
RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK WITH SOFT 'WINNER
TAKES ALL' PRINCIPLE FOR THE TSP
Paulo Henrique Siqueira, Maria Teresinha Arns Steiner and Sérgio Scheer
Federal University of Paraná, PO BOX 19081, Curitiba, Brazil
Keywords: Recurrent neural network, Traveling salesman problem, Winner takes all.
Abstract: This paper shows the application of Wang’s Recurrent Neural Network with the 'Winner Takes All' (WTA)
principle in a soft version to solve the Traveling Salesman Problem. In soft WTA principle the winner
neuron is updated at each iteration with part of the value of each competing neuron and some comparisons
with the hard WTA are made in this work with instances of the TSPLIB (Traveling Salesman Problem
Library). The results show that the soft WTA guarantees equal or better results than the hard WTA in most
of the problems tested.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper shows the application of Wang’s
Recurrent Neural Network with the ‘Winner Takes
All’ (WTA) principle to solve the classical problem
of Operations Research called the Traveling
Salesman Problem. The upgrade version proposed in
this paper for the WTA is called soft, because the
winner neuron is updated with only part of the
activation values of the other competing neurons.
The problems of the TSPLIB (Reinelt, 1991)
were used to compare the soft with the hard WTA
version and they show improvement in the results
when using the soft WTA version.
The implementation of the technique proposed in
this paper uses the parameters of Wang’s Neural
Network for the Assignment problem (Wang, 1992;
Hung & Wang, 2003) using the WTA principle to
form Hamiltonian circuits (Siqueira et al. 2007) and
can be used both in symmetrical and asymmetrical
TSP problems.
Other heuristic techniques have been recently
developed to solve the TSP and the work of
Misevičius et al. (2005) shows the use of the ITS
(iterated tabu search) technique with a combination
of intensification and diversification of solutions for
the TSP. This technique is combined with the 5-opt
and errors are almost zero in almost all problems
tested from the TSPLIB. The work of Wang et al.
(2007) shows the use of Particle Swarm to solve the
TSP with the use of the quantum principle to better
guide the search for solutions.
In the area of Artificial Neural Networks an
interesting technique can be found in Massutti &
Castro (2009), where changes in the RABNET
(Real-Valued Antibody Network) are shown for the
TSP and comparisons made with the problems
presented in TSPLIB and solved with other
techniques show better results than the original
RABNET. Créput & Kouka (2007) show a hybrid
technique called Memetic Neural Network
(MSOM), with self-organizing maps (SOM) and
evolutionary algorithms to solve the TSP. The
results of this technique are compared with the CAN
(Co-Adaptive Network) technique developed by
Cochrane & Beasley (2003), where both have results
that are regarded as satisfactory. The efficient and
integrated Self-Organizing Map (eISOM) was
proposed by Jin et al. (2003), where a SOM network
is used to generate a solution where the winner
neuron is replaced by the position of the midpoint
between the two closest neighboring neurons. The
work of Yi et al. (2009) shows an elastic network
with the introduction of temporal parameters,
helping neurons in their motion towards the
positions of the cities. Comparisons with the
problems in the TSPLIB solved with the traditional
elastic network show that it is an efficient technique
to solve the TSP, with less error and less
computational time. In Li et al. (2009) a Lotka-
Volterra’s class of neural networks is used to solve
the TSP with the application of global inhibitions.
The equilibrium state of this network corresponds to
a solution for the TSP.
265
Siqueira P., Arns Steiner M. and Scheer S..
RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK WITH SOFT ’WINNER TAKES ALL’ PRINCIPLE FOR THE TSP.
DOI: 10.5220/0003059102650270
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Computation and 2nd International Conference on Neural Computation (ICNC-2010), pages
265-270
ISBN: 978-989-8425-32-4
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

This paper is divided into 4 sections, including
this introduction. In section 2 are shown Wang’s
Recurrent Neural Network and the soft 'Winner
Takes All' technique applied to the TSP. Section 3
shows the comparative results and in Section 4 the
conclusions are made.
2 WANG'S NEURAL NETWORK
WITH THE SOFT WTA
The mathematical formulation for the TSP is the
same of the problem of Assignment with the
additional constraint (5) that ensures that the route
starts and ends in the same city.
Minimize:
C =
n
i
n
j
ijij
xc
11
(1)
Subject to:
1
1
n
i
ij
x
, j = 1,..., n
(2)
1
1
n
j
ij
x
, i = 1,..., n
(3)
x
i
j
{0, 1}, i, j = 1,…, n
(4)
x
~
forms a Hamiltonian circuit
(5)
The objective function (1) minimizes costs. The
set of constraints (2) and (3) ensures that each city
will be visited only once. Constraints (4) guarantee
the condition of integrality of the
x
ij
binary variables.
Vector
x
~
represents the sequence of the TSP’s
route.
To obtain a first approximation for the TSP,
Wang’s Recurrent Neural Network is applied to the
problem of Assignment, this is, the solution satisfies
constraints (1)-(4), which can be written in matrix
form (Hung & Wang, 2003):
Minimize:
C = c
T
x
(6)
Subject to:
Ax = b
(7)
x
i
j
{0, 1}, i, j = 1,…, n
(8)
where c is the vector with dimension n
2
that contains
all rows of the cost matrix c in sequence, vector x
contains the n
2
decision variables x
ij
and vector b
contains the number 1 in all positions. The matrix A
has dimension 2n × n
2
and has the following format:
n
BBB
III
A
...
...
21
where I is the identity matrix of order n and each
matrix B
i
has zeroes in all of its positions with the
exception of the i
th
line, which has the number 1 in
all of its positions.
Wang’s Recurrent Neural Network is defined by
the following differential equation (Wang, 1992;
Hung & Wang, 2003):
n
k
n
l
t
ijijljik
ij
ectxtx
dt
tdu
11
)()(
)(
(9)
where x
ij
= g(u
ij
(t)), the equilibrium state of this
network is a solution for the problem of Assignment
(Wang, 1997) and g is the sigmoidal function with
parameter
:
g(u) =
u
e
1
1
.
(10)
The threshold is the vector
= A
T
b of order n
2
,
which has the number 2 in all of its positions.
Parameters
,
and
are constant and chosen
empirically (Hung & Wang, 2003), where
penalizes the violations to constraints (2) and (3) and
parameters
and
control the minimization of the
objective function (1). Considering W = A
T
A, the
matrix form of Wang’s Neural Network is the
following:
t
cetWx
d
t
tdu
))((
)(
,
(11)
The method proposed in this paper uses the
‘Winner Takes All’ principle, which accelerates the
convergence of Wang’s Recurrent Neural Network
and solves problems that appear in multiple
solutions or very close solutions (Siqueira et al.,
2008).
The adjustment of parameter
was made using
the standard deviation of the problem’s costs
matrix’s rows coefficients, determining the vector:
n
1
,...,
1
,
1
21
,
(12)
where
i
is the standard deviation of row i of matrix
c (Siqueira et al., 2007).
The adjustment of parameter
uses the third
term of Wang’s Neural Network definition (9), as
follows: when c
ij
= c
max
, the term
i
c
ij
exp(t/
i
) =
k
i
must satisfy g(k
i
) 0, this is, x
ij
will have minimal
value (Siqueira et al., 2007); considering c
ij
= c
max
and
i
= 1/
i
, where i = 1, ..., n,
is defined by:
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
266

max
ln
c
k
t
i
i
i
.
(13)
After a certain number of iterations, the term
Wx(t)
of equation (10) has no further substantial
alterations, thus assuring that
constraints (2) and (3)
are almost satisfied and the WTA method can be
applied to determine a solution for the TSP.
The soft WTA technique is described in the
pseudo-code below:
Choose the r
max
maximum number of routes.
{While r
r
max
{While Wx(t)
(where 0
2):
Find a solution x for the problem of
Assignment using Wang’s Neural Network.
}
Make
x = x and m = 1;
Choose a row k in decision matrix
x ;
Make p = k and
x
~
(m) = k;
{While m
n:
Find
kl
x
= argmax{
ki
x , i = 1, …, n};
Do the following updates:
2
11
n
i
n
j
kjilklkl
xxxx
(14)
kjkj
xx )1(
, j = 1,…, n, j l, 0
1
(15)
ilil
xx )1(
, i = 1,…, n, i k, 0
1
(16)
Make x
~
(m + 1) = l and m = m + 1;
To continue the route, make k = l.
}
Do
2
11
n
i
n
j
kjipkpkp
xxxx
and x
~
(n+1) = p;
Determine the cost of route C;
{If C
C
min
, then
Make C
min
= C and x = x .
}
r = r + 1.
}
In the soft WTA algorithm the following
situations occur: when
= 0 updating of the WTA is
nonexistent and Wang’s Neural Network updates the
solutions for the problem of Assigment without
interference, and when
= 1 the update is called
hard WTA, because the winner gets all the activation
of the other neurons, the losers become null and the
solution found is feasible for the TSP. In other cases,
the update is called soft WTA and the best results
are found empirically with 0.25
0.9. The
experiments for each problem were made 5 times
with each of the following values for the parameter
: 0.25, 0.5, 0.7 and 0.9. The best results were found
the value 0.7, as shown in Tables 2 and 4.
An improvement of the technique applied to
results of SWTA is the application of improving of
routes 2-opt after determining routes for SWTA. In
pseudo-code this improvement is made before
determining the cost of route made by SWTA.
3 RESULTS
The results of the technique proposed in this paper to
solve the symmetric TSP were compared with the
results obtained using Self-Organizing Maps for
TSPLIB problems. These comparisons are shown in
Table 1, where 8 of the 12 problems tested showed
better results with the technique proposed in this
paper, with improving of routes 2-opt technique.
Table 1: Comparisons between the results of symmetric
instances of the TSPLIB, the techniques Soft WTA
(SWTA), Soft WTA with 2-opt (SWTA2), EiSOM
(Efficient Integrated SOM), RABNET (Real-Valued
Antibody Network), CAN (Co-Adaptive Network) and
MSOM (Memetic SOM).
TSP
name
Average error (%)
EiSOM RABNET CAN MSOM SWTA SWTA2
eil51 2.56 0.56 0.94 1.64 0.47 0.00
eil101 3.59 1.43 1.11 2.07 3.02 0.16
lin105 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 3.70 0.00
bier127 - 0.58 0.69 1.25 3.11 0.25
ch130 - 0.57 1.13 0.80 4.52 0.80
rat195 - - 4.69 4.69 5.42 2.71
kroA200 1.64 0.79 0.92 0.70 8.03 0.75
lin318 2.05 1.92 2.65 3.48 8.97 1.89
pcb442 6.11 - 5.88 3.57 8.76 2.79
att532 3.35 - 4.24 3.29 9.10 1.48
rat575 2.18 4.05 4.89 4.31 9.86 4.50
pr1002 4.82 - 4.18 4.75 14.39 4.39
The computational complexity of the proposed
technique is O(n
2
+ n) (Wang, 1997), considered
competitive when compared to the complexity of
Self-Organizing Maps, which have complexity O(n
2
)
(Leung et al., 2004).
Table 2 shows the comparison between the Soft
WTA and Hard WTA techniques, with the
respective values of parameter
that represent the
best result for each problem. Results of applying
Wang’s Neural Network with Soft WTA with the
routes 2-opt improving technique (SWTA2) have
RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK WITH SOFT 'WINNER TAKES ALL' PRINCIPLE FOR THE TSP
267

average error ranging between 0 and 4.50%. The
results without the application of the 2-opt technique
vary between 0.47 and 14.39%, and are better in
almost all problems tested when compared to the
results obtained with the Hard WTA technique.
Figure 1 shows a comparison between the Soft WTA
and Hard WTA techniques applied to 12 problems
from the TSPLIB, showing the best and worst results
found for each technique. The worst results found by
Soft WTA are worse than those found by Hard WTA
on 5 symmetrical problems tested, as shown in
Figure 1:
fl417, lin318, ch130, bier127 and eil51.
Table 2: Comparisons between the results for symmetrical
instances of the TSPLIB with the Hard WTA (HWTA)
and the Soft WTA (SWTA) techniques.
TSP
name
Optimal
solution
Average error (%)
HWTA SWTA HWTA2 SWTA2
eil51 430 0.7 1.16 0.47 0.00 0.00
eil101 629 0.9 3.02 3.02 0.48 0.16
lin105 14383 0.9 4.33 3.70 0.20 0.00
bier127 118282 0.7 4.22 3.11 0.37 0.25
ch130 6110 0.25 5.06 4.52 1.39 0.80
gr137 69853 0.7 9.09 6.65 2.07 0.21
rat195 2323 0.5 5.55 5.42 3.32 2.71
kroA200 29368 0.5 8.95 8.03 0.62 0.75
lin318 42029 0.25 8.35 8.97 1.90 1.89
fl417 11861 0.25 10.11 9.05 1.58 1.43
pcb442 50783 0.5 9.16 8.76 2.87 2.79
att532 87550 0.25 14.58 9.10 1.28 1.48
rat575 6773 0.25 10.03 9.86 4.98 4.50
u724 41910 0.5 16.85 10.18 6.28 4.06
pr1002 259045 0.7 15.66 14.39 4.68 4.39
Figure 2 shows the best result found with the soft
WTA technique for the pr1002 problem of the
TSPLIB and Figure 3 shows the best result found
with the same technique with the routes 2-opt
improvement. In Figures 4 and 5 are the best results
for the fl417 problem.
The techniques compared with the TSP’s
asymmetric problems are described in the work of
Glover et al. (2001). The Karp-Steele’s arcs method
(KPS) and Karp-Steele’s general method (GKS)
start from a cycle, removing arcs and placing new
arcs until a Hamiltonian cycle is found. The path
recursive contraction method (PRC) forms an initial
cycle, removing sub-cycles to find a Hamiltonian
cycle. The heuristic contraction of paths (COP) is a
combination of the GKS and PRC techniques. The
heuristic random insertion (RI) starts with 2 vertices,
inserting a vertex not yet chosen, creating a cycle.
This procedure is repeated until a route that contains
all vertices has been created.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
12%
14%
16%
pr1002
u724
rat575
att532
fl417
lin318
pcb442
kroA200
gr137
rat195
ch130
lin105
bier127
eil101
eil51
HWTA:worst HWTA:best HWTA2
SWTA:worst SWTA:best SWTA2
Figure 1: Comparison between the results of the Hard
WTA (HWTA) and the Soft WTA (SWTA) techniques for
the symmetrical problems of the TSPLIB.
Figure 2: Example of the pr1002 problem with the
application of Wang’s Neural Network with the soft WTA
principle and average error of 14.39%.
Table 3 shows that the technique proposed in this
paper have equal or better results than the techniques
mentioned in 11 of the 20 tested asymmetric
problems in the TSPLIB.
Table 4 compares the Hard and Soft WTA
techniques applied to asymmetric problems in the
TSPLIB, with the respective values of parameter
that represent the best result for each problem.
Results demonstrate that the Soft WTA technique
exceeds or equals the Hard WTA technique in all
problems, except for ft70. The average error of the
Soft WTA technique varies between 0 and 10.56%
and with the Hard WTA technique this error varies
between 0 and 16.14%.
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
268
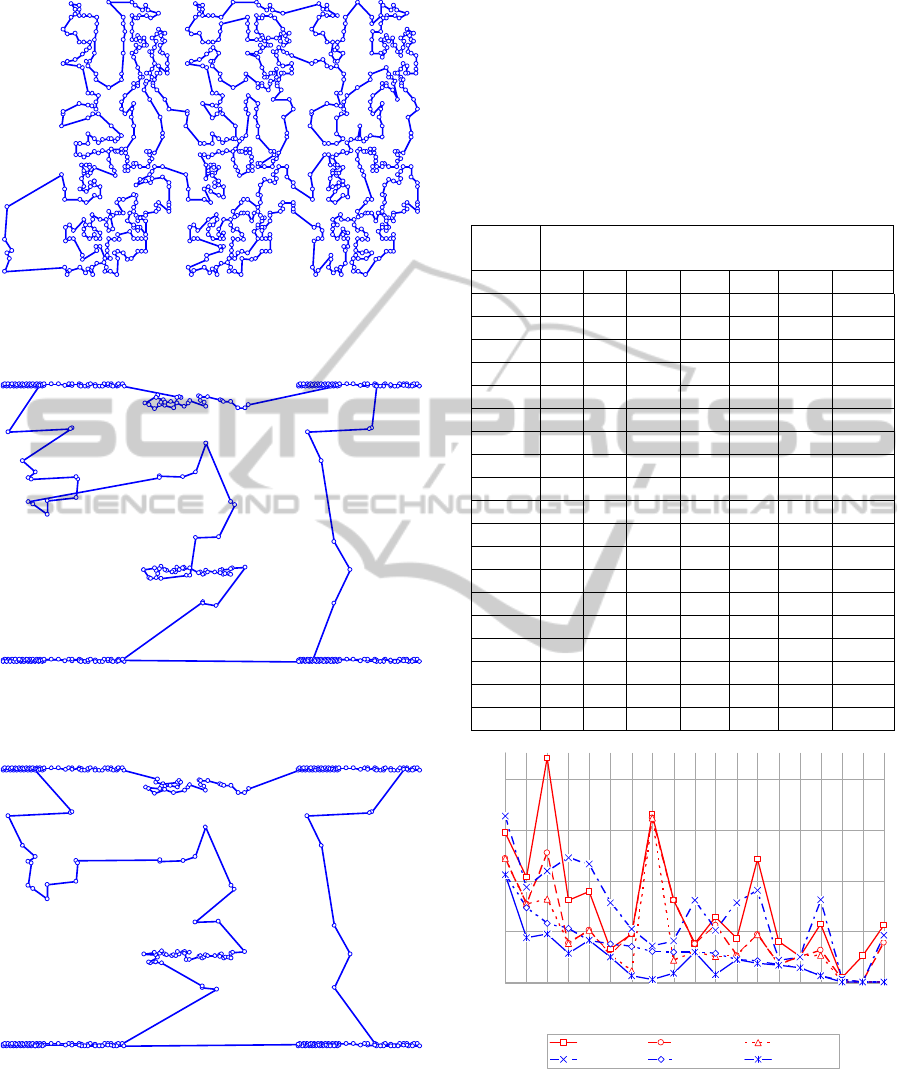
Figure 3: Example of the pr1002 problem with the
application of Wang’s Neural Network with the soft WTA
principle and 2-opt, with an average error of 4.39%.
Figure 4: Example of the fl417 problem with the
application of Wang’s Neural Network with the soft WTA
principle and average error of 9.05%.
Figure 5: Example of the fl417 problem with the
application of Wang’s Neural Network with the soft WTA
principle and 2-opt, with an average error of 1.43%.
Figure 6 shows the comparison between the Hard
and Soft WTA techniques showing the best and
worst results found for each asymmetrical problem
in the TSPLIB. The worst results found by Soft
WTA are worse than those found by Hard WTA on
7 asymmetrical problems tested, as shown in Figure
6: ftv35, ftv44, ftv38, ft53, ftv70, ftv47 and ftv170.
Table 3: Comparisons between the results of asymmetric
instances in the TSPLIB of the techniques Soft WTA
(SWTA), Soft WTA with 2-opt (SWTA 2opt), RI (random
insertion), KSP (Karp-Steele path), GKS (general-Karp
Steele path), PRC (path recursive contraction) and COP
(contraction or path).
TSP
name
Average error (%)
RI
KSP GKS PRC COP
SWTA SWTA2
br17 0 0 0 0 0
0 0
ftv33 11.82 13.14 8.09 21.62 9.49
0 0
ftv35 9.37 1.56 1.09 21.18 1.56
0.61 0.61
ftv38 10.20 1.50 1.05 25.69 3.59
2.94 2.94
pr43 0.30 0.11 0.32 0.66 0.68
0.20
0
ftv44 14.07 7.69 5.33 22.26 10.66
2.23 2.23
ftv47 12.16 3.04 1.69 28.72 8.73
5.29 2.82
ry48p 11.66 7.23 4.52 29.50 7.97
2.85
0.76
ft53 24.82 12.99 12.31 18.64 15.68
3.72
2.49
ftv55 15.30 3.05 3.05 33.27 4.79
2.11
1.87
ftv64 18.49 3.81 2.61 29.09 1.96
1.41 1.41
ft70 9.32 1.88 2.84 5.89 1.90
4.10 4.10
ftv70 16.15 3.33 2.87 22.77 1.85
1.70 1.70
kro124p 12.17 16.95 8.69 23.06 8.79
7.27
4.36
ftv170 28.97 2.40 1.38 25.66 3.59
10.56 10.56
rbg323 29.34 0 0 0.53 0
3.02 0.23
rbg358 42.48 0 0 2.32 0.26
5.76 4.73
rbg403 9.17 0 0 0.69 0.20
3.53 0.65
rbg443 10.48 0 0 0 0
2.98 0.85
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
ftv170
kro124p
rgb358
ftv47
ftv70
ft53
rgb403
rgb323
rgb443
ftv38
ry48p
ftv44
ftv55
ft70
ftv64
ftv35
pr43
br17
ftv33
HWTA:worst HWTA:best HWTA2
SWTA:worst SWTA:best SWTA2
Figure 6: Comparison between the results of the Hard
WTA (HWTA) and Soft WTA (SWTA) techniques for the
asymmetrical problems of the TSPLIB.
RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK WITH SOFT 'WINNER TAKES ALL' PRINCIPLE FOR THE TSP
269

Table 4: Comparisons between the results for asymmetric
instances in the TSPLIB of the techniques Hard WTA
(HWTA) and Soft WTA (SWTA).
TSP
name
Optimal
solution
Average error (%)
HWTA SWTA HWTA2 SWTA2
br17 39 0.7 0
0
0
0
ftv33 1286 0.7 0
0
0
0
ftv35 1473 0.5 3.12
0.61
3.12
0.61
ftv38 1530 0.9 3.73
2.94
3.01
2.94
pr43 5620 0.7 0.29
0.20
0.05
0
ftv44 1613 0.25 2.60
2.23
2.60
2.23
ftv47 1776 0.9 3.83
5.29
3.83
2.82
ry48p 14422 0.5 5.59
2.85
1.24
0.76
ft53 6905 0.5 2.65
3.72
2.65
2.49
ftv55 1608 0.7 11.19
2.11
6.03
1.87
ftv64 1839 0.9 2.50
1.41
2.50
1.41
ft70 38673 0.7 1.74
4.10
1.74
4.10
ftv70 1950 0.5 8.77
1.70
8.56
1.70
kro124p 36230 0.7 7.66
7.27
7.66
4.36
ftv170 2755 0.25 12.16
10.56
12.16
10.56
rbg323 1326 0.7 16.14
3.02
16.14
0.23
rbg358 1163 0.7 12.73
5.76
8.17
4.73
rbg403 2465 0.9 4.71
3.53
4.71
0.65
rbg443 2720 0.9 8.05
2.98
2.17
0.85
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents a modification to the application
of the 'Winner Takes All' technique in Wang’s
Recurrent Neural Network to solve the Traveling
Salesman Problem. This technique is called Soft
'Winner Takes All', because the winner neuron
receives only part of the activation of the other
competing neurons.
The results were compared with the Hard
'Winner Takes All' variation, Self-Organizing Maps
and insertion heuristics and removal of arcs,
showing improvement in most of the tested
symmetric and asymmetric problems from the
TSPLIB.
REFERENCES
Cochrane, E. M., Beasley, J. E. (2003). The Co-Adaptive
Neural Network Approach to the Euclidean Travelling
Salesman Problem. Neural Networks, 16 (10), 1499-
1525.
Créput, J. C., Koukam, A., (2009). A memetic neural
network for the Euclidean travelling salesman
problem. Neurocomputing, 72 (4-6), 1250-1264.
Glover, F., Gutin, G., Yeo, A., Zverovich, A., (2001).
Construction heuristics for the asymmetric TSP.
European Journal of Operational Research, 129 (3),
555-568.
Hung, D. L., Wang, J. (2003). Digital Hardware
realization of a Recurrent Neural Network for solving
the Assignment Problem. Neurocomputing, 51, 447-
461.
Jin, H. D., Leung, K. S., Wong, M. L., Xu, Z. B., (2003).
An Efficient Self-Organizing Map Designed by
Genetic Algorithms for the Traveling Salesman
Problem. IEEE Transactions On Systems, Man, And
Cybernetics - Part B: Cybernetics, 33 (6), 877-887.
Leung, K. S., Jin, H. D., Xu, Z. B., (2004). An expanding
self-organizing neural network for the traveling
salesman problem. Neurocomputing, 62, 267-292.
Li, M., Yi, Z., Zhu, M., (2009). Solving TSP by using
Lotka-Volterra neural networks, Neurocomputing, 72
(16-18), 3873-3880.
Masutti, T. A. S., Castro, L. N., (2009). A self-organizing
neural network using ideas from the immune system to
solve the traveling salesman problem. Information
Sciences, 179 (10), 1454-1468.
Misevičius, A., Smolinskas, J., Tomkevičius A., (2005).
Iterated Tabu Search for the Traveling Salesman
Problem: new results. Information Technology And
Control, 34 (4), 327-337.
Reinelt, G. (1991). TSPLIB – A traveling salesman
problem library. ORSA Journal on Computing, 3 (4),
376-384.
Siqueira, P. H., Steiner, M. T. A., Scheer, S., (2007). A
new approach to solve the Traveling Salesman
Problem. Neurocomputing, 70 (4-6), 1013-1021.
Siqueira, P. H., Scheer, S., Steiner, M. T. A., (2008). A
Recurrent Neural Network to Traveling Salesman
Problem. In Greco, F. (Ed.), Travelling Salesman
Problem (pp. 135-156). In-teh: Croatia.
Wang, J. (1992). Analog Neural Network for Solving the
Assignment Problem. Electronic Letters, 28 (11),
1047-1050.
Wang, J. (1997). Primal and Dual Assignment Networks.
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 8 (3), 784-
790.
Wang, Y., Feng, X. Y., Huang, Y. X., Pu, D. B., Liang,
C.Y., Zhou, W.G., (2007). A novel quantum swarm
evolutionary algorithm and its applications,
Neurocomputing, 70 (4-6), 633-640.
Yi, J., Yang, G., Zhang, Z., Tang, Z., (2009). An
improved elastic net method for travelling salesman
problem, Neurocomputing, 72 (4-6), 1329-1335.
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
270
