
SCRUMPL
Software Product Line Engineering with Scrum
Antônio Santos Jr. and Vicente Lucena Jr.
Electrical Engineering Degree Program, Federal University of Amazonas, Av. Gal. Rodrigo Octávio Jordão Ramos
nº 300, Campus da UFAM, Faculdade de Tecnologia. CEP 69077-000, Bairro Aleixo, Manaus, AM, Brazil
Keywords: Software Product Line Engineering, Agile Methods, Scrum, Agile Product Line Engineering.
Abstract: This paper presents the ScrumPL process, which combines the Software Product Line Engineering (SPLE)
methodology and the agile method Scrum to develop Software Product Lines (SPL). This process uses the
Requirements Engineering and Design sub-processes from both Domain and Application Engineering SPLE
processes to create a reference architecture with reusable component descriptions. Those components are
then added to a product backlog. Finally, the Scrum principles and lifecycle are launched to implement, test,
change requirements and deliver products. A preliminary result is also presented: a software product line
reference architecture and product backlog of an interactive TV navigation system.
1 INTRODUCTION
The industry, to reach more consumers, has adopted
the mass customization concept to develop several
and different products sharing the same components.
In other words, launch similar products attending
specific requirements from several market segments.
The methodoloy used to develop software for mass
customization is the software product line
engineering (SPLE) (Pohl et al., 2005; Northrop and
Clements, 2007), that uses component reuse
concepts in an efficient and sistematic way, resulting
on several software products sharing a common
plataform, which are part of a software product line
(SPL) (Pohl et al., 2005; Northrop and Clements,
2007), developed in less time, better cost and quality
compared to the development of those same several
software products isolatedly.
Scrum is an agile process that can be used to
manage and control complex product and software
development by using iterative and incremental
practices (Schwaber and Beedle, 2002). It was
invented to rapidly drive new products to market,
and was designed for hyperproductive teams where
productivity increases by 5-10 times over industry
averages and many colocated teams have achieved
this effect (Sutherland et. al, 2009).
Both, SPLE and Scrum, are designed to develop
software products in a productive way, but SPLE has
adopted the sistematic reuse as its main principle,
and Scrum has adopted the self-management teams
and agile manifesto (Beck et. al, 2001).
Nevertherless, one question rises: is it possible to
combine those methods?
This paper shows the ScrumPL, a method
combining both SPLE and Scrum methodologies
based on their input and output needs and the Scrum
lifecycle (Larman, 2004). The rest of this paper is
organized as follow: Section 2 briefly describes the
SPLE and its main processes, Section 3 shows the
Scrum skeleton and lifecycle, Section 4 describes
the ScrumPL process while Section 5 shows a SPL
reference architecture defined through part of this
process. Section 6, compare ScrumPL to other
methods, and Section 7 shows the conclusions.
2 SOFTWARE PRODUCT LINE
ENGINEERING
Software product lines are designed to provide
customized products at reasonable costs, enhanced
quality and reduction to time to market (Pohl et al.,
2005). The costs are reduced when artefacts from the
platform – which contains common artefacts and
tecnological capabilities – are reused in several
different kinds of system.
The quality enhancement comes from the
platform artefacts reviewing and testing in many
239
Santos Jr. A. and Lucena Jr. V. (2010).
SCRUMPL - Software Product Line Engineering with Scrum.
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering, pages 239-244
DOI: 10.5220/0003038302390244
Copyright
c
SciTePress
products. The time to market is initially higher, as
the common artefacts have to be built first; after
having passed this hurdle, the time to market is
considerably shortened as many artefacts can be
reused for each new product (Pohl et al., 2005).
The cost and time to market are better after the
3rd product, compared to the development of each
product individually (Northrop and Clements, 2007).
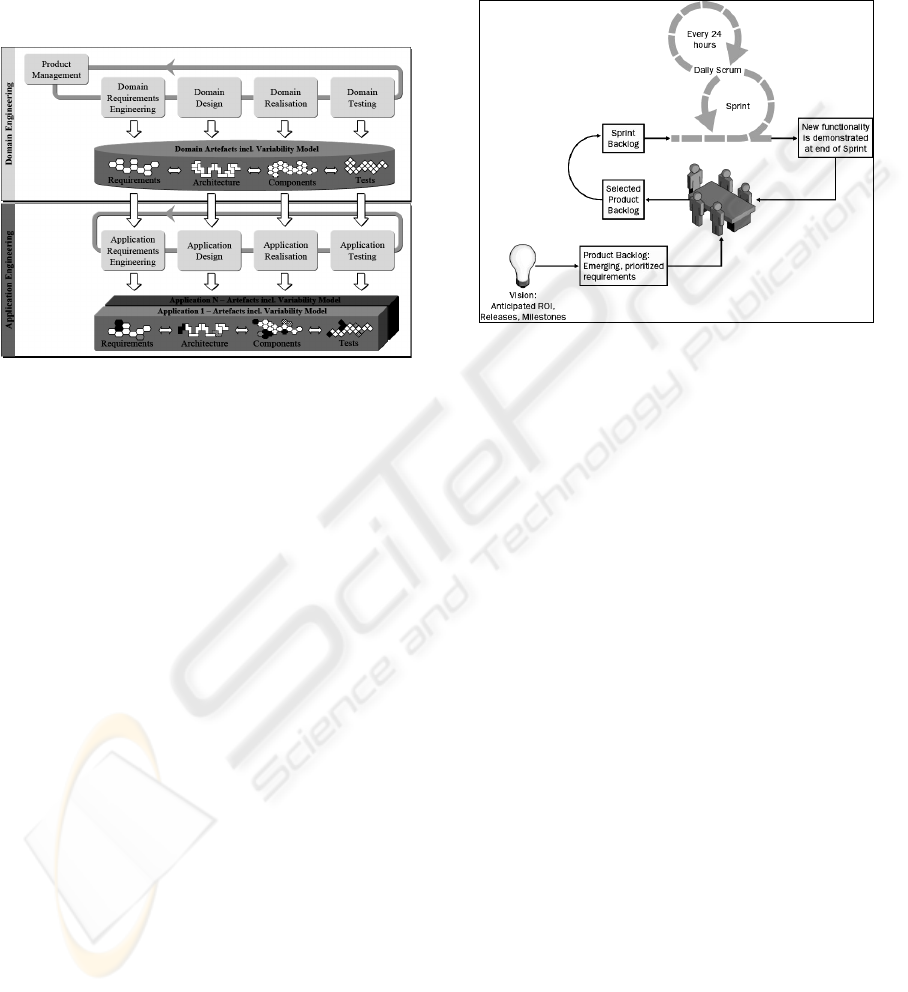
Figure 1: The Software Product Line Engineering
Framework (Pohl et al., 2005).
To develop an entire SPL two processes are used:
the domain engineering and the application
engineering, see Figure 1. The former realises the
commonality and the variability of the product line.
And the last builds the applications (individual
products) of the product line by reusing artefacts
from the domain engineering and exploiting the
product line variability (Pohl et al., 2005).
The domain engineering process has 5 sub-
processes: product management, domain
requirements engineering, domain design, domain
realization and domain tests. Those are designed to
define, implement and test the reusable artefacts of
the product line common platform.
The application engineering process has the
following sub-processes: application requirements
engineering, application design, application
realization and application tests. Those are designed
to achieve as high a reuse of the domain assets as
possible, when defining and developing each
application.
3 SCRUM
Scrum starts with a vision of the system to be
developed (Schwaber, 2004), see Figure 2. The
Product Owner formulates a plan for doing so that
includes a Product Backlog, which is a list of
functional and nonfunctional requirements that,
when turned into functionality, will deliver this
vision. The Product Backlog is prioritized so that the
items most likely to generate value are top priority
and is divided into proposed releases.
Figure 2: Scrum Process Overview (Schwaber, 2004).
All work is done in Sprints, which is an iteration of
30 consecutive calendar days initiated with a Sprint
planning meeting, in which the Product Owner and
Team get together to collaborate about what will be
done for the next Sprint. The tasks that compose this
plan are placed in a Sprint Backlog.
Every day, the team gets together for a 15-
minute meeting called daily meeting, where each
Team member answers three questions: What have
you done on this project since the last daily meeting?
What do you plan on doing on this project between
now and the next daily meeting? What impediments
stand in the way of your meeting your commitments
to this Sprint and this project? The purpose of the
meeting is to synchronize the work of all Team
members daily and to schedule any meetings that the
Team needs to forward its progress.
At the end of the Sprint, a Sprint review meeting
is held. This is a four-hour, time-boxed meeting at
which the Team presents what was developed during
the Sprint to the Product Owner and any other
stakeholders. Scrum requires Teams to build an
increment of product functionality every Sprint. This
increment must be potentially shippable. This
requires that the increment consists of thoroughly
tested, well-structured, and well-written code, and
the documented user operation of the functionality.
This is the definition of a “done” increment.
ENASE 2010 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
240

Planning Staging
Domain EngineeringApplication Engineering
Pre-Game
Development Release
Figure 3: ScrumPL Process Overview.
3.1 The Scrum Lifecycle
The Scrum lifecycle (Larman, 2004) is composed of
four phases: Planning, Staging, Development, and
Release. The Planning phase purpose is to establish
the vision, set expectations, and secure funding. Its
output are an initial product backlog and an
exploratory design and prototypes.
The Staging phase purpose is to identify more
requirements and prioritize enough for the first
iteration. Its outputs are plan, exploratory design and
prototypes. Together with Planing phase, Staging
form the pre-game phase, also called Sprint 0.
The Development phase purpose is to implement
a system ready for release in a series of Sprints, its
output is a potential shippable part of the system.
This phase is also called Game phase.
The release phase purpose is to perform
deployment activities. Training, documentation and
marketing activities are performed during this phase.
This fase is also called Postgame phase.
4 ScrumPL – AN AGILE
PRODUCT LINE
ENGINEERING PROCESS
ScrumPL process is intended to develop SPLs
combining activities from SPLE and Scrum. It has
activities from both methods.
Figure 3 presents an overview of ScrumPL
process. It is composed by the Scrum lifecycle’s
phases Planning, Staging, Development and Release
(represented by columns) and the software product
line engineering processes Domain Engineering and
Application Engineering (represented by rows).
Scrum lifecycle phases and the SPLE sub-processes
combination to form ScrumPL will be explained in
the following Subsections.
4.1 Pre-game Phase
The vision, anticipate ROI (Return on Investiment),
releases and milestones are given by the domain
engineering product management sub-process.
Those information are used by the domain
requirements engineering sub-process to provide
products features, added to the product backlog
during the Planning Phase.
Those features are inputs to application
requirements engineering sub-process to elicit
requirements for a particular application and reuse
those features as much as possible, during the
planning phase; and are also inputs to domain
design sub-process to create and maintain the
reference architecure.
The reference architecture contains variation
points, variants, and reusable components
descriptions and interfaces. The architect, which is
also the product owner, is responsible to create and
maintain the reference architecture, and add each of
its components to the product backlog as product
backlog items. This is done during the stage phase.
The reference architecture’s reusable componen-
ts, added to product backlog, are realized during the
development phase, and they are the inputs to the
application design sub-process, in the stage phase.
SCRUMPL - Software Product Line Engineering with Scrum
241

The application design sub-process produces the
applications architectures, deriving it from reference
architecture by selecting variants and adapting the
design according to application requirements. The
applications components of the architecture are
added to product backlog as product backlog items.
4.2 Development and Release Phases
The development phase starts when the product
backlog, containing a list of components from both
reference architecture and applications architectures,
is prioritized and ready for estimation. The pre-game
phase is finished and the Scrum team works
according to Scrum process described in Section 3,
starting with Sprint planning meeting and finishing
with Review meeting.
The results of the Scrum team activities are
potentially shippable components (realized and
tested), as well as unit and integration test cases
(from domain tests and application tests) used to
perform Scrum acceptance tests in this Sprint, and to
be reused in future regression tests.
During the sprint, the Scrum team can provide
the domain realization goals: the detailed design
and implementation of reusable software assets; or
provide the application realization goals:
applications that can be tested and brought to the
market after ensuring sufficient quality. Although
Scrum states that the product owner can’t change the
product backlog items being realized by Scrum
teams, the architect, as product owner, can make any
changes in other product backlog items.
Those changes are made due to, for instance,
problem reports, new requirements, changes in
interfaces, defects in interface descriptions, issues in
domain and application artefacts realization, and
other.
Scrum states that the team is self-managed and
determines which activities will be performed to
achieve Sprint goals. Due to this they don’t have the
obligation to follow the domain or application
realization activities.
Those changes, together with current product
backlog items, are reprioritized by the product
owner and are estimated and selected by Scrum
teams during Sprint Planning in future Sprints. In the
release phase, applications are deployed according
to planned releases. Before that, system integration
and tests are performed and eventual bugs are fixed.
4.3 Applying Part of the ScrumPL
The domain requirements engineering sub-process
was followed to define the product line
requirements, based on the state of the art on TV
navigation system requirements.
Through this process, the variation points and
variants where defined resulting on the variability
diagram in Figure 4, and also the TV navigation
goals and features (not described here due to space
restrictions). A prioritization was made and
documented in the product backlog (Figure 5).
The domain design sub-process was then
followed to create the reference architecture and
validate it, checking how requirements are reflected
in the architecture.
5 TV NAVIGATION SYSTEM
REFERENCE ARCHITECTURE
AND PRODUCT BACKLOG
A TV Navigation System combines program
recommendation, sorting and retrieval to make it
easier for the viewer to select programs based on
various individual viewing habits (Isobe et. al,
2003), and is viewer’s guide to select services and
applications, initiate interoperable applications, boot
loading, and store user profiles (Peng et. al, 2002).
5.1 Reference Architecture
The reference architecture is a core architecture that
captures the high level design for the applications of
the SPL. It includes the variation points and variants
documented in the variability model realized by
components (Pohl et. al, 2005). Figure 4 (next page)
presents the component diagram representing all
navigation system components and the variability
model, in which there are 3 variation points
(represented by triangles): language, market segment
and standard.
The language variation point has variants
representing languages for the TV navigation
system, depending on the countries which it will be
used. Although some languages were specified in
the variability model, other languages can be added.
At least one of those languages is required.
The market segment (MS) variation point has
variants representing low-end, mid-end and high-end
market segments. The arrows pointing to the
component diagram indicates the required
components that implements those variants.
The low-end variant implements the this channel
information component. The mid-end variant is
implemented by the this channel information,
ENASE 2010 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
242

Figure 4: Variability and Component Diagrams (reference architecture).
reminder, block programs and search programs
components. The high-end variant is implemented
by all components in TV navigation system
component diagram (Figure 4). Each application
product requires only one market segment.
The standard variation point has variants
representing the ISDB (ABNT, 2007), DVB (ETSI,
1997) and ATSC (ATSC, 1997) DTV standards,
which are implemented by the components with the
same name, described in Language and Standard
Component Diagram (Figure 4). Each product
requires only one standard. Three examples of
individual products based on this software product
line of TV navigation system reference architecture
are the products A, B and C, specified bellow:
Product A: this product designed for the
american high-end market segment. The language is
english, the standard is ATSC.
Product B: this product is designed for the
european mid-end market segment. The language is
english, the standard is DVB, the features are: this
channel information, reminder on products/events
(through manual reservation), electronic program
guide, block programs, search programs.
Product C: this product designed for the brazilian
low-end market segment. The language is
portuguese, the standard is ISDB, the features are
this channel information and block programs.
5.2 Product Backlog
The TV navigation system product backlog is in
Figure 5. The Product Backlog Item column
identifies the requirements name, and the
Prioritization column describes the high, low and
medium prioritized product backlog items.
Product Backlo
g
Item Prioritization
Estimate
(
size
)
Sprint
This channel info bar
High
This channel guide High
This channel Program guide
High
Implicit recomendation Low
Explicit recomendation
Low
Timezone rec omendation Low
Personal favorites reminder Low
Reserve program Medium
Electronic Program Guide Medium
Search programs Medium
Personal video recorder Low
Block programs High
Enhanced DB population Low
Mosaic EPG Low
English language High
Portuguese language High
Japanese language Low
French language Low
Spanish language Medium
Chinese language Low
ISDB standard High
ATSC standard Medium
DVB standard Low
Product Backlog
Figure 5: TV Navigation System Product Backlog.
The estimate is the number of sprints to realize the
product backlog item; Sprint refer to the sprint in
which it will be realized. Those colums will be
defined during the sprint planning meetings. All
components from reference architecture were added
to the product backlog as product backlog items.
SCRUMPL - Software Product Line Engineering with Scrum
243

6 RELATED WORK
ScrumPL is related to the Agile Product Line
Engineering, that investigates commonalities and
differences between agile and SPLE, and the
potential costs and benefits combining them (Cooper
and Franch, 2006). (Carbon et al., 2006) integrated
agile practices and principles, specially XP, with the
the reuse-centric application engineering process –
PuLSE-I. (Noor et al., 2007) presents practical
experiences of adopting agile principles with
collaboration engineering in product line planning.
(Hanssen and Faegri, 2007) combined the agile
method EVO with SPLE in a practical case.
(Ghanam and Maurer, 2008) combined Test Driven
Development and Scrum with a bottom-up approach
to extract reusable artefacts from existing products.
In ScrumPL process we use only Scrum with
SPLE, combining artefacts from both methods as
inputs and outputs of the ScrumPL process, using
the Scrum lifecycle as foundation for the
integration, providing the phases for requirements
identification and elicitation (pre-game), platform
and applications components development and
applications releases.
ScrumPL makes it easier for Scrum teams to
develop components and other artefacts for SPLs, as
only few changes were made to Scrum: architect as
“product owner”, components as “product backlog
items”, which, when developped as “shippable
increments”, will be reused and integrated into
applications as “releases”.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The ScrumPL process is mainly based on Scrum
lifecycle described by (Larman, 2004), which
describes its phases, purposes and activities. Based
on those purposes, the Domain Engineering and
Architecture Engineering sub-processes from SPLE
where applied and fit in each phase.
Main artefacts for each phase were also defined:
the pre-game phase creates the reference architecture
and product backlog; the development phase creates
the components; and the release phase integrate the
components into applications. The product backlog
and reference architecture of a TV navigation system
were defined following the domain requirements
engineering and domain design sub-processes.
For future work, the product backlog items will
be realized and tested in the development phase.
REFERENCES
ABNT NBR15603-2. 2007. Televisão digital terrestre –
Multiplexação e serviços de informação (SI). Parte 2:
Estrutura de dados e definições da informação básica
de SI – Brazilian Specification for System Information.
ATSC – Advanced Television Systems Committee A/65,
1997. Program and System Information Protocol for
Terrestrial Broadcast and Cable (PSIP).
ETSI – European Telecommunication Standard Institute
300 468. 1997. Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB);
Specification for Service Information (SI).
Beck, K. et al., 2001. Agile Manifesto. Available at
http://agilemanifesto.org/.
Cooper, K. and Franch, X., 2006. APLE – 1
st
International
Workshop on Agile Product Line Engineering. In 10
th
Intern. Software Product Line Conference (SPLC’06)
Ghanam, Y. and Maurer, F., 2008. An Iterative Model for
Agile Product Line Engineering. In 12th Int. Software
Product Line Conference – SPLC 2008. pp 377- 384.
Hanssen, G. and Faegri, T., 2008. Process fusion: An
industrial case study on agile software product line
engineering. In J. of Syst. and Softw. 81. pp 843-854.
Isobe, T., Fujiwara, M., Kaneta, H., Uratani, N., Morita,
T., 2003. Development and features of a TV
navigation system. In IEEE Transactions on Consumer
Electronics.Vol. 49, Issue 4, Nov, 2003. 1035–1042.
DOI = 10.1109/TCE.2003.1261192.
Larman C., 2004. Agile and Iterative Development – A
Manager’s Guide. Addison Wesley.
Noor, M. A., Rabiser, R., and Grünbacher, P., 2008. Agile
product line planning: A collaborative approach and a
case study. In J. Syst. Softw. 81, 6 (Jun. 2008), 868-
882. DOI= http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.10.028
Northrop, L., Clements, P., 2007. A Framework for
Software Product Line Practice, Version 5.0.
http://www.sei.cmu.edu/productlines/framework.html.
Peng, C., Lugmayr, A., Vuorimaa, P. 2002. A Digital
Television Navigator. In Multimedia Tools and
Applications. Volume 17, Number 1. May, 2002. 121-
141. DOI= 10.1023/A:1014687823960
Pohl, K., Böcke, G., Linder, F., 2005 Software Product
Line Engineering – Foundations, Principles and
Techniques. Springer-Verlag Berlin hedelberg.
Germany.
Schwaber, K., 2004. Agile Project Management with
Scrum. Microsoft Press. United States.
Schwaber, K., Beedle, M., 2002. Agile Software
Development with Scrum. Prentice Hall. United States.
Sutherland, J., 2009. Fully Distributed Scrum: Replicating
Local Productivity and Quality with Offshore Teams.
In Proc of 42nd Hawaii Int. Conf. on System Sciences.
ENASE 2010 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
244
