages of the BI maturity model refer to
out-of-date analyses made by using a data warehouse
and/or data marts updated overnight (within the
traditional “batch window”) with data from
operational systems. However, over the past few
years, organizations have explored technology to
support more real-time data collection, analysis and
decision-making in a BI environment in order to
reduce latency in the decision process.
According to (Azvine et al., 2006), real-time BI
or operational BI can have several meanings such
as:
The requirement to obtain zero-latency within a
process; the possibility that a process has access to
information and provides it whenever it is required;
the ability to derive key performance indicators
(KPI’s) that relate to the situation at the current point
in time and not just to some historic situation.
Hence, we can say that operational BI is the
ability to manage more effectively and optimize
daily business activities by integrating BI analytics
within operational processes and by propagating
actions back into business processes in real time
(Davis et al., 2009). All the previous stages of the
BIDM are part of the strategic (long-term goals;
historical data – months or even years old) and
tactical BI (shorter-term goals; historical data – one
to a few months old). The overall goal is to reduce
latencies in the decision process in order to make
faster and better decisions. It is process centric and
user and process driven as it can be initiated by a
business user or a process. Moreover, two
approaches for implementing operational BI
solutions can be defined.
One approach that is more often pursued is called
data or traditional analytics. It is typically based on
data stored in a data warehouse and it involves
reducing the latency of the data by updating the data
warehouse more frequently. The second approach is
called event analytics or embedded BI and it refers to
analyzing business and system events as they flow
into the organization. These operational applications
might be directly embedded in operational processes
BIDM - The Business Intelligence Development Model
291

or may be called at specific points in an operational
process workflow (Davis et al., 2009).
2.1.6 Business Performance Management
(BPM)
The last stage from our BI maturity model is called
Business Performance Management (BPM). It can
also be found under different names such as
Corporate Performance Management or Enterprise
Performance Management. So far, each stage
referred to a stage of the BI process. This last stage
refers to a new way of thinking and of managing an
organization that involves BI, but other fields also.
BPM can be defined as “a set of processes that help
organizations optimize business performance by
encouraging process effectiveness as well as
efficient use of financial, human, and material
resources” (Golfarelli et al., 2004).
BPM takes a closed-loop approach as it includes
data warehousing, but it also requires a reactive
component (usually called Business Activity
Monitoring – BAM) capable of monitoring the time-
critical operational processes to allow tactical and
operational decision-makers to tune their actions
according to the company strategy (Golfarelli et al.,
2004). One could say that BPM is the combination
between data warehousing, data mining and
operational BI. It ensures the collaboration between
the strategic, tactical and operational levels in an
organization. BPM is an enabler for businesses in
defining strategic goals and then measuring and
managing performance against these goals by
tracking the evolution of KPI’s and scorecards. In
the case of BPM, the focus is on the global business
goals rather than on the single tasks. Of course,
employees involved in processes must share the
business strategy in order to synchronize their
behavior.
2.2 BI Maturity Model Characteristics
Now that we have surveyed the overall range in BI
development capabilities as depicted in the columns
of the table, it is the moment to turn our attention to
the rows of the model. They represent twenty
characteristics related to the BI field that we
consider important after doing the literature research
and discovering all the BI maturity stages. Each
attribute can fit one or more BI development stages,
some of them being more appropriate for the less
mature stages, whereas others characterize the stages
with higher maturity. These characteristics are
grouped into the following six categories: temporal
characteristics, decision insights, data characteristics,
output insights, BI-process approaches,
miscellaneous, each having several attributes and are
summarized below.
2.2.1 Temporal Characteristics
This category refers to some characteristics
regarding the focus of our data and data analysis,
whether the data analysis is done in real-time or in a
longer period of time. Hence, the characteristics in
this category are: focus (historical, near-real time
(seconds to minutes old data), real-time (current
data)); refreshing period (periodically, near-real
time, real-time); action type (static, dynamic).
2.2.2 Data Characteristics
This category refers to the data types and data
sources used for doing the data analysis: data types
(structured (e.g: relational), semi-structured (e.g:
XML) unstructured (e.g: documents, web pages,
etc.); data sources (files and databases, application
tools and packages (e.g: Excel spreadsheets, Word
documents, etc.), web based, uncommon data
sources that require custom a interface, processes);
granularity level (low; aggregated, summary data).
2.2.3 Decision Insights
As the main scope of BI is to make faster and better
decisions, this category comprises of several
characteristics of the necessary analysis and the
resulting decisions: decisions (strategic, tactical,
operational); analysis (standard reporting, ad-hoc
analysis, trends analysis, data mining, predictive
modeling, exception handling); orientation
(deductive, inductive); decision making (manually,
automatically).
2.2.4 Output Insights
Once we have the data, it is important to have more
possibilities of doing the analysis and showing the
results. Also, the ways in which this is possible can
differentiate a maturity stage from another: output
(analyses, recommendations and actions); visuals
(tables, charts and reports, dashboards and
scorecards, alerts).
2.2.5 BI-Process Approaches
As can be seen throughout the paper, whether BI
analytics is integrated or not in the business process
can strongly affect the decision making process.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
292

Hence, we consider this category to be a very
important one when delimiting a maturity stage:
initiation (user driven – activity initiated by the user,
process driven – activity initiated by a process);
process integration (data centric – BI analytics is
usually supported by a data warehouse, process
centric – BI analytics is integrated in the business
processes); processing model (store and analyze;
analyze and store); event stream processing; “closed-
loop” environment.
2.2.6 Other Characteristics
This last category contains some characteristics that
can distinguish a maturity stage from another, but do
not fit in the other categories and they refer to: users
(specialized, casual); implementation (departmental,
enterprise-wide); semantics (common, different).
3 CONCLUSIONS AND
FURTHER RESEARCH
This paper has presented the Business Intelligence
Development Model (BIDM). By doing a thorough
literature study, we came up with six BI maturity
stages and a selection of twenty characteristics that
best describe and differentiate these stages. Each of
the characteristics has several attributes that might fit
one or more of the development stages. This is how
BIDM can help determine which characteristics are
necessary for reaching a desired BI maturity stage.
Furthermore, we would like to refine our framework
in the future to include support for companies to
assess their BI capability. One promising approach
might be to apply the type of maturity matrix model
developed by (van de Weerd, 2009). Moreover, case
studies as well as expert interviews or surveys may
help validate how our framework works in practice.
REFERENCES
Airinei, D. (2002). Depozite de date. Iasi: Polirom.
Azvine, B., Cui, Z., Nauck, D. & Majeed, B. (2006). Real
Time BI for the Adaptive Enterprise. Proceedings of
the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Enterprise
Computing, E-Commerce and E-Services. San
Francisco, California, USA.
Ballard, C., White, C., McDonald, S., Myllymaki, J.,
McDowell, S., Goerlich, O. & Neroda, A. (2004).
BPM Meets…BI. San Jose: IBM Corporation.
Chamoni, P. & Gluchowski, P. (2004): Integrationstrends
bei Business-Intelligence-Systemen, Empirische
Untersuchung auf Basis des Business Intelligence
Maturity Model. Wirtschaftsinformatik, 46(2).
Chaudhuri, S. & Dayal, U. (1997). An Overview of Data
Warehousing and OLAP Technology. ACM Sigmod
Record, 26(1), 65-74.
Davis, J., Imhoff, C. & White, C. (2009). Operational
Business Intelligence: The State of the Art. Business
Intelligence Research. Retrieved November 18, 2009,
from http://www.beyeresearch.com/study/11012 .
Eckerson, W. (2007). Predictive Analytics. Extending the
Value of Your Data Warehousing Investment. The
Data Warehousing Institute. Retrieved November 16,
2009, from http://download.101com.com/pub/tdwi/
Files/PA_Report_Q107_F.pdf .
Fayyad, U., Gregory, P. S. & Padhraic S. (1996). From
Data Mining to Knowledge Discovery in Databases.
The AI Magazine, 17(3), 37-54.
Golfarelli, M., Rizzi, S. & Cella, I. (2004). Beyond Data
Warehousing – What’s Next in Business Intelligence?
Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Workshop
on Data Warehousing, Washington, D.C., USA, 1-6.
Gray, P. & Negash, S. (2003). Business Intelligence.
Proceedings of the 9
th
Americas Conference on
Information Systems, Tampa, Florida, USA.
Inmon, W. H. (2002). Building the Data Warehouse. New
York: John Wiley & Sons.
Holsheimer, M. & Siebes, A. (1994). Data Mining: the
Search for Knowledge in Databases. Centrum voor
Wiskunde en Informatica Report, R9406, 1-78.
Kimball, R., Ross, M., Thornthwaite, W., Mundy, J. &
Becker, B. (2008). The Data Warehouse Lifecycle
Toolkit (2
nd
edition). Indianapolis: John Wiley & Sons.
Klimko, G. (2001). Knowledge Management and Maturity
Models: Building Common Understanding.
Proceedings of the 2
nd
European Conference on
Knowledge Management, Bled, Slovenia, 269-278.
Misner, S., Luckevich, M. & Vitt, E. (2002). Making
Better Business Intelligence Decisions Faster.
Redmond: Microsoft Press.
Nagpal, A. & Krishan, K. (2008). Business Performance
Management: Next in Business Intelligence.
Proceedings of the 2
nd
National Conference on
Challenges and Opportunities in IT, India.
Panian, Z. (2007). Just-in-Time Business Intelligence and
Real-Time Decisioning. International Journal of
Applied Mathematics and Informatics, 1(1), 28-35.
Sacu, C. & Spruit, M. (2010). BIDM: The Business
Intelligence Development Model (2010-010). Utrecht:
Utrecht University.
Vaishnavi, V. K., & Kuechler, W. (2007). Design Science
Research Methods and Patterns: Improving and
Innovating Information & Communication
Technology. Boca Raton: Auerbach Publications.
Weerd, I., van de (2009). Advancing in Software Product
Management: An Incremental Method Engineering
Approach. Utrecht: Utrecht University.
BIDM - The Business Intelligence Development Model
293
