
DECODING SSVEP RESPONSES USING TIME DOMAIN
CLASSIFICATION
Nikolay V. Manyakov, Nikolay Chumerin, Adrien Combaz, Arne Robben and Marc M. Van Hulle
Laboratory for Neuro- and Psychofysiology, K. U. Leuven, Herestraat 49, POBox 1021, 3000 Leuven, Belgium
Keywords:
Steady-state visual evoked potential, EEG, Decoding, Brain-computer interafce.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a new time domain method for decoding the steady-state visual evoked potential
recorded while the subject is looking at stimuli flickering with constant frequencies. Using several such
stimuli, with different frequencies, a brain-computer interface can be built. We have assessed the influence
of the number of electrodes on the decoding accuracy. A comparison between active wet- and bristle dry
electrodes were made. The dependence between accuracy and the length of the EEG interval used for decoding
was shown.
1 INTRODUCTION
Research on brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) has
witnessed a tremendous development in recent years
(see, for example, the editorial in IEEE Signal Pro-
cessing Magazine (Sajda et al., 2008)), and is now
widely considered as one of the most successful ap-
plications of the neurosciences. BCIs can signif-
icantly improve the quality of life of patients suf-
fering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, stroke,
brain/spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, muscular dys-
trophy, etc.
Brain computer interfaces are either invasive
(intra-cranial) or noninvasive. The first ones have
electrodes implanted mostly into the premotor- or
motor frontal areas (Santhanam et al., 2006) or
into the parietal cortex, whereas the noninvasive
ones mostly employ electroencephalograms (EEGs)
recorded from the subject’s scalp.
The noninvasive methods can be further subdi-
vided into three groups. The first group is based
on the P300 (’oddbal’) event-related potentials in the
parietal cortex which is used to differentiate between
an infrequent, but preferred stimulus, versus a fre-
quent, but non-preferred stimuli in letter spelling sys-
tems (Farwell and Donchin, 1988; Combaz et al.,
2009; Manyakov et al., 2010). The second group of
BCI’s tries to detect imagined of right/left limb move-
ments. This BCI uses slow cortical potentials (SCP)
(K¨ubler et al., 2001; Birbaumer et al., 2000), event-
related desynchronization (ERD) of the mu- and beta-
rhythm (Pfurtscheller et al., 2000) or the readiness
potential (bereitschaftspotential) (Blankertz et al.,
2007). And the third group, which is also the sub-
ject of this study, uses the steady-state visual evoked
potential (SSVEP). This type of BCI relies on the psy-
chophysiological properties of EEG brain responses
recorded from the occipital area during the peri-
odic presentation of identical visual stimuli (flicker-
ing stimuli). When the periodic presentation is at a
sufficiently high rate (> 6 Hz), the individual transient
visual responses overlap and become a steady state
signal: the signal resonates at the stimulus rate and
its multipliers (Luck, 2005). This means that, when
the subject is looking at stimuli flickering at the fre-
quency f
1
, we can detect f
1
, 2f
1
, 3f
1
,... in the Fourier
transform of the EEG signal recorded form the oc-
cipital pole. Since the amplitude of a typical EEG
signal decreases as 1/ f in the spectral domain, the
higher harmonics become less prominent. Further-
more, the fundamental harmonic f
1
is embedded into
other on-going brain activity and (recording) noise.
Thus, when considering a small recording interval it
is quite likely to detect an (irrelevant) increase in the
amplitude at frequency f
1
. To overcome this problem,
averaging over several time intervals (Cheng et al.,
2002), or recording over longer time intervals (Gao
et al., 2006) are often used for increasing the signal-
to-noise ratio in the spectral domain. Finally, in order
to establish a means of direct communication from
the brain to the computer, not one stimulus frequency
f
1
, but several frequencies are used at the same time,
f
1
,..., f
n
, each one corresponding to a particular com-
mand one wants to communicate. The detection prob-
376
V. Manyakov N., Chumerin N., Combaz A., Robben A. and M. Van Hulle M..
DECODING SSVEP RESPONSES USING TIME DOMAIN CLASSIFICATION.
DOI: 10.5220/0003106103760380
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Computation and 2nd International Conference on Neural Computation (ICNC-2010), pages
376-380
ISBN: 978-989-8425-32-4
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

lem, therefore, becomes more complex since now, one
of several possible flickering frequencies f
i
need to be
detected from the EEG recordings.
For decoding the SSVEP BCI paradigm, tradition-
ally, a representation in the spectral domain of the
recorded EEG signal is used, hence, a variety of meth-
ods and classifiers have been described in the litera-
ture that rely on features based on amplitudes at par-
ticular frequencies (Cheng et al., 2002; Gao et al.,
2006; de Peralta Menendez et al., 2009). In spite of
the reported high transfer rates, achieving a reliable
and fast classification still remains problematic. This
can be due to the fact that, when using a computer
screen for the stimuli, we don’t have a precise refresh-
ing rate of 60 Hz
1
(in our case it is 59.83 Hz). This
can cause, for example, the oscillation, produced by
two consecutive frames (intended to be at 30 Hz), not
to exactly correspond to the desired one, which can
deteriorate the decoding based on the Fourier trans-
form (FT), when using short intervals. Furthermore,
when using too short intervals, neighboring frequen-
cies can not be distinguished because of the limited
spectral resolution. For example, 60/9 = 6.67 Hz and
60/8 = 7.5 Hz oscillations are indistinguishable af-
ter performing a fast FT based on a 500 ms inter-
val (in other words, we have here a spectral resolu-
tion of 2 Hz). As was recently shown by Luo and
co-workers (Luo and Sullivan, 2010), time domain
classifiers yield a better performance than frequency-
based ones for the SSVEP paradigm.
In this paper, we describe our time domain clas-
sifier for SSVEP signal detection, and evaluate the
detection performance as a function of the recording
interval, for 3 subjects. The issue of using one vs.
several electrodes for decoding is also discussed.
2 METHODS
2.1 EEG Data Acquisition
The EEG recordings were performed using a pro-
totype of an ultra low-power 8-channels wireless
EEG system, which consists of two parts: an ampli-
fier coupled with a wireless transmitter and a USB
stick receiver. The data is transmitted with a sam-
pling frequency of 1000 Hz for each channel. We
used a brain-cap with large filling holes and sockets
for active Ag/AgCl electrodes (ActiCap, Brain Prod-
1
When using light-emitting diodes (LEDs), one could
precisely achieve 60 Hz, as was done in (Luo and Sullivan,
2010).
ucts). This system was developed by IMEC
2
and built
around their ultra-low power 8-channel EEG ampli-
fier chip (Yazicioglu et al., 2009). The recordings
were made with eight electrodes located on the occip-
ital pole (covering the primary visual cortex), namely
at positions Oz, O1, O2, POz, PO7, PO3, PO4, PO8,
according to the international 10–20 system (see Fig-
ure 1). The reference electrode and ground were
placed on the left and right mastoids.
The raw EEG signal is filtered in the 4-45 Hz fre-
quency band, with a fourth order zero-phase digital
Butterworth filter, so as to remove DC and the low
frequency drifts, and to remove the 50 Hz powerline
interference.
Figure 1: Electrode placement on a subject’s head. Elec-
trodes marked in red are the recording sites; those in blue
are the reference and ground.
2.2 Experiment Design
Three healthy subjects (all male, aged 26–33 with av-
erage age 30, two righthanded, one lefthanded) partic-
ipated in the experiments. In the beginning of the ex-
periment, a square is shown in the center of the screen,
flickering at a frequency of approximately 60/3 Hz,
for 15 seconds. After that, during 2 seconds, a blank
screen is shown, and then a new square flickering at
60/4 Hz is shown for 15 seconds, and so on. In total,
7 different flickering stimuli are presented to the sub-
ject, with frequencies corresponding to the integer di-
visions of 60 by 3,4,...,9 (note that these are equal to
the lengths of flickering periods in frames). From the
recorded EEG signal, the spectrogram is calculated
(see, for example, Figure 2). The four most promi-
nent frequencies are later considered for futher evalu-
ation for a 4-command SSVEP BCI application. We
choose 20, 15, 12 and 10 Hz for subject 1; 12, 60/7,
7.5, 6.67 Hz for subject 2; 10, 60/7, 7.5, 6.67 Hz for
subject 3.
2
Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC),
http://www.imec.be.
DECODING SSVEP RESPONSES USING TIME DOMAIN CLASSIFICATION
377
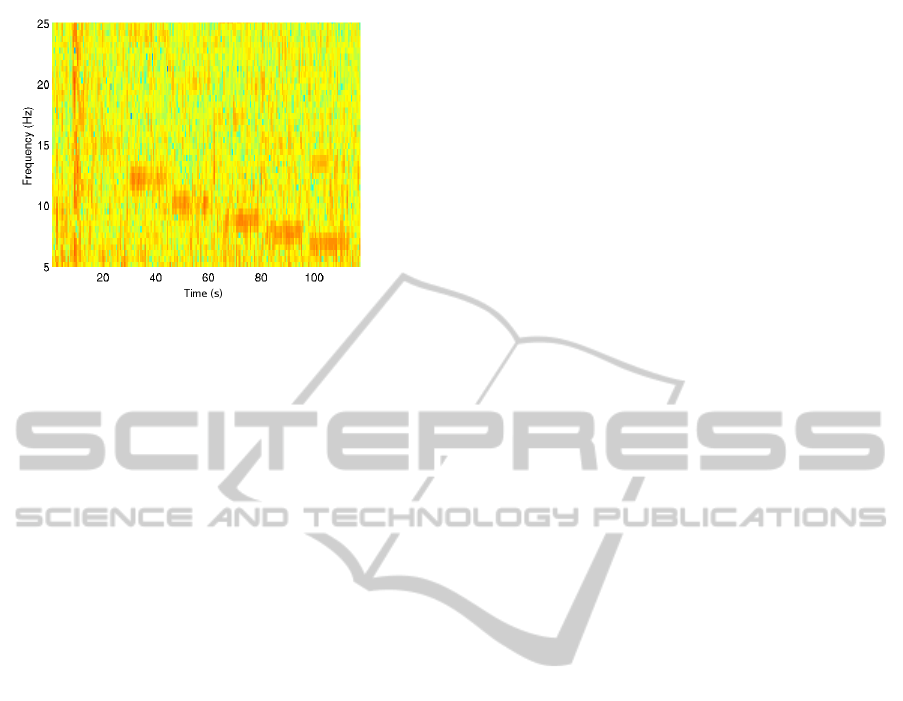
Figure 2: Spectrogram of EEG recordings from electrode
Oz for subject 3, based on a 15 s visual stimulation at fre-
quencies 60/3,...,60/9 Hz, using a 2 s interval between two
consecutive stimuli. Note that not only the fundamental fre-
quencies, but also their harmonics are visible.
2.3 Features and Classification
As a feature, we took the average response expected
for each of the flickering stimuli. For this, the
recorded EEG signal of length t ms was divided into
n
i
= [t/ f
i
] nonoverlapping, consecutive intervals ([.]
denotes the integer part of the division), where each
interval is linked to the stimulus onset. For exam-
ple, for 2000 ms recordings, and for a stimulus fre-
quency of 10 Hz, we have 2000/10 = 20 such inter-
vals of length 100 ms ([1,100], [101 200],...). This
procedure is repeated for all frequencies used in the
BCI set-up, thus, for i = 1..4 (the actual four frequen-
cies used for the different subjects was discussed in
Sec. 2.2). After that, the average response for all such
intervals, for each frequency, is computed. Such av-
eraging is necessary because the recorded signal is
a superposition of all ongoing brain activities. By
averaging the recordings, those that are time-locked
to a known event, are extracted as evoked potentials,
whereas those that are not related to the stimulus pre-
sentation are averaged out. The stronger the evoked
potentials, the fewer trials are needed, and vice versa.
To illustrate this principle, Fig. 3 shows the result of
averaging, for a 2 s recording interval, while the sub-
ject was looking at a stimulus flickering at a frequency
of 20 Hz. It can be observed that, for the intervals
used for detecting the frequencies 12 and 15 Hz, the
averaged signals are close to zero, while for those
used for 10 and 20 Hz, a clear average response is
visible. Note that the average response does not ex-
actly look like integer period of a sinusoid, because
the 20 Hz stimulus was constructed using two con-
secutive frames of intensification followed by frame
of no intensification. There is also some latency
present in
the responses since the evoked potential does not ap-
pear immediately after the stimuli onset. It could also
be the case that, in the interval used for detecting the
10 Hz oscillation, the average curve consists of two
periods. This is as expected, since a 20 Hz oscillation
has exactly 2 whole periods in a 100 ms interval.
In order to assess the decoding performance, the
EEG recordings were divided into two nonoverlap-
ping subsets (training and testing). This division was
made 10 times for every time interval of length t ms,
which provides us with statistics for result compari-
son. Based on the training set, we built 4 classifiers
based on linear discriminant analysis (LDA). Each of
these classifiers was built for the averaged responses
for the time intervals of the stimulus frequencies con-
sidered (see Figure 3 where, e.g., 4 of such intervals
are shown). These classifiers were constructed so as
to discriminate the stimulus flickering frequency f
i
in
window i from all other flickering frequencies, and for
the case when the subject does not look at the flicker-
ing stimuli at all. As a result of LDA classification (on
testing data), we have four posterior probabilities p
i
,
which characterize the likelihood of a subject’s gaze
on one of the 4 stimuli flickering at different frequen-
cies f
i
. If all four probabilities p
i
are smaller then
0.5, we conclude that the subject is not looking at the
flickering stimuli. In all other cases, we take, as an in-
dication of the stimulus the subject’s gaze is directed,
the flickering frequency f
i
response that generates the
largest posterior probability p
i
. Since we do not take
the raw EEG signal, but rather a 4-45 Hz filtered one
(see above), our 1000 Hz sampling frequency is in
fact largely redundant. This can lead to zero determi-
nants of the covariance matrices in the LDA estima-
tion. To overcome this, we downsampled our data to
a lower resolution (we took only every fifth sample
in the recordings), and took only those time instants,
for which the p-values were smaller than 0.05 in the
training data, using a Student t-test between two con-
ditions: averaged response in interval i corresponding
to the given stimulus with flickering frequency f
i
ver-
sus the case when the subject is looking at an other
stimulus, with another flickering frequency, or look-
ing at no stimulus at all. This feature selection proce-
dure, which is based on a filter approach, enables us
to restrict ourselves to relevant time instants only.
All what was described above is valid only for the
case when we have a single electrode. In the case of
several electrodes (8 electrodes in our case), the same
feature selection was performed for each electrode,
but the 4 LDA classifiers were build based on pooled
features from all electrodes.
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
378
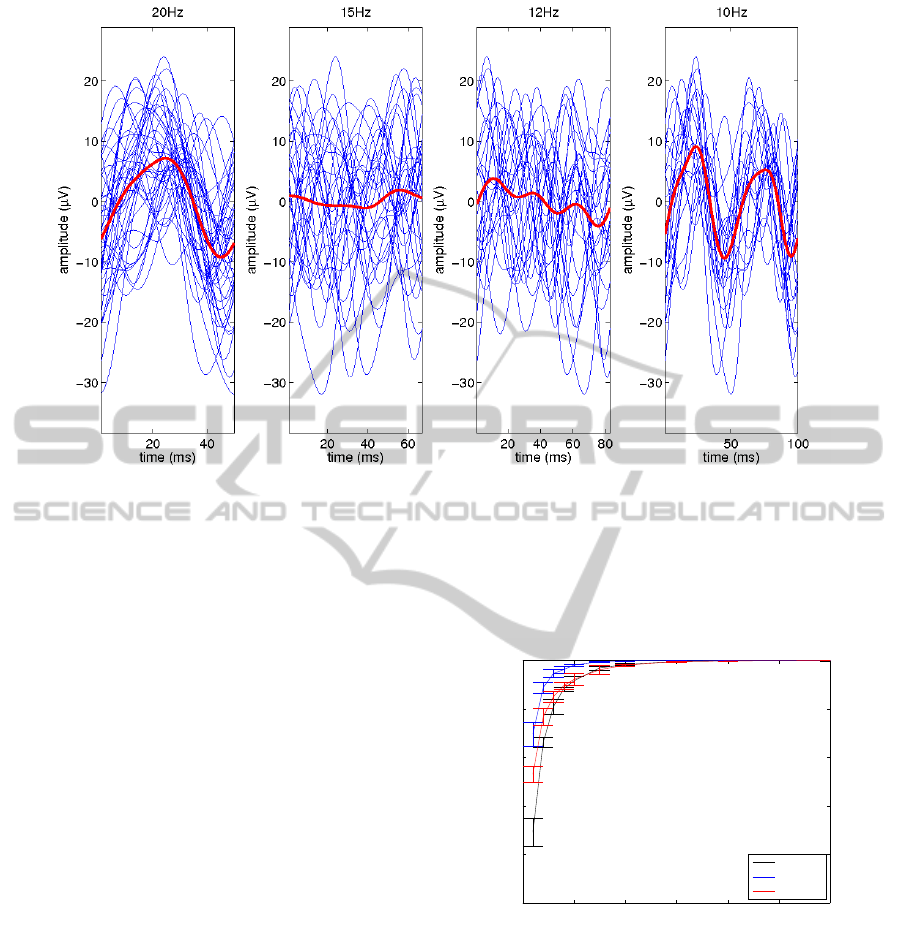
Figure 3: Individual traces of EEG activity (blue) and their averages (red), time locked to the stimuli onset. Each individual
trace shows changes in electrode Oz for subject 1. The lengths of the shown traces correspond to the durations of the flickering
periods of 3, 4, 5 and frames (from left to right panel), and with a screen refreshing rate of 59.83 Hz. The subject was looking
to the stimulus flickering at ≈ 20 Hz (period equal to 3 frames). One observes that, in the left panel, we obtain one complete
period for the average trace, and in the right panel, two complete periods, while in the other panels, the average trace is almost
flat.
3 RESULTS
After constructing the classifiers on the training data,
they can be applied to test data of all 3 subjects. We
obtained the results shown in Figure 4, plotted as a
function of the interval length t. It can be seen that a
1 second interval is sufficient to make a decision with
high accuracy for all subjects, and for a BCI appli-
cation with four different frequencies (+ also distin-
guishing the case where the subject is not looking at
any stimuli). This shows that the proposed time do-
main BCI is able to achieve a performance with a high
information transfer rate (Pierce, 1980).
We have also verified the dependency of the de-
coding accuracy on the number of electrodes used for
decoding. As was expected, the highest accuracy for
a single electrode design is obtained for the electrodes
placed along the central line (Oz or POz). Taking all
eight electrodes together generates a significantly bet-
ter performance than the case of only a single elec-
trode. Finally, for EEG recordings with an interval
length above 1.5 sec, there is no difference in decod-
ing performance.
We have also tested bristle dry electrodes (Med-
Cat) instead of active wet ones (ActiCap, Brain Prod-
ucts). Dry electrodes enable the preparation time of
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
50
60
70
80
90
100
EEG segment length (s)
accuarcy
subject 1
subject 2
subject 3
Figure 4: Decoding accuracy (vertical axis) as a function of
the length of the EEG interval used for averaging (horizon-
tal axis).
the subject to be reduced to the absolute minimum,
since one does not require any gel or scraping away
of dead skin cells: the EEG cap is put on and one is
ready for recording, all in a few seconds. But on the
other hand, they have a large impedance, which leads
to weak signals and inferior decoding results. Given
the positions O1 and O2 for the dry electrodes, we
estimated the decoding accuracy as a function of the
EEG recoding length, and compared with the accu-
racy obtained with the active electrodes, for the same
DECODING SSVEP RESPONSES USING TIME DOMAIN CLASSIFICATION
379

electrode locations. We found that, to achieve the
same accuracy as with the active wet electrodes, we
have to at least consider a 4 times longer EEG inter-
vals. Nevertheless, we still believe that this to be an
encouraging result for a dry electrode SSVEP BCI ap-
plication.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
NVM is supported by the European Commission
(IST-2004-027017),NC is supported by the European
Commission (IST-2007-217077), AC is supported
by a specialization grant from the Agentschap voor
Innovatie door Wetenschap en Technologie (IWT)
(Flemish Agency for Innovation through Science
and Technology), MMVH is supported by research
grants received from the Excellence Financing pro-
gram (EF 2005) and the CREA Financing program
(CREA/07/027) of the K.U.Leuven, the Belgian Fund
for Scientific Research – Flanders (G.0234.04 and
G.0588.09), the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Pro-
gramme – Belgian Science Policy (IUAP P6/054), the
Flemish Regional Ministry of Education (Belgium)
(GOA 10/019), and the European Commission (IST-
2004-027017 and IST-2007-217077). This work is
also supported by a SWIFT grant from the King Bau-
douin Foundation of Belgium for developing patient
BCI applications (2009).
The authors wish to thank Refet Firat Yazicioglu,
Tom Torfs, and Chris Van Hoof, from the Interuniver-
sity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC) in Leuven, for
providing us with the wireless EEG system and for
their support.
REFERENCES
Birbaumer, N., K¨ubler, A., Ghanayim, N., Hinterberger, T.,
Perelmouter, J., Kaiser, J., Iversen, I., Kotchoubey,
B., Neumann, N., and Flor, H. (2000). The thought
translation device (ttd) for completely paralyzedpa-
tients. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineer-
ing, 8(2):190–193.
Blankertz, B., Dornhege, G., Krauledat, M., M¨uller, K.-
R., and Curio, G. (2007). The non-invasive berlin
braincomputer interface: fast acquisition of effec-
tive performance in untrained subjects. NeuroImage,
37(2):539–550.
Cheng, M., Gao, X., Gao, S., and Xu, D. (2002). De-
sign and implementation of a brain-computer inter-
face with high transfer rates. IEEE Transactions on
Biomedical Engineering, 49(10):1181–1186.
Combaz, A., Manyakov, N., Chumerin, N., Suykens, J., and
Van Hulle, M. (2009). Feature Extraction and Classifi-
cation of EEG Signals for Rapid P300 Mind Spelling.
In 2009 International Conference on Machine Learn-
ing and Applications, pages 386–391. IEEE.
de Peralta Menendez, R., Dias, J., Soares, J., Prado, H., and
Andino, S. (2009). Multiclass brain computer inter-
face based on visual attention. In ESANN2009 pro-
ceedings, pages 437–442.
Farwell, L. and Donchin, E. (1988). Talking off the top of
your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-
related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neu-
rophysiol., 70(6):510–523.
Gao, Y., R., W., X., G., B., H., and S., G. (2006). A practical
VEP-based brain-computer interface. IEEE transac-
tions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineer-
ing, 14(2).
K¨ubler, A., Kotchoubey, B., Kaiser, J., Wolpaw, J., and
Birbaumer, N. (2001). Brain-computer communica-
tion: unlocking the locked. Psychological Bulletin,
127(3):358–375.
Luck, S. J. (2005). An introduction to event-related po-
tentials technique. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Mas-
sachusetts.
Luo, A. and Sullivan, T. (2010). A user-friendly SSVEP-
based brain–computer interface using a time-domain
classifier. Journal of Neural Engineering, 7:026010.
Manyakov, N., Chumerin, N., Combaz, A., and Hulle, M.
(2010). On the Selection of Time Interval and Fre-
quency Range of EEG Signal Preprocessing for P300
Brain-Computer Interfacing. In XII Mediterranean
Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering
and Computing 2010, pages 57–60. Springer.
Pfurtscheller, G., Guger, C., M¨uller, G., Krausz, G., and Ne-
uper, C. (2000). Brain oscillations control hand ortho-
sis in a tetraplegic. Neuroscience letters, 292(3):211–
214.
Pierce, J. (1980). An Introduction to Information Theory.
Dover, New York.
Sajda, P., M¨uller, K. R., and Shenoy, K. V. (2008). Brain-
computer interfaces. IEEE Signal Proccessing Maga-
zine, 25(1):16–17.
Santhanam, G., Ryu, S. I., Yu, B. M., Afshar, A., and
Shenoy, K. V. (2006). A high-performance brain–
computer interface. Nature, 442:195–198.
Yazicioglu, R., Torfs, T., Merken, P., Penders, J., Leonov,
V., Puers, R., Gyselinckx, B., and Van Hoof, C.
(2009). Ultra-low-power biopotential interfaces and
their applications in wearable and implantable sys-
tems. Microelectronics Journal, 40(9):1313–1321.
ICFC 2010 - International Conference on Fuzzy Computation
380
