
CSMA Multi-stage Anti-collision Protocol for Active
RFID Systems
Alejandro Palomo-L´opez, M. Victoria Bueno-Delgado, Esteban Egea-L´opez
Juan J. Alcaraz-Esp´ın and Javier Vales-Alonso
Department of Information Technologies and Communications
Technical University of Cartagena
Plaza del Hospital 1, 30202, Cartagena, Spain
Abstract. Current anti-collision protocols for active RFID systems stem from
the ISO-18000-7 standard, which selects Frame Slotted Aloha as the underly-
ing Medium Access Control protocol. However, these approaches neglect the
possibility of using the Listen-Before-Talk mechanism already available in ac-
tive RFID tags. In this work, a Carrier Sense Multiple Access mechanism with
Multi-Stage, (CSMA/MS), derived from the quasi-optimal Sift distribution, is de-
veloped in order to substitute the anti-collision procedure in active tags. The key
of CSMA/MS is to concatenate various contention windows, where only win-
ners contend in the next contention windows. We demonstrate that this approach
nearly achieves a 100% of identification probability per slot, improving Sift re-
sults and outperforming standard procedure.
1 Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems are one of the enabling technologies for
the ubiquitous computing paradigm [1]. Its foreseen applications cover from replace-
ment of bar-code systems to location of containers in large cargo vehicles. All of them
share a common architecture: a basic RFID cell consists of a reader device and a (po-
tentially large) set of RFID tags, which reply to the queries or enforce the commands
from the interrogator. RFID devices are classified according to the source of energy
of the tags: passive ones do not have a power source and obtain the energy from the
reader signal (via induction), whereas active ones incorporate their own battery. On the
one hand, passive tags are targeted to be inexpensive and, thus, very simple, usually
read-only, devices. Their coverage typically ranges from centimeters to a couple of me-
ters. On the other hand, active tags are more complex devices, with more sophisticated
capabilities (usually integrating a microprocessor and memory) and they can be read
and written from distances in excess of 100 meters [1]. Whereas passive RFID sys-
tems are the most deployed and have been studied for years [2–4], active RFID systems
have recently been standardized [5] using Frame Slotted Aloha (FSA) as the underlying
medium access control mechanism.
Palomo-Løspez A., Bueno-Delgado M., Egea-Løspez E., Alcaraz-Espà n J. and Vales-Alonso J.
CSMA Multi-stage Anti-collision Protocol for Active RFID Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0003051900660078
In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on RFID Technology - Concepts, Applications, Challenges (ICEIS 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-8425-11-9
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In both cases, the tag collision problem arises: in a RFID cell, if multiple tags are
to be identified simultaneously, reply messages from tags can collide and cancel each
other. Thus, an anti-collision mechanism is needed. Since, in a typical application, items
(with attached tags) enter and leave the reader coveragearea, the goal of this mechanism
is to communicate with the tags as quickly and reliably as possible, ensuring that all
tags have been identified. An additional goal for active tags is to save energy in order
to maximize the battery lifetime. Therefore, the tag identification problem deals with
identifying multiple objects with minimal delay and power consumption, reliability,
line-of-sight independence and scalability. Unlike classical medium access protocols,
channel utilization and fairness are not usually issues in RFID systems.
DATA
DATA
DATA
1 2 k
...
Slot
Contention micro-slots
Fig.1. General identification procedure in CSMA.
In a previous paper [6], we proposed the use of non-persistent Carrier Sense Mul-
tiple Access (CSMA) as anti-collision mechanism for active RFID tags. This protocol
can be seamlessly integrated with current active tags, since they already include the
Listen-Before-Talk capability. In this case, time is divided in slots (see Figure 1) which
include contention periods. During the contention period tags select a contention micro-
slot, and transmit their identities only if medium is empty. Contention winners (note that
if there is more than one winner a collision takes place and that tags are not aware of si-
multaneous transmissions) continue transmitting their identifications in the data period.
Our performance evaluation shown that using a classical uniform distribution for
contention micro-slots do not necessarily improves the identification process. However,
performance is greatly improve if the micro-slot selection is based on the optimal dis-
tribution CSMA/p
∗
proposed by Tay et. al in [7]. In this work authors determines the
best probability distribution assignment if the number of contenders is known. Never-
theless, in a general situation, this parameter is unknown. Therefore, in [7] is already
proposed a distribution named Sift which nearly approximates the optimal one, and
which depend only on a maximum boundary for the number of competitors. Both dis-
tributions outperform the FSA mechanism used in active RFID systems in performance
and scalability.
The new proposal is called CSMA/Multi-Stage (henceforth, CSMA/MS) and it is
based on the concatenation of several micro-contention windows before data transmis-
sions, where only contention winners transmits in the successive windows. In this work
we show that, for an equal overall number of contention micro-slots, even though the
optimal distribution and its approximation are able to achieve almost 96% of trans-
24
mission success in each slot, CSMA/MS improves further the identification process,
achieving 99% of success and, more importantly, providing linear identification time
with the number of tags. That is, our proposal scales well to large sets of tags. Let us
remark that the optimal distribution itself cannot be improved obviously, but, combined
with the efficient splitting procedure proposed the overall identification process im-
proves. The key difference is the following: the goal of the optimal distribution p
∗
is to
minimize the latency of the first few successful transmissions in an event-based traffic
pattern, whereas in an RFID system the goal is to minimize the collision probability of
all the transmissions. The optimal distribution achieves 96% percent of success of any
transmission. This is an outstanding result but, as we say, it may be insufficient in some
scenarios: we consider a scenario where a very large number of tags must be identified
as fast as possible. The optimal result that can be achieved is to identify a tag every
identification cycle, which implies 100% of transmission success which would render a
linear identification time.
The rest of this work is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the ISO-18000-7
standard for active RFID solutions. Section 3 discusses related works, with an em-
phasis on solutions for active RFID anti-collision protocols. Section 4 introduces the
CSMA/Multi-Stage mechanism, and describes how it can be adapted with minor modi-
fications to the ISO 18000-7 standard. Section 5 shows the performance evaluations of
CSMA/MS in comparison with CSMA/p
∗
, Sift and conventional FSA. Finally, Section
6 concludes this work.
2 ISO 18000-7
ISO 18000-7 [5] is the de facto global standard for active UHF RFID solutions. It de-
fines the Physical and the MAC layer requirements and the communication protocol for
active RFID systems communicating at 433 MHz. ISO 18000-7 was ratified in 2004,
and has undergone modifications in 2008 and 2009.
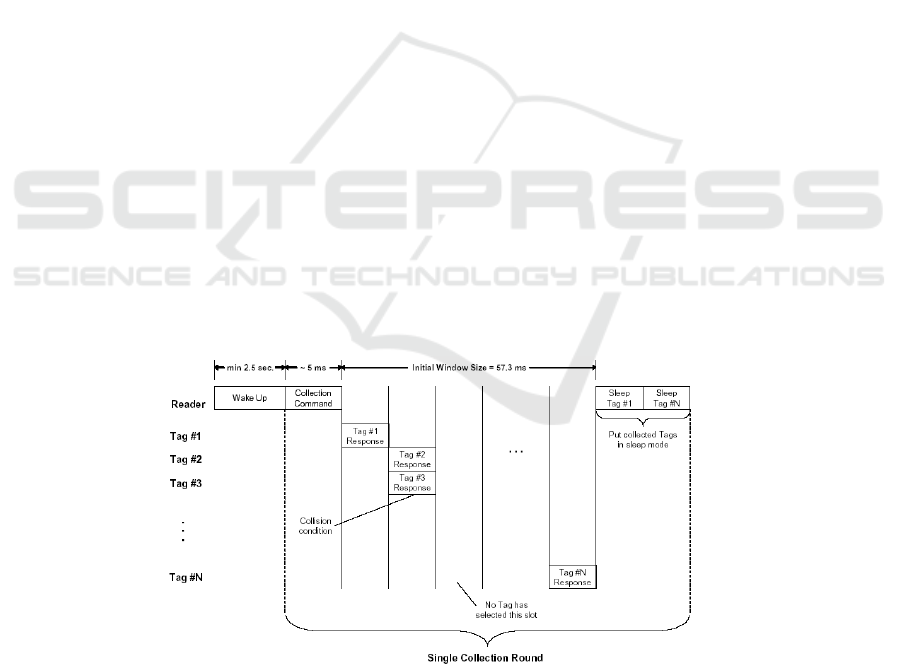
Fig.2. Anti-collision procedure of ISO/IEC 18000-7 (from [5].)
25

2.1 Anti-collision Procedure
The anti-collision algorithm defined in ISO 18000-7 is based on a FSA procedure. Fig-
ure 2 illustrates the identification sequence. The reader initiates the identification proce-
dure sending a Wake-Up signal, which wakes up the N tags within its coverage range.
Tags move to idle mode, listening to the channel. Then, the reader initiates a collection
round by sending a Collection command, with two parameters:
– The time the reader will be listening to the channel, waiting for tag responses. The
standard denotes this parameter as Window Size (W
S
).
– The length of the tag responses (T
tag
), determined by the field type in the Collection
command. Note that this parameter determines the type of tag response (e.g tag
identifier ID or specific data).
After transmitting the Collection command, the reader senses carrier signals during
Windows Size time, waiting for tag responses. Every time the reader detects a tag re-
sponse, it processes the corresponding tag identifier and inserted it into a buffer, called
sleep queue. After the collection round, the reader extracts the identifiers from the sleep
queue one by one and, for each identifier, the reader transmits an unicast Sleep com-
mand (see Figure 2). When tags receive the Sleep command, they change to sleep mode
(saving energy mode) and do not participate in the next collections rounds. Afterwards,
the reader starts a new collection round, resuming the identification process, which
eventually finishes after three consecutive collection rounds without reply.
In the identification procedure, tags operate as follows: When they receive a Collec-
tion command, extract the value of Windows Size parameter (in seconds) and calculate
the number of slots (K) and the slot size (T
slot
). The latter is calculated as follows:
T
slot
= T
tag
+ T
pr oc
(1)
being T
proc
the time the reader needs to process the data received from a tag and
the time to be ready to listening to the following tag response. By default, the standard
sets T
proc
=2 ms. Once T
slot
is calculated, the tag uses it to calculate K as follows,
K =
l
W
S
T
slot
k
(2)
K is rounded up to the nearest integer.
The process continues with tags selecting a random slot (with uniform distribution)
to send their Response packet. Each tag controls when the slot selected starts by means
of an internal clock. Let us remark that carrier sensing is not performed in this procedure
although active tags implement this capability. When a slot selected by a determined
tag starts, this tag changes to transmit mode and sends its identifier. After that, the tag
changes to receive mode and listens to the channel. If the tag is successfully identified,
it will receive a Sleep command to change to the sleep mode. Otherwise, tag will receive
a new Collection command, indicating a new slot starts.
The most extended operational mode in ISO-18000-7 is Fixed Windows Size pro-
cedure,where the reader uses the same W
S
in every collection round i. The general
formula to calculate W
S
is as follows:
26

W
S
i+1
= W
F
i
· 57.3 (3)
for i= 0,1,2,. . . , C. Note that C is the total number of collection rounds in a identi-
fication procedure. W
F
i
is defined by the standard as the Windows Factor to adjust W
S
i
in every cycle. In Fixed Windows Size procedure, W
F
i
takes the same value for every
collision round i. The standard recommends to set W
F
i∈C
=1.
Fig.3. Collection command format (from [5]).
3 Related Work
There is a lack of scientific literature that specifically addresses the collision prob-
lem for active tags. The ISO 18000-7 standard [5] deals with it and proposes FSA
as an anti-collision protocol, suggesting a frame length adaption mechanism but with-
out specifying a particular one and leaving it open to the vendors. Some works suggest
improvements of ISO 18000-7 identification procedure, such as in [10][11], where the
authors suggest new tags and readers designed to save energy, and compatible with the
standard. However, they do not propose any mechanism to improve the identification
performance. In [12] the authors focus their proposal on the sleep round (see Figure
2), suggesting a mechanism to reduce the number of Sleep commands to exchange
between reader and tags. However, this procedure does not reduce the collisions. In
[13] it is proposed to modify the content of the Collection commands to improve the
performance. The reader, instead of sending the windows size value in the collection
command, sends the values of T
slot
and K, previously calculated by it. Hence, tags
only have to calculate the guard time T
proc
. This solution has some drawbacks: the
maximum K value is limited to 256 slots. Therefore, if the number of tags in coverage
(N) is higher than the maximum K (a likely condition due to the large communication
range of active devices), collisions will raise up and the number of collection rounds
will increase. Besides, the proposal forces tags to calculate T
proc
, though they do not
suggest any procedure to do it. Finally, [13] also suggests to use the variable window
size mechanism proposed in [14]. However, as we demonstrate in [15], it is not efficient.
On the other hand, a typical active tag has the capabilities of an on-board micropro-
cessor and a sophisticated transceiver and may use Bluetooth or IEEE 802.11 protocols
or Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) MAC protocols [9]. It is clear that these proto-
cols are designed with different requirements in mind and, at the moment, the cost of
these devices is still possibly too high. Therefore, it seems that the possible choices are:
very simple approaches also suitable for passive tags or very sophisticated proposals
designed for different purposes.
In [6] we propose the use of CSMA with the optimal probability distribution (p
∗
)
for the selection of CSMA contention micro-slots derived in [7].This distribution max-
imizes the probability of success when N stations become simultaneously backlogged,
27

but depends on the number of slots in use (K) and the number of nodes (N ) contending.
Since the latter is usually unknown (also in RFID), an approximation is also provided,
the Sift distribution, which not only keeps close to the optimal for a wide range of its
configuration parameters but it is also scalable. The authors of reference [7] discuss
different applications in wireless sensor networks, but RFID is not mentioned. In this
paper we show that RFID is a major field of application of this optimized distribution.
CSMA/p* and Sift [7] are probability distributions that optimize the probability
of success in a CSMA contention compared with the uniform distribution. In this pa-
per we discuss the key aspects of these distributions and make a new proposal: the
CSMA/Multi-stage protocol.
The key idea of CSMA/p* and Sift distributions is to unbalance the probability of
selecting a contention micro-slot, increasing the probability of selecting one of the last
ones available. Thus, transmission is successful when the the first micro-slots are se-
lected by very few nodes with a higher probability. CSMA/p* is optimal, in the sense
that given K contention micro-slots, there is no other distribution that provides a higher
probability of success. However, it requires knowledge of the number of contenders.
Since usually this information is not available, it is not practical. Fortunately, the Sift
distribution approximates CSMA/p* without knowing number of contenders. It only
needs a parameter, M , that is the maximum number of contenders, and is the analog
of 802.11 maximum window size. Sift works very well, compared to the uniform dis-
tribution, and also has the desirable property it scales linearly as the maximum number
of contenders raises. That is, an exponential increase of the number of contenders only
need a linear increase of K, keeping the probability of success around 99%. In this pa-
per we propose the slotted multi-stage CSMA protocol, based on the Sift distribution,
but with an additional procedure that approximates the probability of success to 100%.
4 Slotted Multi-Stage Proposal
In this section we describe CSMA/MS algorithm. Before, the operation of CSMA-Sift
based is also introduced in depth since CSMA/MS uses also this distribution.
4.1 Sift Operation
The operation of the identification protocol when using CSMA would be as follows:
after receiving a collection command from the reader all N tags listen to the channel for
a number of micro-slots chosen randomly from a set of K. If the channel remains idle
after the number of selected micro-slots, a node sends its ID. Otherwise, it withdraws
until the next collection command. If there is no collision, the reader sends an ACK-
Collection command, which indicates the node already identified and asks for more
IDs. The remaining nodes start the process again.
The probability of success π
p
(N) when N nodes select a contention micro-slot us-
ing probability distribution p, where p
r
is the probability each contender independently
picks slot r, is [7]:
π
p
(N) = N
K−1
X
s=1
p
s
(1 −
s
X
r=1
p
r
) (4)
28

k + k
1
2
k +1
11
k
... ... ... ...
N tags
21 K
stage 1 stage 2
poles in 1st stage
(to 2nd stage)
poles in 2nd stage
(to 3rd stage)
p(success) =
transmits data
Slot selection probability
Tags
stage G
poles in (G−1)th stage
(to Gth stage)
p(1 pole in stage G)
Fig.4. Slotted Multi Stage procedure.
Let us assume first that the slots are chosen uniformly. In this case p
r
=
1
K
. Like
FSA, this procedure does not scale well either. In fact, its performance is worse and
together with the additional device complexity it may be one of the reasons why it has
never been proposed as an anti-collision procedure for RFID systems.
Besides, let us assume now the Sift distribution is used, which is an approximation
to the optimized distribution derived in reference [7]. In this case, p
r
=
α
−r
(1−α)α
K
1−α
K
for
r = 1 . . . K and α = M
−1
K−1
. M is a parameter of the Sift distribution, pre-configured
before deployment and representing the maximum number of contenders (as expected
by the designer). The results reveal [6] that the number of cycles increases almost lin-
early with the number of tags, unlike the exponential increment of FSA. Therefore, this
procedure scales well. In addition, by increasing the number of micro-slots the num-
ber of cycles tends to the minimum necessary (N cycles), but it implies increasing the
duration of a cycle and may be even counterproductive.
These results show that after choosing carefully the distribution for the contention
window CSMA becomes an scalable technique for the identification of RFID tags. In
Section 5, the different proposals for active tags are compared and discussed.
4.2 CSMA/MS
CSMA Multi-Stage proposal is based on the idea of splitting the original contention
micro-slots (K) into G stages of respective lengths k
1
, k
2
, . . ., where k
1
+ k
2
+ ... +
k
G
=K, where tags are dropping from the contention process from one stage to the
following. The operation is as follows (see Figure 4):
– In the first stage (of length k
1
), all tags select randomly (using an arbitrary distribu-
tion p) a micro-slot i, being i= 1,2,· · ·,k
1
. Note that one or more tags ‘win’ in this
stage selecting the same initial slot. Let us denote these tags as the poles of stage
#1. Remainder tags detects the medium busy and withdraw from contention. Note
that if the number of poles is greater than 1, a collision has taken place. Hopefully,
this collision is solved in next stage.
– In the second stage (of length k
2
) the poles of the first stage contends again. Each
one select again a random micro-slot i, being i= k
1
+ 1, k
1
+ 2, · · · , k
1
+ k
2
, and
the same procedure of the first stage takes place.
29

– This process continues until to stage G, where only the poles from stage M − 1
contend. In this case, if there is only one pole, or there is a single winner in this
stage, one tag can successfully transmits its identification. Otherwise, a collision
takes place.
Let us remark that more than one tag may compete in consecutive slots since several
tags may select the same lowest slot (a collision event). Moreover, the overall collision
probability depends on the number of stages and its relative length, henceforth let us
denote CSMA/MS(k
1
+ · · · + k
M
) to the specific configuration selected for the MS
protocol. Also note that at each stage, a micro-slot can be chosen with any arbitrary
distribution. We propose to use the Sift distribution since it is quasi-optimal for a single-
stage scenario. Therefore, in each stage, the Sift distribution is configured using two
parameters, the number of k
i
micro-slots in this stage, and the parameter M . In the first
stage, M is the maximum number of contenders, as shown in [7], but in the following
ones the number of contenders that reach a stage i is a random variable N
i−1
, which
depends on the number of contenders that have reached the previous stage, and the
number of micro-slots of that stage. Usually, as we will be discuss in section 5, the
highest probability corresponds to a single tag reaching to the next stage. So in stages
2, · · · the Sift parameter M is set at 2 (note that Sift does not allow M=1).
4.3 Modified Anti-collision Algorithm
The adaptation of the mechanism proposed in the previous section the ISO 18000-7
involves minor modifications in the anti-collision algorithm of the current standard,
without adding extra hardware in readers or tags. The operational mode is as follows:
The reader transmits the Collection command indicating, not only the Windows Size,
but also the number of stage (s ∈ 1, 2, . . . , S). The latter is sent to the tags in the
reserved byte field of Collection command (see Figure 3).
If s=1, tags in coverage which were not identified previously calculate the number
of contention micro-slots of that stage using the same procedure defined by the stan-
dard and select one of them randomly using the Sift distribution. Each tag listens to
the channel (Carrier Sense) until the number of micro-slot chosen starts. If the channel
remains idle after the number of selected micro-slot, the tag sends its ID. If there is no
collision, the reader sends an command, which confirms the tag has won the contention
and it can send its Data. After that, the reader asks for more IDs using a new Col-
lection command setting s=1 (see Figure 4). The tag identified changes to sleep mode
(saving energy mode) and the remaining tags start the process again. Otherwise, if two
or more tags select the same micro-slot, a collision occurs. Then, the procedure works
as follows:
– Colliding tags do not detect the collision because they were in transmitting mode.
Hence, they keep waiting for a reader response.
– Those tags listening the channel while the collision was happening, do not partici-
pate in the identification process until they receive a new Collection command with
s=1.
30
– Reader, that has also detected the collision, send a new Collection command, indi-
cating a new Windows size and a new stage, s=2. Colliding tags receive the com-
mand and compete again.
Fig.5. Collection command with Data format (from [5]).
The contention procedure continues until the maximum s value configured in the
reader. If, after S stages no new tags are identified, the reader starts a new Collection
command, setting s=1, and provoking all tags in coverage not identified previously
compete again.
Note that the duration of each micro-slot (denoted as T
m−slot
) depends on the dura-
tion and accuracy of carrier sensing Clear Channel Assessment (CCA), which depends
on the technology, device and implementation [18]. There are many possibilities, but
we assume that devices use coherent CCA, that is, the channel is busy when the packet
preamble is detected. Thus, we set the micro-slot time as follows:
T
m−slot
= T
tt
+ T
preamble
(5)
being (T
preamble
) the duration of the preamble and T
tt
the time a tag needs to start
transmitting its identifier. ISO 18000-7 fixes T
preamble
=1 ms and T
tt
=1 ms [5]. Hence,
T
m−slot
=2 ms can be considered a conservative value, since current devices can per-
form this task in less time [18].
Tags calculate the number of contention micro-slots K
m−slot
in every stage as fol-
lows,
K
m−slot
=
W
S
− T
tag
− T
proc
T
m−slot
(6)
As in the standard, W
S
and T
tag
values are extracted from Collection command. K
is rounded up to the nearest integer.
In summary, our proposal only involves the use of the reserved field of the typical
Collection command (see Figure 3) and a slight modification of the Collection with data
format command defined by the standard (see Figure 5) to be used as ACK-Collection
command. Figure 6 shows how the Start Address and Number of Data bytes fields of
Collection with data format command are replaced by Tag ID field.
Fig.6. ACK-Collection command.
31
5 Simulation Results
As stated in the previous section, CSMA/MS performance depends on the number of
stages and on their size. We evaluated the performance of different configurations by
means of Montecarlo methods using Matlab. For each point (configuration) evaluated
100000 samples has been averaged. In addition, CSMA/MS has been compared with
CSMA/p
∗
, Sift and a uniform selection of slots in a single stage CSMA protocol. Let
us remark that the total available micro-slots does not change among these options,
only its distribution in different stages (for CSMA/MS) or the probability function used
to select the micro-slot. Of the different configurations possibilities of CSMA/MS the
configuration (7+7+7+7) has been selected for these tests. Besides, for CSMA/MS the
parameter M is adjusted as explained in section 4. In this case, for the first stage M =
250, and the following ones sets M = 2.
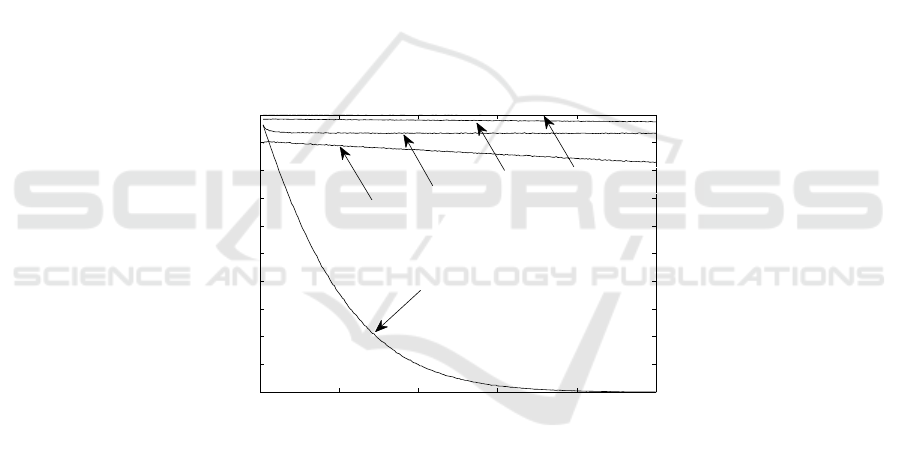
Figures 7 and 8 show the identification success probability for each one of these op-
tions (note that 8 providesa zoom viewof 7). Clearly, configuration CSMA/MS(7+7+7+7)
improves the success ratio, and sets it nearly optimal. Moreover, the uniform distribu-
tion is evidently disastrous.
0 50 100 150 200 250
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Number of tags
Probability of succes
CSMA/p*
Uniform distribution
SMS(14+14)
SMS(7+7+7+7)
Sift distribution
Fig.7. Identification success probability.
Besides, Figure 9 shows the overall identification delay (in time slots) as a function
of the number of initial contenders. CMSA/MS(7+7+7+7) improves Sift by a 15%,
and it is slightly better than CSMA/p
∗
(however let us remarks that CMSA/p
∗
can be
implemented in actual systems as discussed in the introduction).
Finally, Figure 10 shows the mass probability function of the random variable “num-
ber of contenders at stage i” for the different stages i = 1, · · · , 4. Note how the system
behaves as a filter, removing in each stage a significant ratio of the tags contending,
increasing the probability of having a winner at the end.
32

50 100 150 200 250
0.82
0.84
0.86
0.88
0.9
0.92
0.94
0.96
0.98
1
Number of tags
Probability of succes
SMS(14+14)
CSMA/p*
Uniform distribution
SMS(7+7+7+7)
Sift distribution
Fig.8. Identification success probability (zoom view).
50 100 150 200 250
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
Number of tags
Average time (timeslots)
CSMA/p*
SMS(14+14)
Uniform distribution
SMS(7+7+7+7)
Sift distribution
+15%
Fig.9. Identification time.
2 4 6 8
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tags
p
mpf poles in 1st stage
2 4 6 8
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tags
p
mpf poles in 2nd stage
2 4 6 8
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tags
p
mpf poles in 3rd stage
2 4 6 8
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Tags
p
4th stage: p(success) = p(1 tag)
Fig.10. Mass probability function for CSMA/MS(7+7+7+7).
33

6 Conclusions and Further Works
In this work we have demonstrated how a multi-stage strategy which uses CSMA-Sift
distribution at different contention windows improves the identification delay of a pop-
ulation of tags. By means of simulation an evaluation was carried out for a 4-stage
configuration with 7 micro-slots each, which outperforms FSA and uniformly selected
micro-slots CSMA. This distribution also improves a Sift distribution of 28 micro-slots,
yielding to a feasible MAC strategy. A discussion is also developed on how to seam-
lessly adapt our approach to ISO-18000-7 compliant systems.
Several question remain open: given a number of K micro-slots which are the op-
timal number of stages, and which slot distribution is optimal? which is the analytical
expression for the probability of success and for the identification delay of a population
of N tags?.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supportedby project DEP2006-56158-C03-03/EQUI,funded by the
Spanish Ministerio de Educacion y Ciencia, projects TEC2007-67966-01/TCM (CON-
PARTE-1), TSI-020301-2008-16(ELISA)and TSI-020301-2008-2(PIRAmIDE), funded
by the Spanish Ministerio de Industria, Turismo y Comercio and is also developed
within the framework of ”Programa de Ayudas a Grupos de Excelencia de la Region
de Murcia”, funded by Fundacion Seneca, Agencia de Ciencia y Tecnologia de la Re-
gion de Murcia (Plan Regional de Ciencia y Tecnologia 2007/2010).
References
1. Stanford, V., “Pervasive Computing Goes the Last Hundred Feet with RFID Systems”, IEEE
Pervasive Computing, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 9–14, April–June 2004.
2. Shih, D., Sun, P., Yen, D., Huang, S., “Taxonomy and survey of RFID anti-collision proto-
cols”, Elsevier Computer Communications, vol. 29, pp. 2150–2166, 2006.
3. Vogt, H., “Efficient Object Identification with Passive RFID Tags”, Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, vol. 2414, pp. 98–113, 2002.
4. Zhou, F., Chen, C., Jin, D., Huang, C., Min, H., “Evaluating and Optimizing Power Con-
sumption for Anti-Collision Protocols for Applications in RFID Systems”, in Proc. Int.
Symp. on Low Power Electronics and Design 2004, pp. 357–362, 2004.
5. ISO/IEC 18000-7:2004 Information technology–Radio frequency identification for item
management–Part 7: Parameters for active air interface at 433 MHz, 2004.
6. Egea-Lopez, E., Vales-Alonso, J., Martinez-Sala, A. S., Bueno-Delgado, M. V., Garcia-Haro,
J. “Performance Evaluation of non-persistent CSMA as anti-collision procedure for active
RFID tags”, Lecture Notes in Computer Sciences, vol. 4517, 2007.
7. Tay, Y., C., Jamieson, K., Balakrishnan, H., “Collision-Minimizing CSMA and its Applica-
tions to Wireless Sensor Networks”, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,
vol. 22(6), pp. 1048–1057, 2004.
8. Class 1 Generation 2 UHF Air Interface Protocol Standard Version 1.0.9: “Gen 2”. Available
online at: http://www.epcglobalinc.org/standards
9. Zhao, F. y Guibas, L., Wireless Sensor Networks. An information processing approach.
Morgan Kaufmann, 2004.
34

10. Jones, A.K., Hoare, R., Dontharaju, S., Tung, S., Sprang, R., Fazekas, J., Cain, J.T., Micke,
M.H., “An Automated, FPGA-based reconfigurable low-power RFID tag”, Journal of Mi-
croprocessors and Mircosystems, vol. 31 (2), 2007, pp. 116-134.
11. Cho, H., Choi, H., Lee, W., Jung, Y., Baek, Y., “LITeTag: design and implementation of an
RFID system for IT-based port logistics”, Journal of Communications, vol. 1 (4), 2006, pp.
48-57.
12. Jang, S.J., Chung, S.H., Yoon, W.J., Lee, S.J., “An effective design of an active RFID reader
using a cache of tag memory data”, in Proc. International Workshop on Service, Security
and its Data management for Ubiquitous Computing, vol. 4819, 2007, pp. 584-595.
13. Yoon, W.J., Chung, S.H., Lee, S.J., “Implementation and performance evaluation of an active
RFID system for fast tag collection”, Journal on Computer Communications, vol 31, 2008,
pp. 4107-4116.
14. Cha, J-R., Kim, J-H., “Novel Anti-collision Algorithms for Fast Object Identification RFID
System”, in Proc. 11th Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. 2, 2005, pp.
63-67.
15. Bueno Delgado, M.V., Vales Alonso, J., Gonz´alez Castao, F.J, “Analysis of DFSA Anti-
collision Protocols in Passive RFID Environments”, in Proc. 35tn International Conference
of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Porto (Portugal), 2009, pp. 2630-2637.
16. Kleinrock, L., Tobagi, F., “Packet Switching in Radio Channels: Part I-Carrier Sense Multi-
ple Access and their throughput-delay characteristics”, IEEE Transactions on Communica-
tions, vol. 23, pp. 1400–1416, 1975.
17. Wieselthier, J. E., Ephremides, A., Michaels, L. A., “An exact analysis and performance
evaluation of framed ALOHA with capture”, IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol.
37(2), pp. 125–137, 1988.
18. Ramachandran, I., Das, A., Roy, S., “Clear Channel Assessment in Energy-constrained
Wideband Wireless Networks”, IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, forthcoming.
35
