
EVALUATING AN INTELLIGENT COLLABORATIVE
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT FOR UML
Kalliopi Tourtoglou and Maria Virvou
Department of Informatics, University of Piraeus, 80 Karaoli & Dimitriou St., Piraeus 18534, Greece
Keywords: Collaboration, Learning, Collaborative Learning, CSCL, Group, Team, Group Formation, Stereotypes,
Student Modelling, UML, Evaluation.
Abstract: In this paper, we present an evaluation experiment of AUTO-COLLEAGUE conducted at the University of
Piraeus. AUTO-COLLEAGUE is a collaborative learning environment for UML. Students are organized
into groups supported with a chat system to collaborate with each other. It builds integrated individual
student models aiming at suggesting optimum groups of learners. These optimum groups will allow the
trainer of the system to organize them in the most effective way as far as their performance is concerned. In
other words, the strengths and weaknesses of the students are blended for the best of the individuals and the
groups. The student models concern the level of expertise and specific personality characteristics of the
students. The results of the evaluation were quite optimistic, as they indicated a better individual
performance of the students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning
(CSCL) systems are a special category of learning
systems that allow distant users to work together.
The advantages of CSCL environments are related to
the great opportunity they offer to people from all
over the world to learn together and share their
knowledge and experience. The use of such systems
has been expanded in schools, open universities and
training courses of industries. The cost of CSCL
systems is rather low considering the money saved
from gathering students together in a physical
computer laboratory. These are the main reasons
why CSCL systems have become a trend.
There are many fields that have the potential to
be developed in the frame of CSCL systems, such as
team learning. However, there is not yet substantial
research on supporting team-learning procedures in
CSCL systems. This was our motive to design and
implement AUTO-COLLEAGUE (AUTOmated
COLLaborativE leArning Uml Environment), a
CSCL environment that would trace the
characteristics of the students and find optimum
combinations of them into groups. The
characteristics would not be competent enough to
indicate which students match together, unless they
included not only the knowledge on the domain, but
their personality as well. For this reason, AUTO-
COLLEAGUE builds individual student models
recording the level of expertise and specific
personality characteristics of the students. The
personality characteristics are in accordance with the
Five Factor Model of Personality (Norman, 1963)
and are related to the learning process. The student
models are based on the stereotype-based theory
introduced by Rich (1983) and the perturbation
modelling technique (Holt, Dubs, Jones, and Greer,
1994). Stereotypes are sets of characteristics that
describe categories of users. The technique of using
stereotypes is suitable for complex student models
like in our case. The stereotypes we have included in
our student-modelling component are classified in
two categories: the Personality and the Level of
Expertise.
2 RELATED WORK
Many effective Computer-Supported Collaborative
Learning (CSCL) systems have been developed
during the last decade, such as COLER
(Constantino-Gonzaléz and Suthers, 2000), LECS
(Rosatelli and Self, 2004), COLLECT-UML
(Baghaei and Mitrovic, 2005), DEGREE(Barros and
Verdejo, 2000), HABIPRO (Vizcaíno, Contreras,
462
Tourtoglou K. and Virvou M. (2010).
EVALUATING AN INTELLIGENT COLLABORATIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT FOR UML.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 462-467
DOI: 10.5220/0003011604620467
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Favela and Prieto, 2000), CoLeMo (Chen, Pedersen
and Pettersen, 2006), FLE3 (Muukkonen,
Hakkarainen and Lakkala, 1999), CoLab (Martínez
Carreras, Gómez-Skarmeta, Martínez Graciá and
Mora Gónzalez, 2004), CSCL Environment for “Six
Thinking Hats” Discussion (Tamura and Furukawa,
2008), I-MINDS (Khandaker, Soh, and Jiang,
(2006), CoPAS (Jondahl and Mørch, (2002), CURE
(Lukosch., Hellweg and Rasel, 2006),
PENCACOLAS (Blasco, Barrio, Dimitriadis,
Osuna, González., Verdú and Terán, 1999), CoWeb
(Rick and Guzdial, 2006) and AquaMOOSE 3D
(Edwards, Elliott and Bruckman, 2001). The main
purpose of these systems is to allow remote users to
collaborate with each other while working in the
same environment at the same time. Some of them
(FLE3, CoLab, CSCL Environment for “Six
Thinking Hats” Discussion, CURE, CoWeb) are
platforms where users can share data in various
formats (e.g. documents). In these systems, there is
no advice mechanism and no common goal/problem
to solve as a team. Also, some of the rest of the
systems (CoLab, PENCACOLAS, CoWeb) do not
offer advice to users. The content of the advice of
the systems that do offer is generated after
evaluating the level of expertise and the participation
of the users in social activities (chat, whiteboard
etc). Moreover, only two of these systems (Baghaei
and Mitrovic, 2005), (Chen, Pedersen and Pettersen,
2006) include a trainer/moderator, but his/her role is
limited. I-MINDS includes the facility of
automatically forming teams of students based
mainly on the performance of the students related to
their expertise and participation in the collaborative
activities.
AUTO-COLLEAGUE is, also, a CSCL system.
Unlike the aforementioned CSCL systems, AUTO-
COLLEAGUE suggests to the trainer optimum
groups of learners taking into consideration
individual integrated student models that include
personality characteristics of the student along with
the level of expertise. Another element that
differentiates AUTO-COLLEAGUE from other
CSCL systems is the contribution of the trainer in
the system. In AUTO-COLLEAGUE, the trainer
may adjust any setting (groups’ structure,
stereotypes etc).
3 DESCRIPTION OF THE
SYSTEM
AUTO-COLLEAGUE is a collaborative learning
system for training people on UML. It is a multi-
user environment where trainees login via the
network. They are organized into groups and try to
solve problems/tests on UML. They can collaborate
with each other through a chat system in order to
either simply communicate or help each other.
AUTO-COLLEAGUE supports mechanisms that
build stereotype-based student models of the trainees
as they use it. It, then, evaluates the characteristics
of these student models in order to suggest the most
effective groups between them. To achieve this it
takes into consideration the stereotypes of the
trainees and the desired group structures.
Except from the trainees, there is also another
user in the system, the trainer. The trainer is the
administrator of the system whose duty is to
supervise the learning process, insert data and define
important settings.
Because of the nature of the UML diagrams it
would be difficult to trace the errors of the trainees
in a UML diagram: there could be many possible
diagrams-solutions and even the nomenclature could
vary. For this reason, as the quality and quantity of
students’ errors constitute critical information for the
system, we implemented wizard forms for the tests
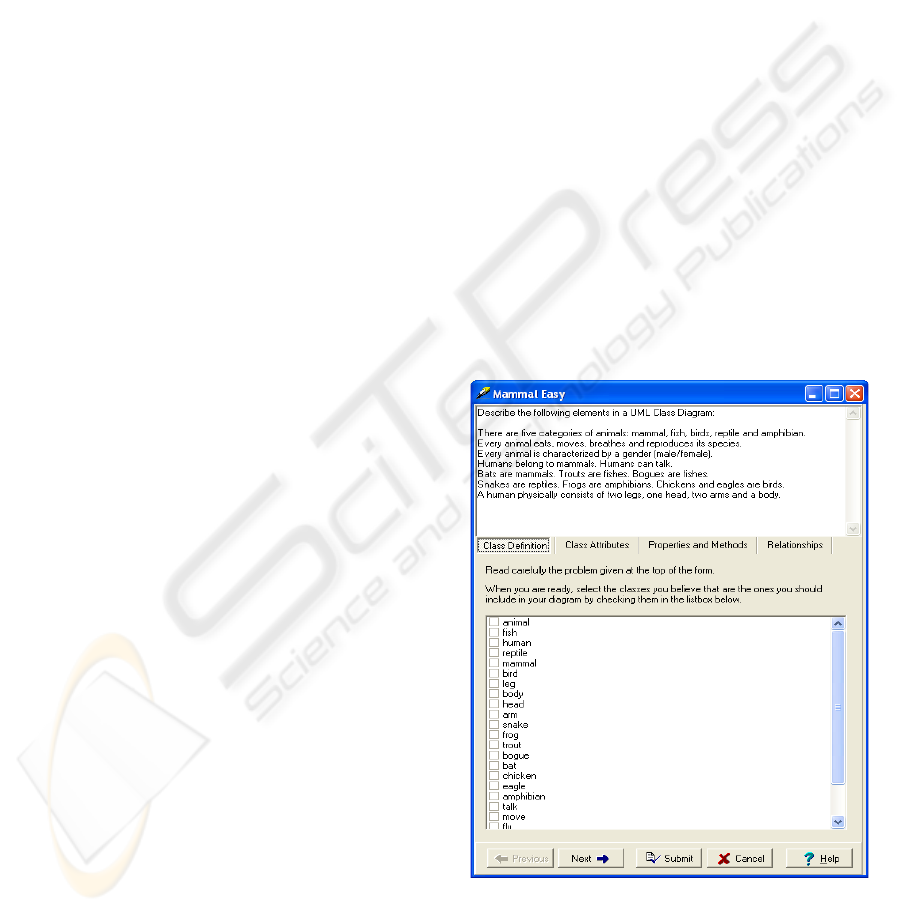
that the trainees would have to solve. This form is
illustrated in figures 1 and 2.
The stereotypes used in our system concern the
level of expertise and the personality of the student.
The Level of Expertise describes the knowledge
level of the student on the domain, which is UML.
There are four stereotypes in this category: Basics,
Junior, Senior and Expert. Each of these stereotypes
represents a specific structure of knowledge and its
degree. This degree can get values between 0 and 1,
indicating the level of knowledge upon each UML
concept. The level of expertise stereotypes are
associated with a subset of the expert’s model built
using the perturbation model discussed in the
previous section.
The Personality stereotypes we use in the system
are: Self-confident, Diligent, Participative, Willing-
to-help, Sceptical, Hurried, Unconcentrated and
Efficient. They are related to the characteristics that
influence the student behaviour as far as the
possession of knowledge and the way of
collaboration with others are concerned.
4 CRITERIAS FOR FINDING
OPTIMUM GROUPS OF
LEARNERS
The criteria for finding optimum groups of learners
EVALUATING AN INTELLIGENT COLLABORATIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT FOR UML
463
include the stereotype combinations and the groups’
structure. The trainer of the system parameterizes
both of them.
The trainer can determine the criteria related to
the desired and undesired combinations between
user stereotypes. The trainer may estimate that in the
optimum groups should not coexist specific pairs of
stereotypes (undesired combinations of stereotypes)
and would be effective for other specific pairs of
stereotypes to coexist (desired combinations of
stereotypes). The default criteria used by our system
are the results of an empirical study (Tourtoglou and
Virvou, 2008) conducted in order to find the most
effective pairs of stereotypes to avoid and to aim at.
The structure of the groups describes of what
kind and of how many roles each group is consisted.
A role reflects the status (connected with the level of
expertise) of a trainee in a group. The predefined
roles assigned are: Junior Student, Senior Student
and Expert Student. Each of these roles is associated
with specific levels of expertise. The levels of
expertise describe the degree of knowledge of the
trainees on the UML domain.
5 AIMS AND SETTINGS OF THE
EVALUATION
The aim of the evaluation experiment was to study
the educational effectiveness of our system itself (as
a learning environment) and of the proposed by the
system organization ways of the trainees into
groups.
The experiment took place in the University of
Piraeus among 80 postgraduate students during the
Software Engineering course. All of these students
were the trainees and the teacher of the course was
defined as the trainer.
The experiment consisted of two parts. At the
first part the students were organized into 20 groups
of 4 trainees in alphabetical order. At the second part
the students were reorganized according to the
proposed groups of trainees.
The aim of the evaluation was to observe the
effect of these proposed groups on the progress of
the trainees as individuals and as groups. For this
reason, the values of specific characteristics of the
users during the first and the second part of the
experiment were examined. These characteristics,
which are related to the facets of stereotypes, are
useless mouse movements and clicks frequency,
average idle time, number of actions, error
frequency, correct frequency, help utilization
frequency, advice given frequency, help given to a
member/non member of the group, help request
from a member/non member of the group,
communication frequency and number of
upgrades/downgrades in level of expertise.
6 EXAMPLE OF AN
EVALUATION EXPERIMENT
The trainees preceded two different tests, one during
each part of the experiment. These tests were given
in a wizard form as illustrated in figures 1 and 2.
Before giving these tests, the trainees attended two
lessons of UML basics. The difficulty of both of
these tests was similar. The second one is slightly
more difficult than the first one, so that the degree of
difficulty would not influence the results of the
experiment. On the other hand, the second test
should be more difficult as the trainees would have
more experience on UML after the first part of the
experiment. The experienced teacher of the software
engineering course authored these tests. The initial
assignment of the level of expertise of all users was
basics in both of the days of the experiment.
Figure 1: Test of Day 1.
As the trainees were trying to solve the tests,
they could send text messages to the members of
their group. In this way they collaborated with each
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
464

other and, simultaneously, the system traced these
collaboration processes to make evaluations.
Figure 2: Test of Day 2.
7 RESULTS
During the first day of the experiment, the 80
trainees were organized into 20 groups of 4 in
alphabetical order. Every trainee was considered by
the system as junior. Team 1 included Trainee1,
Trainee2, Trainee3 and Trainee4. Team 2 included
Trainee 5, Trainee6, Trainee7 and Trainee8 and so
forth until Team 20.
For the second day, 20 teams of specific
structure of roles were defined in the system. The
structure of teams 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 was: two juniors,
one senior and one expert. The structure of teams 6,
7, 8, 9 and 10 was: one junior, two seniors and one
expert. The structure of teams 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15
was: two juniors, two seniors and no expert. Finally,
the structure of teams 16, 17, 18, 19 and 20 was: one
junior, one senior and two experts. Furthermore, the
desired and undesired combinations between
stereotypes were defined as explained in section 7.
For the organization of the trainees into optimum
groups, the administrator of the system run the
Groups Building form illustrated in figure 3 and
pressed the “Suggest Best Groups” button. In the
Evaluation Report, the results of the group
organization are listed. The system runs a process of
finding the most fitted groups to the criteria given.
These criteria are related to the desired and
undesired combinations between stereotypes and the
role structure of the groups. However, the values of
the stereotypes and roles of the trainees are rarely
ideal for every group to fit into the desired scheme.
However, the trainer can manually change the
formation of the groups after consulting the
individual learner models. For example, supposed
there were totally 4 trainees, all whom were find by
the system to be juniors, and the system had to fit
them in one group whose role structure was one
junior, two seniors and one expert, the Advisor
would organize them having one failed group, 3
failed combinations, 0 successful group and 3
successful combinations. Things get more
complicated considering the effect of the user
stereotypes in the process. In detail, Failed Groups
refer to the number of the groups that the system
failed to form and was forced to include trainees that
it should not in the same group. Failed Combinations
are the number of these failures individually. In
similar way, Successful Groups and Successful
Combinations refer to the successful matching of
trainees into groups.
Figure 3: Groups Building Form (Suggested Groups).
In our case (shown in figure 3), we had: 13
Failed Groups, 19 Failed Combinations, 19
Successful Groups and 159 Successful
Combinations.
In order to evaluate the effect of this
organization of the trainees, we gathered the values
of some critical user characteristics during the first
and the second day of the experiment. These
characteristics are cited in table 1 and concern the
upgrades of the students in the level of expertise and
the number of errors they made. The upgrades in the
level of expertise express the progress of the student
in UML. They indicate the times that the system
EVALUATING AN INTELLIGENT COLLABORATIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT FOR UML
465

assigned the student to a better level of expertise
stereotype.
Table 1: Values of trainees’ characteristics per day of
experiment.
Upgrades In Level Of
Expertise
Number of Errors
Day 1 Day 2 Day 1 Day 2
Trainee1 1 2 12 7
Trainee2 2 2 10 9
Trainee3 1 1 18 21
Trainee4 1 2 15 9
Trainee5 0 1 24 15
Trainee6 0 0 25 22
Trainee7 1 1 14 12
Trainee8 2 2 10 8
Trainee9 2 2 11 10
Trainee10 2 3 12 1
Trainee11 3 3 2 4
Trainee12 1 1 23 22
Trainee13 3 3 4 3
Trainee14 1 1 22 20
Trainee15 0 0 28 25
Trainee16 3 1 2 18
Trainee17 2 1 10 17
Trainee18 2 2 12 10
Trainee19 2 0 13 27
Trainee20 1 1 21 19
Trainee21 2 2 14 13
Trainee22 3 1 3 14
Trainee23 2 1 9 13
Trainee24 3 3 2 2
Trainee25 2 3 9 2
Trainee26 3 2 5 9
Trainee27 1 1 14 12
Trainee28 2 2 13 11
Trainee29 1 1 18 15
Trainee30 1 1 16 16
Trainee31 2 2 8 6
Trainee32 2 3 9 1
Trainee33 2 2 7 7
Trainee34 2 2 10 8
Trainee35 1 1 15 16
Trainee36 2 1 10 9
Trainee37 1 0 20 23
Trainee38 2 1 14 19
Trainee39 1 1 16 17
Trainee40 1 0 19 24
Trainee41 0 1 22 13
Trainee42 1 1 18 17
Trainee43 3 3 5 1
Trainee44 3 3 5 2
Trainee45 2 1 12 14
Table 1: Values of trainees’ characteristics per day of
experiment. (Cont.)
Upgrades In Level Of
Expertise
Number of Errors
Day 1 Day 2 Day 1 Day 2
Trainee46 2 2 8 6
Trainee47 2 2 14 13
Trainee48 2 0 12 21
Trainee49 1 2 18 8
Trainee50 1 0 20 22
Trainee51 1 2 15 10
Trainee52 2 3 6 1
Trainee53 2 0 12 21
Trainee54 1 1 17 15
Trainee55 2 2 11 9
Trainee56 1 1 12 10
Trainee57 3 2 5 10
Trainee58 1 3 18 3
Trainee59 2 3 6 2
Trainee60 2 0 12 21
Trainee61 3 3 4 3
Trainee62 2 1 7 14
Trainee63 3 3 4 0
Trainee64 1 1 20 18
Trainee65 2 2 8 6
Trainee66 1 1 19 13
Trainee67 1 1 17 14
Trainee68 2 3 8 1
Trainee69 2 3 9 0
Trainee70 2 0 12 25
Trainee71 2 2 12 11
Trainee72 2 1 10 14
Trainee73 1 0 20 21
Trainee74 3 2 4 8
Trainee75 2 1 11 13
Trainee76 2 3 6 2
Trainee77 1 0 19 24
Trainee78 3 3 4 1
Trainee79 2 1 12 13
Trainee80 1 1 19 18
After analysing these results, we calculated that
30% of the trainees presented no difference, 65% of
the trainees presented progress and 4% of the
trainees presented reduction in their level of
expertise comparing the two days of the experiment.
Furthermore, as far as number of errors is
concerned, 1.25% of the trainees presented no
difference, 90% presented reduction and 8.75%
presented increase in the number of errors. As a
conclusion, it seems that the organization into
groups that the system proposed is effective for the
majority of the trainees that participative in the
experiment.
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
466

8 CONCLUSIONS
Adding functionality that supports the team learning
process can enhance CSCL systems. At this aim, we
have developed AUTO-COLLEAGUE that provides
suggestion of optimum groups of learners using
student-modelling techniques taking into account
integrated student characteristics, such as the
personality. The results of the conducted evaluation
are promising that the individual students may
enhance their performance and knowledge by
working into teams organized by a systematic
approach of combining their personality features and
their level of knowledge.
REFERENCES
Baghaei N. and Mitrovic A. (2005). Collect-UML:
Supporting Individual and Collaborative Learning of
UML Class Diagrams in a Constrain-Based Intelligent
Tutoring System. Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
Vol. 3684, Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, 458-464.
Barros, B. and Felisa Verdejo, M. (2000):Analysing
student interaction processes in order to improve
collaboration. The DEGREE approach. International
Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 11.
Blasco, M., Barrio, J., Dimitriadis, Y., Osuna, C.,
González, O., Verdúa and M., Terán, D. (1999). From
cooperative learning to the virtual class. An experience
in composition techniques. ultiBASE journal.
Chen, W. Pedersen and R. H. Pettersen, O. (2006).
CoLeMo: A collaborative learning environment for
UML modelling. Interactive Learning Environments,
14:3, 233-249.
Constantino-Gonzaléz, M. d. and Suthers, D. D. (2000). A
Coached Collaborative Learning Environment for
Entity-Relationship Modeling. In Proceedings of the
5th international Conference on intelligent Tutoring
Systems (June 19 - 23, 2000). G. Gauthier, C. Frasson,
and K. VanLehn, Eds. Lecture Notes In Computer
Science, vol. 1839. Springer-Verlag, London, 324-
333.
Edwards, E., Elliott, J. and Bruckman, A. (2001).
AquaMOOSE 3D: math learning in a 3D multi-user
virtual world. In CHI '01 Extended Abstracts on
Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seattle,
Washington, CHI '01. ACM, New York, NY, 259-260.
Holt, P., Dubs, S., Jones, M. and Greer, J. (1994). The
State of Student Modelling. In Greer, J., McCalla, G.
(Eds.), Student Modelling: The Key To Individualized
Knowledge-Based Instruction (pp. 3-35). Springer-
Verlag: Berlin.
Jondahl, S.and Mørch, A. (2002). Simulating Pedagogical
Agents in a Virtual Learning Environment. In Stahl,
G, ed. Proceedings Computer Support for
Collaborative Learning (CSCL 2002). Boulder, CO,
USA: Lawrence Erlbaum, 531-532.
Khandaker, N. and Soh, L. K., Jiang, H. (2006). Student
Learning and Team Formation in a Structured CSCL
Environment, In Proceedings of ICCE'2006. 185-192.
Beijing, China.
Martínez Carreras, M. A., Gómez-Skarmeta, A. F.,
Martínez Graciá E. and Mora Gónzalez, M. (2004).
COLAB: A platform design for collaborative learning
in virtual laboratories. WORKSHOP held on the 18th
IFIP World Computer Congress.
Muukkonen, H., Hakkarainen, K. and Lakkala, M. (1999).
Collaborative technology for facilitating progressive
inquiry: Future learning environment tools. In
Hoadley, C., Roschelle, J. (eds.): Proceedings of
CSCL'99. Standord University. 406-415.
Norman,W. T. (1963).Toward an adequate taxonomy of
personality attributes: Replicated factor structure in
peer nomination personality ratings. Journal of
Abnormal and Social Psychology, 66, 574-583.
Rich, E. (1983). Users are individuals: Individualizing
user models. Journal of Man-machine Studies, 18(3),
199-214.
Rick, J. and Guzdial, M. (2006). Situating CoWeb: a
scholarship of application. International Journal of
Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 1, 89-
115.
Rosatelli M. C. and Self, J. (2004). A Collaborative Case
Study System For Distance Learning. International
Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 14, 1-
29.
Tamura, Y. and Furukawa, S. (2008). CSCL Environment
for “Six Thinking Hats” Discussion. Knowledge-
Based Intelligent Information and Engineering
Systems. 583-589.
Tourtoglou, K. and Virvou, M. (2008). User Stereotypes
for Student Modelling in Collaborative Learning:
Adaptive Advice to Trainers. In Proceeding of the
2008 Conference on Knowledge-Based Software
Engineering: Proceedings of the Eighth Joint
Conference on Knowledge-Based Software
Engineering. M. Virvou and T. Nakamura, Eds.
Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications,
vol. 180 (pp. 505-514). IOS Press: Amsterdam, The
Netherlands.
Vizcaíno, A., Contreras, J., Favela, J. and Prieto M. 2000).
An Adaptive, Collaborative Environment to Develop
Good Habits in Programming. In ITS 2000, LNCS
1839, Springer, pp. 262-271.
EVALUATING AN INTELLIGENT COLLABORATIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT FOR UML
467
