
AN APPROACH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT
OF DOOH-ORIENTED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Pietro D’ambrosio
1
, Filomena Ferrucci
2
, Federica Sarro
2
and Maurizio Tucci
2
1
NET FIRST srl – Salerno, Italy
2
University of Salerno,Via Ponte don Melillo, 84084, Fisciano (SA), Italy
Keywords: DOOH-oriented Information Systems, Development Methodology, Autonomic Computing, Context
Awareness.
Abstract: The last years are characterised by an increasing demand of using digital services and multimedia content
“out of home”. This poses new challenges to software factories in terms of integration and extension
systems. In this paper, we report on an industrial research project realized by some ICT companies together
with some researchers of the University of Salerno. The goal of the project was to define a new approach for
developing Enterprise systems able to integrate traditional applications with Digital Out Of Home (DOOH)
extensions. The experience was carried out defining a methodology and some tools to develop such type of
systems in an industrial context. The proposed approach was evaluated carrying out two case studies.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the last years there is an increasing demand for
using digital services and contents “out of home”.
Hardware and software solutions that allow users to
interact with content distribution systems in public
environment (e.g., streets, stations, airports,
shopping centres) are classified as a new family of
systems named “Digital Out Of Home” (DOOH). In
market areas where the competitiveness and
attention to the customer is very high, such as the
financial/banking and tourism, it has been
recognized that these new ways of consuming digital
services can be crucial for the continuity and
expansion of the business. This results in a growing
attention to this kind of products and in an emerging
need to evolve the companies’ information systems
to integrate DOOH features, giving rise to a new
kind of systems that we name DOOH-Oriented
Enterprise Information Systems (DOOHIS). Some
features characterize this kind of systems, such the
use of multi interaction devices, multimedia content,
multimodal interaction, context awareness. Indeed,
the ICT technologies advances of last years make
available on the market a great variety of multimedia
devices (interactive showcases, interactive tables,
virtual or augmented reality systems, etc...) that
allow forms of interaction with users more and more
fascinating. Moreover, these systems are supposed
to execute in a ubiquitous, heterogeneous
infrastructure (possibly mobile) and in different
execution environments or contexts. They should be
able to sense the context in which they are executing
and change their behaviour in response to external
changes (Inverardi and Tivoli, 2009). Thus,
traditional information systems have to be integrated
with new "channels", new devices and
environmental sensors.
This poses new challenges in terms of
integration and extension. Indeed, DOOH features
are usually realized employing custom technologies,
which make difficult the integration with pre-
existing information systems. Moreover, the strong
demand of these systems forces software factories to
redefine their development process to adapt it to the
complexity of these new products. On the same
time, companies have to deal with crucial issues
critically increased by the current economic scenario
and the high competitiveness requested by the
globalized market, such as:
The production of DOOHISs is very expensive
since the cost to develop a system exponentially
grows with the increase of system complexity.
The market sector is characterised by high
competitiveness and frequently changes in rules.
326
D’ambrosio P., Ferrucci F., Sarro F. and Tucci M. (2010).
AN APPROACH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF DOOH-ORIENTED INFORMATION SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages
326-331
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The reuse of software component is very low.
This is mainly due to the fact that often the cost
of adaptation of these components is too high.
The strong dynamism of the market. This
phenomenon forces ICT companies to a dynamic
organization of their staff, also considering the
opportunity to take the form of "virtual
enterprise".
Starting from the above considerations an industrial
research project has been jointly carried out by some
Italian software companies and some academic
researchers of University of Salerno. The aims of the
project were to define a new approach able to reduce
development costs for DOOHISs and at the same
time improve their quality. The critical aspects to be
addressed to achieve these goals were:
Support the component software reuse;
Reduce domain application knowledge transfer
risks, such as misunderstanding system
requirements;
Automate a significant part of the development
process without missing the possibility to
manually realize integrations and modifications.
Thus, we defined an approach, named EMAF
(Enterprise Multilevel Applicative Framework)
which is specialized for the development of
DOOHISs. In particular, to realize such systems we
proposed an architecture (i.e., EMAF Architecture),
a development methodology (i.e., the EMAF
Methodology) and a set of tools which support the
stakeholders in the various phases of the proposed
development process. The approach was employed
to develop two information systems for two different
application domains, namely financial and tourism.
The remainder of the paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 provides a background on DOOH
applications and highlights issues and challenges in
integrating them in an enterprise information system.
Section 3 describes the approach we propose. In
Section 4 we describe the two case studies related to
the use of the proposed approach and the lessons
learned. Some final remarks and future work
conclude the paper.
2 DOOH-ORIENTED
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Hardware and software solutions that allow users to
interact with content distribution systems in public
environment (e.g., streets, stations, airports,
shopping centres) are classified as “Digital Out Of
Home” (DOOH) applications. The first kind of
DOOH-applications was the Digital Signage, ideated
to reduce production and distribution costs of paper
advertisements in busy environments. The
technology and the habits in using such type of
systems are evolved quickly to the point to introduce
new forms of communication with users and content
fruition. At the same time it has been recognized the
effectiveness of these systems in improving
emotional involvement, attracting user attention and
influencing its purchase decision (increases up to
75% were observed) and, more generically,
increasing a positive perception of the environment
and the brand.
All this has encouraged the ICT sector to search
for applications, technologies and modality of use
more and more involving and spectacular with the
aim to directly interact with the consumer by
delivering content personalized and adaptable on the
basis of the current time or the specific fruition
location. Moreover, the opportunity to reach specific
customers in a specific moment has also allowed for
customizing and personalizing information and
making more comfortable the fruition of services.
Thus, the use of DOOH solutions to communicate
and to interact with consumers in an urban context
or in public environments offers some important
advantages in terms of effectiveness and economy of
management. Furthermore it allows delivering new
services, creating new opportunities of interaction
with consumers and new opportunities of business.
The majority of DOOH solutions are able to
manage networks of different devices, such as LCD
displays, video-walls, and PDAs. Thus, there is the
need to realize a sort of dynamic content fruition that
allows differentiating the content and the planning
for groups of devices, typology of device,
geographical area or a single device. These
advanced systems should also be able to acquire data
from existing information systems and to plan
actions based on specific events (e.g., activated by
temporal advance, by local devices or by particular
information received from the environment). For
instance, in the case of an airport, this feature should
allow us to relate the displaying of a particular
advertisement/information or the start of a specific
application to an event such as the opening or the
closing of a gate.
The extreme variety of multimedia devices (each
one characterized by specific features) introduces
new challenges in terms of ability in using them and
integration with specialized applications. These
difficulties together with the need to contain the
development costs determine that in the majority of
present solutions the interaction with users is
AN APPROACH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF DOOH-ORIENTED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
327

PHASE1
PHASE2PHASE3
Applicative
Domain
Expert
Developer
EMAF
specialist
IT Analyst
Graphic
Designer
1
2
3
5
4
(1). Functional requirements elicitation
and logic interface definition
(2). Non-functional
requirements
elicitation
(3). Graphic interface
and layout definition
Authoring Environment
(4). Automatic generation of target system
components based on
transactional models, reference architecture,
and information gatherde in phase 1
(5). Business kogic and database development,
service implementation, system testing
Generation Environment
Development Environment
PHASE1
PHASE2PHASE3
Applicative
Domain
Expert
Developer
EMAF
specialist
IT Analyst
Graphic
Designer
1
2
3
5
4
(1). Functional requirements elicitation
and logic interface definition
(2). Non-functional
requirements
elicitation
(3). Graphic interface
and layout definition
Authoring Environment
(4). Automatic generation of target system
components based on
transactional models, reference architecture,
and information gatherde in phase 1
(5). Business kogic and database development,
service implementation, system testing
Generation Environment
Development Environment
(1). Functional requirements elicitation
and logic interface definition
(2). Non-functional
requirements
elicitation
(3). Graphic interface
and layout definition
Authoring Environment
(4). Automatic generation of target system
components based on
transactional models, reference architecture,
and information gatherde in phase 1
(5). Business kogic and database development,
service implementation, system testing
Generation Environment
Development Environment
Figure 1: The proposed methodology.
managed only by dedicated stations which run
specific applications. Moreover, few differentiations
of the content are realized usually based on static
information such as typologies of terminals or their
locations. It is obvious that the traditional forms of
content management based on palimpsests and
planning become inadequate in presence of complex
environments or content characterised by high
variability. Moreover, it is worth noting that to
realize effective content and schedules, an editorial
structure composed by people with different and
specialized know-how and skills is required with
consequent increasing of costs and operational
complexity.
Thus, the challenges that are currently presented
to the industry of DOOHISs concern the
introduction of "intelligence" in the management of
complex terminal networks with the goals to
maximize the characteristics of content geolocation
and context awareness, to reduce the costs of
planning of the program schedule, to improve the
interactivity with users and to support a greater and
easier integration with external systems and
technologies.
3 THE PROPOSED APPROACH
To address the issues highlighted in the previous
section we propose a solution where a DOOHIS is
formed by two different components: an
“intelligent” DOOH-application and a web
application. The former acts as container, while the
latter is a traditional web application that can be
executed also out the container. In particular, the
DOOH-system manages the devices and sensors
Domain Knowledge
Technical Skills
EMAF
Skills
Application
Domain
Expert
• Functional requirements
...elicitation
• Functional analysis
• Interface definition
• Rapyd prototyping
EMAF
Designer
• Automatic generation of
..system components based
..on transaction models, a ..
..reference architecture, and
..information gathered in .. ..
..the prevoiuse phase.
Technical
Expert
• Business logic and
..database.
• Sevice deployement
• System testing
Developer
PHASE ROLES
•Non-functional requirements
..elicitation
• Graphical Layout definition
Domain Knowledge
Technical Skills
EMAF
Skills
Application
Domain
Expert
• Functional requirements
...elicitation
• Functional analysis
• Interface definition
• Rapyd prototyping
EMAF
Designer
• Automatic generation of
..system components based
..on transaction models, a ..
..reference architecture, and
..information gathered in .. ..
..the prevoiuse phase.
Technical
Expert
• Business logic and
..database.
• Sevice deployement
• System testing
Developer
PHASE ROLES
•Non-functional requirements
..elicitation
• Graphical Layout definition
Figure 2: The methodology hourglass.
network and makes actions on the basis of a defined
plan or triggered by specific events and context
changes recognized by a smart engine. The web
application when it is executed in the DOOH
container is capable of interacting with the
environment and sending events-messages to the
DOOH-system. This event-message can be used to
activate computing processes, modify a previously
defined plan, or, more in general, modify the state of
the system.
As an example, let us consider a video-wall
placed in a strategic point to display a multimedia
show composed by videoclip, news, advertisement
or tourist information. This show can vary on the
basis of a specific happening, such as the
identification of an RFID tag contained in a tourist
card, the recognition of people standing in front of
the video-wall and watching the show, a specific
request (e.g., a button pressed by the user). Indeed,
the DOOH-system is capable to capture several
events and to activate for each one a specific web
application that provides the user with a set of
functionality related to the profile identified.
Moreover, when the application is activated the
system can choose how display it on the basis of the
capabilities (e.g., display size) of the device on
which it will be visualized and the priority given to
the other running applications. Thus, in the reported
example the DOOH-system recognizes the need to
start a specific application and decides the way to
present it to the final user, while the web application
manages the interactive functionalities.
3.1 The EMAF Methodology
To design and develop the described kind of DOOH-
oriented information systems we devised a
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
328

“multilevel methodology” characterised by the
subdivision of the activities in some levels and by a
high involvement of non-ICT stakeholders. The
proposed subdivision let each professional figure
involved in the development process to design a
specific view of the system (e.g., graphic interface,
menu and interaction style, business logic, ...) using
the tools and the interface metaphors more suitable
for his/her role. This approach reduces the effort
needed to transfer the knowledge from experts of the
application domain to technology specialists.
Moreover, it has the appreciable advantage to reduce
the risk of misunderstanding system requirements
allowing an immediate validation of the target
system behaviour (interface, page layout, glossary,
etc...).
The proposed methodology decomposes the
development process in three macro phases (see
Figure 1):
1. Systematic elicitation of functional requirements,
project design choices, interfaces, business logic,
etc. These tasks require the involvement of
several professional figures (application domain
experts, analyst, graphic designer, multimedia
experts, communication experts,...) and are
supported by some authoring tools.
2. Automatic generation of software code (i.e.
skeleton) on the basis of models and reference
architecture and framework;
3. Manual fulfilment of skeletons realized by
developers on specific “change points”.
Figure 2 shows how the competences are distributed
during the software development process. In
particular, the middle point of the hourglass
highlights a significant reduction of the professional
figures with specific technical skills needed to the
software factory to realize the products. On the
contrary, there is an increasing involvement of
application domain experts and system analysts and
developers. This aspect is crucial to facilitate a
dynamic organization of project teams and to share
factory infrastructure between different companies.
3.2 The EMAF System
The EMAF system we designed to support the
proposed methodology is composed by several
components each one belonging to one of these
subsystems: authoring tool, automatic generation
tool, run-time environment (see Figure 3). The
authoring system is composed by two subsystems:
the DOOH Authoring System (DAS) and the
Services Authoring System (SAS). The first is used
to define the DS/DOOH container, while the latter is
used to define the Web application. In particular,
DAS (Figure 4) is composed by two main
components: (i) the Multimedia Management
Console (MMC) employed to manage multimedia
resources, to define program schedules and content
plans for the various system channels and (ii) the
Layout Management System (LMS) employed to
define the multimedia container layout and to
identify the area where players able to show specific
content are executed.
On the other hand, SAS (Figure 5) provides
stakeholders with a set of authoring tools which
allow defining web application structure and the
related logic aggregating information coming from
multiple sources. Indeed, several stakeholders can be
involved in the development process (multilevel
approach) and each of them can use a specific tool to
work with the system representation more
appropriate to his/her role.
Figure 3: The proposed system.
Authoring System
Multimedia Application
Layout, Areas, Channels
DOOH Designer
Data Base
Multimedia Contents
Mutlimedia Content
ManagementSystem
Definition of program
schedules and plans
Media Expert
EMAF ICT
Specialist
Events Rules
Actions
Autonomic
Engine
Cooperative Agents Network (“Sensors”)
AG AG AG AG
Run Time Environment
Applicative Service (“Effectors”)
Plan &
Analysis
Multimedia Player
(DOOH Client )
Content Distribution
for DOOHClients
Authoring System
Multimedia Application
Layout, Areas, Channels
DOOH Designer
Data Base
Multimedia Contents
Mutlimedia Content
ManagementSystem
Definition of program
schedules and plans
Media Expert
EMAF ICT
Specialist
Events Rules
Actions
Autonomic
Engine
Cooperative Agents Network (“Sensors”)
AG AG AG AG
Run Time Environment
Applicative Service (“Effectors”)
Plan &
Analysis
Multimedia Player
(DOOH Client )
Content Distribution
for DOOHClients
Figure 4: The DOOH Authoring System (DAS).
AN APPROACH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF DOOH-ORIENTED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
329
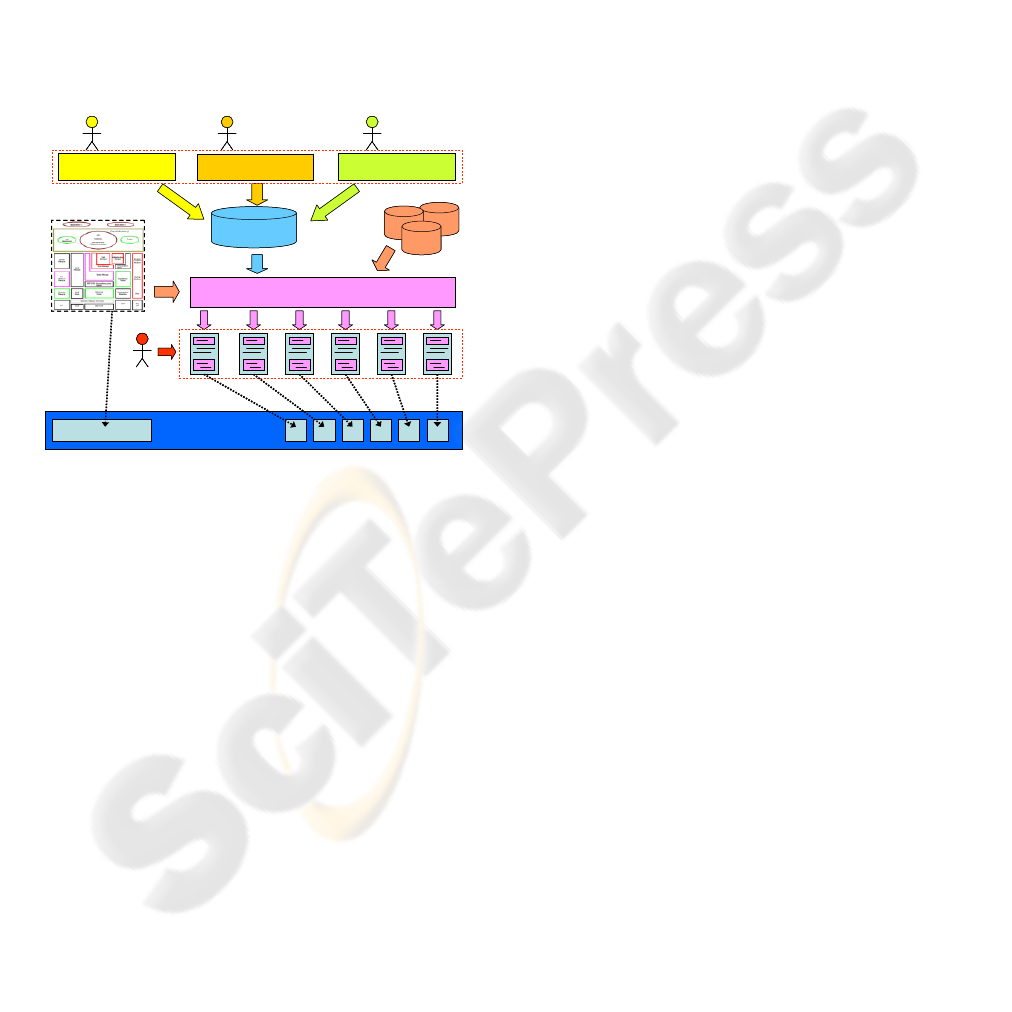
As an example, Figure 5 shows three authoring
tools employed to define the graphic, functional, and
technological features of the DOOH-oriented system
to be realized. All the information produced by the
authoring tools is stored in a centralized repository.
This information is used by the generation system to
automatically develop pieces of code (i.e., skeletons)
that have to be completed by developers to realize
system functionality. It is worth to note that the
automatic generation is accomplished exploiting
component models that are modifiable. This
simplifies the system adaptation when the software
factory needs to make changes or the use of new
standards or technologies is imposed by the
customer.
Models
Authoring System
Functional Level
Software
Analyst
Authoring System
Tecnical Level
System Analyst
Data Base
Models
Models
Generation System
(automatically produces software code pieces modifiable by developers)
Developer
Authoring System
Graphic Level
Graphic Designer
Reference
and
Architecture
Framework
Run Time System
Comp Comp Comp CompCompComp
Predefined components
Models
Authoring System
Functional Level
Software
Analyst
Authoring System
Tecnical Level
System Analyst
Data Base
Models
Models
Generation System
(automatically produces software code pieces modifiable by developers)
Developer
Authoring System
Graphic Level
Graphic Designer
Reference
and
Architecture
Framework
Run Time System
Comp Comp Comp CompCompComp
Predefined components
Figure 5: The Service Authoring System (SAS).
The run-time system is composed by some
reusable components and by all the components
produced by developers starting from the skeletons
generated by the system. In particular, based on the
reference architecture and framework the following
components were employed:
A component for the dynamic rendering of
interfaces which manages at run-time the
building of a customized layout for specific users
and channels.
An autonomic engine (IBM, 2006) (Muller et al.,
2009) (Brittenham et al., 2007) which makes
decisions on the basis of a logic defined by
events, rules and actions. In particular, this
engine is able to monitor the events collected by
a network of cooperative agents (i.e.,
environmental sensors and interactive devices)
and perform the appropriate actions (i.e., execute
a specific application services);
A distribution system which allocates content
and applications on the devices belonging to the
DOOH network on the basis of program
schedules and content plans defined by the
Multimedia Management Console.
4 CASE STUDIES
To evaluate the cost/effectiveness of the proposed
approach we carried out two case studies. In
particular, the proposed approach was applied to
develop two DOOHISs for two different application
domains, namely financial and tourism domains.
Indeed, we believe that in these sectors the
application of DOOHISs will grow in the next years.
The first case study is related to a system
developed with the aim to improve the relationship
between a bank and its customers. Indeed, we
developed a DOOHIS to manage the internal and
external communication and provided services to the
customers through new interaction modalities. In
particular, the bank was equipped with I/O devices
and environmental sensors which provided the
DOOHIS with the information needed to make
decisions and supply the appropriate services to each
customer. The I/O devices represent
“communication channels” and for each device
several DOOH functionalities and application
services were developed. As an example we
introduced the use of an interactive totem which
displayed information and multimedia contents
following the programs schedule defined by the
Multimedia Management Console. The
environmental sensors allow the system to recognise
whether an user is near the totem and a face
detection algorithm is employed to count how many
users are seeing the display. Moreover RFID tags
contained in customer card, allow the system to
univocally identify the customers. This information,
together with the ones gathered by environmental
sensors (e.g., number of people present in the bank
office, current day, time) are exploited by the
autonomic engine to decide the more suitable
contents to show through the totem suggesting
specific contents for the customers and providing
him/her with interactive functionalities.
The second DOOHIS was designed to meet the
growing demands of digital tourism products,
especially for tourism service customizations and
integrations of public services (e.g., security, health,
transport) with tourist information in urban areas.
Indeed, such a system can be used in a city to
manage the network of sensors and devices (e.g.,
multimedia Totem, videowall) employed to offer a
service to a final user (i.e., a tourist). The user can
interact with the system in various way using his/her
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
330

device (e.g., PDA, cellular phone, netbook) or the
devices placed in the environment and can use
information and services provided in push or pull
mode. Differently from the first case study, we
extended the type of devices employed to access to
the services and experimented interface metaphors
to deal with different devices. Moreover, a web
application for a tourist assistance centre was
developed employing the proposed authoring tools.
The application let to collect and manage the
requests coming from tourists or a supplier network.
The case studies played an important role in our
project since let us to evaluate the industrial
employment of the proposed approach and to study
the impact that the proposed methodology and
systems had on the software factories organization.
To this aim, the project team was composed by
people coming from the different companies which
took part to the industrial research project. This let
us to observe the learning times and the
methodology effectiveness in a heterogeneous and
“not yet consolidated” context. The case studies
allowed us to derive the following remarks.
A successfully involvement of non-ICT
stakeholders was observed in requirements
elicitation and user interface definition phases.
Indeed, the involved non-ICT stakeholders found
very easy the use of the proposed models.
A consistent reduction of development and
testing time was obtained (i) employing a reference
framework, (ii) defining the application logic on a
set of rules, services and service workflow, and (iii)
automatically generating skeletons for software
components which have to be fulfill by developers.
Moreover, we observed that the second case
study was conducted more easily and quickly than
the first one. This was due to the reuse of several
components. Indeed, a reduction of lines of code
construction to realize system functionality, were
observed.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the paper we have highlighted the challenges that
software companies have to address for the
development of a new typology of information
systems (DOOHISs), whose demand is highly
increasing in the last years and that provide great
opportunities for business and services. The specific
contributions of the paper are:
The definition of a development methodology for
DOOHISs;
The development of a tool based on the proposed
methodology, compatible with a reference
software architecture and a reference functional
framework;
The validation of the proposed approach in two
application domains, namely financial and
tourism, to evaluate whether it is cost/effective in
an industrial reality. The demonstrative systems
for financial and tourism application domains
were characterised by the integration of some
application services in a network of devices with
interactive digital functionality.
The results achieved were encouraging and
motivate further experimentations of the proposed
approach with the aim to refine and transfer it to the
industrial context. The ICT companies that took part
into the industrial research project are introducing in
their development processes some authoring
components. Systematically collecting feedbacks
from stakeholders and comparing them with data
acquired by company reporting systems is very
useful to have an evaluation of the advantages that
derive by employing the proposed methodology.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research has also been carried out thanks to the
“Misura 3.17- POR Campania 2000/2006. Progetto
Metadistretto del settore ICT” funded by the
following partners: DMI Unisa, Gruppo Net Srl, Net
First Srl, Acube Lab Srl.
REFERENCES
Brittenham, P., Cutlip, R.R., Draper, C., Miller, B.A.,
Choudhary, S., Perazolo, M., 2007. IT Service
Management Architecture and Autonomic Computing.
IBM Systems Journal 46(3), pp. 565–581.
IBM Corporation 2006. “An Architectural Blueprint for
Autonomic Computing”, 4th ed, http://www-
03.ibm.com/autonomic/pdfs/ACBlueprintWhitePaper4
th.pdf
Inverardi P., Tivoli M., 2009. The Future of Software:
Adaptation and Dependability. In A. De Lucia, F.
Ferrucci (Eds.) Software Engineering, International
Summer Schools, ISSSE 2006-2008. LNCS
5413Springer, pp. 1-31.
Müller H.A., Kienle H.M., Stege U., 2009. Autonomic
Computing Now You See It, Now You Don't. In A. De
Lucia, F. Ferrucci (Eds.) Software Engineering,
International Summer Schools, ISSSE 2006-2008.
LNCS 5413Springer, pp. 32-54.
AN APPROACH FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF DOOH-ORIENTED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
331
