
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTIVE APPROACH FOR
BUSINESS PROCESS RE-ENGINEERING
From the Perspective of Organizational Factors
Kayo Iizuka
School of Network and Information, Senshu University, Tokio, Japan
Yasuki Iizuka
School of Science, Tokai University, Tokio, Japan
Kazuhiko Tsuda
Graduate School of Business Science, University of Tsukuba, Ibarati, Japan
Keywords: Business Process re-Engineering (BPR), Effective Approach, Organizational Factors.
Abstract: This paper presents analysis results of business process re-engineering (BPR) effects including customer
satisfaction and their formative factors. Although BPR has been studied for some decades, additional issues
have come into existence recently, e.g., balance of efficiency and internal control (including information
security management), organization reform or enterprise integration including the causes of recent economic
circumstances. Analyses in this paper are aimed at addressing these issues. By clarifying the mechanism for
achieving BPR effectiveness, analysis is focused on organization perspectives and communication
infrastructure.
1 INTRODUCTION
Various methods have been used to evaluate
information systems and business process re-
engineering (BPR). However, attempts to evaluate
the total system integration service have been
lagging somewhat behind that of other evaluation
methods which have focused on the technical
aspects of information systems. Some of the system
integrators had started to conduct customer
satisfaction surveys that focus on each element of
current system integration satisfaction scored by IT
sections, although satisfaction of the system
integration service is implicated by various
organizations within each firm, not just the IT
section.
Iizuka attempted to construct a customer
satisfaction structure model of system integration
service from the perspective of organization
structure (Iizuka 1993, 1999). Some satisfaction
theories that had been adapted to consumer products
(Hannan 1989) (Shimakuchi 1986), etc.) were
arranged to create a satisfaction structure model.
Correlation between ‘expectation’, ‘performance’
and ‘current satisfaction’ was analyzed and verified.
Organization behavioural factors and theories such
as those proposed by Sheth were also arranged and
built into the model (Sheth 1977). Survey sheets
were sent to three sections (IT sections, business
planning sections, and end user sections) for each
firm, in order to analyze aggregated organizational
satisfaction structure. In 1997, Chikara adapted
customer satisfaction theories (Shimakuchi 1998) to
the information system audit area. The customer
satisfaction model was used as part of the audit
items (Chikara1997), and it was heralded as a type
of epoch-making research. Although these trials for
applying customer satisfaction theories to system
information evaluation were successful at the time,
some relevant issues did emerge. Various
relationship types between the IT section and
business planning (BP) section were identified. The
384
Iizuka K., Iizuka Y. and Tsuda K. (2010).
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTIVE APPROACH FOR BUSINESS PROCESS RE-ENGINEERING - From the Perspective of Organizational Factors.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages
384-389
DOI: 10.5220/0003020403840389
Copyright
c
SciTePress

structure of an organization is one such example; the
IT section and business planning section are
independent sections in some firms, but they belong
to the same superordinate organization in other
firms; the IT section is part of the business planning
section in some firms, and all IT service
functionality is supported by IT subsidiary
companies in other firms. BPR policy is another
aspect that also shows variety; drastic business
process re-engineering and the as-is process are
based on business improvement. System
implementation policy also shows variety, such as
“system specification should comply with user
business process requirements”, or “define business
process considering IT capability”. In order to
clarify customer satisfaction structure considering
these relevant issues, we created and conducted
another customer survey and analyzed it from
various aspects. The details are described in later
chapters.
2 RELATED WORKS
Related works about the BPR effect induced by IT
implementation or IT operation could be classified
into analysis of success factors of IT
implementation, analysis of success factors of IT
management, and return on investment of IT. Based
on the BPR theory presented by Hammer and
Champy, researchers had conducted studies from
various perspectives (Hammer 1993). Grover
focused on the implementation problem (Grover
1995), Earl analyzed the relationship between BPR
and strategic planning (Earl 1995), and Attaran
explored the relationship between IT and BPR from
capabilities and barriers to effective implementation
(Attaran 2004). Taguchi analyzed the success factors
of IT management, especially for ERP systems
(Taguchi 2007). Kadono focused on the mechanism
of how IT creates business value, particularly from
the viewpoint of IT management (Kadono 2006).
Chikara attempted to adapt the customer satisfaction
method to the information system as part of the
information system audit measurement (Chikara
1997). However, these works do not thoroughly
focus on the relationship of organizations or the
difference of the satisfaction structure of
organizational sections. Moreover, there are
additional issues that have come to light recently,
e.g., balance of efficiency and internal control
(including information security management),
organization reform or enterprise integration
including the causes of recent economic
circumstances. In order to address these issues, we
endeavour to conduct research to clarify the
mechanism for achieving BPR effectiveness.
3 RESEARCH FRAMEWORK
Our research aims to clarify the mechanism for
achieving BPR effectiveness, and we formed
hypotheses based on our framework as follows:
• Hypothesis 1: BPR effectiveness differs by SI
element factor (e.g., system design /
development skill, system consulting skill,
system maintenance skill, integrator’s knowledge
about business and customers’ industry, support
level for system)
• Hypothesis 2: “Total satisfaction” differs by each
organizational section in a firm.
• Hypothesis 3: Structure of “total satisfaction”
(correlation between “total satisfaction” and
“satisfaction of each factor such as satisfaction of
technical matter factors, project management
factor, and business impact of using IT”) differs
by each organizational section in a firm.
• Hypothesis 4: Structure of “total satisfaction”
differs by BPR policy (drastic BPR, or as-is
business process based improvement)
• Hypothesis 5: Structure of “total satisfaction”
differs by system implementation policy (system
specification should comply with user business
process requirements, or define business process
considering IT capability)
• Hypothesis 6: Structure of “total satisfaction”
differs by organization structure of the
information system section and business
planning section.
• Hypothesis 7: Structure of “total satisfaction”
differs by the IT subsidiary firm’s organization
structure and function.
• Hypothesis 8:“Total satisfaction” score secular
change (delta) differs by BPR policy type.
• Hypothesis 9: “Total satisfaction” score change
(delta) differs by IT implementation policy.
• Hypothesis 10: BPR effect factor differs by
organizational factor (e.g. organization structure,
communication infrastructure, section-related
satisfaction structure).
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTIVE APPROACH FOR BUSINESS PROCESS RE-ENGINEERING - From the Perspective of
Organizational Factors
385
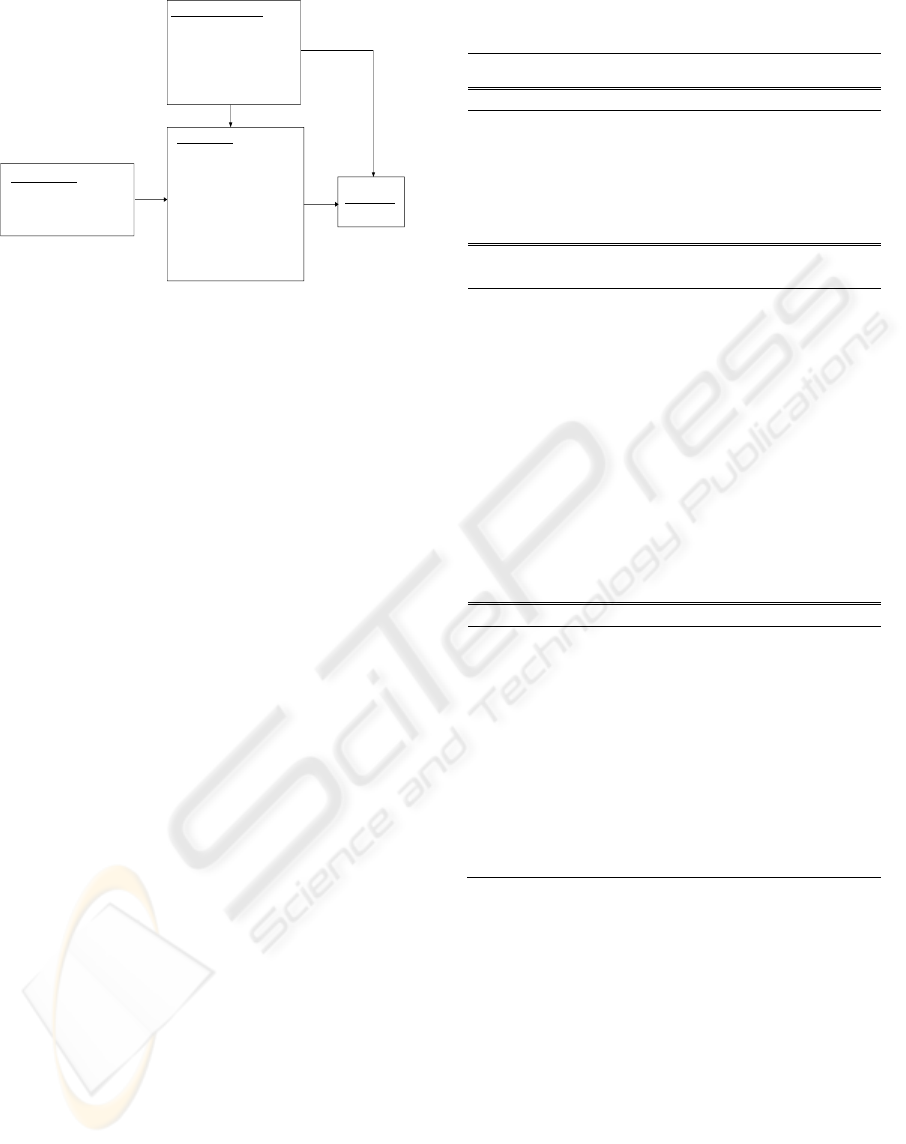
SI Element Satisfaction Factor
-System design / development skill
-System Consulting skill
-System maintenance skill
-Integrator’s knowledge about business
and customers’ industry
-Support level for system
BPR Effect Factor
-Cost reduction among entire firm
-Cost reduction of IT section
-Cost reduction within business Planning
section
-Cost reduction within end users‘ section
-Strategic decision making speed
improvement among entire firm
-Workload reduction among entire firm
-Workload reduction among each section
Organizational Factor
-Organization Structure
-Communication Infrastructure
-Section Related Satisfaction Structure
Total Satisfaction
<1>SI-CS I (Survey on Customer Satisfaction of System Integration Service I )
<2>SI-CS II (Survey on Customer Satisfaction of System Integration Service II )
<3>SI-BPR (Survey on Business Process Re-engineering and System Integration)
<3>SI-BPR
<2>SI-CSII
<2>SI-CSII
<1>SI-CSI
<2>SI-CSII
Figure 1: BPR effectiveness and satisfaction
4 RESEARCH RESULT AND
FINDINGS
We conducted several surveys for firms, two
customer satisfaction surveys and an organization
survey. Customer surveys are CSS-OBP (customer
satisfaction survey from Organization Buying
Perspective) I and CSS-OBP II. The organization
survey is SEC-BPR (security and BPR survey). And
we also planned an additional survey for the
construction extended model. Most of the
hypotheses listed in Chapter 3 were verified. Some
of the analysis results are explained in the following
sections.
4.1 Customer Satisfaction Survey
Result
This survey is conducted aiming to determine the
metrics of how to maximize customer satisfaction as
one of the effects. The result of multi regressions of
various factors to “total satisfaction” (tested by
organizational section) is reported in Table 1.
The number of integration elements that correlate
with “total satisfaction” reduced in 2002. However,
the system elements that are listed above seem to
carry less conviction. One of the reasons is the
coefficient value does not appear to be large enough.
Therefore, we tried to develop multi regression
including satisfaction of effect of using the
information system (Table 2).
This result seems to have more conviction. That
means effectiveness using the information system
has become an important issue for the system
integration service.
Table 1: Multi Regression Result for Total Satisfaction
and SI Elements (By section, CSS-OBP I).
Predictor Variable Coefficient
s
F-value P-value
IT section
(n=97)
Satisfaction of end user
0.55 30.79 ***
System maintenance skill
0.27 9.58 ***
Integrator’s knowledge
about business and
customers’ industry
0.19 5.00 **
Constant
-0.12
Overall model
30.73 ***
Business planning
section
(n=60)
System design /
development
skill
0.51 26.33 ***
Cost performance
0.55 25.12 ***
Ability to avoid company
risk
0.29 6.00 **
Skill level about
advanced IT
-0.26 8.64 ***
Trustful company
-0.37 13.11 ***
Integrator’s knowledge
about
business and customers’
industry
0.38 9.83 ***
Integration skill of multi
vendor’s products
0.21 5.11 **
System maintenance skill
-0.14 2.30 **
Constant
-0.35
Overall model
14.39 ***
End users section
(n=69)
System design /
development
skill
0.51 26.47 ***
Ergonomics
0.44 19.93 ***
Integrator’s knowledge
about
business and customers’
industry
0.23 5.05 **
System management skill
0.29 6.11 **
System consulting skill
-0.18 2.47
Specification of each
product
-0.15 2.11 ***
Constant
-0.44
Overall model
34.27 ***
Level of significance *:10%, **:5%, ***:1%
In terms of the “total satisfaction” change delta for
each firm, the average score differed by BPR policy.
The average satisfaction score of firms whose policy
is “drastic BPR” was a 0.59 point increase, while the
“As-is business process based improvement” group
did not change on average.
In terms of the “total satisfaction” delta (secular
change) for each firm, the average score differed by
BPR policy. The average satisfaction score of firms
whose policy is “draw to-be business process at first,
and consider IT deployment” was a 0.47 point
increase, while the “consider to-be business process
and IT deployment opportunity collaterally” group
shows a negative change on average.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
386

Table 2: Multi Regression Result for Total Satisfaction
and SI Elements and the Effect Induced by Using
Information Systems (By section, CSS-OBPII).
Predictor Variable Coefficients F-value P-value
IT section
(n=56)
Cost reduction among entire
firm
0.64 18.09 ***
Integrator’s knowledge about
business and customers’
industry
0.27 4.543 **
Support for system problems
0.26 5.13 **
Cost reduction of IT section
-0.22 3.52 *
Constant
-0.08
Overall model
12.76 ***
Business planning
section
(n=52)
Cost reduction within business
planning section
0.85 22.01 ***
Strategic decision making
speed
improvement among entire
firm
0.47 10.37 **
Satisfaction of end user
0.44 8.25 *
Cost reduction among entire
firm
-0.36 4.45 **
Specification of each product
-0.36 2.36 -
Constant
-0.29
Overall model
14.39 ***
End users section
(n=51)
Workload reduction within end
user section
0.44 19.42 ***
Having good connection (from
integrators)
0.57 25.53 ***
Strategic decision making
speed
improvement among entire
firm
0.42 17.53 ***
Cost reduction among entire
firm
0.21 5.73 **
Support for system problems
-0.19 3.42 *
Ability for avoiding company
risk
-0.20 3.03 *
Constant
-0.61
Overall model
-0.61 20.59 ***
Level of significance *:10%, **:5%, ***:1%
Table 3: “Total Satisfaction” Score Average
(by BPR policy type).
BPR Policy (CSS-OTC02)
Change Delta
From CSS-OBP I
To CSS-OBP II
Drastic BPR 0.59
As-is business process based
improvement
0.00
Table 4: “Total Satisfaction” Score Average (by IT
implementation policy type).
IT implementation policy
(CSS-OTCII)
Change Delta
From CSS-OBPI
To CSS-OBPII
Draw To-be business process
at first, and consider IT
deploy-ment
0.46
Consider To-be business
process and IT deployment
opportunity collaterally
‐0.1700
4.2 Organization Structure and
Projects Survey Result (BPR, BSC,
Information Security)
Research on BPR effectiveness of the IT
implementation or operation includes: analysis of
success factors of IT implementation, analysis of
success factors of IT management, and return on
investment of IT. Therefore, we analyzed the
effectiveness difference caused by these
organization type differences (Figure2~4).
Relationships between the IT section and BP
section have diversified over the last few years. The
change has been seen in the relationship between IT
sections and BP sections because IT has changed
their mission from a mere man-hour saving tool to a
decision making support tool of management. For
instance, some of the IT sections that had been
independent organizations are beginning to have a
strong relationship with BP sections. Therefore,
analyzing the relevance of correlation of BPR
effectiveness with organization types is considered
valuable from these viewpoints.
Figure 2 shows the result of the analysis of the
relationship between setting metrics (“Setting
numerical target of BPR?”) and BPR effects (“Had
effective BPR result?”). These questions were only
asked to the firms that answered “BPR status is now
implemented”. By organization pattern (1) IT
section and BP section have an independent relation,
(2) the IT section and BP section belong to the same
higher level organization and (3) the IT section is
located under the BP section.
The ratio of the firms that answered “setting of
numerical targets-yes” was high for the groups of
the firms that answered that the IT section and BP
section have an independent relation (Figure 2).
However, the ratio of the firms that answered
“effective result-yes” was high for the firms that
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTIVE APPROACH FOR BUSINESS PROCESS RE-ENGINEERING - From the Perspective of
Organizational Factors
387

2
2
12
3
15
1
1
5
13
1
131
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
(4)others
(3)ITsection is located under BP
section
(2)belonging to the same higher level
organization
(1)independent relations
Setting of numerical targets-yes,
Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets-yes,
Effective Result-no
Setting of numerical targets-no,
Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets-no,
Effective Result-no
n/a
Others
Figure 2: BPR Effectiveness by Organization Type (SEC-BPR).
2
2
12
1
1
5
13
3
15
1
131
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
(4)others
(3)ITsection is located under
BPsection
(2)belonging to the same higher level
organization
(1)independent relations
Setting of numerical targets-yes,
Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets-no,
Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets-yes,
Effective Result-no
Setting of numerical targets-no,
Effective Result-no
n/a
Others
Figure 3: BPR Effectiveness by Organization Type (SEC-BPR)(Sort order changed).
8
2
6
16
2
2
14
1
2
1
1
31
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
(3)BSC not implmented
(2)BSC no w implementin g
(1)BSC implemented
Setting of numerical targets
-
yes, Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets
-
no, Effective Result-yes
Setting of numerical targets
-
yes, Effective Result-no
Setting of numerical targets
-
no, Effective Result-no
n/a
Others
Figure 4: BPR Effectiveness by BSC Implementation Status (SEC-BPR).
answered that the IT section and BP section belong
to the same organization (Figure 2), and in this
organization pattern, “setting of numerical targets-no,
effective result-yes” is much more prevalent than
other organization patterns. The reason for this fact
is that the organization infrastructure compensates
by setting specific numerical targets. In other words,
setting numerical targets may enable compensation
of an organization of communication infrastructure
in some way. As communication infrastructure, a
balanced scorecard (BSC) is also effective (Figure 4).
The firms that answered “BSC implemented” have a
greater tendency to achieve BPR effectiveness than
“BSC not implemented” firms.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
RESEARCH
As for BPR effectiveness, there are various
influencing parameters: e.g., management issues,
project task issues, and in addition there are
emerging issues that have only come to light
recently, e.g., balance of efficiency and internal
control (including information security
management), organization reform or enterprise
integration including the causes of recent economic
circumstances. In order to address these issues, we
conducted surveys including questionnaires and
interviews from several viewpoints for the various
sections (IT, BP, end users) of the firms.
Consequently, correlation between BPR
effectiveness and organization types or organization
of communication infrastructure was demonstrated.
Correlation between various BPR effects and total
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
388

satisfaction was also verified. The integrated BPR
effectiveness model, in which parameters are set,
would be attained with a combination of these
results. We will continue our research and analysis
in order to complete the overall model of our BPR
effectiveness frameworks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
A part of this work was supported by Grant-in-Aid
for Scientific Research in Japan. And we really
appreciate the firms were cooperation in the
questionnaire.
REFERENCES
Grover V. et al., 1995. The implementation of business
process re-engineering, Journal of Management
Information Systems Archive Volume 12 , Issue 1
(June 1995) pp.109 – 144.
Hammer. M., Champy. J., 1993.re-engineering the
Corporation: A Manifesto for Business Revolution,
Harper Business; Reprint.
Earl. M.J., Sampler. J. L., Short. J.E., 1995. Strategies for
Business Process re-Engieering: Evidence from Field
Studies, Journal of Management Information Systems
Archive, Volume 12 , Issue 1 (June 1995), pp.31 - 56
Attaran. M., 2004. Exploring the Relationship between
Information Technology and Business Process re-
Engineering, Information & Management. Volume 41,
Issue 5, May 2004, pp.585-596
Taguchi, Y., Iizuka, K. et al. 2007., Study for the Success
Factors of ERP System Utilization, - Analysis of
Utilization Pattern and Management, Proceedings of
the National Convention 2007 Autumn of JASMIN
Oowada T., 2007. "Measurements of IT Investment (IT
Toushi no Hyoka Hoho)", Chuo Keizaisha.
Kadono Y., and Tsubaki., H., 2006, Development of "IT
Management Effectiveness" and Analysis, Journal of
the Japan Society for Management Information,
Vol.14 No. 4 March 2006
Chikara., T,. and Takahashi. T., 1996. Research of
Measuring the Customer Satisfaction for Information
Systems, Computers & Industrial Engineering Volume
33, Issues 3-4, December 1997, pp.639-642
Iizuka (Hirotsu), K., 1993,“Customer Satisfaction of
System Integration Business (SI Business ni Okeru
Kokyaku Manzoku ni Tsuite, in Japanese)”, Master’s
thesis, Keio University, 1993
Iizuka K. and Wada M., 1999. “Customer Satisfaction of
Information System Integration Business in Japan”,
Informatica – An International Journal of Computing
and Informatics Vol.23 No.4, 1999 pp.473-476
Hanan M. and Karp P., , “Customer Satisfaction”,
American Management Association, 1989
Shimakuchi, M., 1986 “Theories of Strategic Marketing
(Senryakuteki Marketing no Ronri, in Japanese)”,
Nihon Keizai Shimbumsha
Sheth J.N., 1977, Industrial Buying Behaviour, North-
Holland Publishing. Co.
ANALYSIS OF EFFECTIVE APPROACH FOR BUSINESS PROCESS RE-ENGINEERING - From the Perspective of
Organizational Factors
389
