
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING
SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
Daniel Slamanig
1
and Stefan Rass
2
1
Department of Medical Information Technology, Healthcare IT & Information Security Group
Carinthia University of Applied Sciences, 9020 Klagenfurt, Austria
2
Institute of Applied Informatics, System Security Group, Klagenfurt University, 9020 Klagenfurt, Austria
Keywords:
Anonymity, Privacy, Anonymous authentication, Anonymous transactions, Public-key encryption, One-show
tokens, Blind signatures.
Abstract:
While privacy was more or less neglected in the early days of the Internet, in recent years it has emerged to
be a hot topic in computer security research. Among other reasons, since the use of the Internet is becoming
more and more ubiquitous, cloud computing emerges and consequently users provide a lot of information to
potentially untrusted third parties. In this paper we propose an approach which provides a means for users to
anonymously conduct transactions with a service-provider such that those transactions can neither be linked to
a specific user nor linked together. At the same time, a service-provider can be sure that only authorized users
are able to conduct transactions. In particular, we bring together the concepts of anonymous authentication
from public-key encryption and anonymous as well as unlinkable token based transactions in order to profit
from the advantages of the two single approaches. Since full anonymity is usually not desirable, we provide
mechanism to identify misbehaving anonymous users behind transactions. More precisely, we realize selective
traceability, which allows revocation of the anonymity of a suspicious users along with the identification of
all of her transactions, without violating the privacy of all remaining users.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, many services and applications are provided
via the Internet resulting in advantageous “anytime,
anywhere” access for users. However, privacy be-
comes a major concern, and its protection is chal-
lenging in several ways. Ideally, a user is able to
conduct transactions with a service-provider in a way
such that a transaction cannot be assigned to an iden-
tity (anonymity), nor may two or more transactions
be related to each other efficiently (unlinkability). On
the other hand, preserving security for the provider re-
quires that only authorized users are able to consume
a service and users can be revoked in case of suspi-
cion (traceability).
Interesting applications are in the field of cloud-
computing and especially if even seemingly harmless
information about the service-usage behavior, e.g.
access frequencies, frequencies of transactions, ac-
cessed content, can be valuable information for the
service or the cloud provider and needs to be pro-
tected from those insiders and wiretappers. One il-
lustrative example is within the healthcare domain,
where applications allowing the management of very
sensitive health-information for everyone via the In-
ternet, so called Personal Health Records, are grow-
ing rapidly (e.g. Google Health, Microsoft Health
Vault). In this context, such information can reveal
a lot about the state of health of a specific person,
e.g. access frequencies will correlate with the state
of health. Hence, if such information are available
for instance to human resource managers, this could
massively influence the chances of getting a job.
1.1 Contribution
In this paper we propose an approach to realize
anonymous and unlinkable, but authorized service us-
age based on a combination of anonymous authentica-
tion from public-key encryption and one-show tokens
obtained from blind signatures. Our approach is espe-
cially applicable for services with many users, which
dynamically join and leave a service, and frequently
conduct transactions with a service-provider. Further-
more, our proposed construction achieves all aspects
discussed in the introduction at very low computa-
132
Slamanig D. and Rass S. (2010).
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 132-141
DOI: 10.5220/0002994501320141
Copyright
c
SciTePress

tional overhead, whilst coming at negligible cost for
implementation, as only standard (and already widely
implemented) public-key cryptography and state of
the art smart-cards are used. This is especially of
interest, since public-key infrastructures are widely
available today.
Our contributions in this paper are manifold.
Firstly, we introduce a novel paradigm called postac-
tive anonymous authentication from public-key en-
cryption, which allows us to realize anonymous au-
thentication at the cost of a single decryption for
users, in contrast to O(n) decryption resp. encryp-
tion operations for schemes known so far. Thereby n
is the number of users, the so called anonymity-set.
Secondly, we introduce a combination of anonymous
authentication from public-key encryption and anony-
mous one-show tokens from blind signatures. Finally,
we present several extensions to one-show tokens in-
cluding fine-grained validity periods and most notable
selective traceability. The latter propertymeans, that a
trusted traceability authority is able to link all transac-
tions of a suspicious anonymous user as well as iden-
tify this user, without violating the privacy of the re-
maining users.
1.2 Intuition behind our Construction
In a nutshell, our construction is as follows. A
user registers with a service-provider by providing
a public-key of a public-key encryption scheme and
registers with a traceability authority. Additionally,
we assume that user’s are in possession of a tamper
resistant smart-card. The service-provider maintains
a directory D of these public-keys along with a valid-
ity of service usage. Users anonymously authenticate
against a subset of users in this directory and if the
authentication succeeds they obtain a blind signature
for a token. On presenting a valid token-signature pair
along with a query for a service, the service-provider
checks whether the signature is valid, the token was
not already used and is valid for the current time-
period. If all these checks hold, he responds with the
answer to the query. Simultaneously, he issues a blind
signature for a new token. Consequently, users can
conduct sequences of transactions with the service-
provider. If suspicion occurs, the service-provider can
give the token corresponding to a suspicious transac-
tion and the blacklist containing already spent tokens
to a traceability authority, who in turn is able to (1)
identify the respective user and (2) find all transac-
tions of this user without violating the anonymity of
other users (opening tokens of other users). Note, that
all actions of users are anonymous and unlinkable.
2 RELATED WORK
Several token-based approaches have been proposed
so far, although having in mind quite diverge appli-
cations. The most prominent are anonymous creden-
tial systems introduced in (Chaum, 1985). The basic
idea is that users are able to obtain credentials (to-
kens) for different pseudonyms from different orga-
nizations and can prove the possession of these cre-
dentials without revealing anything more than the fact
that they own such credentials. Over the years there
have been proposed different approaches to design
anonymous credential systems providing quite dif-
ferent functionalities (Lysyanskaya et al., 2000; Ca-
menisch and Lysyanskaya, 2001; Verheul, 2001). Al-
though anonymous credential systems are very pow-
erful, realizing identity-escrow, limiting the number
of showings as well as realizing dynamical joining
and revoking of users comes at high computational
costs. Furthermore, we do not focus on systems that
involve multiple credential (token) issuers and veri-
fiers and are looking for more efficient solutions.
Another class of schemes are multi-coupon (MC)
systems (Canard et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2007),
whereas a MC represents a collection of coupons
(or tokens) that is regarded as a single unit. Ba-
sically, a user is issued a batch of tokens (which
are tied together) and is allowed to spend one to-
ken after another in an anonymous and unlinkable
fashion. The most sophisticated schemes (Canard
et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2007) are based on signa-
ture schemes that allow users to obtain signatures on
(committed) sequences of messages and provide ef-
ficient zero-knowledge proofs of knowledge of sig-
natures and properties of signed message elements
(Camenisch and Lysyanskaya, 2002; Camenisch and
Lysyanskaya, 2004). Although these schemes are
conceptually very elegant, they are quite expensive
and do not provide (selective) traceability.
Recently, a scheme for anonymous subscriptions,
based on one of those signature schemes was pro-
posed in (Blanton, 2008). The concept is very ap-
pealing and it provides an elegant solution to re-
alize validity-periods of subscriptions using zero-
knowledge range proofs, but it does not support (se-
lective) traceability, which is an important feature
of our construction. Another construction of (Ca-
menisch et al., 2006) focuses on n-times anonymous
authentication, which allows to identify a user if he
spends more than n tokens within one time-period.
However, they also do not focus on selective trace-
ability.
To the best of our knowledge, the only solution
to selective traceability so far are traceable signatures
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
133
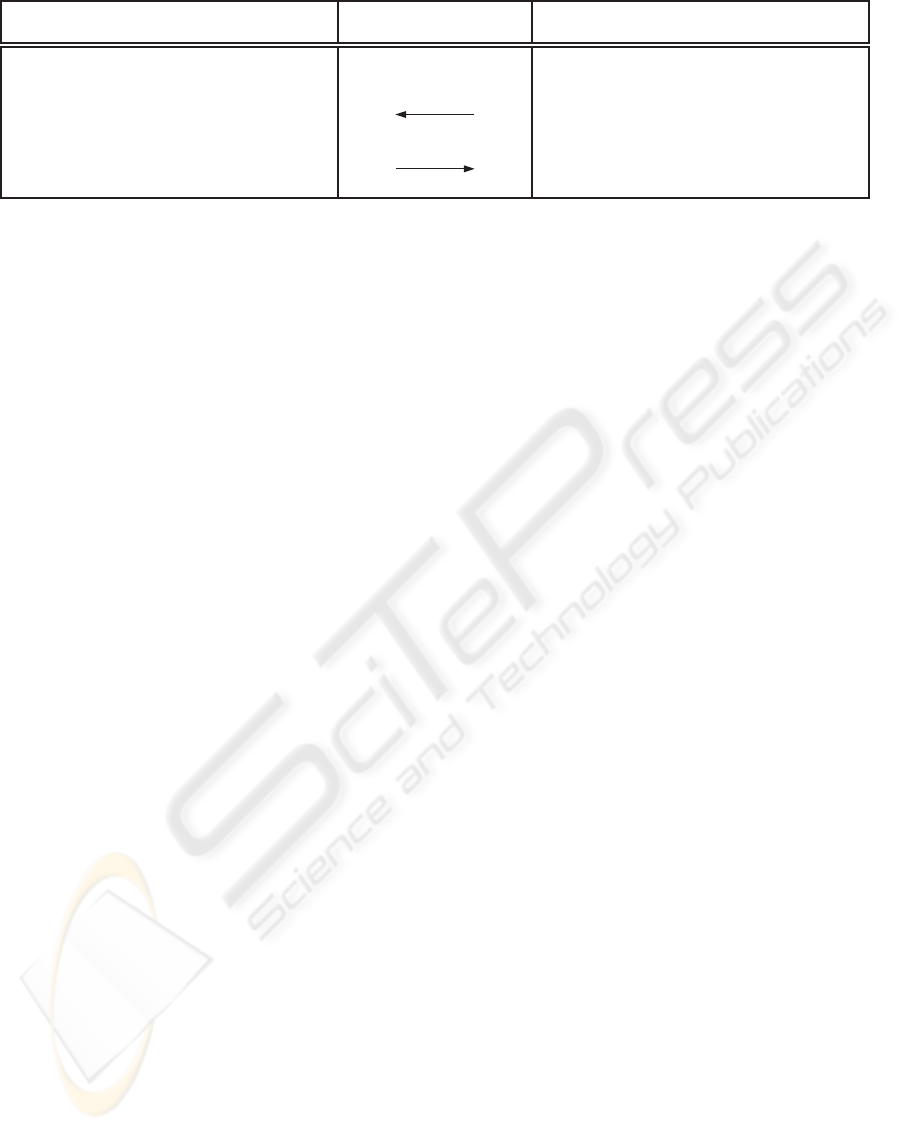
User Verifier
SK
u
i
D
c ∈
R
{0,1}
κ
c
c = (E
PK
u
1
(c),.. . ,E
PK
u
n
(c))
c
′
= D
SK
u
i
(c[i])
c
′
?
= c
Protocol 1: Anonymous authentication from PKE.
(Kiayias et al., 2004; Libert and Yung, 2009), which
are, however, rather of theoretical interest. In con-
clusion, none of the aforementioned approaches pro-
vides an efficient way to realize selective traceabil-
ity, whereas our construction presented in this paper
achieves this goal at a reasonable overall cost.
3 POSTACTIVE ANONYMOUS
AUTHENTICATION
In this section we present a novel paradigm for
anonymous authentication schemes from public-key
encryption (PKE), which we call postactive anony-
mous authentication. Anonymous authentication
from public-key encryption and its application is not
absolutely new (Schechter et al., 1999; Lindell, 2007;
Xi et al., 2008; Slamanig et al., 2009), but allows a
convenient way for a prover to anonymously authen-
ticate to a verifier providing user-chosen bandwidth-
anonymity trade off. More precisely, users can deter-
mine on their own the size of the anonymity-set (as
a subset of all users) and consequently determine the
bandwidth consumption of the protocol (see below).
3.1 Deterministic from Probabilistic
Public-key Encryption
The notion of deterministic public-key encryption
was introduced in (Bellare et al., 2007). Basically,
the idea behind this concept is to turn any probabilis-
tic PKE into a deterministic scheme. One general
and efficient construction is the so called “Encrypt-
with-Hash” (EwH) construction introduced in (Bel-
lare et al., 2007), which will be discussed subse-
quently. An EwH scheme is based on a probabilistic
PKE scheme and deterministically encrypts a plain-
text m by applying the encryption algorithm of the
probabilistic scheme, whereas the used random coins
ω are not chosen uniformly at random, but are com-
puted as a hash of the public key PK and the plain-
text m. Consequently, everybody who knows a mes-
sage m and a ciphertext c (presumably an encryption
of m), can deterministically infer the random coins
used for the encryption, i.e. compute ω = H(PK, m)
and c
∗
= E
PK
(m;ω) and check whether the encryp-
tion c
∗
computed by him equals the given ciphertext.
If c
∗
= c holds, they are both encryptions of the same
message m. It should be noted that the output of the
hash-function needs to be suitable for the use as ran-
dom coins in the respective PKE scheme.
3.2 Anonymous Authentication from
Public-key Encryption
Loosely spoken, the basic idea behind anonymous au-
thentication protocols is that a verifier runs n paral-
lel instances of a challenge-response protocol based
on public-key encryption using n distinct public keys
with one anonymous prover, who represents n “vir-
tual” provers (we call this set the anonymity-set).
Recall, in a challenge-response protocol authentica-
tion is achieved by demonstrating the ability to cor-
rectly decrypt an encrypted challenge. In anonymous
authentication, the verifier chooses one (fixed) chal-
lenge and encrypts it with everyones public-key (of
the anonymity-set). Hence, if the prover is able to
provide the challenge bit-string to the verifier, the
verifier can be sure that the unknown prover is in
possession of at least one secret which corresponds
to one of the n public-keys. In protocol 1, we as-
sume that a user u
i
authenticates against a directory
D = ((ID
u
1
,PK
u
1
),... ,(ID
u
n
,PK
u
n
)).
However, the verifier can cheat by encrypting dis-
tinct challenges c
1
,. .. ,c
n
for distinguishing differ-
ent responders based on the specific challenge. If
the encryptions of all ciphertexts in the challenge-
sequence are deterministic (such as RSA or Rabin’s
scheme), then u
i
may as well encrypt c
i
using all re-
maining public-keys to see whether or not the chal-
lenges match (Schechter et al., 1999). This is what
we call trial encryptions. The same can be done by
turning probabilistic public-key encryption schemes
into deterministic ones (see section 3.1) as proposed
in (Slamanig et al., 2009), which is no longer prone to
SECRYPT 2010 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
134

known security flaws of the aforementioned schemes
and retains the efficiency. Nevertheless, the compu-
tational effort for the user is linear in the size of the
anonymity-set in any case and furthermore the user
needs to be in possession of all other public-keys.
To reduce the computational effort, users could per-
form trial encryptions only for a reasonably small ran-
domly subsequence of the challenge-sequence result-
ing in more efficient protocols providing probabilis-
tic anonymity (Slamanig et al., 2009). However, the
need for the public-keys of the respective users still
remains.
3.3 Postactive Anonymity
The basic idea behind postactive anonymous authen-
tication is that users do not compute trial encryptions
anymore, but post their received challenge-sequence
along with the signature for the challenge-sequence
of the verifier along with the decrypted random chal-
lenge to a public bulletin-board. Clearly, this should
not be done until the user has successfully authenti-
cated and the challenge is invalidated.
Now, we assume that users help each other and
visit the bulletin-board frequently to check whether
the verifier behaves honest. This can be done, when
deterministic PKE schemes (obtained by applying the
EwH construction discussed in section 3.1) are used
and the challenge (the plaintext) is known. If a user
notices that a verifier has cheated, the user can show
this transcript to a judge and can convincehim that the
verifier has cheated. Since the verifier has digitally
signed the transcript, he cannot repudiate the cheat-
ing behavior. The verifier can still cheat in this sce-
nario and thus identify a single user who authenticates
anonymously, but his trustworthiness is in jeopardy as
he is likely to be caught.
The beauty of post-active anonymity is that it
passes back the full risk to the dishonest verifier: if
he attempts to discover an anonymous enquirer, then
he takes a high risk of loosing the trust of the com-
munity. Postactive anonymity therefore makes hon-
esty verifier’s best behavior strategy. Furthermore,
it should be noted that this paradigm provides a su-
perior feature, namely users may register public-keys
of arbitrary cryptosystems and only the verifier needs
to support all algorithms (and those users checking
entire challenge-sequences). The user solely uses
the respective algorithm corresponding to his public-
key cryptosystem and furthermore needs to compute
only one decryption operation. This results in a low
and constant computational effort, whereas all other
approaches require effort linear in the size of D ,
which can be enormous for large sets of authorized
users. However, it should be noted that the size of
the ciphertext-sequence grows linear with the size of
D , which can be quite large. In these cases, users
may randomly choose a subset D
′
⊂ D for their
anonymity-set such that the size of the ciphertext-
sequence is acceptable. For instance, if the public-
key encryption scheme of choice will be ElGamal
(ElGamal, 1984) on Elliptic Curves E(Z
p
), where
p is a prime with |p| = 192 bits, then, a choice of
the anonymity-set with |D
′
| = 100 will lead to a
ciphertext-sequence of ≈ 5 KB, which is reasonably
small.
4 OUR APPROACH
To realize anonymous and unlinkable but authorized
transactions, we briefly review the concept of blind
signatures and provide a generic construction of a
protocol for such transactions based on one-show to-
kens from blind signatures. Thereafter, we intro-
duce our approach by combining postactive anony-
mous authentication with such one-showtokens. Sub-
sequently, we gradually augment this construction to
achieve (1) fine-grained validity periods for tokens,
(2) selective traceability and (3) discuss how to pre-
vent resp. detect cloning attacks.
4.1 Blind Signatures
Blind signatures are a well known cryptographic
primitive introduced in (Chaum, 1982), which pro-
vide a means such that an entity is able to obtain a
valid signature on a message without the signer be-
ing able to learn anything about the message at the
time of signing. More precisely, the signer actually
signs a randomly blinded message and the resulting
signature can subsequently be unblinded by the orig-
inator, wheres the originator obtains a valid signature
for the original message. Consequently, the signed
message cannot be linked to the originator by the
signer. We rely our construction on efficient two-
move blind signature schemes. Therefore, we can
take the RSA based scheme of (Chaum, 1982), which
was proven to be secure for the full-domain hash
RSA scheme (FDH-RSA) in the random oracle model
under the chosen-target-one-more-RSA-inversion as-
sumption (Bellare et al., 2003). Alternatively, we
can take the blind signature scheme form (Boldyreva,
2003) which is based on the BLS signature (Boneh
et al., 2004) and is provably secure in the random or-
acle model under the chosen-target Computational-
Diffie-Hellman assumption. Subsequently, we ab-
stract from the concrete protocol and denote the blind-
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
135

User Service-Provider
t
i
= (t
i
,σ
t
i
),PK SK,BL
create
t
i+1
t
i+1
= B(H(t
i+1
))
(t
i
,t
i+1
,Q
i
) (t
i
,t
i+1
,Q
i
)
t
i
?
/∈ BL
V
PK
V
(H(t
i
),σ
t
i
)
?
= accept
σ
t
i+1
= S
SK
V
(
t
i+1
)
(σ
t
i+1
,R
i
) (σ
t
i+1
,R
i
)
σ
t
i+1
= B
−1
(σ
t
i+1
)
t
i+1
= (t
i+1
,σ
t
i+1
)
Protocol 2: Simple Blind Signature-Based Transactions (SBSBT).
ing operation of a message m as m = B(m) and the
unblinding of the signature σ as σ = B
−1
(σ).
4.2 Anonymous Unlinkable One-show
Tokens
Below, we provide a generic protocol to obtain one-
show tokens from a verifier which can be shown to
the same party (spent) in an anonymous and unlink-
able fashion. The basic idea behind this construction
was proposed in (Stubblebine et al., 1999), however,
providing non of the functionalities discussed in this
section and not combined with anonymous authenti-
cation.
We define a token as a simple data-structure which
can be described as a tuple (id
t
,id
sp
,id
s
), whereas id
t
is a unique token-ID, id
sp
is an ID of the service-
provider and id
s
may represent an ID of the respective
service (the token may be augmented by further ele-
ments, e.g. validity-period, as discussed subsequently
in this section). We want to note, that what we de-
note as a token is often also referred to as a ticket,
a credential, a coupon, a transaction-pseudonym or a
one-time-pseudonym.
For now, assume that user u
i
holds an initial token-
signature pair t
i
= (t
i
,σ
t
i
) from the service-provider
(also denoted as the verifier V, for short), e.g. the
user registers to the service-provider, pays and ob-
tains a signed token t
i
. Furthermore, assume that
the service-providergenerates a key-pair with suitable
parameters for issuing blind signatures, with public-
key PK
V
and private-key SK
V
. The generic proto-
col for conducting anonymous and unlinkable trans-
actions with V is illustrated in protocol 2. In order
to make the tokens one-time-usage-only, the verifier
maintains a blacklist BL to blacklist already seen to-
kens and discard tokens upon seeing them again. As-
sume now that user u
i
wants to authorize a query
Q
i
to the service-provider. In order to obtain a new
signed token for another transaction, u
i
computes a
blinded token t
i+1
= B(H(t
i+1
)), whereas H denotes
a suitable collision resistant cryptographic hash func-
tion and t
i+1
represents a new token. User u
i
sends
(t
i
,t
i+1
,Q
i
) to the verifier, who checks whether the
token is well formed and the ID of t
i
is not already
contained in the blacklist. If this holds, he computes
σ
t
i+1
= S
SK
V
(t
i+1
), i.e signs the blinded token, and
sends the resulting signature σ
t
i+1
along with the re-
sult R
i
of the query Q
i
back to u
i
. The user in turn
unblinds the signature and obtains σ
t
i+1
= B
−1
(σ
i+1
),
a valid signature for H(t
i+1
). Consequently, u
i
can use
t
i+1
to authorize a new transaction resp. query Q
i+1
for some data at the verifier.
4.3 A Combined Approach
The idea is to combine the aforementioned approach
to realize one-show tokens with the concept of anony-
mous authentication. It should be noted that one
could use several classes of anonymous authentica-
tion schemes for this purpose, e.g. ring signatures
(Rivest et al., 2001), group signatures (Ateniese et al.,
2000), but we will assume that anonymous authenti-
cation from public-key encryption (PKE) is used. The
combination can be realized as follows:
1. Registration. Initially a user u
i
registers once to
the service-provider (verifier) by providing iden-
tifying information ID
u
i
together with a the user’s
public-keyPK
u
i
. The verifier adds the user and the
public-key to the public directory D of authorized
users.
2. Authentication. The user anonymously authenti-
cates to the verifier and after a successful authen-
tication the user obtains a blind signature for a to-
SECRYPT 2010 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
136

ken t
0
and thus holds a token-signature pair t
0
=
(t
0
,σ
t
0
) for a subsequent transaction. Later, the
user posts the challenge-sequence along with the
signature and the challenge such that other users
can check whether the service-provider cheats.
3. Access. The user provides t
0
and a new blinded
token together with a query to the verifier and ob-
tains a response, which is either a response to the
query and a signature on the new blinded token
for a subsequent transaction or an indication that
the transaction was not authorized.
The register procedure is carried out once for every
user. In order to obtain access to the system, a user
conducts the authentication procedure with the veri-
fier. Every authentication procedure is connected to
a set of subsequent transactions, whereas the number
of sequenced transaction is not limited by the verifier.
Subsequently, we will discuss how a subscription of a
user can be terminated, since this is impossible in the
aforementioned setting.
4.4 Fine-grained Validity Periods
A natural and efficient approach to exclude users from
being able to conduct further transactions be realized
as follows:
• The service-provider discretizes the time into
time-periods ∆
0
,∆
1
,. .. of duration d
∆
i
(they may
also differ for different time-periods) and assigns
a unique random number δ
i
to every time-period
∆
i
. The most important point is, that the service-
provider solely publishes δ
i
for the current time-
period δ
i
and given all random numbers of previ-
ous and the actual time-periods it is infeasible to
compute δ
j
for some future time-period.
• The random number δ
i
needs to be included into
the token by the user, otherwise the token will
be rejected. Hence, we augment our token by an
additional element and tokens can now be repre-
sented as a tuple t = (id
t
,id
sp
,id
s
,δ
i
). Within a
time-period an authorized user can obtain an “ini-
tial” token by means of a successful anonymous
authentication.
• Service-providers can easily manage the termina-
tion of service accesses of a user by removing a
user from the directory D . It should be noted, that
the termination of service access during a time-
period is impossible, but the service-provider is
able to control the granularity by choosing ade-
quate durations of time-periods.
• Since the validity of tokens is restricted to a
specific time-period, the service-provider solely
needs to blacklist tokens within the actual period.
Due to the limited duration, the blacklist is bound
in size and previous blacklists can be discarded,
which makes the approach entirely practical from
this point of view.
4.5 Selective Traceability
Traceability in this context means, that a trusted third
party (TTP), a so called traceability authority (TA), is
able to identify the owner of a token as well as it’s
position within a sequence of transactions conducted
by a user. Besides, it is desirable to achieve selective
traceability for all tokens of the user within a specific
time-period ∆
i
. This means, that all tokens of a suspi-
cious user can be found, without violating the privacy
of other users. But it is important, that the service-
provider has no means to revoke the anonymity of
honest users by himself. In order to achieve this, we
require the user to register a pseudonym γ
u
i
(which
is randomly sampled from an appropriate space) with
the TA, and this pseudonym is solely known to the
TA and the user’s smart-card (and not to the service-
provider). The tamper resistant smart-card of the user
has to maintain an internal counter
cnt
, which is ini-
tialized to a fixed user-specific value (which we will
discuss below) during every instance of an anony-
mous authentication protocol and incremented during
every generation of a new token.
Basically, the user’s smart-card includes addi-
tional traceability information e into the token on
behalf of the user. Hence, every token t will be
augmented by an element e and will be a tuple
t = (id
t
,id
sp
,id
s
,δ
i
,e), where e = E
PK
TA
(γ
u
i
,
cnt
u
i
;ω)
represents a probabilistic encryption of the tuple
(γ
u
i
,
cnt
u
i
) under TA’s public-key. Note that ω are
the random coins for the probabilistic encryption al-
gorithm, which will be discussed below. After com-
puting a token, the smart-card increments the counter
cnt
u
i
for the next token. In order to avoid partial
knowledge about the plaintext we choose user- and
time-period-specific start values of counters by com-
puting the initial value of
cnt
u
i
denoted as
cnt
init
(which is initialized during every anonymous authen-
tication) based on a suitable pseudorandom function.
Working in the random oracle model, we can use a
suitable cryptographic hash function H and compute
the initial value as
cnt
init
= H(γ
u
i
,δ
j
) which pro-
vides us an initial counter value that depends on the
pseudonym and on the current time-period.
4.5.1 Tracing of Single Showings
It is obvious that in case of suspicion the respective
token (which is maintained by the service-provider in
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
137

his blacklist) can be given to the TA, which in turn
can decrypt e and obtain the pseudonym of the user.
Consequently, the identity corresponding to the user’s
pseudonym can be returned to the service-provider.
To prevent this user from being able to conduct any
future transaction, the service-provider has to remove
the respective user from his directory D used for au-
thentication. Consequently, this user will no longer be
able to conduct anonymous authentications with the
system. In this setting, the TA is very powerful, since
it can identify all users behind all transactions. How-
ever, we assume that the TA is trusted and only pro-
vides “necessary” information to the service-provider
if and only if the service-provider can credibly argue
that fraud or misuse has happened. It should be noted,
that in order to decrease the trust, we could share the
private-keyof the TA among a set of TA’s and perform
threshold-decryption to reveal the identity of a user.
4.5.2 Efficient Selective Traceability
It order to protect the privacy of other (innocent) users
and to reduce the amount of workload for the TA,
we propose a novel way to achieve selective trace-
ability. Trivially, the TA could realize this feature
by decrypting all remaining tokens in the blacklist
and picking out those of the suspicious users. How-
ever, we want to protect the privacy of the remaining
users and go the other way round. Essentially, the TA
re-encrypts potential escrow information of the user
and searches the blacklist for these potential values.
How this is achieved will be discussed in the follow-
ing. The TA knows the counter value
cnt
act
and the
pseudonym of the user by decrypting the escrow in-
formation e of the suspicious token. Since the TA
also knows that the counter is incremented during the
creation of a new token and knows the value for the
current time-period δ
j
, it is able to compute the start-
ing value of the user as
cnt
init
= H(γ
u
i
,δ
j
). Conse-
quently, the TA has to look for tokens in the counter-
interval [
cnt
init
,
cnt
act
+ k], where k is some positive
integer. Basically, the TA looks k tokens ahead from
the start, since it cannot determine the actual number
of transaction of the suspicious user within his “ses-
sion”. The concrete choice of k mainly depends on
the application, however, when assuming that transac-
tions are distributed uniformly among users we could
take k = |BL|/|D |, where |BL| represents the arith-
metic mean of the sizes of all previous blacklists.
Now, we need a measure for the TA to actually
find the respective tokens within the blacklist. This
can be easily achieved by converting the probabilistic
public-key encryption scheme used by the TA into a
deterministic one, i.e. by applying the EwH construc-
tion. We apply exactly this strategy to the construc-
tion of the escrow information e. More precisely, we
construct the random coins ω for the encryption algo-
rithm as ω = H(PK
TA
,(γ
u
i
,
cnt
u
i
)), whereas PK
TA
is
TA’s public-key. Algorithm 1 illustrates how the TA
realizes selective traceability when given a suspicious
token and the blacklist of the service-provider.
Algorithm 1: Selective Tracing.
Input: A suspicious token
˜
t = (t,e), the value δ of
the current time-period, a parameter k, a blacklist
BL and a key-pair (PK
TA
,SK
TA
) of a public-keyen-
cryption algorithm.
Output: A sequence T = (
˜
t
1
,. .. ,
˜
t
n
) of transactions.
(γ,
cnt
act
,δ) ⇐ D
SK
TA
(e)
cnt
init
⇐ H(γ,δ)
pos ⇐ 0;
for all i =
cnt
init
to
cnt
act
+ k do
ω
i
⇐ H(PK
TA
,(γ,i))
e
i
⇐ E
PK
TA
(γ,i;ω
i
)
˜
t
i
⇐
searchBL
(e
i
,BL)
if
˜
t
i
6= null then
T[pos] ⇐
˜
t
i
pos+ +
end if
end for
return T
The algorithm
searchBL
simply searches the black-
list BL for tokens with escrow information e
i
. By
realizing the strategy discussed above, the workload
of the TA can be significantly decreased. If we de-
note the size of the interval [
cnt
init
,
cnt
act
+ k] by m,
we achieve O(m) encryption operations over O(n) de-
cryption operations in the trivial case, since we can
assume that m ≪ n holds. Furthermore, the privacy of
innocent users does not need to be violated.
4.6 Enforcing Traceability
A very simple attack to circumvent the traceability
property is as follows. Assume that the smart-card
performs the identity-escrow on behalf of the user
and assume further that the user behaves malicious,
i.e. wants to hinder the TA to identify him in case of
fraud or misuse. Therefore, assume that a user is cur-
rently conducting transactions and obtains a response
R along with the blind signature σ
t
for the new token
from the service-provider in the first step (it could,
however, also be the initial transaction). The user
passes the signature to his smart-card, which in turn
computes σ
t
= B
−1
(σ
t
), generates a new blinded to-
ken t
′
(including the traceability information e) and
passes the tuple (t, σ
t
,t
′
) to the user. Although t
′
SECRYPT 2010 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
138

is well-formed, the malicious user can easily replace
t
′
with another blinded token t
′′
that is nearly well-
formed. More precisely, the token is well-formed, ex-
cept for the traceability information (which could ei-
ther be chosen at random or represents the encryption
of some random value).
The conceptually most straightforward approach
to solve this problem is, that the smart-card simply
encrypts the tuple (t,σ
t
,t
′
) under a service-provider’s
public-key of a secure public-key encryption scheme.
Consequently, the user will never have access to a tu-
ple of the form (t,σ
t
), which would allow him to con-
duct a transaction with a replaced “self-constructed”
non-traceable new blinded token t
′′
. However, the
public-key of the service-provider needs to be in-
tegrated into the smart-card in an authentic fash-
ion. Otherwise, a malicious user can easily mount a
person-in-the-middle attack by providing some arbi-
trary public-key(for whom the correspondingprivate-
key is known to the user) to the smart-card. Conse-
quently, the user can decrypt the ciphertext and obtain
a tuple (t, σ
t
,t
′
) which he can modify to (t,σ
t
,t
′′
) and
send this tuple encrypted under the service-provider’s
public-key.
4.7 Cloning Protection
The drawback of fine-grained validity periods is,
that it is potentially susceptible to what we call the
cloning-attack. Loosely spoken, this attack means
that a fraudulent authorized users may obtain valid
token-signature pairs that he can make available to
a set of unauthorized users. These users, the so
called clones, are consequently able to anonymously
conduct a sequence of transactions with the service-
provider within the respective time-period, although
they are not authorized to do so. Note that this at-
tack is still possible when the smart-card only gives
the ciphertext of the tuple (t,σ
t
,t
′
) to the user. How-
ever, the attack is somewhat reduced, since the clone
will solely be able to conduct a single transaction.
By applying counters
cnt
as discussed in section 4.6,
this attack is easy to detect. Therefore, the service-
provider only has to search for identical escrowvalues
e in his blacklist.
• If a user u
i
gives away his encrypted tuple
(t
0
,σ
0
,t
1
) to a clone and the clone spends the
token, the entry in the blacklist will contain
traceability information e
0
= E
PK
TA
(γ
u
i
,
cnt
u
i
;ω),
whereas ω = H(PK
TA
,(γ
u
i
,
cnt
u
i
)) and
cnt
u
i
=
H(γ
u
i
,δ
j
).
• If the user authenticates again within the same
time-period, the traceability information e
′
0
of the
token t
′
0
will be identical, since the counter is
reinitialized to
cnt
u
i
= H(γ
u
i
,δ
j
).
Hence, if the service-provider detects such a cloning
attack (tokens where e
i
= e
j
for some i 6= j), he can
give both entries of the blacklist to the TA to revoke
the anonymity of the misbehaving user. It should be
noted, that this could be problematic in case of bro-
ken connections. The service-providercould have dif-
ferent strategies for handling this, whereas we briefly
sketch two of them below.
Upon presenting exactly the same token multiple
times, the service-provider may re-send the response
to the query Q attached to the respective token t.
However, that incidence should be indicated by not
attaching a query, whenever re-showing a token, as
this query has been submitted anyway. Still, a request
to re-send the answer should come with the token, in
case the query did not make it through in the first in-
stance. However, if neither is done, and a known to-
ken t with a new (different to the previous) query Q
′
(6= Q) is coming in, then the verifier should become
wary and start tracing. This ensures robustness of the
protocol as well it creates a simple mechanism to de-
tect piracy
Alternatively, the service-provider could realize
some kind of glitch-tolerance, by defining some
threshold K of “clone-activity”, which need to be
reached before revoking users.
5 SECURITY ANALYSIS
In this section we will discuss the threat model and
investigate the security of the proposed construction.
Therefore, we assume that users communicate their
messages to service-providers over a communication
channel that provides perfect anonymity and unlinka-
bility of exchanged messages, as it is the case with all
interactive protocols providing such features.
5.1 Threat Model
We assume that the manufacturer of the smart-cards
is trustworthy and hence the smart-cards are tamper
resistant and do not contain any backdoors, Trojan
horses, etc. Furthermore, users are assumed to be
dishonest (active adversaries), i.e. will actively try
to fool the service-provider resp. authorize unautho-
rized users, which is a reasonable assumption for real-
world scenarios. Service-providers are honest-but-
curious, i.e. follow the protocol specification but use
any gathered information in order to try to identify
anonymous users. However, service-providers can
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
139

also be active adversaries, but only with respect to the
anonymous authentication protocol.
5.2 Anonymous Authentication
For the used anonymous authentication protocol we
require anonymity, correctness, unforgeability and
unlinkability, which can be proven to hold for exist-
ing protocols (Slamanig et al., 2009; Lindell, 2007).
However, the known definitions of anonymity and un-
linkability are less formally ensured in the post-active
anonymity setting. Clearly, anonymity can be bro-
ken if the verifier encrypts distinct random challenges,
which consequently can restore linkability too. How-
ever, it is equally obvious that a cheating verifier acts
completely on his own risk, as the community will
accuse him of being dishonest. In that case, the ser-
vice will not be used any more, and a cheating veri-
fier could loose more than he could win. The correct-
ness and unforgeability properties are retained, since
solely trial encryptions are omitted. Finally, it should
be noted that when using standard anonymousauthen-
tication (Schechter et al., 1999; Slamanig et al., 2009;
Lindell, 2007), we obtain security with respect to
existing definitions, however, at substantially higher
costs.
5.3 Security of our Construction
In our investigation of the security of the construc-
tion we investigate the anonymity of transactions, the
unlinkability of transactions and the unforgeability of
tokens. We inspect every property below and sketch
the ideas:
• Transaction Anonymity. Every token showing
integrates the issuing of a new token. Hence, we
firstly need to look at the token which is shown
and secondly the blinded token which is signed
by the verifier. The anonymity of the token t
shown reduces to inspecting the escrow informa-
tion e. The anonymity follows from two ob-
servations concerning the escrow information e.
Firstly, (Bellare et al., 2007) prove that for any at
least IND-CPA secure probabilistic public-key en-
cryption that is converted into a deterministic one
(by applying the EwH construction), it holds that
an adversary provided with encryptions of plain-
texts drawn from a message-space of high min-
entropy (which is clearly the case, since we en-
crypt randomly chosen pseudonyms along with
a value obtained by evaluating a pseudorandom
function on this value) will have negligible ad-
vantage in computing any public-key independent
partial information function of the plaintexts (this
notion is called PRIV in (Bellare et al., 2007)).
Hence, the so obtained deterministic public-key
encryption scheme provides the required security
guarantees and can be seen as a computationally
hiding commitment. Secondly, the pseudonyms
of users are sampled at random from a large
enough space and are solely known to the TA and
the user’s smart-cards (which are assumed to be
tamper-proof). Consequently, any adversary can
solely guess the respective pseudonym of a user,
which would allow him to identify or trace one
user. By choosing the space for the pseudonyms
accordingly large, this probability can be made
negligible. The anonymity of the blinded token
follows from the properties of the blind signature
scheme.
• Unforgeability. Since the smart-card solely gives
ciphertexts of tuples (t,σ
t
,t
′
) to the users, a user
would need to forge a signature from the veri-
fier. However, this means that a user would need
to existentially forge a signature for the signature
scheme underlying the blind signature scheme.
• Unlinkability. The unlinkability of the issuing
and showing of a token t reduces to the blind-
ness property of the used blind signature scheme.
Hence, there is no way for the signer to relate
the issuing and showing of a token. Furthermore,
we need to look at the unlinkability of different
showings, which means that it cannot be decided
whether a set tokens was shown by the same user.
Therefore, our argumentation is similar to that
used for the transaction anonymity property. Let
us assume without loss of generality that we have
two tokens t and t
′
. Only e and e
′
contain infor-
mation about the user. However, as already dis-
cussed in context of transaction anonymity e and
e
′
are computationally hiding commitments.
6 FUTURE ASPECTS
One drawback of the approach presented in this paper
is that we cannot realize a fine-grained access con-
trol for resources connected to services. However,
this can be solved by using partially blind signatures
(Abe and Fujisaki, 1996; Abe and Okamoto, 2000)
instead of blind signatures. Loosely spoken, in a par-
tially blind signature scheme, a receiver blinds a mes-
sage m, obtains m = B(m) and sends m to the signer.
The signer computes a partially blind signature σ =
S
SK
S
(m,info), which includes a common information
info and sends σ to the receiver. The receiver unblinds
σ by computing σ = B
−1
(σ), can verify whether the
SECRYPT 2010 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
140

common information info was included and obtains a
valid signature σ for the tuple (m, info). Note, that the
message m is entirely unknown to the signer. We can
use them as follows: The service-provider defines the
set of privileges P (which are connected to resources
of services) and during registration privileges are as-
signed to users. By choosing the anonymity-set ac-
cording to required privileges (users which have the
same privileges) an encoding of these privileges can
be integrated by means of common information info
into the blinded token. Hence, when presenting the to-
ken, the service-provider can decide whether a query
Q will be authorized or not. It should be noted, that
anonymity and unlinkability are preserved.
REFERENCES
Abe, M. and Fujisaki, E. (1996). How to Date Blind Sig-
natures. In ASIACRYPT ’96, volume 1163 of LNCS,
pages 244–251. Springer.
Abe, M. and Okamoto, T. (2000). Provably Secure Partially
Blind Signatures. In CRYPTO ’00, volume 1880 of
LNCS, pages 271–286. Springer.
Ateniese, G., Camenisch, J., Joye, M., and Tsudik, G.
(2000). A Practical and Provably Secure Coalition-
Resistant Group Signature Scheme. In CRYPTO ’00,
volume 1880 of LNCS, pages 255–270. Springer.
Bellare, M., Boldyreva, A., and O’Neill, A. (2007). De-
terministic and Efficiently Searchable Encryption. In
CRYPTO 2007, volume 4622 of LNCS, pages 535–
552. Springer.
Bellare, M., Namprempre, C., Pointcheval, D., and Se-
manko, M. (2003). The One-More-RSA-Inversion
Problems and the Security of Chaum’s Blind Signa-
ture Scheme. J. Cryptology, 16(3):185–215.
Blanton, M. (2008). Online Subscriptions with Anonymous
Access. In ASIACCS 2008, pages 217–227. ACM.
Boldyreva, A. (2003). Threshold Signatures, Multisigna-
tures and Blind Signatures Based on the Gap-Diffie-
Hellman-Group Signature Scheme. In PKC 2003, vol-
ume 2567 of LNCS, pages 31–46. Springer.
Boneh, D., Lynn, B., and Shacham, H. (2004). Short Sig-
natures from the Weil Pairing. Journal of Cryptology,
17(4):297–319.
Camenisch, J., Hohenberger, S., Kohlweiss, M., Lysyan-
skaya, A., and Meyerovich, M. (2006). How to Win
the Clone Wars: Efficient Periodic n-Times Anony-
mous Authentication. In CCS ’06, pages 201–210.
ACM.
Camenisch, J. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2001). An Efficient
System for Non-transferable Anonymous Credentials
with Optional Anonymity Revocation. In EURO-
CRYPT ’01, volume 2045 of LNCS, pages 93–118.
Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2002). A Signature
Scheme with Efficient Protocols. In SCN’ 02, volume
2576 of LNCS, pages 268–289. Springer.
Camenisch, J. and Lysyanskaya, A. (2004). Signature
Schemes and Anonymous Credentials from Bilinear
Maps. In CRYPTO 2004, volume 3152 of LNCS,
pages 56–72. Springer.
Canard, S., Gouget, A., and Hufschmitt, E. (2006). A
Handy Multi-coupon System. In ACNS 2006, volume
3989 of LNCS, pages 66–81. Springer.
Chaum, D. (1982). Blind Signatures for Untraceable Pay-
ments. In CRYPTO’82, pages 199–203. Plemum
Press.
Chaum, D. (1985). Security without identification: Trans-
action systems to make big brother obsolete. Com-
mun. ACM, 28(10):1030–1044.
Chen, L., Escalante, A. N., L¨ohr, H., Manulis, M., and
Sadeghi, A.-R. (2007). A Privacy-Protecting Multi-
Coupon Scheme with Stronger Protection Against
Splitting. In FC 2007, volume 4886 of LNCS, pages
29–44. Springer.
ElGamal, T. (1984). A Public Key Cryptosystem and a
Signature Scheme Based on Discrete Logarithms. In
CRYPTO ’84, volume 196 of LNCS, pages 10–18.
Springer.
Kiayias, A., Tsiounis, Y., and Yung, M. (2004). Trace-
able Signatures. In EUROCRYPT ’04, volume 3027
of LNCS, pages 571–589. Springer.
Libert, B. and Yung, M. (2009). Efficient Traceable Signa-
tures in the Standard Model. In Pairing 2009, volume
5671 of LNCS, pages 187–205. Springer.
Lindell, Y. (2007). Anonymous Authentication - Preserving
Your Privacy Online. Black Hat 2007.
Lysyanskaya, A., Rivest, R. L., Sahai, A., and Wolf, S.
(2000). Pseudonym Systems. In SAC ’00, volume
1758 of LNCS, pages 184–199. Springer.
Rivest, R. L., Shamir, A., and Tauman, Y. (2001). How to
Leak a Secret. In ASIACRYPT ’01, volume 2248 of
LNCS, pages 552–565. Springer.
Schechter, S., Parnell, T., and Hartemink, A. (1999).
Anonymous Authentication of Membership in Dy-
namic Groups. In FC 1999, volume 1648 of LNCS,
pages 184–195. Springer.
Slamanig, D., Schartner, P., and Stingl, C. (2009). Practi-
cal Traceable Anonymous Identification. In SECRYPT
2009, pages 225–232. INSTICC Press.
Stubblebine, S. G., Syverson, P. F., and Goldschlag, D. M.
(1999). Unlinkable Serial Transactions: Protocols and
Applications. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur., 2(4):354–
389.
Verheul, E. R. (2001). Self-Blindable Credential Certifi-
cates from the Weil Pairing. In ASIACRYPT ’01, vol-
ume 2248 of LNCS, pages 533–551. Springer.
Xi, Y., Sha, K., Shi, W., Schwiebert, L., and Zhang, T.
(2008). Probabilistic Adaptive Anonymous Authen-
tication in Vehicular Networks. J. Comput. Sci. Tech-
nol., 23(6):916–928.
ANONYMOUS BUT AUTHORIZED TRANSACTIONS SUPPORTING SELECTIVE TRACEABILITY
141
