
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT
A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis
Uffe Kock Wiil, Jolanata Gniadek and Nasrullah Memon
Counterterrorism Research Lab, The Maersk Mc-Kinney Moller Institute, University of Southern Denmark
Campusvej 55, 5230 Odense M, Denmark
Keywords: Social network analysis, Terrorist network analysis, CrimeFighter assistant.
Abstract: A terrorist network is a special kind of social network with emphasis on both secrecy and efficiency. Such
networks (consisting of nodes and links) need to be analyzed and visualized in order to gain a deeper
knowledge and understanding that enables network destabilization. Previous research on terrorist network
analysis has to a large degree focused on analysis of nodes. This paper presents the CrimeFighter Assistant,
a novel knowledge management tool for terrorist network analysis. CrimeFighter Assistant treats links as
first class objects and provides a better balance between network, node, and link analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
A terrorist network is a special kind of social
network with emphasis on both secrecy and
efficiency. Such networks are intentionally
structured to ensure efficient communication
between members without being detected (Baccara
and Bar-Isaac 2009; Lindelauf, Borm, and Hamers
2009; Enders and Su 2007; Baker and Faulkner
1993; Latora and Marchiori 2004).
Knowledge about the structure and organization
of terrorist networks is important for both terrorism
investigation and the development of effective
strategies to prevent terrorist attacks. Theory from
the knowledge management field plays an important
role in dealing with terrorist information.
Knowledge management processes, tools, and
techniques can help intelligence analysts in various
ways when trying to make sense of the vast amount
of data being collected in relation to terrorism (Wiil,
Memon, and Gniadek 2009). The collected data
needs to be analyzed and visualized in order to gain
a deeper knowledge and understanding of the
terrorist network.
A terrorist network can be modeled as a
generalized network (graph) consisting of nodes and
links. Nodes are entities (people, places, events, etc.)
and links are relationships between the entities.
Techniques from social network analysis (SNA) and
graph theory (Wassermann and Faust 1994) can be
used to identify key nodes in the network, which is
helpful for network destabilization purposes. Taking
out key nodes will decrease the ability of the
terrorist network to function normally (Carley, Lee,
and Krackhardt 2001).
Previous research on terrorist network analysis
(TNA) has to a large degree focused on analysis of
nodes. Links are seldom first class objects in the
terrorism domain models with the same properties as
nodes. This is in contrast to the fact that the links
between the nodes provide at least as much relevant
information about the network as the nodes
themselves (Gloor and Zhao 2006).
A terrorism domain model with both nodes and
links as first class objects will allow for a better
balance between analysis of nodes and analysis of
links, which will result in more precise knowledge
about the terrorist network. This paper presents the
CrimeFighter Assistant, a novel knowledge
management tool for TNA that supports a balanced
analysis of network, node, and link measures to
address the above issue.
Section 2 briefly describes our overall
knowledge management approach to
counterterrorism called CrimeFighter. In Section 3,
we present the CrimeFighter Assistant tool for TNA.
In Section 4, we demonstrate the use and evaluate
our tool through a case study of the 2002 Bali
bombing. Section 5 compares our approach with
related work. Section 6 concludes the paper and
discusses future work.
15
Kock Wiil U., Gniadek J. and Memon N..
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT - A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0003091500150024
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2010), pages 15-24
ISBN: 978-989-8425-30-0
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
FOR COUNTERTERRORISM
The CrimeFighter toolbox for counterterrorism is a
novel approach to TNA. The goal is to provide a
number of desktop tools that are grouped into three
overall software packages each containing
knowledge management tools and services relevant
to counterterrorism (Wiil, Memon, and Gniadek
2009). These tools and services are designed and
implemented to enable them to interoperate and
exchange information. The CrimeFighter toolbox is
depicted in Figure 1.
CrimeFighter
Knowledge Base
CrimeFighter
Explorer
package
CrimeFighter
Assistant
package
CrimeFighter
Investigator
package
Figure 1: The CrimeFighter toolbox for counterterrorism.
The Explorer and Investigator packages each
support different knowledge management processes
that result in generation of terrorist networks
consisting of nodes and links. These terrorist
networks are stored in the knowledge base. The
Assistant package provides various features to
analyze and visualize networks – as generated by the
Explorer and Investigator packages.
The research on CrimeFighter can be divided
into four overall areas:
1. CrimeFighter Explorer is a software
package with various services aimed at
acquiring data from open sources and
extracting valuable information from the
data by processing it in various ways
(filtering, mining, etc.).
2. CrimeFighter Investigator is a software
package that provides various services that
enables an intelligence analyst to work with
emergent and evolving structure of terrorist
networks to uncover new relationships
between people, places, events, etc.
3. CrimeFighter Assistant is a software
package with various services that supports
analysis and visualization of terrorist
networks. TNA is aimed at finding new
patterns and gaining a deeper knowledge and
understanding about terrorist networks.
Terrorist network visualization deals with
the complex task of visualizing the structure
of terrorist networks.
4. CrimeFighter toolbox architecture. In
order for the developed tools and services to
be able to interoperate and exchange
information, the overall software
architecture of the toolbox must enable a
service in one package to use a service in
another package. For instance, the structure
generated by the services of the Investigator
package must be able to use the analysis and
visualization services available in the
Assistant package.
The remainder of this paper focuses on
describing the various TNA and visualization
techniques available in the CrimeFighter Assistant.
As mentioned, the starting point for TNA is the
existence of a network structure. Hence, much
knowledge management work needs to take place
prior to network analysis. These prerequisite
knowledge management processes (see Wiil,
Memon, and Gniadek 2009 for details) are not the
focus of this paper.
3 CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT
The goal from an intelligence analysis perspective is
to support the analysts in making informed decisions
regarding possible actions to destabilize the network
by determining the most important nodes and links
in the network.
Looking at the diversity of terrorist groups (e.g.,
al-Qaeda, ETA, or Liberation Tigers of Tamil
Eelam), the way they work, their goals, and their
means are different. Therefore, using just one
strategy to counter them is impossible.
To gain the best possible knowledge and
understanding about a terrorist network, one should
analyze the network as a whole together with the
properties of its nodes and the properties of its links.
Various questions might be asked in this process,
such as:
Network Measures:
• How covert is the network?
• How efficient is the network?
• What is the density of the network?
KMIS 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
16

• What is the trade-off between secrecy and
efficiency in the network?
Node Measures:
• Who are the central (important) persons in
the network?
• What makes the person important?
• What role does a particular person have?
• How is the network affected after removal of
a particular node?
Link Measures:
• What links are important for communication
in the network?
• How important is a particular link in relation
to network efficiency and secrecy?
• What is the information backbone of the
network?
Answering the above questions without any tools
to support the task would be very time consuming.
CrimeFighter Assistant provides various TNA
features that can support intelligence analysts in
answering the above questions.
In the following sections, the system architecture
and analysis and visualization features are presented.
3.1 System Architecture
The overall system architecture of CrimeFighter
Assistant is shown in Figure 2.
CrimeFighter
Knowledge Base
GraphML
file
JPG
file
CSV
file
GraphML
parser
ODBC
driver
Network
visualization
Network, node, and link
analysis
import
export
export
load
save
Figure 2: CrimeFighter Assistant system architecture.
CrimeFighter Assistant provides two primary
features: network, node, and link analysis and
network visualization. Networks can be loaded from
the knowledge base or from GraphML files.
GraphML is extensively used in SNA applications.
Therefore, CrimeFighter Assistant supports this file
format as an interchange format to provide
interoperability with other SNA and TNA tools.
Network data stored in GraphML files can be loaded
into the workspace and the same analysis and
visualizations can be performed as for network data
stored in the CrimeFighter knowledge base.
Analysis results can be exported to CSV
(comma-separated values) format to be used in other
applications such as Microsoft Excel. Visualized
networks can be exported to a printable format
(JPEG format). Visualization is based on the JUNG
(Java Universal Network/Graph) library
(O'Madadhain et. al 2005). The entire package is
coded in Java.
3.2 Analysis and Visualization
A screenshot of CrimeFighter Assistant is shown in
Figure 3. The panel to the left is used for visualizing
the network, while the panel to the right is used for
displaying network, node, and link analysis results.
If the user clicks on a node or a link in the analysis
results part, the corresponding node or link in the
network visualization part will be highlighted in red.
A number of analysis measures are supported.
Some standard domain independent SNA measures
are relevant also for analysis of terrorist networks.
However, there is also a need for specialized TNA
measures that take into account the specifics of
terrorist networks. The measures listed below in
black font color are standard SNA measures
(Wassermann and Faust 1994), while the measures
listed in red font color are specific TNA measures
(secrecy, efficiency, performance, position role
index, and link importance).
A few definitions are needed regarding graphs to
explain the analysis measures.
A graph G consists of two sets of information: a
set of nodes, N = {n
1
, n
2
, …, n
n
}, and a set of links L
= {l
1
, l
2
, …, l
l
} between pairs of nodes. There are n
nodes and l links. In a graph, each link is an
unordered pair of distinct nodes, l
k
= {n
i
, n
j
}.
Additional relevant definitions are:
• Size is defined as the number of nodes (n) in
the network.
• Nodal degree is defined as the number of
links that are incident with the node.
• A cluster is a part of the graph with high
density of nodes and links between them.
• The average shortest path is the average
length of the geodesic between two nodes.
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT - A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis
17

Figure 3: A screenshot of CrimeFighter Assistant.
3.2.1 Network Analysis
The following network measures are supported:
• Density is the number of links (l) in
proportion to the number of links that are
possible in G (if all nodes where connected
to each other).
• Diameter is the maximum distance between
any pair of nodes in the network (calculated
using the shortest path).
• According to Lindelauf, Borm, and Hamers
(2009), secrecy is a measure which is
defined by two parameters: the exposure
probability and the link detection
probability. The exposure probability applies
to individual nodes and depends on the
location in the structure. It is defined as the
probability of a member of the network to be
detected as a terrorist. Link detection
probability represents the chance of
exposure of a part of the network if a
member is detected. The secrecy depends on
the number of links, the number of nodes,
and their degree. The higher the degree of
nodes, the lower the secrecy is in the
network.
• According to Latora and Marchiori (2004),
efficiency is a measure to quantify how
efficiently the nodes of a network can
exchange information. To calculate the
efficiency of a network, all the shortest path
lengths between any pair of nodes in the
graph must be calculated. The assumption is
made that every link can be used to transfer
information in the network. The efficiency is
calculated in two parts: (1) the inverse of the
sum of the shortest paths between any pair
of nodes are calculated; (2) the result from
(1) is divided by the possible number of
pairs of nodes to find the average efficiency
of the network.
• According to Lindelauf, Borm, and Hamers
(2009), performance is a measure of the
overall performance of a network calculated
as the product between secrecy and
efficiency. This measure is used to assess the
performance of the network in the light of
the goals of terrorist network to reach a
balance between secrecy and efficiency.
Lindelauf, Borm, and Hamers (2009) use the
term information performance instead of efficiency.
Information performance is calculated in a manner
similar to efficiency as proposed by Latora and
Marchiori (2004).
KMIS 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
18

3.2.2 Node Analysis
The following node measures are supported:
• Degree Centrality. A node is central when
it has many ties (links) to other nodes in the
network. This kind of centrality is measured
by the degree of the node. The higher the
degree, the more central the node is.
• Closeness Centrality indicates that a node
is central when it has easy access to other
nodes in the network. This means that the
average distance (calculated as the shortest
path) to other nodes in the network is small.
• Betweenness Centrality. Usually, not all
nodes are connected to each other in a
network. Therefore, a path from one node to
another may go through one or more
intermediate nodes. Betweenness centrality
is measured as the frequency of occurrence
of a node on the geodesic connecting other
pairs of nodes. A high frequency indicates a
central node.
• Eigenvector Centrality is like a recursive
version of degree centrality. A node is
central to the extent that the node is
connected to other nodes that are central. A
node that is high on eigenvector centrality is
connected to many nodes that are themselves
connected to many nodes.
• According to Memon (2007), position role
index (PRI) is a measure aimed at making a
distinction between the gatekeeper and
follower roles. PRI evolved from testing
efficiency of a network based on the
assumption that a network without followers
has a higher efficiency as followers are less
connected within the structure. PRI is
measured as the change of network
efficiency after removal of a node. A high
PRI value indicates a large loss of
efficiency, if a particular node is removed.
3.2.3 Link Analysis
The following link measures are supported:
• Link Betweenness measures the frequency
of link occurrence on the geodesic
connecting pairs of nodes (Girvan and
Newman 2002). Link betweenness indicates
how much information flows via a particular
link. The assumption is that communication
flows along the shortest path. A high
frequency indicates a central link.
• According to Wiil, Gniadek, and Memon
(2010), link importance measures how
important a particular link is in a terrorist
network by measuring how the removal of
the link will affect the secrecy and efficiency
(performance) of the network. A high loss of
efficiency (when removing the link)
indicates an important link.
3.2.4 Visualization
CrimeFighter Assistant can visualize networks using
various visualization layouts (Di Battista et al.
1994):
• Fruchterman-Reingold layout
• Kamada-Kawai layout
• Spring layout
• Radial layout
• Self-organizing map layout
• Tree layout
The user decides which layout is the most
appropriate for a given network by selecting a menu
item in the “Visualize” menu. It is possible to switch
between different layouts at any time by simply
selecting a different menu item.
In network visualizations with many nodes,
vertices might overlap. This might make the graph
somewhat unclear. To cope with this issue, a
zooming feature has been added.
4 CASE STUDY: 2002 BALI
BOMBING
At 23:05 on October 12, 2002 an electronically-
triggered bomb blew apart Paddy's Bar, a popular
night spot in Kuta on the Indonesian island of Bali.
Seconds later, as the terrified and injured customers
fled, another more powerful bomb hidden in a white
Mitsubishi minivan detonated in front of the Sari
Club across the street. 202 victims died in the
explosions and more than 200 were injured. (Wise
2005).
Members of the South East Asian militant
network Jemaah Islamiah were responsible for the
attack. It is believed that Riduan Isamuddin (a.k.a.
Hambali) ordered a new strategy of hitting soft
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT - A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis
19
targets such as nightclubs and bars. Hambali, who is
currently in US custody in Guantanamo Bay, is
believed to have been the South East Asian contact
for Osama Bin Laden's al-Qaeda network. But he is
not thought to have played an active part in the Bali
plotting. Instead, 43-year-old Islamic teacher
Mukhlas (a.k.a. Huda bin Abdul Haq) was convicted
as the overall coordinator of the attacks. He also
recruited two of his younger brothers, Amrozi and
Ali Imron, to play key roles in the attack.
Important roles were also played by Imam
Samudra (a.k.a. Abdul Aziz), Azahari Husin (a
Malaysian who was alleged to be Jemaah Islamiah’s
top bomb-making expert and to have helped
assemble the Bali bombs; he was killed by police in
eastern Indonesian in November 2005) and alleged
bomb-maker Noordin Mohammad Top (killed
during a police raid in Solo, Central Java in
September 2009). (BBC News 2010).
Additionally, Khalid Sheikh Mohammed
(leading member of 9/11 attacks) confessed during
his hearing at Guantanamo Bay on March 10, 2007
to have been the leader of the Bali bombing plot.
The perpetrators mentioned above were not the
only ones involved in planning and carrying out the
attack. Therefore based on known facts, a terrorist
network for the Bali bombing can be built. The
dataset used in this case study is based on the work
by Memon (2007).
CrimeFighter Assistant will be used to analyze
the network, nodes, and links in order to be able to
answer the various questions raised in the previous
section.
After loading the Bali bombing data set, the
status bar shows basic information about the
network (number of nodes and links/edges) and the
various options for network analysis and
visualization become active. Figure 4 shows the
status bar after loading the Bali bombing network.
Figure 4: Status bar after loading the Bali bombing
network.
4.1 Network Analysis
The result of the network analysis is shown in the
right side panel of CrimeFighter Assistant (see
Figure 5).
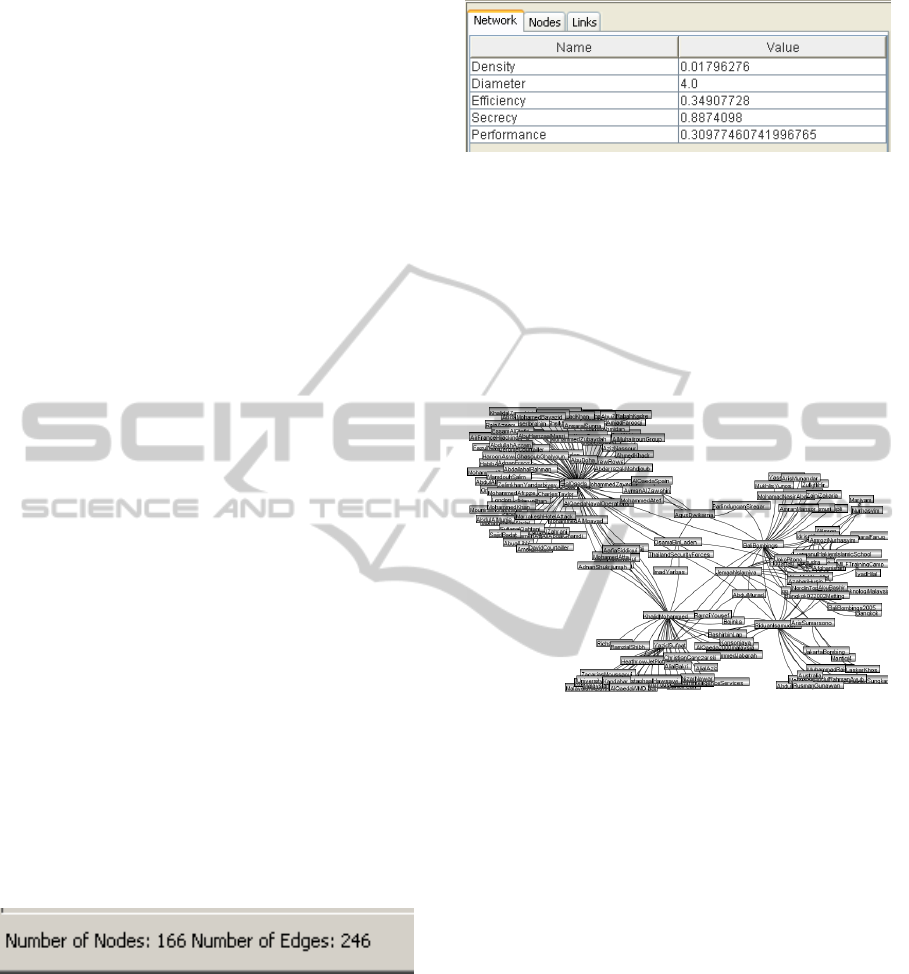
The Bali bombing network is sparsely connected:
for 166 nodes only 246 links (edges) exists. Hence,
the density of the network is low (0.0179): only 1.8
% of all possible links between nodes exist.
Figure 5: Network analysis results.
The structure of the network consists of stars
(clusters of people) that are loosely connected with
each other. Three overall clusters can be identified:
centered on al-Qaeda, Khalid Sheikh Mohammed
(the leader of the plot), and the people directly
responsible for the attack, respectively. The only
dense segment is formed by the people directly
responsible for the attack (see Figure 6).
Figure 6: Bali bombing network structure.
The diameter of the network is 4 meaning that
the largest distance between any pair of nodes is 4.
Taking the diameter and the star structure (clusters)
into account, information does not need to travel
very far in the network.
The structure has a direct impact on the secrecy,
efficiency, and performance of the network. The
terrorist had to work with a high level of secrecy,
which is reflected in the structure of the network. A
star structure (excluding the center node) is resistant
for uncovering since the other nodes only know one
other member. The secrecy value for the network is
0.89, which means that the structure of the network
provided a high level of covertness. The high level
of secrecy had an impact on the communication
possibilities. The efficiency of the network is 0.35.
This is however still a high value taking under
consideration the conditions in which the terrorist
group operated. The overall performance of the
network is 0.31 – measured as the trade-off between
secrecy and efficiency.
KMIS 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
20

Table 1: Node analysis results from the Bali bombing network.
Name Degree Eigenvector Closeness Betweenness PRI
Khalid Sheikh Mohammed 30 0,060020 2,000000 3118,940177 0,064867
Riduan Isamuddin 23 0,046400 2,457831 1610,549559 0,027781
Huda bin Abdul Haq 12 0,024307 2,566265 169,652490 0,000803
Yazid Sufaat 12 0,024291 2,578313 1441,260256 0,030670
Wan Min Wan Mat 11 0,022286 2,596386 366,862572 0,004090
Imam Samudra 9 0,018222 2,686747 118,365560 0,000254
Azahari Husin 9 0,018231 2,710843 176,577028 0,000249
Amrozi Nurhasyim 8 0,016209 2,698795 201,889424 0,000229
Noordin Mohammad Top 8 0,016194 2,704819 163,530717 0,000218
Ali Imron 7 0,014199 2,698795 160,470996 0,000193
Agus Dwikarna 6 0,011954 2,740964 235,378571 0,003376
Aris Sumarsono 5 0,010080 2,746988 372,804052 0,006535
Osama Bin Laden 3 0,006208 2,349398 55,888300 0,000852
Aafia Siddiqui 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
Adnan Shukrijumah 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
Mohamed Atta 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
Abual Zarqawi 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
Hasan Ghul 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
Khalid AlHajj 2 0,004173 2,530120 0,000000 0,000575
The similar values for the 9/11 network is a
density of 0.08, a diameter of 5, a secrecy of 0.86, an
efficiency of 0.34, and an overall performance of the
network of 0.29. Hence, the Bali bombing network
managed to have a good trade-off between secrecy
and efficiency due to the star-like structure
combined with a more densely connected cluster of
people taking directly part in the attack.
4.2 Node Analysis
The results of analyzing the nodes in the Bali
bombing network are shown in Table 1. The five
different node centralities (degree, eigenvector,
closeness, betweenness, and PRI) explained in the
previous section have been calculated. The table
shows the results of the most important nodes
ordered according to the degree centrality (highest at
the top).
Khalid Shaikh Mohammed has the highest score
in all the centrality measures. Thus, the analysis
strongly indicates that he is the most important
person in the network. According to his confession
mentioned earlier, he was in fact the leader of the
plot.
Also, Riduan Isamuddin (believed to be
responsible for strategy) and Huda bin Abdul Haq
(coordinator of the attack) are both ranked very high
according to the centrality measures. The PRI values
suggest that Khalid Shaikh Mohammed, Riduan
Isamuddin, and Yazid Sufaat were sources of
information and gatekeepers. Yazid Sufaat is
believed to be the supplier of explosives. Removal
of those nodes would lead to the highest decrease in
network efficiency.
4.3 Link Analysis
The results of analyzing the links in the Bali
bombing network are shown in Table 2. The link
analysis measures described in the previous section
have been calculated. The table shows link
betweenness and link importance for the most
important links. The influence of each link in
relation to secrecy and efficiency has also been
calculated. The secrecy and efficiency columns
show how these values will be affected in case the
link is removed. The links are ordered according to
their link importance values (highest at the top).
The three most important links (e2, e56, and
e101) connect the three overall clusters in the
network centered on al-Qaeda, Khalid Sheikh
Mohammed, and the Bali bombing actors. Other
important links connect the individual members that
were directly responsible for the attack.
Figure 7 shows the Bali bombing network with the
10 most important links highlighted in red. The most
important links points out the information backbone
of the network. Important communication takes
place between the three clusters and inside the
cluster directly responsible for the attack.
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT - A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis
21

Table 2: Link analysis results from the Bali bombing network.
Link id Betweenness Importance Secrecy Efficiency
e2 3063,266036 0,012770897 0,8892154 0,33512786
e56 1662 0,012521663 0,88919705 0,33489022
e101 1037,131532 0,005704435 0,8882053 0,342512
e112 889,328022 0,00279687 0,88787466 0,34581587
e115 366 0,002569838 0,8878563 0,34603432
e96 249,8333333 0,001689674 0,8878196 0,34702513
e93 335,6526446 0,001261747 0,8877461 0,3475359
e105 160 0,001165225 0,887691 0,3476594
e154 206,6336996 0,001153794 0,88772774 0,3476594
e88 270,5785714 0,001142814 0,88776445 0,3476594
e86 175,0131868 0,001088408 0,8877094 0,34773886
e29 177,4738095 9,93E-04 0,8886828 0,34746537
e39 177,4738095 9,93E-04 0,8886828 0,34746537
e64 177,4738095 9,93E-04 0,8886828 0,34746537
e6 335,9455458 9,65E-04 0,8886828 0,34750062
Figure 7: The 10 most important links in the Bali bombing
network.
The results of the link analysis point in the same
direction as the results of the node and network
analysis. Important links are to a high degree
connected to what was found to be important nodes
(further indicating the importance of those nodes).
Also, important links connect the three overall
clusters of the network (further emphasizing the use
of clusters to structure the network to achieve a good
trade-off between secrecy and efficiency).
4.4 Summary
A case study of the 2002 Bali bombing was used to
show that the network, node, and link analysis
features of CrimeFighter Assistant can provide
significant help in answering the important questions
related to destabilization of terrorist networks (see
Section 3).
5 COMPARISON TO RELATED
WORK
We have studied various existing software packages
for SNA and TNA to see what features they include:
1. Network Workbench (NWB Team 2006)
2. Social Networks Visualizer (SocNetV 2010)
3. UCINET (2010)
4. Visione (Brandes and Wagner 2003)
5. VisuaLyzer (2010)
6. Pajek (Batagelj and Mrvar 2010)
7. NetMiner (2010)
8. Analyst’s Notebook 8.5 (i2 2010)
9. iMiner (Memon 2007)
10. CrimeFighter Assistant
We have compared the software packages against
some of the network, node, and link analysis
features available in CrimeFighter. Table 3
summarizes our results. A minus (–) indicates that
the feature is not supported. A plus (+) indicates that
the feature is supported. All the examined software
packages support visualization of network structures
– some more advanced than others. The software
packages for SNA (1 to 7) as well as Analyst’s
Notebook (8), a commercial tool for analysis and
visualization that is widely used by law enforcement
and intelligence agencies, support to a varying
degree the ordinary SNA features, but do not support
KMIS 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
22

Table 3: Comparison of analysis features in SNA and TNA software packages.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Secrecy – – – – – – – – – +
Efficiency – – – – – – – – + +
Performance – – – – – – – – – +
Degree centrality – + + + + + + + + +
Closeness centrality + + + + + + + + + +
Betweenness centrality + + + + + + + + + +
PRI – – – – – – – – + +
Link betweenness – – + + – + + + – +
Link importance – – – – – – – – – +
the domain specific TNA features (secrecy,
efficiency, performance, PRI, and link importance).
iMiner (Memon 2007) which is also a TNA tool
supports both SNA and TNA features, but lack some
of the latest TNA features that were reported in the
research literature after the tool was developed
(secrecy, performance, and link importance). On the
other hand, some of the software packages (1 to 8)
provide many features not currently supported in
CrimeFighter Assistant such as detecting
communities, k-plex, k-core, clustering coefficients,
etc.
Additional TNA features have been proposed in
the literature by Memon (2007):
• Detecting Hidden Hierarchy. This method
aims to identify hidden hierarchical
structures in horizontal networks. The
method uses SNA measures and graph
theory to indicate parent-child relationships
of nodes in the network.
• Subgroup Detection. A terrorist network
can often be partitioned into cells
(subgroups) consisting of individuals who
interact closely with each other. This method
uses SNA measures and graph theory to
indicate clusters (subgroups) in relation to a
particular node and the diameter from that
node.
Rhodes (2009) proposed the use of Bayesian
inference techniques to predict missing links in a
covert network, demonstrated through a case study
of the Greek terrorist group November 17. The
assumption is that during the analysis of terrorist
networks it is unlikely that the intelligence analysts
have an overview of the full terrorist network.
Prediction of missing links can be a useful method to
gain deeper understanding and conduct detailed
analysis of the terrorist network.
CrimeFigther Assistant provides many of the
typical SNA features as well as features dedicated
for TNA. Some of the latest TNA features are so far
only implemented in CrimeFigther Assistant, thus
making the tool unique in certain aspects. However,
there are still a number of SNA and TNA features
(detecting hidden hierarchy, subgroup detection, link
prediction, k-plex, etc.) that can be implemented in
future versions to make CrimeFigther Assistant a
more complete tool for TNA.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper has described the CrimeFigther Assistant
knowledge management tool for TNA. The network,
node, and link analysis features of the tool were
demonstrated based on a case study of the 2002 Bali
bombing. CrimeFigther Assistant provides the
following contributions:
• CrimeFigther Assistant supports a balanced
approach to TNA focusing on network,
node, and link analysis as an attempt to
support intelligence analysts in making
informed decisions regarding possible
actions to take to destabilize a terrorist
network.
• CrimeFighter Assistant provides the first
implementation of the link importance
measure proposed by Wiil, Gniadek, and
Memon (2010).
• CrimeFighter Assistant also provides the
first implementation of the secrecy,
efficiency, and performance measures
proposed by Lindelauf, Borm, and Hamers
(2009).
Future work will focus on improving and further
developing the tool in various ways:
CRIMEFIGHTER ASSISTANT - A Knowledge Management Tool for Terrorist Network Analysis
23

• We plan to include new algorithms for TNA
including detecting hidden hierarchy,
subgroup detection, and link prediction.
• We are currently looking into how link
weights can be incorporated, since not all
links are equally important. We believe that
incorporation of link weights will result in
more precise link analysis measures.
• We wish to optimize the existing TNA
algorithms to perform more efficient to be
able to analyze large networks of thousands
of nodes and links.
• We are currently including additional data
sets to test and evaluate the usefulness of the
tool more thoroughly.
REFERENCES
Baccara, M., and Bar-Isaac, H. 2009. Interrogation
methods and terror networks. Mathematical Methods
in Counterterrorism, pp. 271-290. Springer.
Batagelj, V., and Mrvar, A. 2010. Pajek – Program for
large network analysis. http://pajek.imfm.si.
Baker, W. E., and Faulkner, R. R. 1993. The social
organization of conspiracy: illegal networks in the
heavy electrical equipment industry. American
Sociological Review, 837-860.
BBC News. 2008. The Bali bombing plot.
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/3157478.stm.
Brandes, U., and Wagner, D. 2003. Analysis and
visualization of social networks. Graph Drawing
Software, pages 321-340.
Carley, K. M., Lee, J. S., and Krackhardt, D. 2001.
Destabilizing networks. Connections, 24(3):31-34.
Di Battista, G., Eades, P., Tamassia, R., and Tollis. I. G.
1994. Algorithms for drawing graphs: an annotated
bibliography. Computational Geometry-Theory and
Application, 4(5):235-282.
Enders, W., and Su, X. 2007. Rational terrorists and
optimal network structure. Journal of Conflict
Resolution, 51(1):33.
Girvan, M., and Newman, M. E. J. 2002. Community
structure in social and biological networks.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
99(12):7821-7826.
Gloor, P. A., and Zhao, Y. 2006. Analyzing actors and
their discussion topics by semantic social network
analysis. Information Visualization (IV 2006), pp.
130-135.
i2. 2010. http://www.i2group.com/template1.asp?id=5.
Latora, V., and Marchiori, M. 2004. How the science of
complex networks can help developing strategies
against terrorism. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals,
20(1):69-75.
Lindelauf, R., Borm, P., and Hamers, H. 2009. The
influence of secrecy on the communication structure
of covert networks. Social Networks, 31, 126-137.
Elsevier.
Memon, N. 2007. Investigative data mining: mathematical
models for analyzing, visualizing and destabilizing
terrorist networks. PhD thesis, Aalborg University,
Denmark.
NetMiner. 2010. http://www.netminer.com.
NWB Team. 2006. Network Workbench Tool. Indiana
University, Northeastern University, and University of
Michigan, http://nwb.slis.indiana.edu.
O'Madadhain, J., Fisher, D., Smyth, P., White, S., and
Boey, Y. B. 2005. Analysis and visualization of
network data using JUNG. Journal of Statistical
Software, VV:1-35.
Rhodes, C. J. 2009. Inference approaches to constructing
covert social network topologies. Mathematical
Methods in Counterterrorism, pp. 127-140. Springer.
SocNetV. 2010. http://socnetv.sourceforge.net.
UCINET. 2010. http://www.analytictech.com/ucinet.
VisuaLyzer. 2010. http://www.mdlogix.com/solutions.
Wasserman, S., and Faust, K. 1994. Social network
analysis: methods and applications. Cambridge
University Press.
Wiil, U. K., Gniadek, J., and Memon, N. 2010. Measuring
link importance in terrorist networks. Accepted for the
International Conference on Advances in Social
Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM 2010),
(Odense, Denmark, August). IEEE Computer Society
Press.
Wiil, U. K., Memon, N., and Gniadek, J. 2009.
Knowledge management processes, tools and
techniques for counterterrorism. Proceedings of the
International Conference on Knowledge Management
and Information Sharing (KMIS 2009), (Funchal,
Portugal, October), pp. 29-36. INSTICC Press.
Wise, W. 2005. Indonesia's war on terror. United States-
Indonesia Society, pp. 1-107.
KMIS 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
24
