
Using MDD to Extend the IMS LD Standard with
Adaptability
Valérie Monfort
1,2
, Slimane Hammoudi
3
and Maha Khemaja
4
1
Université de Sfax, MIRACL, Sfax, Tunisie
2
Université de Paris 1 Panthéon Sorbonne, Sorbonne, France
3
ESEO 4, Rue Merlet de la Boulaye B.P. 9249 009 Angers Cedex 01, Angers, France
4
PRINCE Research Group, ISITC Hammam Sousse, University of Sousse, Sousse, Tunisia
Abstract. A few e-Learning platforms propose a solution for ubiquity and
context aware adaptability. Current standards, as Learning Design (LD), require
an extension to propose context awareness. Based on previous related works,
we define a fully interoperable and learner (ambient) context adaptable
platform, by using meta modeling based approach mixing MDD, parameterized
transformations, and models composition. The scope of this paper is to extend
LD meta model as a first step. We use a concrete software engineering
industrial product that was promoted by French Government.
1 Introduction
E Learning aims the delivery of a learning, training or education program by
electronic and it involves the use of a computer or electronic device (e.g. a mobile
phone), in some way, to provide training, educational or learning material.
Concerning the architecture point of view, e Learning platforms gather two separated
and distributed parts as: authoring tools (for pedagogical contents definition) and
execution platforms. So, e Learning may: i) use several media and devices, ii)
promote specific training according to learner skills, iii) send specific events to
increase complexity of lessons and to assess learner reactions, …
Previous works allowed us to use Web services to get interoperability and
flexibility to changes. But, we noticed the lack of adaptability, so, we extended Web
services to introduce adaptability with aspects [12]. We noticed this very efficient and
pragmatic solution was very technical. Recently, we have investigated a model driven
approach and context awareness to provide developers mechanisms that allow them
representing an application in abstract way (in a model) and, then, automatically
generating the corresponding code [7], [8]. We aimed to explore adaptability and
flexibility on a service platform using context with the benefits of an MDD (Model
Driven Development) [9] development strategy. These benefits are related to
productivity, quality, adaptability and maintenance.
Moreover, e Learning standards tend to extend their semantic to Web services
standards [4]. We studied e-Learning standards metamodels, but, we noticed no
semantics concerning context aware adaptability.
Monfort V., Hammoudi S. and Khemaja M.
Using MDD to Extend the IMS LD Standard with Adaptability.
DOI: 10.5220/0003025600800086
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Future Trends of Model-Driven Development (ICEIS 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-8425-10-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

We aim to propose a fully interoperable and learner (ambient) context adaptable
platform. This paper studies e-Learning standard semantics to introduce context
awareness metamodels. We focus here on Learning Design (LD) that helps to define a
pedagogical scenario with its components (roles, activities, environment, and
outcomes). LD proposes an entity for context in its metamodel but, according to us,
this approach is too semantically poor.
We shall process as followed. Second section presents context and context
awareness, aspect based services models and context aware metamodel. Third section
discusses an extension of LD metamodel with models composition and a concrete
industrial software engineering project. Fourth section presents some related works.
Let us define now context awareness.
2 Context Aware Modelling
2.1 Context and Context Awareness
Context awareness is a quite new discipline in e Learning domain. For instance, in [6]
[11], the authors noticed the context acts like a set of constraints that influence the
behavior of a system (a user or a computer) embedded in a given task. They discussed
the nature and structure of context but they notice the lack of representation of context
in e Learning domain. The emergence of new technologies, in particular wireless
communications and the increasing use of portable devices (smart phones, Personal
Digital Assistants(PDA), laptops…), has stimulated the emergence of a new
computing paradigm called: pervasive computing. In fact we have moved from the
desktop computing paradigm to the mobile and ubiquitous computing paradigm.
Pervasive computing refers to the seamless integration of devices into the user’s
everyday life. “Appliances should disappear into the background to make the user
and his tasks the central focus rather than computing devices and technical
issues.”[13]. Computing applications now operate in a variety of new settings; for
example, embedded in cars or wearable devices. They use information about their
context to respond and adapt to changes in the computing environment. They are, in
short, increasingly context aware. The context awareness of such applications is the
subject of a recent field of studies in pervasive computing called: context-aware
systems. This terminology was discussed in [10] and presented as “software that
adapts according to its location of use, the collection of nearby people and objects, as
well as changes to those objects over time”. Since then, there have been numerous
attempts to define context-aware computing. In [10], [11], they define context-
awareness as the ability of a program or device to sense or capture various states of its
environment and itself. Referring to these latter definitions a context-aware
application must have the ability to capture the necessary contextual entities from its
environment, use them to adapt its behavior (run time environment) and finally
present available services to the user. In this sense and to describe context-awareness
independently from application, function, or interface, [11] proposes four features of
context-aware application : (1) Contextual sensing which refers to the detection of
environmental states and their presentation to the user; (2) Contextual adaptation
81

refers to the adaptation of application behavior to the current context; (3) Contextual
resource discovery is the use of context data to discover other resources within the
same context; (4) Contextual augmentation in which the environment is augmented
with digital data associated to a particular context. In [2], [3], the authors introduce
another definition in which they insist on the use of context and the relevance of
context information. The authors consider that: “a system is context-aware if it uses
context to provide relevant information and/or services to the user, where relevance
depends on the user’s task”. They explain how to use context and propose a
classification of the features of context-aware applications that combine the ideas of
[10].
2.2 Model Driven Development (MDD)
At the beginning of this century, software engineering needs to handle software
systems that are becoming larger and more complex than before. Object-oriented and
component technology seem insufficient to provide satisfactory solutions to support
the development and maintenance of these systems. To adapt to this new context,
software engineering has applied an old paradigm, i.e. models, but with a new
approach, i.e. Model Driven Development (MDD). In this new global trend, Model
Driven Architecture (MDA) is a particular variant. MDA is based on standards from
the Object Management Group (OMG) [9]; it proposes an architecture with four
layers: meta metamodel, metamodel, model and information (i.e. an implementation
of its model). MOF (Meta Object Facility) is a standard from OMG for metamodels
specification. The development is based on the separation of concerns (e.g. business
and technical concerns), which are afterwards transformed between them. So,
business concerns are represented using Platform-Independent Model (PIM), and
technical concerns are represented using Platform-Specific Model (PSM). Finally, it
is well recognized nowadays that model transformation is one of the most important
operations in MDA. In the context of the basic four levels Metamodeling architecture
of MDA, various scenarios of model-to-model transformation have been identified.
The most common scenario of these transformations, which is compatible with the
MOF2.0/QVT standard includes the following elements. Transformation rules specify
how to generate a target model (i.e. PSM) from a source model (i.e. PIM). To
transform a given model into another model, the transformation rules map the source
into the target metamodel. The transformation rules are based on a transformation
language, such as the standard QVT. The transformation engine takes the source
model, executes the transformation rules, and produces the target model as output.
Adaptable Service platforms have been proposed for the development of mobile
context-aware applications. The development of such platforms involves a number of
challenges from which we consider two main issues in the context of our approach of
model driven development:
• The definition of a metamodel to describe the contextual domain in which a given
application or service is defined.
• A mechanism to integrate the context into the business application using a model
driven approach.
82
In [7], [8] we have discussed these two main issues. We have defined a context
metamodel which identifies and adds the most relevant and generic contextual entities
that will be held in account in modelling any mobile and context aware application.
We have then proposed a parameterized transformation technique which allows
merging context information with business logic at model level. We have investigated
this type of transformation which is not explored and there is not a standard
transformation language implementing it.
3 Extension of LD to Context Awareness
3.1 LD Model
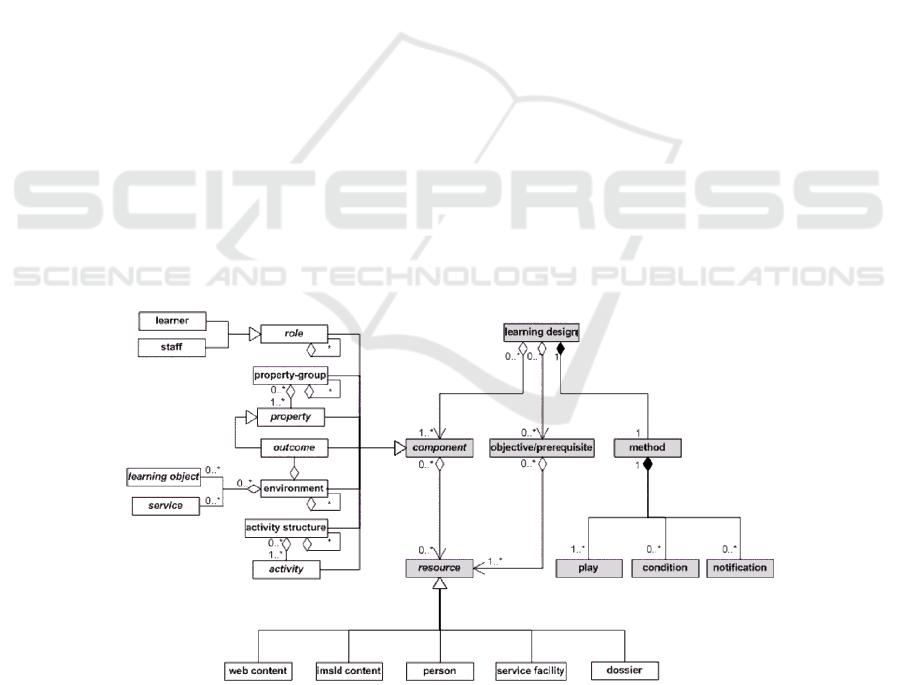
A Learning Design (LD) is a description of a method enabling learners to achieve
intended learning objectives and outcomes by performing predefined learning
activities. More specifically, a learning design is a means allowing the Instructional
designer to describe a learning scenario in terms of a set of activities that learners
should perform according to the different roles that they may play within
environments (i.e Run-time environment). Environments are described in terms of
Learning Objects and Services that should assist learners during the Learning process.
IMS-LD (Instructional Management Systems-Learning Design) [1], [5] specification
provides for previously described concepts a meta-model (Figure 1) that was and is
still used by LD authoring tools developers. According to IMS-LD specification, LD
concepts must meet height requirements. We name the third one because it deals with
personalization that is relevant to our work. The LD specification states that: “The
content and activities within a unit of learning can be adapted based on the
preferences, portfolio, pre-knowledge, educational needs, and situational
circumstances of users. In addition, the control over the adaptation process must be
given, as desired, to the student, a staff member, the computer, and/or the designer”.
Fig. 1. The LD Specification.
83

However, IMS-LD provides neither means nor modeling solutions to take into
account contextual data of mobile users for instance. We should stress that the
contextual data, unlike those already defined for personalization, are dynamic and
may depend on the user’s external environment. We propose to extend this model
with our context metamodel with composition mechanisms according to [14], [15] .
Fig. 2. Generic BPMN Process of the training.
3.2 Illustrative example and Model Composition
We worked for French government to implement a navigation and fishing e learning
application. We proposed following metamodels coming from our research works.
The application aims to train different kind of learners as: young students coming
from fishery schools and adults working for fishery companies. In fine, the aim of the
system is to train learners to be: fishery captain, fishing boat mechanic, sailor, port
manager,…
During course, learner according to his skills receives a navigation and/or fishing
scenario as “ go to 100 miles from Saint Jean de Luz and fish tuna”. So, the learner
has to do obligatory tasks as: to check weather, to define the road, to check the fitted
nets, to check mechanic,… The generic BPMN (Business Process Modeling) [16]
process shows (Figure 2) the different tasks to do by the learner and the teacher. The
teacher programs a course that will be received by the learner anywhere he is, via any
media, … after identifying himself. The learner is assessed in real time and the
teacher may send him events. At the end of the module, the diploma is delivered or
84

not. The learner is in front of his laptop and receives the training. All the navigation
tools (radar, sounder, GPS,…) are simulated. According to his skills, the teacher
(human or system) can send to the learner desktop specific events as mist, rain,… and
the learner has to react properly. Moreover, the system provides an estimation of
learner skills in real time. The resulting composed model is formed by: i) training
metamodel (that could be later formatted to e-learning standards), ii) a contextual
model that was already composed to component class from LD. Another composition
may also be done with fishery business metamodel. For each training module, a link
may be done with specific business data. For instance, a training module about tuna
fishery involves the choice of the fitted net. A mark is put on the required classes.
4 Conclusions
Other approaches aims to use metamodeling: i) to define e Learning interoperable and
platforms independent system ii) and to extend standards as [1], [4], [5]. Some
researchers introduce adaptability with Multi Agent System but we choose an hybrid
approach based on software engineering and Artificial Intelligence. Previous works as
[7], [8], propose solutions to model context. We use these approaches to extend them
to eLearning according to our choices. We did not find any concrete and relevant
related works concerning such an approach in e-Learning domain, but we are
convinced our approach is pertinent because we got good results with fishing
simulators and in other Web based application domains.
This paper proposes a metamodel approach to introduce (ambient) context
awareness in LD model. It is based on our previous works about adaptability and
models composition based MDD. We propose examples coming from a concrete
industrial project. We aim: i) to define an independent platform model based on
services, ii) to implement models transformations to link these models to
implementation platform, iii)to promote automatic code generation… We propose
now transformation rules via a technical platform based on services and supporting
context awareness.
References
1. Boticario, J. Olga. C Santos: An open IMS-based user modeling approach for developing
adaptive Learning managements systems. Retrieved from
www-jime.open.ac.uk/2007/02/.
2. Chen, G., and Kotz, D. (2000). A survey of context-aware mobile computing research.
Tech. rep., Dept. of Computer Science, Dartmouth College.
3. Dey, A. K. (2001). Understanding and Using Context. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing
5, 1, 4-7.
4. Dietze Stefan, Alessio Gugliotta, and John Marko Rosić Vlado Glavinić Branko Žitko:
Intelligent authoring shell based on Web services :
http://www.pmfst.hr/~bzitko/radovi/files/INES2004.pdf
5. Davinia Hernandez Leo, Juan I. Asensio Perez, Yannis A. Dimitriadis, "IMS Learning
Design Support for the Formalization of Collaborative Learning Patterns" Advanced
Learning Technologies, IEEE International Conference on, pp. 350-354, Fourth IEEE
International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT'04), 2004.
85

6. Mary, B., and Patrick, B. (2005). Understanding context before to use it. In 5th
International and Interdisciplinary Conference on Modeling and Using Context vol. 3554 of
Lectures Notes in Artificial Intelligence, Springer-Verlag, pp. 29-40.
7. V. Monfort, S. Hammoudi, When Parameterized MDD Supports Aspect Based SOA ,
IJEBR 2010, International Journal of E-Business Research (To appear).
8. V. Monfort, S. Hammoudi, ICSOC, Towards Adaptable SOA: Model Driven Development,
Context and Aspect The 7th International Conference on Service Oriented Computing,
November 23-27 2009, Stockholm, Sweden.
9. OMG (Object Management Group). (2001). Model Driven Architecture (MDA), OMG
document number ormsc/2001-07-01.
10. Schilit, B. N., and Theimer, M. (1994). Disseminating active map information to mobile
hosts. IEEE Network 8 22-32.
11. Strang, T., and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2004). A Context Modeling Survey. In First
International Workshop on Advanced Context Modelling, Reasoning and Management,
UbiComp.
12. Tomaz, R. F., Hmida, M. B., and Monfort, V. (2006). Concrete solutions for web services
adaptability using policies and aspects. The International Journal of Cooperative
Information Systems (IJCIS), 15(3):415– 438.
13. Weiser, M. (1991). The computer for the 21st century. Scientific American. PP 94-104.
14. J. Klein, L. Hélouet, and J. M. Jézéquel. -- Semantic-based weaving of scenarios. -- In
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Aspect-Oriented Software Development
(AOSD'06), Bonn, Germany, March 2006. ACM
15. Sten Lundesgaard, Arnor Solberg, Jon Oldevik, Robert France, Jan Oyvind Aagedal, Frank
Eliassen, Construction and Execution of Adaptable Applications Using an Aspect- Oriented
and Model Driven Approach, IFIP DAIS 2007, LNCS 4531, 76-89, 2007.
16. BPMN specification web site retrieved from http://www.bpmn.org/
86
