
Identifying Multidocument Relations
Erick Galani Maziero, Maria Lucía del Rosario Castro Jorge
and Thiago Alexandre Salgueiro Pardo
Núcleo Interinstitucional de Lingüística Computacional (NILC)
Instituto de Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação, Universidade de São Paulo
Av. Trabalhador São-carlense, 400, P.O. Box. 668, 13560-970, São Carlos, SP, Brazil
Abstract. The digital world generates an incredible accumulation of information.
This results in redundant, complementary, and contradictory information, which
may be produced by several sources. Applications as multidocument
summarization and question answering are committed to handling this
information and require the identification of relations among the various texts in
order to accomplish their tasks. In this paper we first describe an effort to create
and annotate a corpus of news texts with multidocument relations from the Cross-
document Structure Theory (CST) and then present a machine learning
experiment for the automatic identification of some of these relations. We show
that our results for both tasks are satisfactory.
1 Introduction
There are many sources that report the same information with similar or different
perspectives and focuses. This fact results in the accumulation of information in the
electronic media. Online newspapers are good examples of this multiplicity of
information. News are reported in the moment they happen and many documents are
produced about the same topic. The reader, in this context, need to search and organize
the content to identify the desired information.
GoogleNews is an example of web application that tries to retrieve and organize the
information. It groups news on issues such as “World” and “Business”, among several
others. Although this kind of application is important, Natural Language Processing
(NLP) tasks usually require more sophisticated knowledge. For instance, multidocument
summarization and question answering applications must not only retrieve and organize
texts, but also need to identify how the segments of the texts are related in order to be
able to eliminate redundancy and to appropriately deal with contradictory information
before showing some content to the user. Final users might also directly benefit from
such functionality, e.g., when a user would want to read how different news agencies
reported some politician speech (for example, for contrasting the political tendencies of
the sources) or would simply want to join complementary information pieces.
Systems that perform the task of identifying the relationships among text segments
are called multidocument parsers. Such parsers usually follow multidocument
representation models to structure such relationships. Cross-document Structure Theory
(CST) [15] is one of the most used theories and is the focus of this paper.
Galani Maziero E., del Rosario Castro Jorge M. and Salgueiro Pardo T.
Identifying Multidocument Relations.
DOI: 10.5220/0003028800600069
In Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Cognitive Science (ICEIS 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-8425-13-3
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In this paper we investigate the multidocument parsing task for Brazilian Portuguese
language. We initially report the creation and annotation of a corpus according to CST
and then describe one machine learning experiment for automatically identifying some
of the multidocument relations. We refine the CST model and show that our corpus
annotation has a good agreement level and that our results on relation identification are
satisfactory, although there is still room for improvement.
In the next section we introduce CST and the related works on multidocument
parsing. Section 3 reports our corpus annotation and Section 4 describes our experiment
with machine learning. Finally, some final remarks are made in Section 5.
2 Multidocument Analysis
Proposals on multidocument structuring are not new. [18] and [19] proposed the Textnet
system, one of the first efforts to manually relate segments of scientific texts.
Underlying the system there is a set of semantic relations, which is the first one
proposed, to the best of our knowledge. The system uses the structure of semantic
networks. The text segments (chunks) are nodes and there are links between the nodes
indicating the relationship between the corresponding segments. Besides the chunks, the
system allows the creation of nodes that indicate the structure of the network (tocs -
table of contents), such as indexes of documents, forming a hierarchical structure. It is
possible to define paths in the generated structure, assisting the reader in sequentially
reading the represented texts. The authors justified the non-automation of their textual
analysis with the limited NLP tools in the time.
[16] presented a methodology for summarization of multiple documents, in
particular, online news. The proposed summarization method takes into account the
interests of the user, such as similarities, contradictions, evolution of events in time, etc.
What is interesting in this work is that the system looks for some relations among text
segments for determining how to produce the summary. In fact, this work gave the first
steps towards the development of CST.
In this scenario, [15] proposed CST. Inspired on the Rhetorical Structure Theory
(RST) [11], a theory that proposes the structuring of a single document, CST soon stood
out and showed its potential for several research projects, being mainly used for
multidocument summarization.
Originally, CST proposes a set of 24 multidocument relations. Figure 1 shows these
relations. Refining the original CST relation set, [21] used only 18 relations, which are
shown in Figure 2.
One may notice that there are relations of diverse natures. Some are intended to
mainly relate the content of the text segments (e.g., equivalence and subsumption
relations), while others were designed to capture text perspective and style (e.g., reader
profile and indirect speech relations). It is also interesting to say that, according to CST,
not all segments of the texts under analysis need to be related, since there are segments
that do not directly refer to the same subject. [21] goes further and affirms that CST
relationships are unlikely to exist between segments that are lexically very dissimilar to
each other.
CST relations may also have directionality, being classified as symmetrical or
asymmetrical. The equivalence relation is an example of symmetrical relation (since one
61
may read it in any direction), while the historical background relation is asymmetric,
because one segment provides the historical setting to another one.
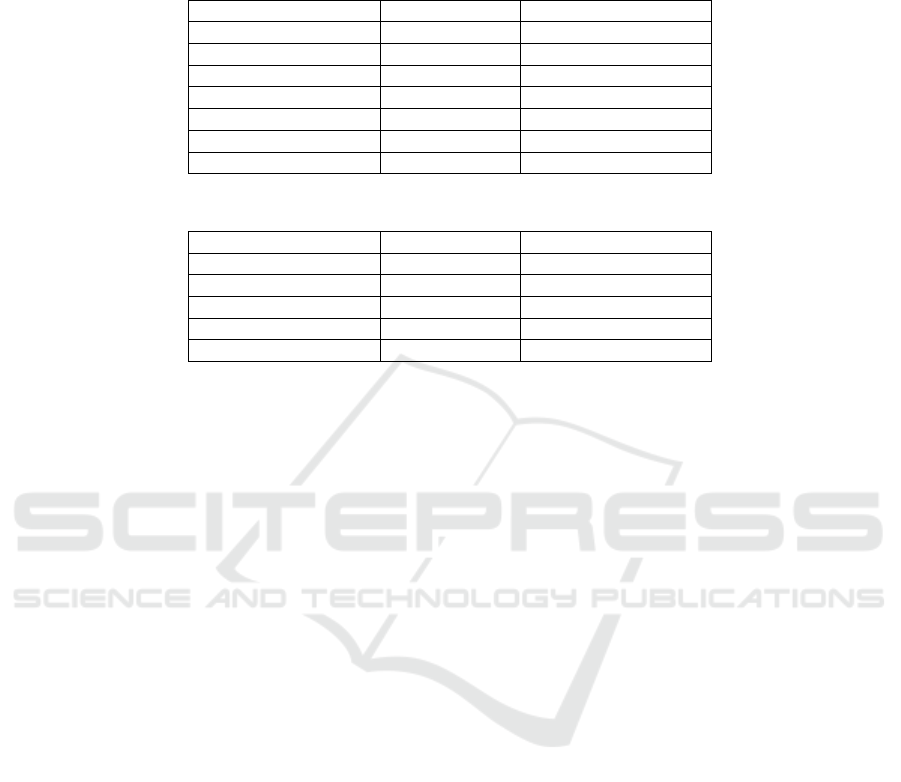
Identity Modality Judgment
Equivalence Attribution Fulfillment
Translation Summary Description
Subsumption Follow-up Reader profile
Contradiction Elaboration Contrast
Historical background Indirect speech Parallel
Cross-reference Refinement Generalization
Citation Agreement Change of perspective
Fig. 1. Original set of CST relations.
Identity Modality Change of Perspective
Equivalence Attribution Fulfillment
Translation Summary Description
Subsumption Follow-up Reader profile
Contradiction Elaboration Change of perspective
Historical background Indirect speech Citation
Fig. 2. Subset of the originally proposed CST relations.
According to CST, any segment size may be considered in the analysis. CST may
relate words, phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs or larger text blocks. While clauses
and sentences are traditionally the adopted segments, particular tasks may require a
relationship between smaller segments. For example, for the fusion of information, the
relationship of phrases may be more appropriate than sentences.
Although CST has been the most used multidocument model, it has several
problems. [1], for instance, discussed important points of it, as the possibility of
multiple segment sizes and the highly generic and subjective relations. They also
suggested another organization of relations, in which there are synchronic and
diachronic relations, but this would be tailored to specific text types and domains.
The works of [21] and [22] are the only known attempts to automate the process of
CST analysis for English. [21] carried out the CST analysis in two steps: firstly, it is
created a classifier to determine whether a pair of segments (sentences, in this case)
from different texts are related by some CST relation, and, in a positive case, it is used
another classifier to determine the CST relation between the segments. For the first
classifier, the features used were based on measures of lexical similarity. For the second
classifier, features of three levels were used: lexical features (e.g., number of words in
each segment and the number of common words), syntactical features (e.g., number of
words of some morphosyntactic tags in each segment and number of words with
common tags) and semantic features (e.g., semantic similarity between the main
concepts of each segment – obtained by the selection of the most important nouns and
verbs from the segments, using Princeton WordNet). In this work it was used a boosting
algorithm. [22] extended the previous work by incorporating and testing the use of
labeled and unlabeled data, applying both bagging and boosting techniques. The
classification was also carried out in two steps and the same features were used. The
authors computed precision, recall and f-measure values for some relations. Parts of the
62
results of the two works above are shown in Table 1. We show the results for the
relations that we also treat in this work. One may see that the results are quite low.
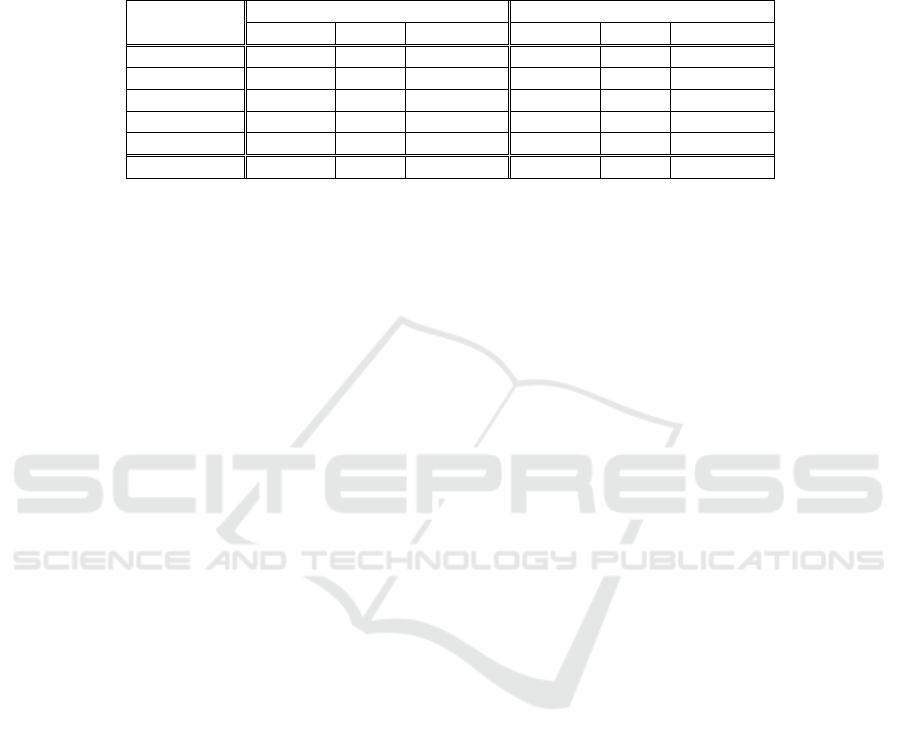
Table 1. Results obtained by [21] and [22].
CST relation
Results by [21] Results by [22]
Precision Recall F-Measure Precision Recall F-Measure
Equivalence 0.6000 0.2400 0.3429 0.5000 0.3200 0.3902
Subsumption 0.0667 0.0417 0.0513 0.1000 0.0417 0.0588
Follow-up 0.5088 0.3222 0.3946 0.4727 0.2889 0.3586
Elaboration 0.4000 0.1795 0.2478 0.3125 0.1282 0.1818
Overlap 0.5581 0.3529 0.4324 0.5263 0.2941 0.3773
Average 0.4267 0.2273 0.2938 0.3823 0.2145 0.2733
The authors used part of the CSTBank corpus [17][23], a corpus for English
language of clusters with news texts. The authors report that the annotators agreed
totally or partially (when the majority of them indicate the same relation) in 58% of the
cases for a sample of 88 related segment pairs from the corpus, remaining 42% of cases
with complete disagreement. The authors do not report kappa agreement measure [8].
There are also some other related works in the area. [12], for instance, tried to detect
only 2 relations for Japanese language. Although dealing with another task, [5]
presented techniques that could also be applied to multidocument parsing.
3 Corpus Annotation
There was already a corpus annotated according to CST for Brazilian Portuguese – the
CSTNews corpus [2]. It was composed of 50 groups of news texts, with each group
containing about 3 texts on the same topic. The texts of each group were manually
collected in the same day from online news agencies, namely, Folha de São Paulo,
Estadão, O Globo, Jornal do Brasil, and Gazeta do Povo. Groups were collected in
2007 during August and September. As the authors present, the annotation of this
corpus used the refined relation set of [21]. The corpus was annotated by 2
computational linguists and the agreement values were quite low: 0.26 average value in
the traditional kappa measure.
For performing this work, we decided to produce a new version of the corpus
CSTNews, in order to better understand the nature of CST and the multidocument
parsing problems as well as to refine the CST model. As it happened for the original
version of the corpus, we used the semi-automatic annotation tool CSTTool [3].
CSTTool was designed to perform the 3 basic tasks of multidocument parsing: text
segmentation, detection of segment pairs that are candidates to be related, and
identification of the relation among the selected segment pairs. We assume sentences to
be the text segments with which we work. For performing the sentence segmentation,
CSTTool use SENTER [13], a freely available rule-based segmentation tool for
Brazilian Portuguese. The detection of segment pairs that are candidate to be related
was extensively investigated for Portuguese, trying to use several tools and resources
[4]. After such work, and following the initiative for English [22], the word overlap
measure was adopted in CSTTool. It computes the similarity between two sentences as
63

the number of common words in the sentences divided by the sum of words in the two
sentences, resulting in a number between 0 and 1, with 1 indicating that the sentences
have the same words. We have used the threshold used for English for considering that
two segments are candidate to have a relation among them: 0.12. CSTTool indicates
such segment pairs for the user to select the relations among them, but the user may
ignore them (if s/he considers that they are not related) or may still select other segment
pairs from the texts to relate, independently from the CSTTool indications. Finally, the
identification of the relations have to be manually done so far. The results of this work
may provide a first automation to this task in CSTTool.
We selected 4 computational linguists to annotate the CSTNews corpus. Initially,
before proceeding to the annotation itself, there were 2 to 3 months of training, in order
to the judgers not to have doubts on the CST model or in the use of CSTTool. As result
of this training process, it was possible to refine even more the CST relation set. The
refinement was carried out (i) by removing a few relations that were never observed and
were not expected to happen for the texts we were working on and (ii) by joining some
relations that were very similar and the judgers could badly distinguish them. Our final
relation set is shown in Figure 3. It contains 14 relations that were better specified.
Identity Modality
Equivalence Attribution
Translation Summary
Subsumption Follow-up
Contradiction Elaboration
Historical background Indirect speech
Citation Overlap
Fig. 3. Refined relation set.
The annotation process took from 3 to 4 months in one-hour daily sessions. Each
group of texts was annotated by a different judger. Occasionally the same group was
annotated by all the judgers in order to compute agreement, which is going to be better
discussed latter.
The annotation allowed not only to refine the relation set, but also to produce a
typology of the relations. Figure 4 shows the complete typology of relations. This
typology classifies the relations in two main groups: the first group includes the
relations whose main purpose is to relate the segments content and the second group the
relations that are more worried with the presentation and form with which the content
was expressed. Each group is divided in more categories. Under the content group, the
relations may be classified as belonging to redundancy, complement or contradiction
categories. Redundancy may be totally or partially indicated by the relations, and
complements may refer to temporal facts/events or not. The second group has the
categories for relations that somehow refer to the authorship of some information and
relations that capture writing style choices. In the typology, under each final category,
the relations that belong to it are listed.
It is interesting to notice that, among the same information piece, only one relation
from the content group may happen. On the other side, relations from presentation/form
group eventually happen with relations from the other group (and in general they do).
After the annotation process, we ended up with refined relations definitions. Figure
5 illustrates a relation definition. The example is for the subsumption relation. Each
64

definition is composed of 5 fields: relation name (for reference only), type of the
relation (i.e., the path from the root to the relation itself in the typology that we
proposed), directionality, restrictions on the relation application, and additional
comments that may be worth inserting (for clarifying or exemplifying the relation
usage). The complete definition for the relation set may be found at [10].
Fig. 4. Relations typology.
Relation name: Subsumption
Type: Content -> Redundancy -> Partial
Directionality: S1->S2
Restrictions: S1 presents the information in S2 and some additional information
Comments: S1 presents some content X and Y, S2 presents only X
Fig. 5. Subsumption definition.
The whole corpus was annotated using CSTTool. This tool codifies the annotation
data in XML format, since it is widely used and accepted. We used the same XML
format used in CSTBank. Figure 6 shows a passage of our XML code. The element R
stands for “Relation”, SDID for “Source Document ID”, SSENT for the number of the
“Source SENTence” in the source document, TDID for “Target Document ID”, and
TSENT for the number of the “Target SENTence” in the target document. RELATION
TYPE indicates the relation itself, and JUDGE stores the name of the judger that
conducted such annotation.
<R SDID="D3_C1_JB.txt.seg" SSENT="1" TDID="D1_C1_Folha.txt.seg" TSENT="1">
<RELATION TYPE="Attribution" JUDGE="name_of_the_judger"/>
</R>
Fig. 6. Example of XML codification.
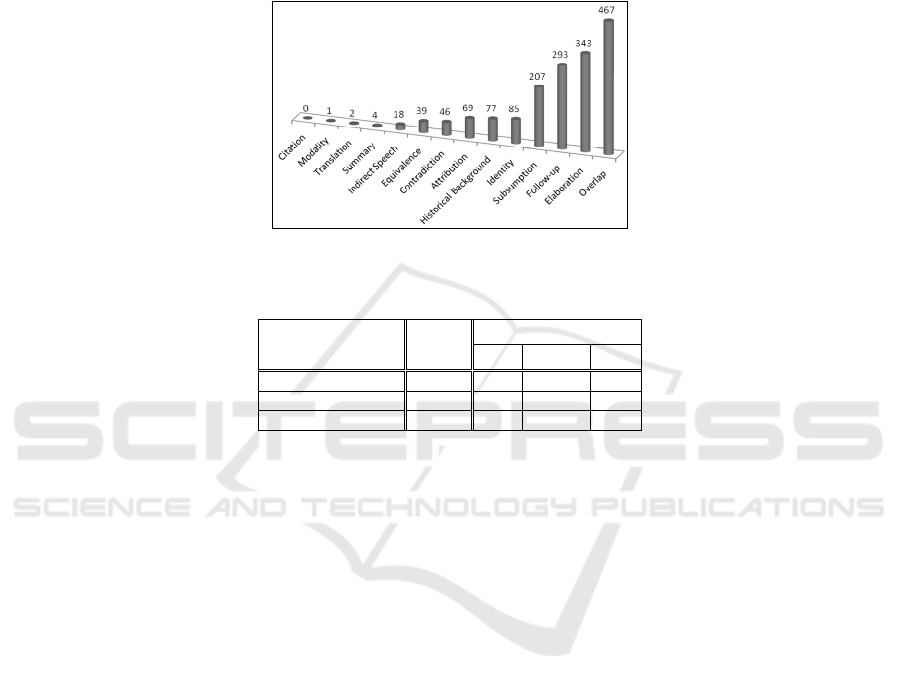
Figure 7 shows the absolute frequency of each relation in our corpus. While some
relations never occurred (e.g., citation) or occurred very rarely (modality, translation
and summary), other are very frequent in the corpus (elaboration, overlap, follow-up
and subsumption, for instance). Such distribution of relations looks natural since we are
dealing with news texts.
During the annotation of the corpus, we periodically computed the agreement
among the judgers over a group of texts. Table 2 shows the average kappa values that
we obtained for the identification of relations (does not mattering their directionality),
for only their directionality (the options were from the first to the second sentence, from
65
the second to the first sentence, or none), and for the relations categories in the typology
that we proposed. For the relations categories, we used the third level of the typology,
namely, the categories redundancy, complement, contradiction, authorship and style.
One may see that our kappa value for the relations is significantly better than the
original version of CSTNews (96% above it, in fact). As expected, when we group the
relations in their categories, the results are better.
Fig. 7. Frequency of relations in CSTNews.
Table 2. Agreement values for CSTNews.
Evaluated item
Kappa
Percentage agreement
Full Partial Null
Relations 0.51 0.54 0.27 0.18
Directionality 0.45 0.58 0.27 0.14
Relations categories 0.61 0.70 0.21 0.09
We also computed the percentage of times that the judgers agreed. We computed
full agreement, partial agreement (when the majority of the judgers indicated the same
relation) and null agreement (when each judger indicated something different from the
others). We performed this evaluation for the same items above. Although this
evaluation does not account for chance agreement (as Kappa measure does), it allows us
to better understand the results. Besides this, Kappa measure may penalize a lot some
disagreements. The average percentage results are also shown in Table 2 (in the last
three columns). One may see that the percentage of full and partial agreement are very
good, accounting for more than 80% of the relations (against 58% for English language
[23]) and their directionalities. Results are again better when we consider the categories
of the relations.
4 Experiment
We conducted an experiment for identifying some of the CST relations using machine
learning techniques. We used the CSTNews corpus for this task, as well as the typology
of relations that we proposed in this work. In this initial experiment, we used only the
relations from the content groups.
We considered each related sentence pair in the corpus as a learning instance. For
each instance, we extracted a set of machine learning features. Only relatively shallow
66
features were used at this moment, namely: difference in length of sentences (in number
of words), percentages of common words in the sentences, position of each sentence in
the text that it belongs to, a flag indicating whether a sentence is shorter than the other, a
flag indicating whether the sentences are identical, and the number of nouns, proper
nouns, adverbs, adjectives, verbs and numerals in each sentence. Such information was
obtained from syntactically parsed versions of the sentences, using the parser
PALAVRAS for Portuguese [7]. The class for each learning instance was the relation
among the sentences (not considering the directionality). Our corpus provided 1.561
learning instances.
One may observe in Figure 7 that the frequency of CST relations in the corpus is
very unbalanced, i.e., there are relations that have hundreds of examples, such as
overlap and elaboration, and others that have 1 or 2 examples, such as modality and
translation. Although this is natural in several NLP tasks, this may be a problem for
machine learning techniques, since they typically require many examples to induce
models with good results. To try to solve the problem of unbalanced classes, many
techniques are possible [14], e.g., to remove examples of the majority class or to
include/duplicate examples of the minority classes. In this work, we followed this last
strategy by applying the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique [9].
We used WEKA [20] for performing our experiments. We selected J48 for decision
tree generation, which belongs to the symbolic paradigm. Naïve-bayes was also tested,
but worse results were obtained. We used the stratified ten-fold cross-validation
technique for training and testing.
Table 3 shows the results in terms of the traditional measures of precision, recall and
f-measure for each relation. It also shows the average results.
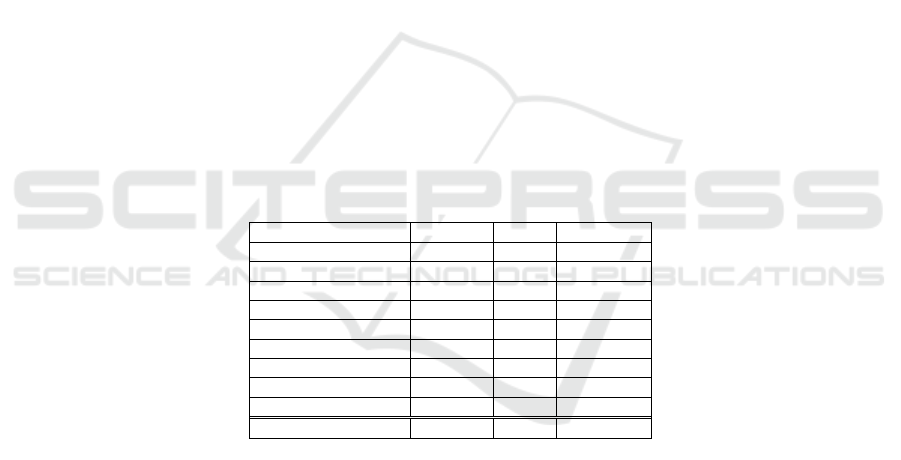
Table 3. Experiment results.
Relation Precision Recall F-Measure
Subsumption 0.439 0.507 0.471
Overlap 0.413 0.437 0.425
Identity 0.927 0.965 0.945
Equivalence 0.514 0.462 0.486
Elaboration 0.361 0.347 0.354
Follow-up 0.342 0.324 0.333
Historical-background 0.689 0.591 0.636
Contradiction 0.341 0.326 0.333
Summary 0.000 0.000 0.000
Average 0.447 0.439 0.442
Table 4 shows the confusion matrix for this experiment. From the tables, one may see
that the summary relation was not correctly identified in any occasion. We attribute this
to the fact of it being very rare in the corpus, even after balancing the data. Other
relations – as follow-up, elaboration, and contradiction – presented poor results, while
some relations had relatively good results – as historical background and identity. In
average, we achieved a 0.44 f-measure.
We did not include the presentation/form relations in this experiment to avoid
dealing with a multiclass classification task at this moment, since such relations usually
happen with content relations. We intend to investigate this point in future work.
67
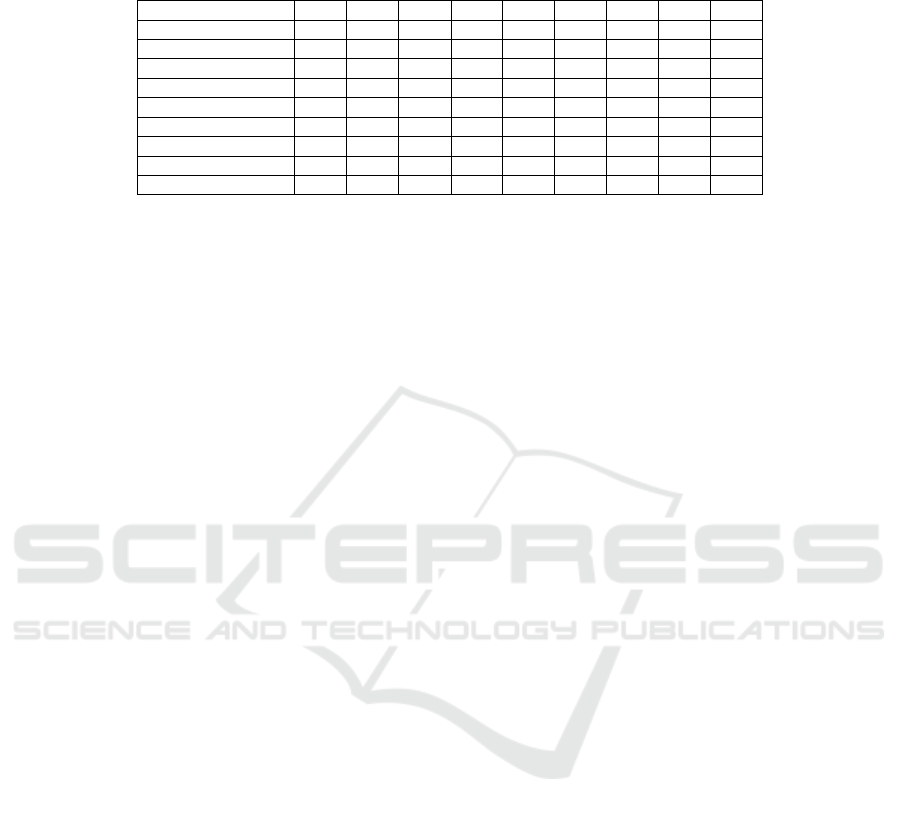
Table 4. Confusion matrix for the experiment.
A B C D E F G H I
Subsumption (A)
105 20 49 15 4 7 1 6 0
Elaboration (B)
27 119 115 56 17 5 0 3 1
Overlap (C)
52 96 204 81 7 14 1 11 1
Follow-up (D)
25 56 83 95 7 22 1 4 0
Historical B. (E)
9 22 12 10 91 7 0 3 0
Contradiction (F)
8 12 17 18 5 30 0 2 0
Identity (G)
0 0 3 0 0 0 164 3 0
Equivalence (H)
12 4 8 2 1 3 10 36 2
Summary (I)
1 1 3 1 0 0 0 2 0
Although a direct comparison is not fair, since corpora are different, comparing our
results with the results of [21] and [22] (see Table 1) may show the state of the art in the
task. One may see that almost all of our results are better than the results for English.
One possible reason for this may be that our corpus has better agreement values, which
might be reflected in our results.
5 Final Remarks
While presentation/form relations introduce a multiclass problem, we believe that some
CST relations need world or contextual information to be better identified. Such
knowledge may be obtained from online databases such as Wikipedia and Open Mind
Common Sense [6]. We intend to investigate such possibilities in the near future as well
as to develop and use more sophisticated statistical models.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to FAPESP and CNPq for supporting this work.
References
1. Afantenos, S. D.; Doura, I.; Kapellou, E.; Karkaletsis, V. (2004). Exploiting Cross-Document
Relations for Multi-document Evolving Summarization. In the Proceedings of SETN, pp. 410-
419.
2. Aleixo, P. e Pardo, T. A. S. (2008). CSTNews: Um Córpus de Textos Jornalísticos Anotados
segundo a Teoria Discursiva Multidocumento CST (Cross-document Structure Theory). Série
de Relatórios Técnicos do Instituto de Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação, Universidade
de São Paulo, no. 326. São Carlos-SP, Maio, 12p.
3. Aleixo, P. e Pardo, T. A. S. (2008). CSTTool: Uma Ferramenta Semi-automática para
Anotação de Córpus pela Teoria Discursiva Multidocumento CST. Série de Relatórios
Técnicos do Instituto de Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação, Universidade de São Paulo,
no. 321. São Carlos-SP, Maio, 11p.
4. Aleixo, P. and Pardo, T. A. S. (2008). Finding Related Sentences in Multiple Documents for
Multidocument Discourse Parsing of Brazilian Portuguese Texts. In Anais do VI Workshop
68

em Tecnologia da Informação e da Linguagem Humana – TIL, pp. 298-303.
5. Allan, J.; Carbonell, J.; Doddington, G.; Yamron, J.; Yang, Y. (1998). Topic detection and
tracking pilot study: final report. In the Proceedings of the DARPA Broadcast News
Understanding and Transcription Workshop.
6. Anacleto, J. C.; Carvalho, A. F. P.; Pereira, E. N.; Ferreira, A. M.; Carlos, A. F. (2008).
Machines with good sense: How can computers become capable of sensible reasoning?
Artificial Intelligence in Theory and Practice II, Vol. 276, pp. 195-204.
7. Bick, E. (2000). The Parsing System "Palavras": Automatic Grammatical Analysis of
Portuguese in a Constraint Grammar Framework. PhD thesis. Aarhus University. Denmark
University Press.
8. Carletta, J. (1996). Assessing Agreement on Classification Tasks: The Kappa Statistic.
Computational Linguistics, Vol. 22, N. 2, pp. 249-254.
9. Chawla, N. V.; Bowyer, K. W.; Hall, L. O.; Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic
Minority Over-sampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, Vol. 16, pp.
321-357.
10. Jorge, M. L. C. (2010). Sumarização automática multidocumento: seleção de conteúdo com
base no modelo CST (Cross-document Structure Theory). Tese de Doutorado. Instituto de
Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação, Universidade de São Paulo.
11. Mann, W. C. and Thompson, S. A. (1987). Rhetorical Structure Theory: A Theory of Text
Organization. Technical Report ISI/RS-87-190.
12. Miyabe, Y.; Takamura, H.; Okumura, M. (2008). Identifying Cross-Document Relations
between Sentences. In the Proceedings of the Third International Joint Conference on Natural
Language Processing, pp. 141-148.
13. Pardo, T. A. S. (2006). SENTER: Um Segmentador Sentencial Automático para o Português
do Brasil. Série de Relatórios do NILC. NILC-TR-06-01. São Carlos-SP, Janeiro, 6p.
14. Prati, R. C.; Batista, G. E. A. P. A.; Monard, M. C. (2008). Curvas ROC para avaliação de
classificadores. IEEE América Latina, Vol. 6, N. 2.
15. Radev, D. R. (2000). A common theory of information fusion from multiple text sources, step
one: Cross-document structure. In the Proceedings of the 1st ACL SIGDIAL Workshop on
Discourse and Dialogue.
16. Radev, D. R. and McKeown, K. (1998). Generating natural language summaries from
multiple on-line sources. Computational Linguistics, Vol. 24, N. 3, pp. 469-500.
17. Radev, D.R.; Otterbacher, J.; Zhang, Z. (2004). CST Bank: A Corpus for the Study of Cross-
document Structural Relationships. In the Proceedings of Fourth International Conference on
Language Resources and Evaluation.
18. Trigg, R. (1983). A Network-Based Approach to Text Handling for the Online Scientific
Community. Ph.D. Thesis. Department of Computer Science, University of Maryland.
19. Trigg, R. and Weiser, M. (1987). TEXTNET: A network-based approach to text handling.
ACM Transactions on Office Information Systems, Vol. 4, N. 1, pp. 1-23.
20. Witten, I. H. and Frank, E. (2005). Data Mining: Practical machine learning tools and
techniques. Morgan Kaufmann.
21. Zhang, Z.; Otterbacher, J.; Radev, D. R. (2003). Learning Cross-document Structural
Relationships using Boosting. In the Proceedings of the twelfth international conference on
Information and knowledge management, pp. 124-130.
22. Zhang, Z. and Radev, D. R. (2004). Combining Labeled and Unlabeled Data for Learning
Cross-Document Structural Relationships. In the Proceedings of IJCNLP, pp. 32-41.
23. Zhang, Z.; Blair-Goldensohn, S.; Radev, D. R. (2002). Towards CST-enhanced
summarization. In the Proceedings of the Eighteenth National Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, pp. 439-445.
69
