
Context Accommodation in Human Language Processing
Jerry Ball
Air Force Research Laboratory, Warfighter Readiness Research Division, Mesa, U.S.A.
Abstract. This paper describes a model of human language processing (HLP)
which is incremental and interactive, in concert with prevailing psycholinguistic
evidence. To achieve this, the model combines an incremental, serial, pseudo-
deterministic processing mechanism, which relies on a non-monotonic mechan-
ism of context accommodation, with an interactive mechanism that uses all
available information in parallel to select the best choice at each choice point.
1 Introduction
This paper describes a model of human language processing (HLP) which is incre-
mental and interactive, in concert with prevailing psycholinguistic evidence. To
achieve this, the model combines an incremental, serial, pseudo-deterministic
processing mechanism, which relies on a non-monotonic mechanism of context ac-
commodation, with an interactive mechanism that uses all available information in
parallel to select the best choice at each choice point.
The language comprehension model is intended to be at once functional and cogni-
tively plausible [4]. It is a key component of a larger model of a synthetic teammate
which will eventually be capable of functioning as the pilot in a UAV simulation of a
team task involving communication and collaboration with two human teammates in a
reconnaissance mission [8].
To support the development of a cognitively plausible model of HLP, we use the
ACT-R cognitive architecture [3]. ACT-R is a theory of human cognition imple-
mented as a computational system. It integrates a procedural memory implemented as
a production system with a declarative memory (DM). DM consists of symbolic
chunks of declarative knowledge implemented in a frame notation (i.e. a collection of
slot-value pairs) within an inheritance hierarchy. ACT-R is a hybrid system which
combines a serial production execution mechanism with parallel, probabilistic me-
chanisms for production selection and DM chunk retrieval. ACT-R constrains the
computational implementation and provides the basic mechanisms on which the mod-
el relies. Other than adding a collection of buffers to ACT-R to support language
processing by retaining the partial products of retrieval and structure building, and
improving the perceptual processing in ACT-R (Ball et al., to appear), the computa-
tional implementation does not add any language-specific mechanisms.
There is extensive psycholinguistic evidence that HLP is essentially incremental
and interactive [2, 21, 14]. Garden-path effects, although infrequent, strongly suggest
that processing is serial and incremental at the level of phrasal analysis [9]. Lower
level word recognition processes suggest parallel, activation-based mechanisms [19,
Ball J.
Context Accommodation in Human Language Processing.
DOI: 10.5220/0003024500270036
In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Cognitive Science (ICEIS 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-8425-13-3
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

20]. At the level of phrasal analysis, humans appear to pursue a single analysis which
is only occasionally disrupted, requiring reanalysis. One of the great challenges of
psycholinguistic research is to explain how humans can process language effort-lessly
and accurately given the complexity and ambiguity that is attested [11]. As Boden
[10] notes, deterministic processing “would explain the introspective ease and speed
of speech understanding”, but a deterministic mechanism would more frequently
make incorrect local choices requiring reanalysis than is evident. Marcus [18] pro-
posed a lookahead mechanism to improve the performance of a deterministic proces-
sor. However, there is considerable evidence that HLP is inconsistent with extensive
look-ahead, delay or underspecification—the primary serial mechanisms for dealing
with ambiguity [16, 17]. According to Altmann & Mirkovic [1], “The view we are left
with is a comprehension system that is ‘maximally incremental’; it develops the ful-
lest interpretation of a sentence fragment at each moment of the fragment’s unfold-
ing”. Instead of look-ahead, the human language processor engages in “think-ahead”,
biasing and predicting what will come next rather than waiting until the succeeding
input is available before deciding on the current input.
To capture the essentially incremental nature of HLP, we adopt a serial, pseudo-
deterministic processor that builds and integrates linguistic representations, relying on
a non-monotonic mechanism of context accommodation, which is part and parcel of
normal processing, to handle cases where some incompatibility that complicates inte-
gration manifests itself. Serial, incremental processing and context accommodation
are implemented within ACT-R’s procedural memory and production system.
To capture the essentially interactive nature of HLP, we adopt a parallel, probabil-
istic mechanism for activating alternatives in parallel and selecting the most highly
activated alternative. Parallel, probabilistic processing is implemented within ACT-
R’s DM and uses ACT-R’s parallel spreading activation mechanism combined with
the DM retrieval mechanism, to implement probabilistic selection—without inhibi-
tion—between competing alternatives. At each choice point, the parallel, probabilistic
mechanism uses all available information to select alternatives that are likely to be
correct. The parallel, probabilistic mechanism selects between alternatives but does
not build any structure. Structure building occurs during incremental, serial
processing.
The primary mechanisms for building structure within the serial mechanism are in-
tegration of the current input into an existing representation which predicts the occur-
rence of the current input and projection of a novel representation and integration of
the current input into the novel representation. For example, given the input “the pi-
lot”, the processing of “the” leads to projection of a nominal construction and integra-
tion of “the” as the specifier of the nominal. In addition, the prediction for a head to
occur is established. When “pilot” is subsequently processed, it is biased to be a noun
and integrated as the head of the nominal construction. Besides predicting the occur-
rence of an upcoming linguistic element, projected constructions may predict the pre-
ceding occurrence of an element. If this element is available in the current context, it
can be integrated into the construction. For example, given “the pilot flew the air-
plane”, the processing of “flew” can project a transitive verb construction which pre-
dicts the preceding occurrence of a subject. If a nominal is available in the context (as
in this case), it can be integrated as the subject of the transitive construction. Less
likely is the ability of a nominal to predict a clause in which it is functioning as the
subject. Many nominals occur in extra-clausal contexts where they perform a deictic,
28

referential function. Even in clauses, they occur in a range of different grammatical
functions (e.g. subject, object, indirect object, object of preposition).
The use of the term pseudo-deterministic reflects the integration of the parallel,
probabilistic activation and selection mechanism, and non-monotonic context accom-
modation mechanism, with what is otherwise a serial, deterministic processor. The
overall effect is an HLP which presents the appearance and efficiency of deterministic
processing, despite the rampant ambiguity which makes truly deterministic processing
impossible. The context accommodation mechanism is key to achieving a pseudo-
deterministic processing capability.
2 Parallel, Probabilistic Activation and Selection of Existing
Structures
Based on the current input, current context and prior history of use, a collection of
DM elements is activated via the parallel, spreading activation mechanism of ACT-R.
The selection mechanism is based on the retrieval mechanism of ACT-R. Retrieval
occurs as a result of selection and execution of a production—only one production
can be executed at a time—whose right-hand side provides a retrieval template that
specifies which type of DM chunk is eligible to be retrieved. The single, most highly
activated DM chunk matching the retrieval template is retrieved. Generally, the larg-
est DM element matching the retrieval template will be retrieved, be it a word, multi-
unit word (e.g. “a priori”, “none-the-less”), multi-word expression, or larger phrasal
unit.
To see how the spreading activation mechanism can bias retrieval, consider the
processing of “the speed” vs. “to speed”. Since “speed” can be both a noun and a
verb, we need some biasing mechanism to establish a context sensitive preference. In
these examples, the word “the” establishes a bias for a noun to occur, and “to” estab-
lishes a bias for a verb to occur (despite the ambiguity of “to” itself). These biases are
a weak form of prediction. They differ from the stronger predictions that result from
structure projection, although in both cases the prediction may not be realized. In ad-
dition to setting a bias for a noun, “the” projects a nominal which establishes a predic-
tion for a head, but does not require that this head be a noun. If “the” is followed by
“running”, “running” will be identified as a present participle verb since there is no
noun form for “running” in the mental lexicon see [5] for detailed arguments for not
treating present participle verbs as nouns and adjectives in nominals). There are two
likely ways of integrating “running” into the nominal projected by “the”: 1) “running”
can be integrated as the head as in “the running of the bull”, or “running” can project
a modifying structure and set up the expectation for a head to be modified as in “the
running bull”. Since it is not possible to know in advance which structure is needed,
the model must choose one and be prepared to accommodate the alternative. The
choice will be based on the current context and prior history of use of “running” with-
in nominals. The ability to accommodate the alternative is likewise based on the oc-
currence of such alternatives in the past, not just involving “running”, but present par-
ticiples more generally. Currently, the model treats “running” as the head and ac-
commodates “bull” in the same way as noun-noun combinations (discussed below).
This is in contrast to adjectives which project a structure containing a pre-head mod-
29

ifying function and head, with the adjective integrated as the modifier and a predic-
tion for a subsequent head to occur. This structure is integrated as the head of the no-
minal even before the occurrence of the head.
3 Context Accommodation in Pseudo-deterministic Structure
Building
The structure building mechanism is essentially incremental in that the structure
building process involves the serial execution of a sequence of productions that de-
termine how to integrate the current linguistic unit into an existing representation
and/or which kind of higher level linguistic structure to project. These productions
execute one at a time within ACT-R, which incorporates a serial bottleneck for pro-
duction execution. This serial bottleneck is based on extensive empirical evidence,
including the sequential nature of linguistic input and Garden-Path sentences like
Bever´s [9] infamous “the horse raced past the barn fell”.
The structure building mechanism uses all available information in deciding how to
integrate the current linguistic input into the evolving representation. Although the
parallel, constraint-based mechanism considers multiple alternatives in parallel, the
output of this parallel mechanism is a single linguistic unit or very small number of
temporary alternatives. The result of structure building is a single representation with
unused alternatives discarded. The structure building mechanism is deterministic in
that it builds a single representation which is assumed to be correct, but it relies on the
parallel, constraint-based mechanism to provide the inputs to this structure building
mechanism. Structure building is subject to a mechanism of context accommodation
capable of making modest adjustments to the evolving representation. Although con-
text accommodation does not involve backtracking or reanalysis, it is not, strictly
speaking, deterministic, since it can modify an existing representation and is therefore
non-monotonic.
Context accommodation makes use of the full context to make modest adjustments
to the evolving representation or to construe the current input in a way that allows for
its integration into the representation. Context accommodation need not be computa-
tionally expensive. It is most closely related to the limited repair parsing of Lewis
[17]. According to Lewis [17] “The putative theoretical advantage of repair parsers
depends in large part on finding simple candidate repair operations”. Context accom-
modation provides a demonstration of this theoretical advantage by allowing the pro-
cessor to adjust the evolving representation without lookahead, backtracking or reana-
lysis, and limits the need to carry forward multiple representations in parallel or to
rely on delay or underspecification in many cases. Context accommodation also im-
proves and expands on the notion of “slot bumping” as advocated by Yorick Wilks
(p.c.). Slot bumping is an extension to Preference Semantics [22] intended to accom-
modate variation in verb argument structure.
We have already seen an example of accommodation via construal (e.g. “the run-
ning of the bull” where “running” is construed objectively even though it is a present
participle verb). As an example of accommodation via function shifting, consider the
processing of “the airspeed restriction”. When “airspeed” is processed, it is integrated
as the head of the nominal projected by “the”. When “restriction” is subsequently
30
processed, there is no prediction for its occurrence. To accommodate “restriction”,
“airspeed” must be shifted into a modifying function to allow “restriction” to function
as the head. This function shifting mechanism can apply iteratively as in the
processing of “the pressure valve adjustment screw” where “screw” is the ultimate
head of the nominal, but “pressure”, “valve” and “adjustment” are all incrementally
integrated as the head prior to the processing of “screw”. Note that at the end of
processing it appears that “pressure”, “valve” and “adjustment” were treated as mod-
ifiers all along, giving the appearance that these alternatives were carried along in
parallel with their treatment as heads, without the computational expense of building
and carrying forward multiple representations in parallel. At a lower level, there are
accommodation mechanisms for handling conflicts in the grammatical features asso-
ciated with various lexical items. For example, the grammatical feature definite is
associated with “the” and the grammatical feature indefinite is associated with “pi-
lots”. In “the pilots”, the definite feature of “the” blocks the indefinite feature of “pi-
lots” from projecting to the nominal [6].
4 Computational Implementation
The computational implementation is a key component of a functional system which
is under development [8]. The model contains a capability to display the linguistic
representations that are generated in a tree format [15]. The basic capability of the
system will be demonstrated using the following input: “No airspeed or altitude re-
strictions”. In the model, nominals are called object referring expressions (abbreviated
“obj-refer-expr”).
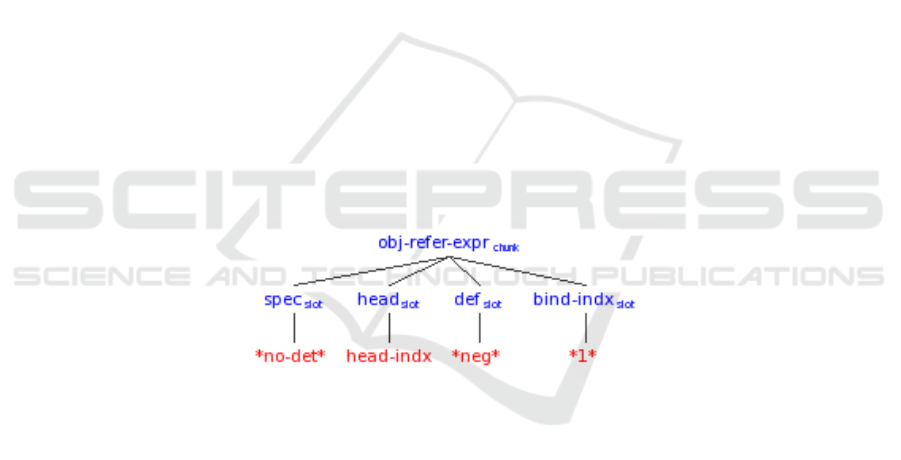
Fig. 1. Representation after processing “no”.
The processing of determiners, including “no”, is special in that they project directly
to an object referring expression and function as the specifier without separate deter-
mination of their part of speech. This efficiency in processing and representation
stems from the frequent occurrence of these functional elements. The projected object
referring expression contains a head slot. The value “head-indx” indicates that this
slot does not yet have a value. The object referring expression also has a definiteness
slot (abbreviated “def”) which has the value negative (abbreviated “*neg*”). This
grammatical feature was projected from “no”. Finally, the object referring expression
has a “bind-indx” slot which contains the index *1*. This index supports the binding
of traces and anaphors in more complex linguistic expressions. It should be noted that
the tree representations are simplified in various respects. In particular, the grammati-
cal features of the individual lexical items are not displayed. Further, only some slots
31
without values are displayed. For example, the head slot is displayed even if it doesn’t
have a value, but grammatical feature slots and modifier slots (pre and post-head)
without values are not displayed.
This nominal construction is made available in a collection of buffers which are
capable of holding up to three nominal constructions, providing a Short Term Work-
ing Memory (ST-WM) [12].
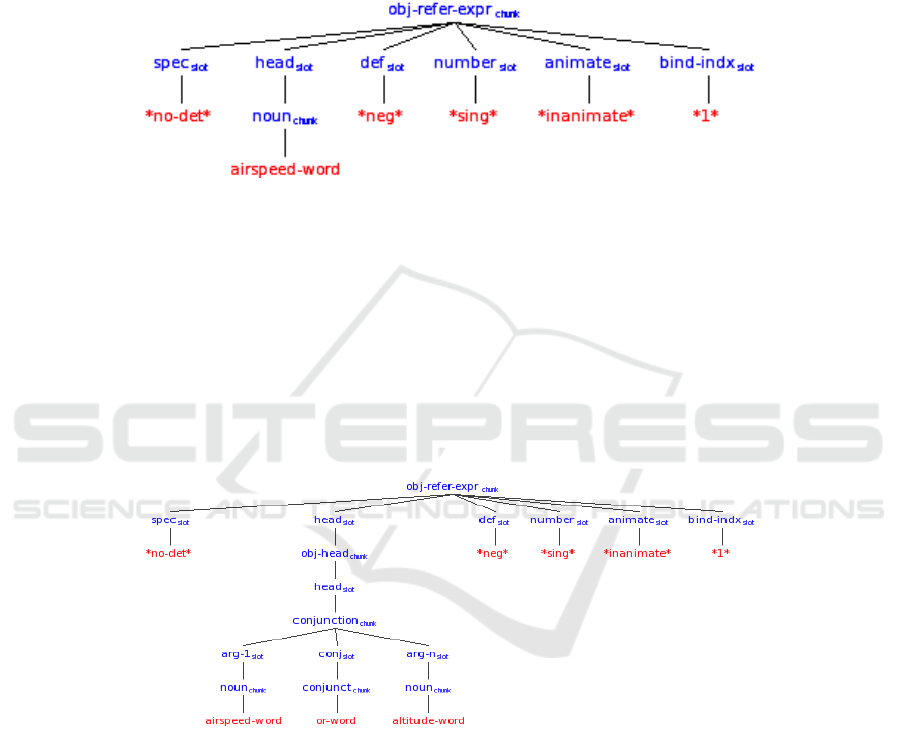
Fig. 2. Representation after processing “no airspeed”.
The processing of the noun “airspeed” leads its integration as the head of the object
referring expression. “Airspeed” also projects the animacy feature inanimate and the
number feature singular (abbreviated “*sing*”) to the nominal. In parallel, an alterna-
tive structure called an object head (abbreviated “obj-head”) is projected. The object
head contains a head slot filled by “airspeed” along with unfilled pre- and post-head
modifier slots. This alternative structure is available to accommodate more complex
inputs.
The processing of the disjunction “or” leads to its addition to ST-WM since the
category of the first conjunct of a conjunction cannot be effectively determined until
the linguistic element after the conjunction is processed—due to rampant ambiguity
Fig. 3. Representation after processing “no airspeed or altitude”.
associated with conjunctions. Note that delaying determination of the category of the
first conjunct until after processing of the linguistic element following the conjunction
provides a form of delayed processing reminiscent of Marcus’s deterministic parser
(substituting delay for lookahead), but delay is highly restricted in the model since it
complicates processing and taxes memory resources when the processing of the cur-
rent input must be temporarily halted and partial products saved to complete the
processing of the previous input.
32
The processing of the noun “altitude” in the context of the disjunction “or” and the
nominal “no airspeed” with head noun “airspeed” results in the accommodation of
“altitude” such that the head of the nominal is modified to reflect the disjunction of
the nouns “airspeed” and “altitude”. This is accomplished by overriding “airspeed” as
the head of the nominal with the alternative structure (projected in parallel) which
supports integration of a conjoined head. Although “airspeed or altitude” is labeled a
conjunction, it projects the number feature singular not plural because it contains the
disjunction “or” which determines the number of the nominal (without being the
head). If the input had been “airspeed and altitude” the plural number feature would
have been projected.
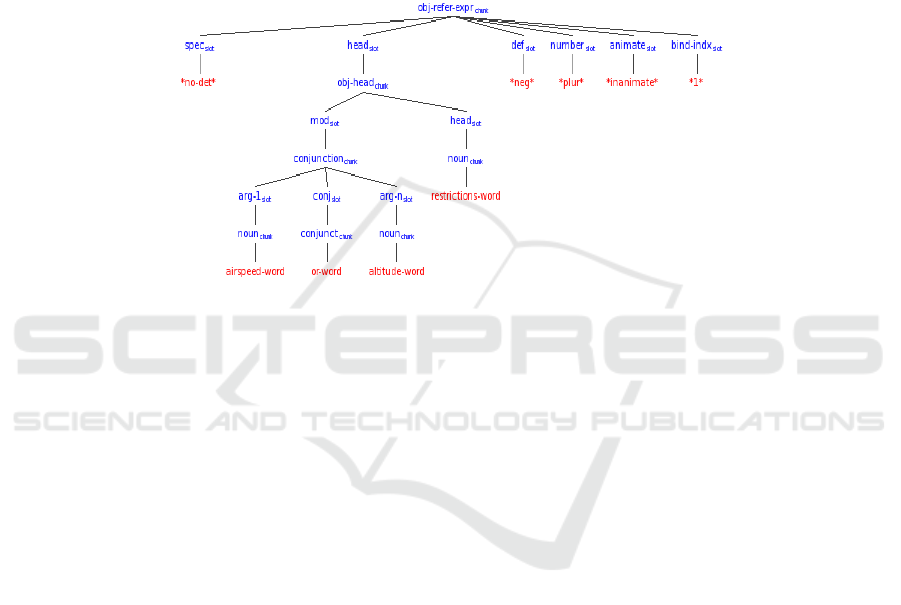
Fig. 4. Representation after processing “no airspeed or altitude restrictions”.
The processing of the noun “restrictions” in the context of the nominal “no airspeed
or altitude” results in accommodation of “restrictions” such that the current head “air-
speed or altitude” is shifted into a (pre-head) modifier slot to allow “restrictions” to
become the head. The plural number feature of “restrictions” (abbreviated “*plur*”)
is also projected to the nominal, overriding the previous singular number feature.
This representation was arrived at using a serial processing mechanism without
backtracking and limited delay and parallelism, despite the rampant local ambiguity
of the utterance!
As another example of the need for context accommodation in an incremental
HLP, consider the processing of ditransitive constructions. Given the input “he gave
the…”, the incremental processor doesn’t know if “the” is the first element of the in-
direct or direct object. In “he gave the dog the bone”, “the” introduces the indirect
object, but in “he gave the bone to the dog”, it introduces the direct object. How does
the HLP proceed? Delay is not a generally viable processing strategy since the
amount of delay is both indeterminate and indecisive as demonstrated by:
1. he gave the very old bone to the dog
2. he gave the verb old dog the bone
3. he gave the very old dog collar to the boy
4. he gave the old dog on the front doorstep to me
In 1, the inanimacy of “bone”, the head of the nominal, suggests the direct object as
does the occurrence of “to the dog” which is the prepositional form of the indirect
33

object, called the recipient in the model. In 2, the animacy of “dog” in the first nomin-
al, and the inanimacy of “bone” in the second nominal suggest the indirect object fol-
lowed by the direct object. Delaying until the head occurs would allow the animacy of
the head to positively influence the integration of the nominal into the ditransitive
construction in these examples. However, in 3, the animacy of “dog” also suggests the
indirect object, but “dog” turns out not to be the head. In 4, the animacy of “dog”
which is the head, suggests the indirect object, but this turns out not to be the case
given the subsequent occurrence of the recipient “to me”. There are just too many
alternatives for delay to work alone as an effective processing strategy. Although
there are only two likely outcomes—indirect object followed by direct object or direct
object followed by recipient—which outcome is preferred varies with the current con-
text and no alternative can be completely eliminated. And there is also a dispreferred
third alternative in which the direct object occurs before the indirect object as in “he
gave the bone the dog”. In the model, ditransitives are handled by projecting an ar-
gument structure from the ditransitive verb which predicts a recipient in addition to an
indirect and direct object. Although it is not possible for all three of these elements to
occur together, it is also not possible to know in advance which two of the three will
be needed. So long as the model can recover from an initial mistaken analysis without
too high a cost, early integration is to be preferred. Currently, the model projects a
nominal from “the” following the ditransitive verb and immediately integrates the
nominal as the indirect object of the verb. Once the head of the nominal is processed,
if the head is inanimate, the nominal is shifted to the direct object. If the first nominal
is followed by a second nominal, the second nominal is integrated as the direct object,
shifting the current direct object into the indirect object, if necessary. If the first no-
minal is followed by a recipient “to” phrase, the first nominal is made the direct ob-
ject, if need be. If the first nominal is inanimate and made the direct object and it is
followed by a second nominal that is animate, the second nominal is integrated as the
indirect object. It is important to note that the prediction of all three elements by the
ditransitive verb supports accommodation at no additional expense relative to a model
that predicted only one or the other of the two primary alternatives. However, unlike a
model where one alternative is selected and may turn out to be incorrect, necessitating
retraction of the alternative, there is no need to retract any structure when all three
elements are simultaneously predicted, although it is necessary to allow for a predic-
tion to be left unsatisfied and for the function of the nominals to be accommodated
given the actual input.
The processing of ditransitive verbs is complicated further within a relative clause.
Consider
5. the book
i
that I gave the man obj
i
6. the man
i
that I gave iobj
i
the book
7. the man
i
that I gave the book to obj
i
In 5, “book” is indexed with the (direct) object of “gave” within the relative clause
based on the inanimacy of “book”. In 6, “man” is indexed with the indirect object
based on the animacy of “man”. Note that animacy is the determining factor here.
There is no structural distinction to support these different bindings. These bindings
are established at the processing of “gave” without delay when the ditransitive struc-
ture is first projected. In 7, “man” is initially bound to the indirect object, but this ini-
tial binding must be adjusted to reflect the subsequent occurrence of “to” which indi
34

cates a recipient phrase even though no object follows the preposition.
As a final example, consider the processing of the ambiguous word “to”. Since “to”
can be both a preposition (e.g. “to the house”) and a special infinitive marker (e.g. “to
speed”) it might seem reasonable to delay the processing of “to” until after the
processing of the subsequent word. However, “to” provides the basis for biasing the
subsequent word to be an infinitive verb form (e.g. “to speed” vs. “the speed”) and if
its processing is delayed completely there will be no bias. How should the HLP pro-
ceed? If the context preceding “to” is sufficiently constraining, “to” can be disambi-
guated immediately as when it occurs after a ditransitive verb (e.g. “He gave the bone
to…”). Lacking sufficient context, the model prefers to treat “to” as the infinitive
marker and projects an infinitive construction. In parallel, the model identifies “to” as
a preposition and projects a locative construction. The model sets a bias for an infini-
tive verb form to follow. If a bare verb form follows the infinitive marker, it is inte-
grated into the infinitive construction as the head. If a nominal element (e.g. noun,
adjective, determiner) follows, the infinitive construction is replaced by the locative
construction, which was projected in parallel, and the nominal element is integrated as
the object of the locative construction.
The model also supports the recognition of multi-word units using a perceptual
span for word recognition that can overlap multiple words (Freiman & Ball, submit-
ted). With this perceptual span capability, an expression like “to speed” can be recog-
nized as a multi-word infinitival unit and there is no need to project a locative con-
struction in parallel. Similarly, “to the” can be recognized as a locative construction
lacking a head. Although not typically considered a grammatical unit in English, “to
the” is grammaticalized as a single word form in some romance languages and its
frequent occurrence in English suggests unitization. The perceptual span is roughly
equivalent to having a single word look-ahead capability—although the entire percep-
tual span must be processed as a unit. Overall, the processing of “to” encompasses a
range of different mechanisms of accommodation which collectively support its
processing. Some of these mechanisms are specific to “to”, and others are more gen-
eral.
5 Summary & Conclusions
This paper proposes and supports a pseudo-deterministic human language processor
which reflects the integration of a parallel, probabilistic activation and selection me-
chanism and non-monotonic context accommodation mechanism with what is other-
wise a serial, deterministic processor. A system with these mechanisms can pursue the
best path through a search space based on the locally available context, and make mi-
nor adjustments when the subsequent context reveals the preceding context to have
led to an inappropriate choice. The accommodation mechanism takes into considera-
tion the entire context available at the time (the current local context) and is itself sub-
ject to subsequent accommodation. The accommodation mechanism can give the ap-
pearance of parallel processing and can be just as efficient as normal serial processing
if the possible structures are predicted in advance or in parallel.
35

References
1. Altmann, G. & Mirkovic, J. (2009). Incrementality and Prediction in Human Sentence
Processing. Cognitive Science, 222, 583-609.
2. Altmann, G., & Steedman, M. (1988). Interaction with context during human sentence
processing. Cognition, 30, 191-238.
3. Anderson, J. (2007). How Can the Human Mind Occur in the Physical Universe? NY: Ox-
ford University Press.
4. Ball, J. (2004). A Computational Psycholinguistic Model of Natural Language Understand-
ing. Proceedings of the Natural Language Understanding and Cognitive Science Work-
shop, 3-14. B. Sharp (ed.). Portugal: INSTICC Press.
5. Ball, J. (2007). A Bi-Polar Theory of Nominal and Clause Structure and Function. Annual
Review of Cognitive Linguistics, 5, 27-54.
6. Ball, J. (2010). Projecting Grammatical Features in Nominals: Cognitive Processing Theory
& Computational Model. Proceedings of the 19
th
Behavior Representation in Modeling and
Simulation Conference. Charleston, SC.
7. Ball, J., Freiman, M., Rodgers, S. & Myers, C. (to appear). Toward a Functional Model of
Human Language Processing. Proceedings of the 32
nd
Conference of the Cognitive Science
Society.
8. Ball, J., Myers, C. W., Heiberg, A., Cooke, N. J., Matessa, M., & Freiman, M. (2009). The
Synthetic Teammate Project. Proceedings of the 18
th
Annual Conference on Behavior Rep-
resentation in Modeling and Simulation. Sundance, UT.
9. Bever, T. (1970). The cognitive basis for linguistic structures. In J. Hayes (Ed.), Cognition
and the development of language (pp. 279-362). New York: Wiley.
10. Boden, M. (2006). Mind as Machine: A History of Cognitive Science, 2 vols. Oxford: Ox-
ford University Press.
11. Crocker, M. (2005). Rational models of comprehension: addressing the performance para-
dox. In A. Cutler (Ed), Twenty-First Century Psycholinguistics: Four Cornerstones.
Hillsdale: LEA.
12. Ericsson, K. and Kintsch, W. 1995. Long-term working memory. Psychological Review,
102 211-245.
13. Freiman, M. & Ball, J. (submitted). Improving the reading rate of Double-R-Language.
14. Gibson, E., & Pearlmutter, N. (1998). Constraints on sentence comprehension. Trends in
Cognitive Sciences, 2(7), 262-268.
15. Heiberg, A., Harris, J. & Ball, J. (2007). Dynamic Visualization of ACT-R Declarative Me-
mory Structure. In Proceedings of the 8
th
International Conference on Cognitive Modeling.
16. Just, M. & Carpenter, P. (1987). The Psychology of Reading and Language Comprehen-
sion. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, Inc.
17. Lewis, R. L. (1998). Leaping off the garden path: Reanalysis and limited repair parsing. In
J. D. Fodor, & F. Ferreira (Eds.), Reanalysis in Sentence Processing. Boston: Kluwer Aca-
demic.
18. Marcus, M. 1980. A Theory of Syntactic Recognition for Natural Language. Cambridge,
MA: The MIT Press.
19. McClelland, J., & Rumelhart, D. (1981). An interactive activation model of context effects
in letter perception: I. An account of basic findings. Psychological Review, 88(5), 375-407.
20. Paap, K., Newsome, S., McDonald, J., & Schvaneveldt, R. (1982). An Activation-
Verification Model of Letter and Word Recognition: The Word-Superiority Effect. Psycho-
logical Review, 89, 573-594.
21. Tanenhaus, M., Spivey-Knowlton, M., Eberhard, K., & Sedivy, J. (1995). Integration of
visual and linguistic information in spoken language comprehension. Science, 268(5217),
1632-1634.
22. Wilks, Y. (1975). A Preferential Pattern-Seeking Semantics for Natural Language Infe-
rence. Artificial Intelligence, 6, 53-74.
36
