
GIVING SHAPE TO AN N–VERSION DEPENDENCY PARSER
Improving Dependency Parsing Accuracy for Spanish using Maltparser
Miguel Ballesteros, Jes
´
us Herrera
Departamento de Ingenier
´
ıa del Software e Inteligencia Artificial, Universidad Complutense de Madrid
C/ Profesor Jos
´
e Garc
´
ıa Santesmases, s/n E–28040 Madrid, Spain
Virginia Francisco, Pablo Gerv
´
as
Instituto de Tecnolog
´
ıa del Conocimiento, Universidad Complutense de Madrid
C/ Profesor Jos
´
e Garc
´
ıa Santesmases, s/n E–28040 Madrid, Spain
Keywords:
Natural language processing, Machine learning, Dependency parsing, Corpus-based training.
Abstract:
Maltparser is a contemporary dependency parsing machine learning–based system that shows great accuracy.
However 90% of the Labelled Attachment Score (LAS) seems to be a de facto limit for these kinds of parsers.
In this paper we present an n–version dependency parser that will work as follows: we found that there is a
small set of words that are more frequently incorrectly parsed so the n-version dependency parser consists of
n different parsers trained specifically to parse those difficult words. An algorithm will send each word to each
parser and combined with the action of a general parser we will achieve better overall accuracy. This work has
been developed specifically for Spanish using Maltparser.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the 10th edition of the Conference of Computa-
tional Natural Language Learning (CoNLL) a first
shared task on Multilingual Dependency parsing was
accomplished (Buchholz and Marsi, 2006). Thirteen
different languages including Spanish were involved
and parsing performance was studied. In this Shared
Task, participants implemented a parsing system that
could be trained for all these languages. Maltparser
0.4 (Nivre et al., 2007) is the publicly available soft-
ware that is contemporary to the system presented by
Nivre’s group to the CoNLL–X Shared Task, in which
Spanish was proposed for parsing and Nivre’s group
achieved great results.
Dependency parsing machine learning–based sys-
tems show exceptional accuracy. However 90% of the
Labelled Attachment Score (LAS) seems to be a de
facto limit for such kinds of parsers. Since generally
such systems can not be modified, we developed some
works to study what can be done with the training cor-
pora in order to improve parsing accuracy. High level
techniques, such as controlling sentences’ length or
corpora’s size, seem useless for these purposes. How-
ever they appeared useful for the design of system-
atic processes for building training corpora (Balles-
teros et al., 2010b). Low level techniques, based on
an in–depth study of the errors produced by the parser
at the word level, seem promising. Prospective low
level studies suggested the development of n–version
parsers. Each one of these n versions should be able
to tackle a specific kind of dependency parsing at
the word level and the combined action of all them
should reach more accurate parsings. Since n–version
parsers could be a valid tool for improving parsing ac-
curacy, we present in this paper a study on their use-
fulness and expected limits, as a continuation of our
previous work described in (Ballesteros et al., 2010a)
and (Ballesteros et al., 2010c).
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes
some state of the art on multilinugal dependency pars-
ing. Section 3 describes the previous work done on
Spanish parsing focusing on the feasibility of an n–
version dependency parser. In Section 4 we describe
the current state of the algorithm that sends every
setence to the more appropriated specific parser and
combines the action of several parsers over a certain
sentence; also we point out which work must be done
to conclude it. Finally, Section 5 shows the conclu-
sions of the presented work and proposes some ideas
for potential future studies.
336
Ballesteros M., Herrera J., Francisco V. and Gervás P..
GIVING SHAPE TO AN N–VERSION DEPENDENCY PARSER - Improving Dependency Parsing Accuracy for Spanish using Maltparser.
DOI: 10.5220/0003116803360341
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR-2010), pages 336-341
ISBN: 978-989-8425-28-7
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 THE CONLL–X SHARED TASK
ON MULTILINGUAL
DEPENDENCY PARSING
The goal of the CoNLL–X Shared Task (Buchholz
and Marsi, 2006) was to label dependency structures
by means of fully automatic dependency parsers. This
task provided a benchmark for evaluating parsers ac-
cross 13 languages, one being Spanish. Systems were
scored by computing their Labelled Attachment Score
(LAS), i.e. the percentage of “scoring” tokens for
which the system had predicted the correct head and
dependency label (Nivre et al., 2004), their Unla-
belled Attachment Score (UAS), i.e. the percentage of
“scoring” tokens for which the system had predicted
the correct head (Eisner, 1996) and their Label Ac-
curacy (LA), i.e. the percentage of “scoring” tokens
for which the system had predicted the correct depen-
dency label (Yamada and Matsumoto, 2003).
The results for Spanish across the 19 participants
ranged from 47% to 82.3% LAS, with an average of
73.5%. The treebank used was AnCora (Taul
´
e et al.,
2008). The two participant groups with the highest
total score for Spanish were (McDonald et al., 2006)
and (Nivre et al., 2006) with 82.3% and 81.3% LAS,
respectively. Maltparser 0.4 is the freely available
software of the system presented by Nivres group to
the CoNLLX Shared Task. It is a tool easy to con-
figure and use. Since we have developed some previ-
ous work on dependency parsing using Maltparser 0.4
(Herrera and Gerv
´
as, 2008; Herrera et al., 2007a; Her-
rera et al., 2007b), we decided to use Nivre’s group
system again to carry out the experiments related not
only to the work presented here but to all the previ-
ous ones (Ballesteros et al., 2010a; Ballesteros et al.,
2010b; Ballesteros et al., 2010c).
In our work, the first step was to replicate the par-
ticipation of Nivre’s group in the CoNLL–X Shared
Task for Spanish (Ballesteros et al., 2010a). We ob-
tained the same results as Nivre’s group, i.e., LAS =
81.30%, UAS = 84.67% and LA = 90.06%. These re-
sults served as a baseline for this work to determine
ways to improve them.
3 PREVIOUS WORK IN
IMPROVING PARSING
ACCURACY FOR SPANISH
USING MALTPARSER
The ideas given in this paper were inspired by (Mc-
Donald and Nivre, 2007), where the performances
of two dependency parsing systems are compared,
showing that they are complementary and when one
of them fails the other one can obtain a good pars-
ing. So if one system can achieve better results for
some kinds of sentences and another system is bet-
ter for others kinds of sentences, why not use them in
synergy? This led us to consider an n–version model
in which we choose a priori what dependency parser
is better for parsing some specific wordforms. This
way, by combining the action of several parsers we
expect to obtain a better overall accuracy by means of
enhancing local accuracy.
As described in (Ballesteros et al., 2010a), when
analyzing the results after parsing the test corpus pro-
vided in the CoNLL–X Shared Task, we found that
there is a small set of words that more frequently show
an incorrect attachment, incorrect labelling or both.
These words are the prepositions “a” (to), “de” (of ),
“ en” (in), “con” (with), “por” (for), the conjunction
and, which has two wordings: “y” or “e”, and the
nexus “que” (that). For instance there are 20 sen-
tences (340 wordforms), in the test corpus, with only
one error after parsing. That is 9.7% of the corpus’
sentences and 5.98% of its wordforms. We found that
in 10 of these 20 sentences the only failure is caused
by one of the words listed above.
These words listed above are very important for
dependency parsing because they are usually connect-
ing major parts of the sentences. In the event of bad
parsing of one of those words, the dependency sub-
tree under these words is badly connected and for all
practical purposes the overall tree is useless.
Our hypothesis was that by enhancing local accu-
racy not only overall accuracy should be enhanced,
but end user satisfaction should be increased. We
carried out a set of experiments to confirm or reject
this hypothesis. The basic idea was to do an in–
depth study for each one of the important words listed
above. This study, as described in (Ballesteros et al.,
2010a) and (Ballesteros et al., 2010c) identified the
set of different cases in which each word could be at-
tached and labelled and a specific parser for each case
found was trained.
By doing so, we analyzed the conjunction, the
prepositions “a”,“de”,“en”, “con” and “por” and the
nexus “que”, to determine the feasibility of the tech-
nique. We found some different cases in which those
words could be attached and labelled. So we trained n
different specific parsers for covering the set of cases
given, being n = 28. After this, the test set was parsed
by combining the action of the general parser and the
28 specific parsers. This way, when parsing a sen-
tence that contains one of the words listed above, the
part of the output tree of the general parser that corre-
sponds with the “wrong” word was ignored and was
GIVING SHAPE TO AN N-VERSION DEPENDENCY PARSER - Improving Dependency Parsing Accuracy for Spanish
using Maltparser
337
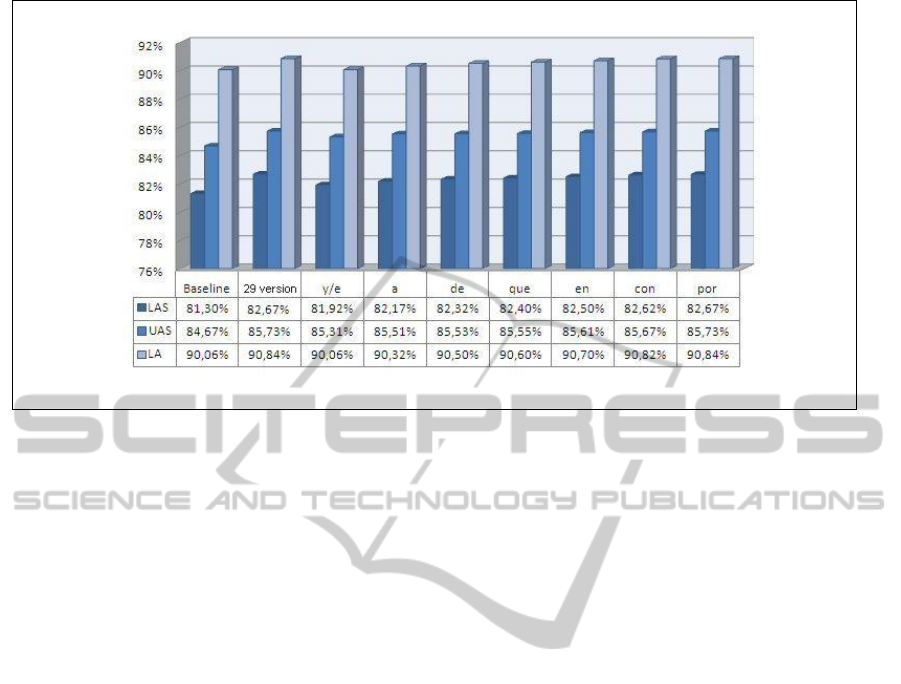
Figure 1: Improvements given by the action of the specific parsers.
substituted by the output given by the specific parser
for the given case. So the attachment and the label
given for this word by the general parser were sub-
stituted by the attachment and the label given by the
specific one. By doing so, not only local but overall
LAS, UAS, and LA were enhanced.
The results given for all these words when apply-
ing the combined action of the general and the 28 spe-
cific parsers (29-version parser) are shown in Figure
1. Our 28 specific parsers improve the results for all
the words that showed an incorrect attachment or la-
belling. These results encouraged us to build an al-
gorithm that could send each different wordform to
the most aproppriate specific parser, as shown in the
following section.
4 COMBINING THE ACTION OF
N PARSERS
Once we concluded that the combination of several
specific parsers could be a feasible technique for
improving parsing accuracy, the following step was
to develop the algorithm that makes all the specific
parsers work in synergy. That brings us to the current
point in our research and in this section we explain
the current state of this development.
4.1 The Algorithm under Development
Our approach for the algorithm that sends each differ-
ent wordform to the most aproppriate specific parser
is based on pattern matching and rules. So when a cer-
tain pattern is recognized in the sentence to be parsed,
it is sent to the most suitable specific parser by means
of a rule. For the time being, this algorithm has been
implemented only for the preposition “a” and for the
conjunction and, that in Spanish has two wordings:
“e” and “y”, because these two words are the most
frequently incorrectly parsed by the general parser. It
works as follows:
1. A sentence is parsed with the general parser
(which is trained with the same specification that
Nivre’s group published in the 2006 CoNLL–X
Shared Task (Nivre et al., 2006)). In Figure 2 we
show how the general parser parses the sentence:
Traslad
´
o el material a Madrid [he (or she) moved
the material to Madrid], we can observe that the
general parser makes an error in the node contain-
ing the preposition “a”. The correct attaching for
this node must be the main action of the sentence:
Traslad
´
o, and the correct label is “CC” that is the
adjunct of the verb. The general parser produces
an error in both things.
2. If the algorithm detects that there is a conjunction
or a preposition “a” in the sentence, it sends the
whole sentence to the most aproppriate specific
parser. Each parser is set with different specifi-
cations.
3. The selected specific parser parses the sentence.
In Figure 3 we can observe how the specific parser
parses the same sentence as the general parser
and it does not make the same error as the gen-
eral parser. In this case, the specific parser parses
correctly the node containing the preposition “a”
(nevertheless it does not correctly parse other sec-
tions of the sentence).
KDIR 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
338
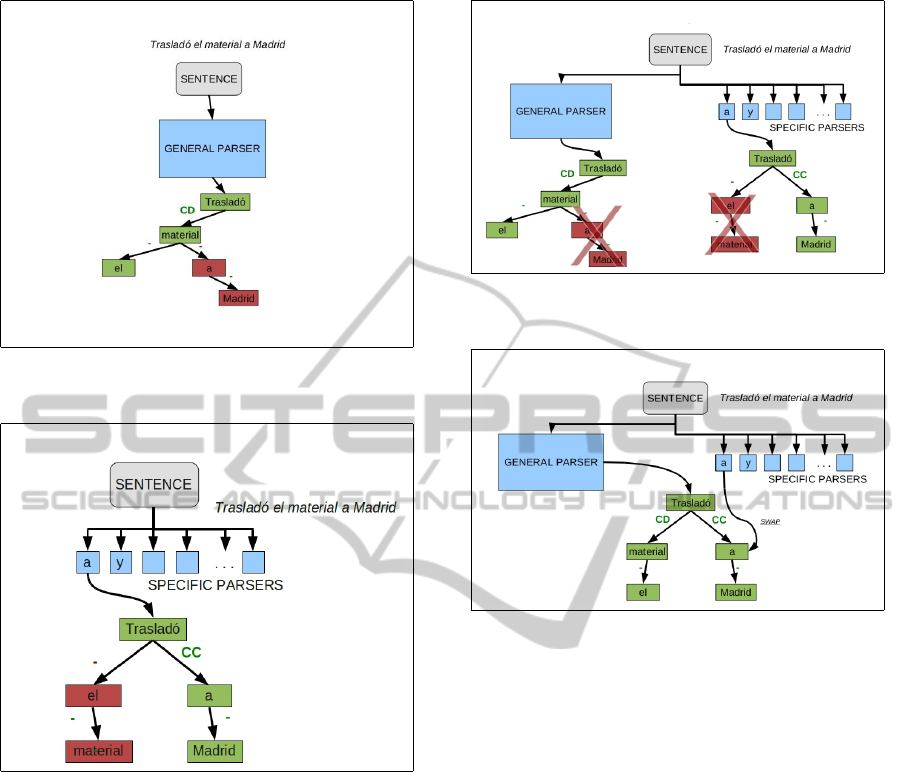
Figure 2: The General Parser parsing the sentence:
Traslad
´
o el material a Madrid.
Figure 3: The Specific Parser parsing the sentence:
Traslad
´
o el material a Madrid.
4. The algorithm removes the node containing the
conjunction or the preposition “a” from the tree
returned by the general parser. In Figure 4 we can
observe how the system avoids the useless infor-
mation given by both parsers, the general parser
and the specific one.
5. The algorithm inserts the node containing the con-
junction or the preposition “a”, produced by the
specific parser into the general parsed tree. In Fig-
ure 5 we can observe how the algorithm inserts the
node containing the preposition “a” into the tree
given by the general parser. When inserting the
node, the algorithm also inserts its subtree.
6. The algorithm returns the whole dependency tree
that is produced from the suitable combination of
the dependency trees given by the general and the
specific parsers.
Figure 4: Removing useless information given by both
parsers.
Figure 5: Swapping the node containing the preposition ‘a’
given by both parsers.
4.2 The Problems we Found
By applying the algorithm described in Subsection
4.1 we get that our n–version system incorrectly
parsed 57 conjunctions while the general parser by it-
self parsed 56 conjunctions incorrectly. For the prepo-
sition “a” we get similar results: our n–version system
parsed incorrectly parsed 50 prepositions and the gen-
eral one parsed 48 prepositions incorrectly.
These very first negative results do not mean that
the n–version technique should be rejected. An ex-
planation to this problem can be found in the AnCora
corpus. This corpus was built automatically with a
strong linguistic and manual validation step, but we
have identified some errors that still remain. For in-
stance, we realized that two sentences with the same
syntactic structure can be found in AnCora with dif-
ferent taggings, as shown in Figure 6. The sentences
of the example are the following: La prensa mostr
´
o
su afecto a los candidatos [The press showed its af-
fection towards the candidates] and La telefon
´
ıa per-
miti
´
o abrir el mercado a operadores externos [The
telephone system opened the market to external oper-
ators]. Since our approach sends both sentences to
GIVING SHAPE TO AN N-VERSION DEPENDENCY PARSER - Improving Dependency Parsing Accuracy for Spanish
using Maltparser
339
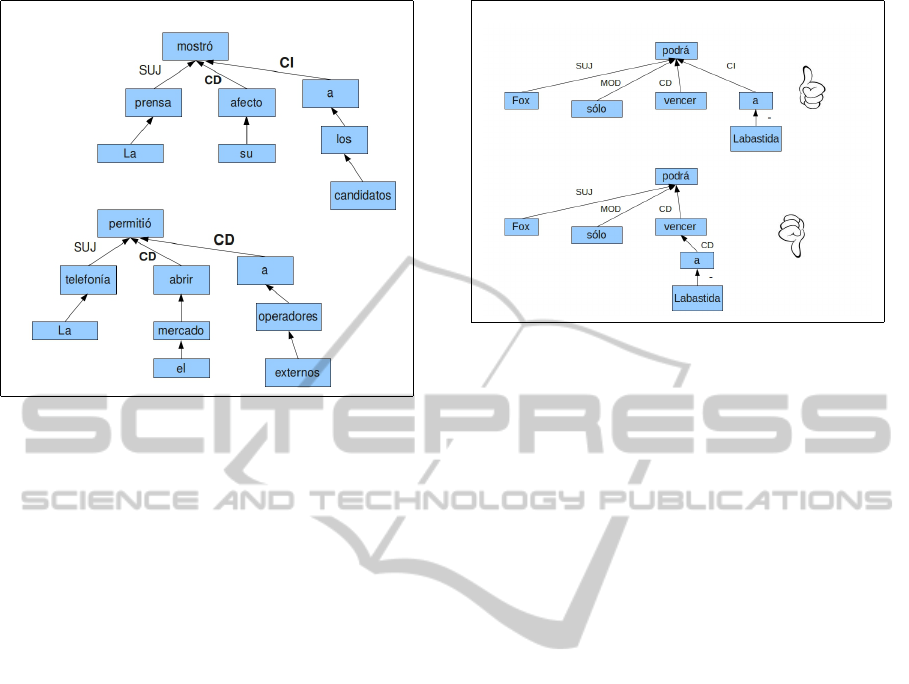
Figure 6: Two sentences with the same syntactic structure
but showing different taggings in AnCora.
the same specific parser when detecting the preposi-
tion “a”, one of them is wrongly parsed according to
the current version of AnCora, but actually it is objec-
tively well parsed.
A second example of an incorrect tagging of the
indirect object when the preposition “a” is involved
is found in the following sentence: Fox s
´
olo podr
´
a
vencer a Labastida [Fox will only be able to beat
Labastida]. This sentence has as its indirect object,
the subsentence a Labastida, but in AnCora the node
containing the preposition “a” is tagged as a direct ob-
ject. When our algorithm finds the preposition “a” in
such a context then it considers any subtree that has
“a” as its root to be an indirect object. Then, once
again we have a sentence that is formally well parsed
by the n–version parser but it is marked as wrong
in the testing process because the test corpus is not
well tagged. In Figure 7 we can observe two depen-
dency trees for the sentence Fox s
´
olo podr
´
a vencer a
Labastida, the first one is its objectively well parsed
tree and the second one is the tree contained in An-
Cora.
Thus, as seen in the previous examples, we have
the problem that we can not suitably evaluate our n–
version model because we do not have a 100% error
free corpus to compare to.
4.3 What is Next?
In spite of having a promising technique for improv-
ing parsing accuracy using Maltparser, we have a sec-
ondary problem that we have to tackle in order to
make progress. So the next step is to find and fix the
Figure 7: Bad and good ways of parsing a sentence.
errors in AnCora that impede us from correctly devel-
oping and testing the proposed n–version dependency
parsing model.
Of course, after fixing the errors found in An-
Cora we will probably find different accuracy values
to the ones presented in Sections 2 and 3. More-
over, we could find that the set of words that are more
frequently incorrectly parsed (showed in Section 3)
could change due to the enhanced training and test-
ing processes. That will lead us to develop a revision
of the set of specific parsers needed to improve the
action of the general parser and to tune the algorithm
that sends each wordform to the more suitable specific
parser.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The study described in (Ballesteros et al., 2010a) and
(Ballesteros et al., 2010c) shows that an n–version de-
pendency parser system is feasible, but there is much
work to do to have an algorithm that sends each differ-
ent wordform to the most aproppriate specific parser.
We are making progress in aquiring a fully auto-
mated n–version dependency parser able to improve
current parsing accuracy. However, this has been
hinded in one of its last steps by tagging errors found
in the train and test corpora. To solve this problem,
the most important thing is to make a strong valida-
tion step of these corpora, tagging the sentences that
follow the same structure in the same way, avoid-
ing the ambiguity. With fixed corpora our algorithm
should send the sentences correctly, and we will ob-
tain the same results given in the previous feasibil-
ity studies. Equally important, is the completion of
the algorithm that sends each wordform to the more
KDIR 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
340

suitable specific parser by implementing the rules re-
lated to the rest of the problematic words, including
the other prepositions explained in Section 3 and the
nexus “que”. In doing so we would get a real and
competitive n–version dependency parser.
A basic aspect that may be strongly consid-
ered when developing machine learning–based de-
pendency parsers is the accuracy and suitability of the
train and test corpora, this has been claimed in our
previous related work and has been observed again
during the development of the present one. Not only
does it mean that the samples must be 100% error free
tagged, but that they should be carefully selected to
ensure a high recall both in the train and the test sets.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially funded by Banco
Santander Central Hispano and Universidad Com-
plutense de Madrid under the Creaci
´
on y Consoli-
daci
´
on de Grupos de Investigaci
´
on program, Ref.
921332–953.
REFERENCES
Ballesteros, M., Herrera, J., Francisco, V., and Gerv
´
as,
P. (2010a). A feasibility study on low level tech-
niques for improving parsing accuracy for spanish us-
ing maltparser. In Artificial Intelligence: Theories,
Models and Applications, volume 6040 of Lecture
Notes in Artificial Intelligence, pages 39–48. Springer.
Ballesteros, M., Herrera, J., Francisco, V., and Gerv
´
as, P.
(2010b). Improving Parsing Accuracy for Spanish us-
ing Maltparser. Journal of the Spanish Society for
NLP (SEPLN), 44:83–90.
Ballesteros, M., Herrera, J., Francisco, V., and Gerv
´
as, P.
(2010c). Towards a N-Version Dependency Parser.
13th International Conference on Text, Speech and Di-
alogue 2010., 6231.
Buchholz, S. and Marsi, E. (2006). Conll-x shared task on
multilingual dependency parsing. In CoNLL-X ’06:
Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Computa-
tional Natural Language Learning, pages 149–164,
Morristown, NJ, USA. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Eisner, J. (1996). Three new probabilistic models for depen-
dency parsing: An exploration. In Proceedings of the
16th International Conference on Computational Lin-
guistics (COLING–96), pages 340–345, Copenhagen.
Herrera, J. and Gerv
´
as, P. (2008). Towards a Dependency
Parser for Greek Using a Small Training Data Set.
Journal of the Spanish Society for Natural Language
Processing (SEPLN), 41:29–36.
Herrera, J., Gerv
´
as, P., Moriano, P., Moreno, A., and
Romero, L. (2007a). Building Corpora for the De-
velopment of a Dependency Parser for Spanish Using
Maltparser. Journal of the Spanish Society for Natural
Language Processing (SEPLN), 39:181–186.
Herrera, J., Gerv
´
as, P., Moriano, P., Moreno, A., and
Romero, L. (2007b). JBeaver: un Analizador de De-
pendencias para el Espa
˜
nol Basado en Aprendizaje.
In Proceedings of the 12th Conference of the Spanish
Society for Artificial Intelligence (CAEPIA 07), Sala-
manca, Spain, pages 211–220. Asociaci
´
on Espa
˜
nola
para la Inteligencia Artificial.
McDonald, R., Lerman, K., and Pereira, F. (2006). Mul-
tilingual dependency analysis with a two-stage dis-
criminative parser. In Proceedings of the 10th Confer-
ence on Computational Natural Language Learning
(CoNLL–X), pages 216–220.
McDonald, R. and Nivre, J. (2007). Characterizing the er-
rors of data–driven dependency parsing models. In
Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empir-
ical Methods in Natural Language Processing and
Computational Natural Language Learning, pages
122–131. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Nivre, J., Hall, J., and Nilsson, J. (2004). Memory–based
dependency parsing. In Proceedings of CoNLL–2004,
pages 49–56. Boston, MA, USA.
Nivre, J., Hall, J., Nilsson, J., Chanev, A., Eryigit, G., Kbler,
S., Marinov, S., and Marsi, E. (2007). Maltparser:
A language-independent system for data-driven de-
pendency parsing. Natural Language Engineering,
13(2):95–135.
Nivre, J., Hall, J., Nilsson, J., Eryi
˘
git, G., and Marinov, S.
(2006). Labeled pseudo–projective dependency pars-
ing with support vector machines. In Proceedings of
the 10th Conference on Computational Natural Lan-
guage Learning (CoNLL–X), pages 221–225.
Taul
´
e, M., Mart
´
ı, M. A., and Recasens, M. (2008). Ancora:
Multilevel annotated corpora for Catalan and Span-
ish. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Lan-
guage Resources and Evaluation (LREC’08), Mar-
rakech, Morocco. European Language Resources As-
sociation (ELRA).
Yamada, H. and Matsumoto, Y. (2003). Statistical depen-
dency analysis with support vector machines. In Pro-
ceedings of International Workshop of Parsing Tech-
nologies (IWPT’03), pages 195–206.
GIVING SHAPE TO AN N-VERSION DEPENDENCY PARSER - Improving Dependency Parsing Accuracy for Spanish
using Maltparser
341
