
A HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS
AND FUZZY LOGIC FOR FAULT IDENTIFICATION IN
ELECTRIC POWER SUBSTATIONS
Daniel da Silva Gazzana, Mario Orlando Oliveira, Arturo Suman Bretas
Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Andre Lerm
Southern Federal Institute of Education and Technology, IFSUL, Pelotas, Brazil
Arlan Bettiol
A Vero Domino Consultoria e Pesquisa, Florianópolis, Brazil
Marcio A. Da S. Gonçalves
AES Uruguaiana, Uruguaiana, Brazil
Keywords: Artificial Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic, Expert Systems, Electric Power Substations, Fault Detection.
Abstract: This paper presents a novel approach for on-line fault identification in an Electric Power Substation (EPS).
The proposed methodology is based on signal processing techniques allied with a Fuzzy Logic and Artificial
Neural Network. The test electric system was rigorously built in an electromagnetic transient numerical
simulator, named Alternative Transient Program (ATP), conformably to the needs presented by a
Thermoelectric Generation Plant of 711 MW - 230 kV, located in southern Brazil. Simulated test cases
demonstrate the generalization capability of the developed hybrid Expert System based on Neural Networks
and Fuzzy Logic, now utilized in a Southern Brazilian Utility.
1 INTRODUCTION
The use of a rapid and efficient method for on-line
fault detection in Electric Power Substations (EPS)
helps both in maintenance tasks and in the prompt
restoration of electrical system. The protection and
substation control have undergone dramatic changes
since the advent of powerful micro-processing and
digital communication equipment.
In the Electric Power System the monitoring and
control of substations are based generally on the
computerized Energy Management System (EMS),
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
and Oscillography Digital Register (ODR). When
faults occur in an automated substation, the faulted
devices are isolated by the operation of
corresponding protection relays and circuit breakers;
meanwhile, the SCADA system will issue alarm
messages in a short time sending them into the
operator’s consoles. In this case, the operators in the
control center are responsible for restoring the
system and must use their judgment and experiences
to determine the possible faulted elements and/or
switches as the first step in the restoration
procedures of the electric system (Chen et al., 2000).
In many cases, the fault location in EPS is
performed only with base on data assessment from
the monitoring system, as for example, the state of
switches and circuit breakers. However, this
procedure can lead to misidentification of the fault
component, especially when the substation is large.
Accordingly, it should be taken into account other
variables such as the magnitude and phase of
voltages and currents, obtained from system data
435
da Silva Gazzana D., Orlando Oliveira M., Suman Bretas A., Lerm A., Bettiol A. and A. Da S. Gonçalves M..
A HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND FUZZY LOGIC FOR FAULT IDENTIFICATION IN ELECTRIC POWER
SUBSTATIONS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003085504350441
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Computation and 2nd International Conference on Neural Computation (ICNC-2010), pages
435-441
ISBN: 978-989-8425-32-4
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
oscillography. Moreover, the evaluation of a greater
number of variables leads to the necessity of using
an Expert System (ES) to support decision making
and fault diagnostic (Fukui and J. Kawakami, 1986;
Tomsovic et al., 1987; Kezunovic et al., 1994;
Protopapas et al., 1991).
In this paper, it is presented a Fault Diagnosis
Integrated System (FDIS) used in a substation of a
Thermoelectric Generation Plant (TGP) located in
the southern Brazil. The proposed approach was
developed based on several simulations performed
under Bonneville Power Administration Alternative
Transients Program (BPA/ATP), Electromagnetic
Transients Program (EMTP) and using a hybrid
system based on Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic.
The results obtained show that the developed
method is able to identify and locate the fault
occurrence, even when subject to operational
failures of circuit breakers.
2 FUZZY SETS AND NEURAL
NETWORK IN FAULT
DETECTION
Fuzzy Logic can systematically translate linguistic
concepts to numbers and associate elements from a
number set to concepts (Zadeh, 1965). This
capability provides a simple method that can be used
to detect and to qualify faults in Electric Power
Substations. Fuzzy based algorithms and Fuzzy
Logic are well adapted to situations where there is
no clear distinction between the concept of true and
false. Fuzzy Logic can handle situations where the
answer lies somewhere in-between. This is the
typical case of substation fault location. In general it
is difficult to estimate the fault location between the
several devices present in the electric power
substation. However, it is more adequate to classify
a fault in terms of the occurrence probability. Fuzzy
Logic permits to infer about the fault location and to
establish its certainty degree level of trust. An
important feature of Fuzzy based systems is that the
human knowledge and experience can be integrated
into the systems in a systematic way, when the
Fuzzy sets and Fuzzy rules have been defined.
In recent years, the use of Artificial Neural
Networks (ANNs) presented it self as a potential
solution to the on-line fault diagnosis in power
substations (Ebron et al., 1990; Yang et al., 1994;
Ranaweera, 1994). ANNs are computational
techniques that try to obtain a performance similar to
a human’s performance when solving problems. An
ANN can be seen as a union of simple processing
units, based on neurons that are linked to each other
through connections similar to synapses. These
connections contain the “knowledge” of the network
and the patterns of connectivity express the objects
represented in the network. The knowledge of the
network is acquired through a learning process
where the connections between processing units are
varied through weight changes. ANN is an efficient
alternative for problem solutions where it is possible
to obtain data describing the problem behavior but a
mathematical description of the process is
impossible.
The basic idea of uniting these two techniques is
to use the qualitative analysis supplied by Fuzzy
Logic, allied to the learning ability of Neural
Networks. Hybrid systems Neuro-Fuzzy can be used
to resolve this kind of problems with good accuracy
and robustness, joining the advantages of these
methodologies (Kezunovic, 2004).
3 FAULT DETECTION
METHODOLOGY
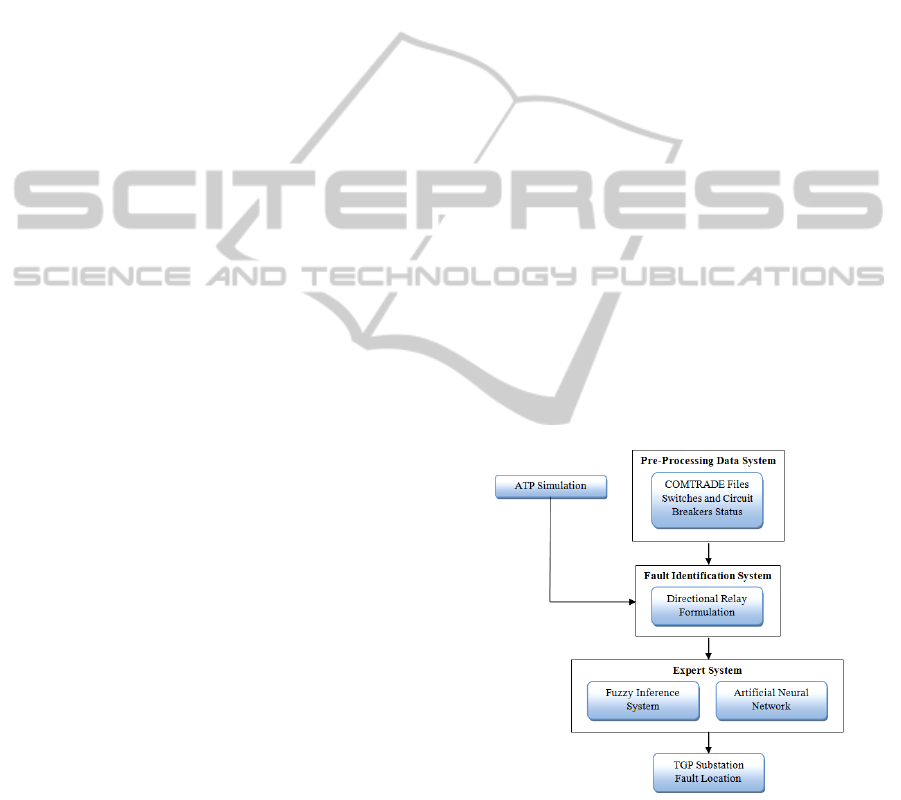
The proposed methodology is based on the three
integrated subsystems: Pre-Processing Data System,
Fault Identification System and Expert System. The
main structure of the proposed automated
disturbance analysis system can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1: General structure of the proposed scheme.
3.1 Pre-Processing Data System
The first procedure of the Pre-Processing Data
System is related to phasors extraction from
COMTRADE files (IEEE Standard C37.11.1.1999,
1999) and the evaluation of the state of switches and
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
436

circuit breakers from SCADA system. This study
used the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and
signal processing techniques to process and
evaluates the signals (Phadke and Thorp, 1999).
Figure 2 presents a basic flow chart for the signal
processing.
Figure 2: Pre-Processing Data System.
The development of fault identification algorithm is
based on the module (amplitude) and the angular
difference between voltage and current phasors
measured at the site of installation of the protective
relay.
3.2 Fault Identification System
Aiming to detect faults in respect to the TGP, it was
developed a directional relay whose main
characteristic is to determine the direction of a
failure from its installation location. Thus, when a
pre-determined threshold value is exceeded by the
current fault, a fault condition is detected and the
direction of failure is indicated by the relay (Suonan
et al., 2004). Figure 3 shows the basic installing
scheme of a directional relay.
Figure 3: Fault Identification System.
Here, the voltage at the relay location is given by:
commmm
ZIUU ⋅
−
=
′
111
(1)
where U
m1
is the voltage phasor positive sequence in
the protection point; I
m1
is the current phasor
positive sequence from the protection point to the
line; Z
com
is the impedance compensating of the
circuit.
The direction of a backward or forward fault is
determined by comparing the angle between of the
voltage and current phasors positive sequence. Thus,
the criterion for detecting a backward fault of the
directional relay is given by:
°≤
′′
≤
−
270)/(º90
11
1
mm
IUtg
&&
(2)
When the above condition is satisfied, a backward
fault is detected. During normal operation or
forward faults, the power flow is always toward the
load (Infinite Power System), in other words, the
source (TGP) provides power. However, when a
fault happens backward of directional relay, the
current I
m1
changes of direction changing the value
of the angle between the voltage and current
phasors.
4 EXPERT SYSTEM (ES)
The developed ES is composed by a hybrid system
based on Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic. In a
first stage, decision rules based on Fuzzy Logic
indicate the local in the substation where a possible
fault occurred (bus, lines, generators, transformers),
supplying a probability index associated with the
disturbance. In a second stage, an ANN classifies the
fault on a more specific manner, estimating the site
of the fault and the associated circuit breaker. The
Fuzzy Logic system runs independently of the ANN.
4.1 Fuzzy Inference System
The developed Fuzzy Inference System is composed
by six input variables (apparent power and angle of
each directional relay output) and for seven output
variables that estimate the fault location. The related
variables can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Fuzzy inference system variables.
Fuzzy Input Variables Fuzzy Output Variables
Angle directional relay 1 Fault on line L1
AP directional relay 1 Fault on Bus A or TR SAT-2
Angle directional relay 2 Fault on Bus B or TR SAT-1
AP directional relay 2 Fault on the CT1 generator
Angle directional relay 3 Fault on the CT2 generator
AP directional relay 3 Fault on the ST generator
Fault on line L2
In the input variables, the angle is composed for two
triangular-shaped membership functions. The first
one is related to negative angles, -360
º ≤ input ≤ 0º
and the second one related to the positive angle, 0º <
input ≤ 360º. The Apparent Power (AP) variables
were composed for one triangular-shaped
membership function corresponding to the positive
values of power, 0 ≤ input ≤ 40 MVA. The range of
the input membership functions was obtained with
base on angle and power data groups that represent
each kind of fault.
A HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND FUZZY LOGIC FOR FAULT
IDENTIFICATION IN ELECTRIC POWER SUBSTATIONS
437

The output variables also are composed by one
triangular membership function for each fault, as
presented in Table 1. The range of output
membership function is in the interval 0 ≤ output ≤
2, so: output values in the mid of interval, output =
1, correspond 100% of probability of the related
fault to have occurred; values in the threshold of the
range, output = 0 or output = 2, correspond 0% of
probability of the related fault to have occurred and
output values inside of the range, 0 < output < 2
represent intermediary values of fault probability.
The base rule is composed for 37 rules that
represent faults proceedings from simulations. In the
inference process the Method of Mamdani was used
and the smallest (absolute) value of maximum was
applied in defuzzification process. In such a way,
some rules can be activated for a same group of
input data. In this case, each fault has its probability
value of occurrence. In the second step, the ANN
can classify more exactly which fault occurred.
Figure 4 illustrates the Fuzzy inference process.
Additionally, others types of membership
functions as gaussian and trapezoidal shapes were
tested presenting acceptable results, but the best
ones were obtained with triangular shape.
Figure 4: Fuzzy Inference Process.
4.2 Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
The second stage in the Expert System is composed
by a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) Feedforward
Artificial Neural Network (Haykin, 1998). This
ANN maps input angle and power data in an
appropriate output fault location estimate. As well as
the Fuzzy System, the input variables of ANN are
the angle and apparent power of each directional
relay output. On the other hand, the ANN fault
identification is more specific than Fuzzy inference.
Beyond the fault location, the MLP structure can
identify the involved circuit breaker. So, six input
variables are mapped in 17 kinds of faults. In the
Table 2 can be seen the ANN performance, in
training stage, to classify substation faults
considering different number of neurons in hidden
layer. Table 3 shows the same faults in test stage.
Figure 5 presents the MLP Feedforward used in the
developed Expert System.
Table 2: ANN error in training process.
Type of fault
ANN Classification
Error (%)
Neurons in hidden
layer
20 50 80
Outage of line L1 for temporary
defect
8.83 0 0
Defect on bus A or transformer
SAT-2
25 0 0
Defect on bus B or transformer
SAT-1
50 0 0
Defect on CT1 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-1
0 0 0
Defect on CT1 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-2
25 0 0
Defect on CT2 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-4
0 0 0
Defect on CT2 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-5
0 0 0
Defect on ST generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-7
0 0 0
Defect on ST generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-8
0 0 0
Defect on line L1 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-2
0 0 0
Defect on line L1 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-3
25 0 0
Fault on CT1 generator with
circ. breaker 52-1 in
maintenance
0 16.7 0
Fault on line L1 with circuit
breaker 52-2 in maintenance
0 0 0
Fault on bus A or tr. SAT-2 with
circ. bre. 52-1 in maintenance
0 0 0
Defect on line L2 with open. of
the circ. break. 52-5 and 52-6
33.3 0 0
Defect on line L2 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-5
16.7 0 0
Defect on line L2 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-6
0 0 0
Global error (%) 10.8 0.98 0
The Feedforward Backpropagation Network is
composed by 6 and 17 perceptrons in the input, and
output layer respectively. For the hidden layers,
different number of neurons was tested and the
convergence results were presented in the following.
To calculate a layer's output from its net input
the hyperbolic tangent sigmoid transfer function
(hidden layer) and linear transfer function (output
layer) were used. The Levenberg-Marquardt
optimization was adopted as training function,
because it is a fast backpropagation algorithm. The
mean squared normalized error (MSE) was used as
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
438

performance function.
Figure 5: MLP structure used in the Expert System.
Table 3: ANN error in test process.
Type of fault
ANN Classification
Error (%)
Neurons in hidden
layer
20 50 80
Outage of line L1 for temporary
defect
16.7 0 0
Defect on bus A or transformer
SAT-2
50 16.7 33.3
Defect on bus B or transformer
SAT-1
33.3 50 50
Defect on CT1 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-1
16.7 0 16.7
Defect on CT1 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-2
16.7 0 33.3
Defect on CT2 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-4
16.7 16.7 50
Defect on CT2 generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-5
0 0 16.7
Defect on ST generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-7
0 0 0
Defect on ST generator with
fault on the circuit breaker 52-8
0 0 0
Defect on line L1 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-2
16.7 0 16.7
Defect on line L1 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-3
16.7 33.3 33.3
Fault on CT1 generator with
circ. breaker 52-1 in
maintenance
33.3 16.7 16.7
Fault on line L1 with circuit
breaker 52-2 in maintenance
16.7 0 0
Fault on bus A or tr. SAT-2 with
circ. bre. 52-1 in maintenance0
33.3 33.3 50
Defect on line L2 with open. of
the circ. break. 52-5 and 52-6
33.3 33.3 16.7
Defect on line L2 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-5
0 0 0
Defect on line L2 with fault on
the circuit breaker 52-6
0 0 0
Global error (%)
17.6 11.8 19.6
The input data was divided in two groups, the first
one corresponding a 2/3 of total data was used in the
ANN training process and remaining data was used
in ANN tests.
Analysing Table 2 and Table 3 it can be seen that the
best ANN response is obtained with a MLP structure
composed by 50 perceptrons in hidden layer. A
major number of neurons in hidden layer not
represent significant improvements in ANN
classification process.
The Table 4 presents the number of epochs and
MSE obtained for the previously MLP structures.
The MLP structure with 6, 50 and 17 perceptrons in
the input, hidden and output layer respectively was
implemented in the developed system.
Table 4: ANN performance.
Neurons in
hidden layer
Epochs MSE
20 200 0.0195
50 150 0.0057
80 300 0.0003
5 SIMULATION AND RESULTS
To illustrate de results obtained with the Fault
Diagnosis Integrated System two cases of
disturbances in the Thermoelectric Generation Plant
substation are presented below. The simulated
system was built, rigorously, conformably to the
needs presented by a TGP of 711 MW, 230 kV,
located in southern of Brazil. Figure 6 illustrates the
electric circuit used in the simulations of the faults in
the EPS.
Figure 6: Substation model used in the simulation faults.
5.1 Defect on Line L1 with Fault on the
Circuit Breaker 52-2
The Figure 7 shows the behaviour of three-phase
voltages and currents in the occurrence of a defect in
line L1 with fault on the circuit breaker 52-2. In the
A HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND FUZZY LOGIC FOR FAULT
IDENTIFICATION IN ELECTRIC POWER SUBSTATIONS
439
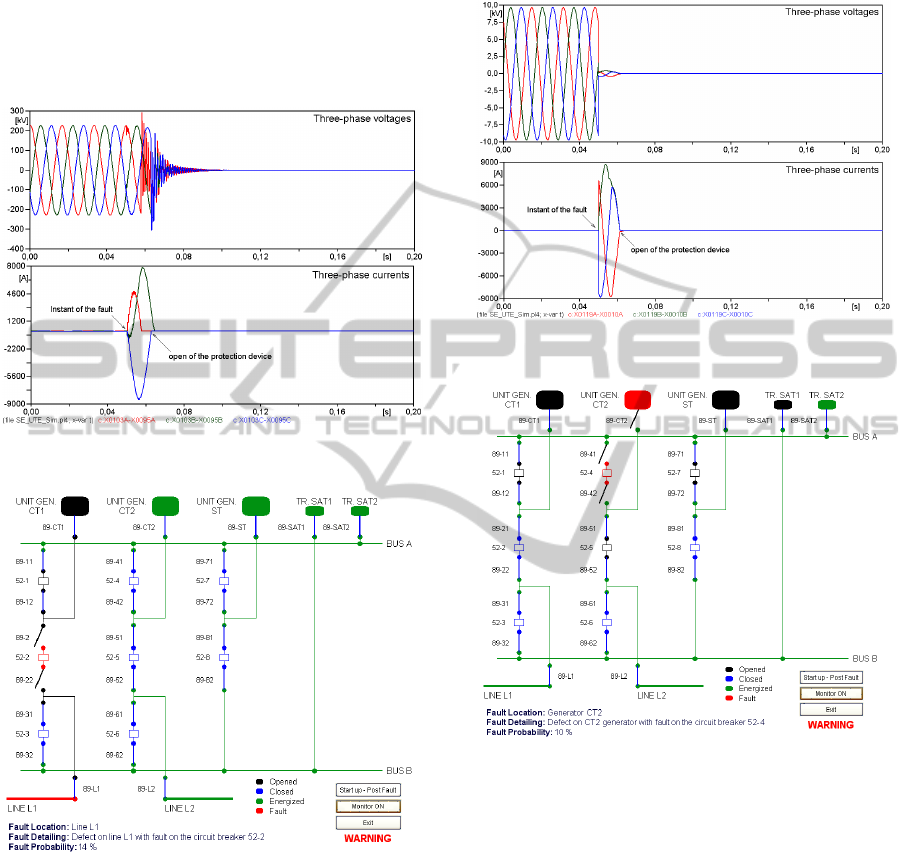
presented case, the defect is a three-phase short-
circuit with fault resistance (R
f
) of 50Ω. In this case
the angle and power used as input variable for the
Expert System are: angle 1 = 73.4º; power 1 = 10.1
MVA; angle 2 = 70.4º; power 2 = 30.7 MVA; angle
3 = 71.7º; power 3 = 33.2 MVA. The Figure 8
illustrates the software interface with the
information of the fault identification.
Figure 7: Voltage and currents on Line L1 due three-phase
short-circuit with fault resistence R
f
= 50Ω.
Figure 8: Software interface shows fault at Line L1.
5.2 Defect on CT2 Generator with fault
on the Circuit Breaker 52-4
In Figure 9 it can be seen the behaviour of three-
phase voltages and currents in the occurrence of a
defect in generator CT2 with fault on the circuit
breaker 52-4. In this case, the defect is a three-phase
short-circuit with low fault resistance of 0.5Ω. The
calculated angle and power used as input variable
for the Expert System are: angle 1 = -273.3º; power
1 = 30.2 MVA; angle 2 = -204.7º; power 2 = 19.3
MVA; angle 3 =-273.4 º; power 3 = 32.6 MVA. The
developed software interface with the fault location
can be seen in Figure 10.
Figure 9: Voltage and currents on out CT2 generator with
fault of the circuit breaker 52-4.
Figure 10: Software interface shows defect in generator
CT2.
6 CONCLUSIONS / DISCUSSION
This paper presented a methodology for fault
location in power electric substation with base on
Fuzzy Sets and Artificial Neural Networks. The
proposal study combine signal processing techniques
with intelligent systems to detect the local and the
related device in a fault occurrence.
This methodology starts with the extraction data
from oscillography files and with base on the state of
circuit breakers in the substation. In the development
stage, this task is replaced by simulation of the
substation operational conditions using the
Alternative Transients Program (ATP). After, the
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
440

signal processing techniques are implemented
supplying input data to the Fuzzy-Neuro Expert
System that classify a possible fault.
The directional relay shows to be a robust
method to provide an indication of the fault
direction, beyond supplying angle information that is
used as input to the ES with satisfactory results.
The developed ATP/EMTP model allows the
simulation of diverse disturbances inside the
substation, which was used for compose Fuzzy Sets,
training the ANN and test the hybrid Fuzzy-Neuro
Expert System.
The Fuzzy-Neuro Expert System classifies the
fault in two levels of details. The Fuzzy System is
more generalist and identifies only the local of fault,
whereas, the ANN is qualified to indicate the related
circuit breaker. For this reason, the fact that the net
is very specialist, a level of classification error can
occur. In some ANN tests, the error is allied with the
wrong of circuit breaker and not with the local of
fault as bus, transformer, line or generators. It is
important to highlight that the ES input data are very
close and the classification process is not a trivial
task.
Several simulations of different values of epochs
was performed in network training process and the
best results were attainment with 150 epochs
converging to a MSE = 0.0057, ANN global test
error = 11.8% considering 6, 50 and 17 perceptrons
in the input, hidden and output layer respectively.
With this configuration the best results was obtained
and this structure was implemented in the fault
detection expert system.
The developed integrated system can become the
management maintenance activities more efficient.
Moreover, such system contributes for the increase
of the reliability, having as one of its benefits, the
reduction of involved time to detect and localize a
possible fault, optimizing the maintenance practices.
Currently, the system is being tested in the TGP
in the Southern Brazilian, but this methodology can
be used to detect and localize faults in similar energy
electric substations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the American Energy
System (AES Uruguaiana) for the financial support
and Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul for the
facilities offered.
REFERENCES
Bonneville Power Administration - BPA “Alternative
Transients Program: ATP/EMTP”. Avalilable in:
http://www.emtp.org/.
Chen, W. H., Liu, C. W., Tsai M.S., 2000. “On-Line Fault
Diagnosis of Distribution Substation Using Hybrid
Cause-Effect Network and Fuzzy Rule-Based
Method,” IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery, vol.
15, no. 2.
Ebron, S., Lubkeman, D. L., White, M., 1990. “A neural
network approach to the detection of incipient faults
on power distribution feeders,” IEEE Trans. On
PWRD, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 905–913.
Fukui, C., Kawakami, J., 1986. “An expert system for
fault section estimation using information from
protective relays and circuit breakers,” IEEE Trans.
On PWRD, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 83–90.
Haykin, S., 1998. “Neural Networks: A Comprehensive
Foundation,” New York: Prentice Hall, 2nd ed.
IEEE Standart Common Format for Transient Data
Exchange (COMTRADE) for Power Systems, IEEE
Standard C37.11.1.1999, 1999.
Kezunovic, M., Rikalo; I., Fromen, C. W., Sevcik, D. R.,
1994. “Expert System Reasoning Streamlines
Disturbance Analysis,” IEEE Computer Application in
Power, vol. 7, pp. 15-19.
Kezunovic, M., 2004. “Intelligent applications in
substations: Disturbance analysis,” In IEEE PES
General Meeting, vol. 1, pp. 719-723, Denver, USA.
Phadke, A. G., Thorp, J.S., 1999. “Computer Relaying for
Power Systems,” England: Research Studies Press
Ltd.
Protopapas, C. A., Psaltiras, K. P., Machias, A. V., 1991.
“An expert system for substation fault diagnosis and
alarm processing,” IEEE Trans. On PWRD, vol. 6, no.
2, pp. 648–655.
Ranaweera, D.K., 1994. “Comparison of neural network
models for fault diagnosis of power systems,” Electric
Power Systems Research, pp. 99–104.
Suonan J. L., Xu Q. Q., Song G. B., Wu Y., 2004. “A
reliable directional relay based on positive sequence
compensated voltage and current components,” The
Institute of Electrical Engineers, Six Hills Way, pp.
104-107.
The Mathworks Inc. “Mathworks MatLab”. Available in:
http://www.mathworks.com/.
Tomsovic, K., Liu, C. C., Ackerman, P., Pope, S., 1987.
“An expert system as a dispatchers’ aid for the
isolation of line section faults,” IEEE Trans. On
PWRD, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 736–742.
Yang, H. T., Chang, W. Y., Huang, C. L., 1994. “A new
neural networks approach to on-line fault section
estimation using information of protective relays and
circuit breakers,” IEEE Trans. On PWRD, vol. 9, no.
1, pp. 220–230.
Zadeh, L. A., 1965. "Fuzzy sets," Information and Control,
vol. 8, pp. 338-353.
A HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM BASED ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND FUZZY LOGIC FOR FAULT
IDENTIFICATION IN ELECTRIC POWER SUBSTATIONS
441
