
THE VALUE OF INFORMATION SHARING IN A SERIAL
SUPPLY CHAIN WITH CENTRALISED AND DECENTRALISED
DECISION
Mansour Rached, Zied Bahroun, Belhassen Zouari
LIP2, FST, 2092, Manar 2 Tunis, Tunisia
Armand Baboli, Jean-Pierre Campagne
Université de Lyon, LIESP, INSA-Lyon, F-69621, Villeurbanne, France
Keywords: Information sharing, Supply chain, Downstream, Upstream information, Centralised, Decentralised
decision.
Abstract: In this paper, we present a simulation based model in order to study the effects of information sharing in a
serial supply chain. This chain is multi-product and multi-echelon. Our approach focuses on the study of
two shared information simultaneously. The first one is the replenishment leadtime coming from the
upstream and the second one is the customers’ demand coming from the downstream of the supply chain.
Thus, we present four scenarios of information sharing. The demand is supposed normally distributed and
the leadtime is random. We develop a cost model consisting of holding, ordering, penalty and transportation
costs. The difference of the optimal costs between each studied scenario represents the performance
indicator of the information sharing. Two different decisions are considered in our work: centralised and
decentralised. The developed model for each studied situation is solved by ILOG CPLEX integrated in a
JAVA program. To conclude, the results of our numerical experimentations are analysed.
1 INTRODUCTION
For many enterprises, the supply chain management
has become an important element of strategic
advantage to gain a competitive edge over their
competitors. In the sever competition times, the
enterprises want to obtain competition advantage,
they must carry on the cooperation with the other
echelons in the same supply chain, and try to
establish win-win cooperation relationship. The
information sharing is the foundation of the
cooperation between different links of supply chain,
and also is one main origin of the supply chain
advantages.
In this context, researches are numerous. The
existing works deal with the study of different types
of information sharing in different circumstances.
Namely, the studied decision and the source of the
share, etc. The centralised decision represents the
most treated case (Chu and Lee, 2006), (Rached et
al., 2009). The decentralised decision is treated in
(Birendra et al., 2007), (Laux et al., 2004), (Li et al.,
2006). However, (Zhao and Qui, 2007) considered
simultaneously centralised and decentralised
decision. Concerning the provenance of the
information to share, on the one hand, many papers
have treated the case of downstream information
sharing (Agrawal et al., 2008), (Hsiao and Shieh,
2006), (Li and Zhang, 2008). On the other hand,
(Chen and Yu, 2005), (Jia et al., 2007) and (Mehrabi
et al., 2007) presented shared information which is
coming from upstream. However, few papers
considered the case of shared information coming
simultaneously from the upstream and the
downstream (Birendra et al., 2007), (Rached et al.,
2009). The solver CPLEX is used in many recent
works including a study of optimisation and the
information sharing in supply chains. In (Li and
Zhang, 2008) authors present an objective function
which includes a cost formulation solved using
GAMS-CPLEX. In (Lehoux et al., 2007), authors
presented seven models aiming to study the value of
collaboration between a supplier and his customer.
269
Rached M., Bahroun Z., Zouari B., Baboli A. and Campagne J. (2010).
THE VALUE OF INFORMATION SHARING IN A SERIAL SUPPLY CHAIN WITH CENTRALISED AND DECENTRALISED DECISION.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 269-272
DOI: 10.5220/0003004202690272
Copyright
c
SciTePress
To compare and analyse their developed models,
they use the solver CPLEX.
According to the above review, we propose to
study the effects of two information shared
simultaneously upon the supply chain performance
with several scenarios and circumstances. The
remainder of this paper is organised as follows.
Section 2 reviews the structure of studied supply
chain and introduces the different studied scenario.
Section 3 presents the simulation and analysis
results. Finally, conclusions are made in Section 4.
2 STRUCTURE OF STUDIED
SUPPLY CHAIN AND THE
RESOLUTION METHOD
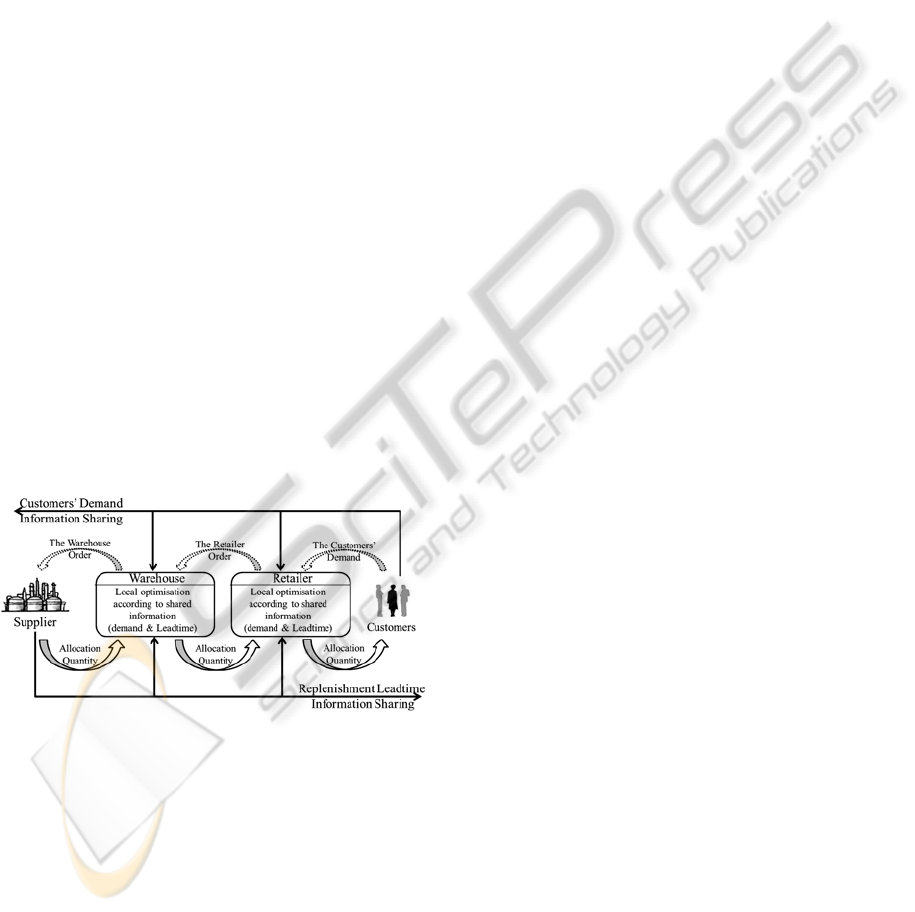
The supply chain structure in this paper is a four-
echelon model Figure 1, which includes several
customers, one retailer, one warehouse and one
supplier. There are various items of information
which can be shared such as inventory level,
production capacity, etc. The shared information
refers to costumers’ demand coming from the
downstream of the supply chain and replenishment
leadtime coming from the upstream. We assume that
the costumers’ demand is normally distributed, the
leadtime between the supplier and the warehouse is
random and the leadtime between the warehouse and
the retailer is fixed for all periods.
Figure 1: Studied supply chain with information and
materiel flows.
We study the sharing of two information
simultaneously, which are the demand coming from
the downstream of supply chain and the leadtime
coming from the upstream.
To investigate the effect of information sharing
upon supply chain performance, for each studied
decision, four scenarios are designed with respect to
the two types of information mentioned above.
In the case of decentralised decision, the retailer
performs a local optimisation of its costs before
placing their orders. According to this order
quantity, the warehouse proceeds to a second local
cost optimisation to place an order to the supplier.
According to the centralised decision presented
in Figure 2, the four studied scenarios are as follows:
Case of Replenishment Leadtime and Demand
Information Sharing: At the beginning of each
period, the decision maker (warehouse) is
informed about the exact replenishment
leadtime and the customers’ demand of the
current period. So, he calculates the order
quantity witch minimise the total system cost
according to the replenishment leadtime and
the exact demand of all periods.
Case of Replenishment Leadtime Information
Sharing Only: The order quantity is calculated
by the decision maker according to the exact
replenishment leadtime and independently of
the customers’ demand.
Case of Demand Information Sharing Only: In
this case, the warehouse calculates the order
quantity according to the exact customers’
demand and independently of replenishment
leadtime.
Case of No Information Sharing: The decision
maker cannot choose the optimal order
quantity according to the replenishment
leadtime and/or the customers’ demand of
each period. So, he uses fixed values of both
information for all periods to calculate the
optimal order quantity.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In our simulation and in order to study the sensibility
and the robustness of our formulation, we use
different combinations of replenishment leadtime
and customers’ demand in each scenario as follows:
Small leadtime
[
]
4 to1
=
t
, noted L1
st
;
L
Large leadtime
[
]
21 to1
=
t
L
, noted L2
nd
;
High leadtime
[
]
12 to8
=
t
L
, noted L3
rd
;
First mean value of demand (high
demand)
380
=
μ
, noted D1
st
;
Small demand 100
=
μ
, noted D2
nd
;
Medium demand
230
=
μ
, noted D3
rd
.
We use in each simulation the same standard
deviation
σ
=80.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
270
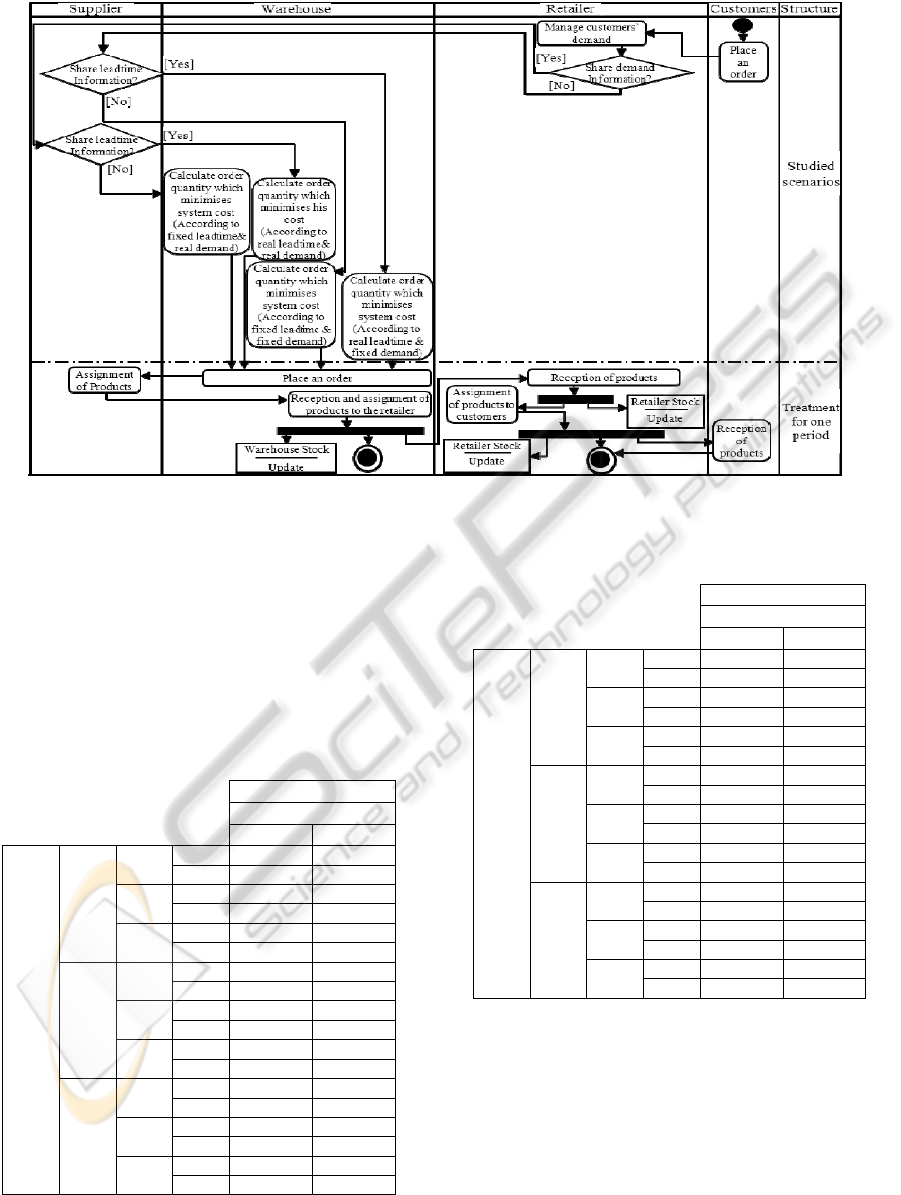
Figure 2: Activity diagram integrating all studied scenarios in a centralised decision.
In our work we deal with the problem of
optimisation based on a centralised (Table 1) and
decentralised decision (Table 2) using CPLEX.
IS: Is the case of Information Sharing;
NIS: Is the case of No Information Sharing;
DemI: Demand Information;
LtI: Leadtime Information.
Table 1: Total system cost in centralised decision.
DemI
TSC (10
3
)
IS NIS
LtI
L1
st
D1
st
IS 5,1347 8,4099
NIS 6,1216 11,1132
D2
nd
IS 3,9821 5,2154
NIS 4,7612 7,1256
D3
rd
IS 4,4782 6,8154
NIS 5,9373 10,0347
L2
nd
D1
st
IS 5,1277 8,2367
NIS 7,4385 10,9521
D2
nd
IS 3,9482 5,9610
NIS 4,5659 6,9581
D3
rd
IS 6,0274 7,7147
NIS 6,8416 8,2618
L3
rd
D1
st
IS 7,1639 9,2184
NIS 8,1374 10,3514
D2
nd
IS 4,1132 4,8952
NIS 4,5173 5,5901
D3
rd
IS 3,2467 5,1458
NIS 3,8962 7,7259
Table 2: Total system cost in decentralised decision.
DemI
TSC (10
3
)
IS NIS
LtI
L1
st
D1
st
IS 6,2704 10,5806
NIS 9,2921 12,8980
D2
nd
IS 5,2502 6,7198
NIS 6,4988 7,5044
D3
rd
IS 5,9443 7,8265
NIS 6,3447 10,5558
L2
nd
D1
st
IS 6,9277 9,5627
NIS 8,8154 12,9171
D2
nd
IS 5,2502 7,2198
NIS 6,4059 8,2461
D3
rd
IS 6,2276 8,0747
NIS 6,7546 8,7996
L3
rd
D1
st
IS 7,8686 9,8018
NIS 8,4053 11,0514
D2
nd
IS 5,3212 6,7635
NIS 5,8177 6,9859
D3
rd
IS 5,2606 7,5315
NIS 5,9153 9,9776
In Table 1 and Table 2, we present nine values of
simulations. Illustrated by the different combinations
of (L1
st
, L2
nd
and L3
rd
) and (D1
st
, D2
nd
and D3
rd
).For
each case we present TSC (10
3
) for four scenarios of
customers’ demand and replenishment leadtime
information sharing.
Based on the simulations in Table 1, we study
the centralised decision. Regarding the total system
cost, the results show an average percentage at
21.12% of reduction of logistic cost in the case of
THE VALUE OF INFORMATION SHARING IN A SERIAL SUPPLY CHAIN WITH CENTRALISED AND
DECENTRALISED DECISION
271

leadtime information sharing compared to the
scenario of no information sharing. Whereas the
demand information sharing compared to the
scenario of no information sharing presents an
average of 33.15% reduction of logistic cost.. When
the two information are simultaneously shared, we
obtain 44.66% of of logistic cost reduction
compared to the case of no information sharing. For
the decentralised decision illustrated by Table 2,
Compared to the case of no information sharing, we
can deduce 16.70% and 27.75% of reduction of
logistic cost concern, respectively, the case of
leadtime information sharing and, the case of
demand information sharing. When the two studied
information are simultaneously shared, we obtain
38.92% of reduction of logistic cost compared to the
case of no information sharing. In the case of no
information sharing, the centralised decision
presents 12.16% of reduction of logistic cost
compared to the case of decentralised decision.
Thus, the centralised decision compared to the case
of decentralised decision presents a percentage at
16.83%, 18.72% and 20.43% of reduction of logistic
cost concern, respectively, the case of leadtime
information sharing, the case of demand information
sharing and the case of two information shared
simultaneously. In the studied circumstances, we can
conclude that the information sharing and the
centralised decision present an advantage in terms of
reduction of logistic cost compared to the case of
decentralised decision.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we are interested to the evaluating of
information sharing in supply chain. We treated in
particular the case of multi-product multi-echelon
supply chain. We studied the value of information,
specially two information shared simultaneously.
The firs information comes from the downstream
(demand) and the second come from the upstream
(leadtime) of supply chain. Moreover, the effect of
two kinds of decision has been also studied
(centralised and decentralised decision). We used the
traditional replenishment policies as a logistic
reference cost. The numerical experimentation
shows that the information sharing allows reducing
the total logistic costs (transportation and storage
costs). Moreover, the centralised decision is more
beneficial in terms of reduction of logistic cost
compared to the decentralised decision.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, S., Sengupta, R.N., Shanker, K., 2008. Impact of
information sharing and lead time on bullwhip effect
and on-hand inventory. European Journal of
Operational Research. 192(2), 576-593.
Birendra, K.M., Srinivasan, R., Xiaohang, Y., 2007.
Information sharing in supply chains: Incentives for
information distortion. IIE Transactions. 39(9), 863-
877.
Chen, F., Yu, B., 2005. Quantifying the Value of Leadtime
Information in a Single-Location Inventory System.
Manufacturing & Service Operations Management.
7(2), 144-151.
Chu, W.H.J., Lee, C.C., 2006. Strategic information
sharing in a supply chain. European Journal of
Operational Research. 174(3), 1567-1579.
Hsiao, J.M., Shieh, C.J., 2006. Evaluating the value of
information sharing in a supply chain. International
Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
27(5-6), 604-609.
Jia, Q., Guo, W., Li, B., 2007. Study On The Effect Of
Information Sharing Strategy To Complex Supply
Chain System Based On Multi-Dimension View By
Simulation. Wireless Communications, Networking
and Mobile Computing WiCom’07, 4847-4850.
Laux, J.S.K., Huang, G.Q., Mak, K.L., 2004. Impact of
information sharing on inventory replenishment in
divergent supply chains. International Journal of
Production Research. 42(5), 919-941.
Lehoux, N., D'Amours, S., Langevin, A., 2007. Cadre
d’évaluation de la valeur de la collaboration:
modélisation de la relation entre un fournisseur et son
client pour le secteur des pâtes et papiers. 7e Congrès
International de Génie Industriel.
Li, J., Sikora, R., Shaw, M.J., Tan, G.W., 2006. A
strategic analysis of inter organizational information
sharing. Decision Support Systems. 42(1), 251-266.
Li, L., Zhang, H., 2008. Confidentiality and information
sharing in supply chain coordination. Management
Science. 54(8), 1467-1481.
Mehrabi, A., Baboli, A., Campagne, J.P., 2007. Evaluer la
valeur de partage d’information de délais dans une
chaîne logistique avec l’algorithme génétique. 7e
Congrès international de génie industriel.
Rached, M., Bahroun, Z., Baboli, A., Campagne, J.P.,
Zouari, B., 2009. A method to evaluate downstream
and upstream information sharing using the genetic
algorithm. International Conference on Computers &
Industrial Engineering CIE’39. 1635-1640.
Zhao, X., Qiu, M., 2007. Information Sharing in a Multi-
Echelon Inventory System. Tsinghua Science &
Technology. 12(4), 466-474.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
272
