
ONTOLOGICAL MODELLING TO SUPPORT THE PLANNING
OF IS DEVELOPMENT PROCESSES
A Position Paper
Robert T. Hughes, Graham Winstanley and Karl Cox
School of Computing, Mathematical and Information Sciences, University of Brighton
Watts Building, Lewes Road, Moulsecoomb, Brighton, BN2 4GJ, U.K.
Keywords: Project planning, Cognitive causal mapping, Process modelling, Method engineering.
Abstract: IT projects are known for the high rate at which they fail. Past work by the authors has investigated the
building of cognitive causal maps to find and represent what the participants in a project feel are factors that
lead to project success or failure. It was found that while agreement can often be reached on the broad
causes of failure, there tended to be differences about the precise nature of the identified factors (for
example the exact meaning of 'inadequate resources'). The position paper proposes the use of ontological
models to enrich and clarify causal maps with information about the classes of object in the real world to
which they refer. This would facilitate more effective planning of new projects. An aspiration of the authors
is to use the information generated by ontology-enriched causal maps to provide guidance on the tailoring of
methodologies, particularly Agile ones, for specific projects.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context and Motivation
This position paper presents a proposed programme
of work that seeks to enrich the understanding of
participants in IT projects of the factors that affect
project success and failure and the likely
effectiveness of actions aimed at promoting success.
It proposes to extend work which captures the
perceptions of stakeholders by means of cognitive
causal maps by adding ontological models to
provide details of ‘real world’ entities and their
attributes implied by the factors that have been
identified. This will support project planners by
clarifying the implications of decisions, particularly
their alignment with the outcomes sought for the
project.
There is justified dissatisfaction with the failings
of IT development projects. For example, a report on
the UK health service’s national programme for
information technology (NPfIT) noted a 30% failure
rate for IT projects. One such IT project failure in
the Wessex Regional Health Authority led to a loss
of £43millions of public money (Hendy et al., 2005).
Reducing the proportion of such failures would
clearly generate financial savings and increase the
benefits of successfully implemented projects.
One response to project failures from the
project management community has been an
emphasis on risk management – see, for example,
Boehm (1991). Risks may be the result of
uncertainty or of ignorance. In some cases, it is
difficult, if not impossible, to predict what occurs –
for example that a fire at a supplier will prevent
specialist IT equipment being delivered. However,
in many cases the risk is caused by a lack of
knowledge. An enterprise with little IT experience
might misguidedly acquire an order processing
system unsuitable for their business. The knowledge
that might have avoided this existed in the world,
but had not been disseminated to those who needed
it. It is this type of risk that is our focus.
It is acknowledged by most writers on the
management of IT projects that it requires attention
to both technical and social issues. For example,
Winter et al. (2006) recognised the inevitably
instrumental nature of much of project management
– the execution of planned activities to achieve
physical outcomes – but emphasised the need to
develop a richer understanding of the ‘concepts and
images which focus on social interaction between
people, illuminating the flux of events and human
action…’. Major projects have a range of
319
T. Hughes R., Winstanley G. and Cox K..
ONTOLOGICAL MODELLING TO SUPPORT THE PLANNING OF IS DEVELOPMENT PROCESSES - A Position Paper.
DOI: 10.5220/0003118003190324
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD-2010), pages 319-324
ISBN: 978-989-8425-29-4
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

stakeholders with distinct interests and developers
with differing expertise, each of whom is aware of
different types of risk. Sharing of viewpoints and
agreement on joint action to reduce risks is needed.
The identification of risks is futile unless projects
are flexible enough to adapt to risks. Agile
approaches address shortcomings in IT development
by measures to promote flexibility, for example,
delivering projects in smaller units with more
interaction between developers and users. However,
we believe that while Agile approaches hold great
promise as an effective way of organising
development projects, they demand a greater
common understanding of the nature and context of
the project by project participants. Our proposed
research attempts to support this understanding.
1.2 Cognitive Causal Maps (CCMs)
This new research direction has grown out of
previous work by the authors and their colleagues
which investigated ways of improving the
management of risk in IT developments – see Al-
Shehab (2007), Al-Shehab et al (2005, 2006),
Hughes et al. (2006). This work used cognitive
causal maps (CCMs) to diagnose the causes of IT
project failure. CCMs are diagrams consisting of
nodes representing the outcomes of a particular
course of action and connectors between the nodes
which indicate where some factors influence others
– see Figure 1. The technique is supported by a
research tradition starting with Axelrod’s seminal
work (Axelrod 1976). In the UK CCMs are
particularly associated with Eden and his colleagues
– see, for example, Eden (2004).
When applying CCMs to the causes of project
success and failure, some nodes represent the
desired outcomes of the project. Other nodes
represent policies, the means by which the desired
outcomes are to be achieved. Further factors are
environmental relating to conditions assisting or
hindering the achievement of the desired outcomes.
The factors are presented as ‘concept variables’
which for a context take a value within a range
bounded by two opposing poles, for example, a
range varying from an abundance of required skills
on the one hand to a severe skills shortage on the
other. Connectors are drawn between these nodes
indicating the influence – positive or negative – of
the factors on one other.
Figure 1 below describes a situation where a
shortage of staff with the skills needed for a task
means that resources available to a project do not
have the expertise envisaged when the project was
planned. (The minus sign indicates that the skill
shortage influences the second pole of
adequate...inadequate resources, i.e. makes
resources inadequate). This leads to the planned
project duration being exceeded. A policy of
additional training can, to a certain extent, offset the
problems caused by the skills shortage.
Figure 1: Notations used in a primitive Cognitive Causal
Map, following Eden 2004.
As part of our previous work, collaborative sessions
with stakeholders involved in problematic projects
were used to generate relevant CCMs. Two
problems emerged from this:
1) There might be agreement on the importance of
a factor such as ‘inexperienced staff’ or ‘poor
project management’, but with differences of
opinion about what the participants meant by
these;
2) Little guidance was generated on the practical
steps needed for success on new projects.
1.3 Adding Ontological Support to
CCMs
CCMs need details of their context to be more
effective. Recent work by Chauvin and colleagues
(2007) shows the scope for ontological models that
describe the context of CCMs. We intend to assess
this approach to ontological modelling as a basis for
enriching the data gathered from the collaborative
creation of CCMs by project stakeholders. In Figure
1, the classes of interest in a project environment
might include:
• Developers who carry out the work
• The technologies with which they are
familiar
• The activities to be carried out
• The technologies that the activities will use.
A collection of such descriptions can form the basis
KEOD 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
320
of a project management ontology. If the
participants in a project agree on this ontology, then
the potential for agreement on the meaning of
higher-level terms such as ‘adequate resources’ is
increased. This facilitates the selection of actions to
reduce or mitigate obstacles to project success.
Technology
type
Developer
Personal
expertise
Project
Actviity
Expertise
requirement
Expertise
match
1
M
1
1
1
11
M
M
M
MM
Figure 2: A fragment of an ERD to support the concept
variable adequate...inadequate resources.
A fragment of an entity relationship diagram (ERD)
which might support the concept variable
adequate...inadequate resources is illustrated in
Figure 2. A developer could be skilled in a number
of technologies which could include particular
programming languages such as Java. A project
consists of a number of activities, each of which
requires the application of one or more technologies.
The relevant expertise of a developer will depend
not just on their innate qualities but the demands of
the new project. Someone who has been highly
regarded as knowledgeable may have their expertise
reduced by the introduction of new technologies.
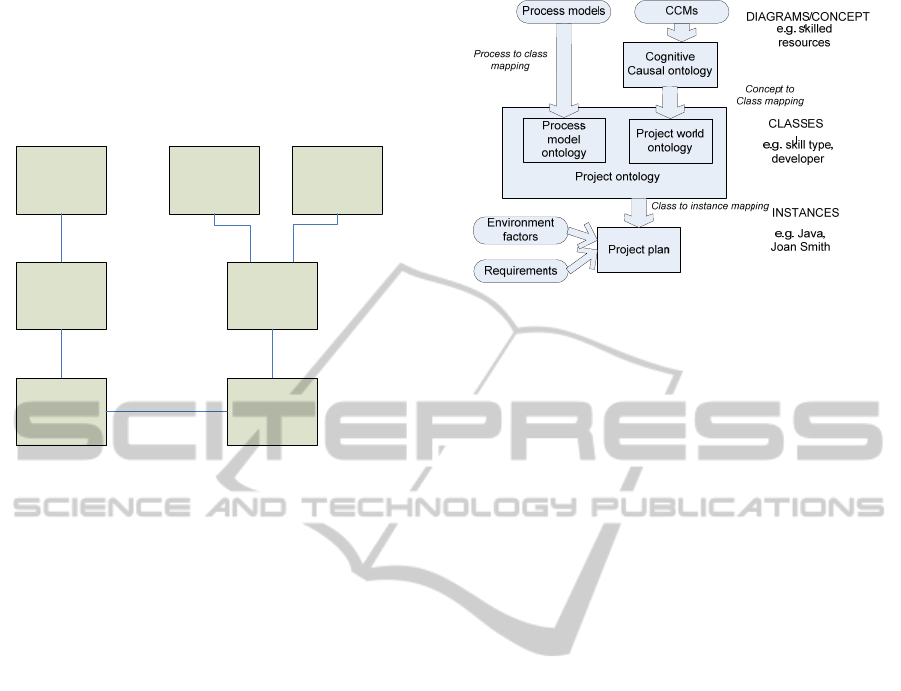
The classes in the project ontology can be
mapped to instances in the project plan. Thus a three
level structure of concept, class and instance can be
envisaged – see Figure 3. In this context ‘concept’
has a broader meaning than class and can be
composed of a number of classes and relationships.
Previous work on ontological modelling has
been mainly associated with artificial intelligence,
seminal work in the field being that of Gruber
(1995). The drive to create a ‘semantic web’
enabling more meaningful and trustworthy
information retrieval has led to a wider interest in
ontology creation.
Eden (2004) and Marshall (2009) have used
CCMs to analyse existing organisational contexts.
The proposed work will also use CCMs as an
investigative tool, but will in addition follow some
of the relatively few examples (most prominently
Abdel-Hamid 1988) where CCMs have been used to
Figure 3: Relationships between a CCM, a Project world
ontology and a project plan.
construct decision-making tools. Techniques have
also been developed which trace linkages between
business objectives and the IS/IT developments
needed to support them (Bleistein et al. 2004, 2006a,
2006b, Babar et al. 2008). These use a CCM-like
goal modelling notation, but generate guidance on
what is to be developed whereas the current work is
concerned with how.
Some ontological modelling techniques are
similar to those of database specialists. Methods in
use in the construction of object-oriented software
are applicable to ontology construction (De Nicola et
al 2009). Conventional data modelling may be
adequate, but a pragmatic advantage of a specifically
ontological approach is that it facilitates the
incorporation of existing project-related ontologies,
for example, PROMONT (Abels et al. 2006),
PLANET (Gil and Blythe 2000) and KANAL (Kim
and Gil 2001), into new ontologies either directly or
in a modified form.
Some research has developed more rigorous
forms of CCMs where the strengths of factors and
the links between them are expressed numerically
and the models executed to produce predictions
(Abdel-Hamid 1988). One middle way uses a fuzzy
quantitative approach (Stach and Kurgan 2004). Our
own work has made extensive use of fuzzy
quantitative mechanisms developed by Montibeller
et al. (2007) to describe, through reasoning maps,
expert decision-making processes. The emphasis on
the new direction of our research is to make CCMs
created in conjunction with stakeholders more useful
by increasing their semantic richness, rather than
simply attempting to quantify factors which may in
any case lack clear definition.
Agile project management is a good fit with the
aspirations of the new work as it emphasises the
tailoring of project processes to fit the project’s
context. The focus will be on DSDM/Atern (DSDM
ONTOLOGICAL MODELLING TO SUPPORT THE PLANNING OF IS DEVELOPMENT PROCESSES - A Position
Paper
321

2007) because: it is applicable to a wider span of
IS/IT development activities than approaches such
as XP (Beck and Andres 2005) which focuses only
on software code production; it has a relatively wide
user base in the UK and, pragmatically, the project
team have links with DSDM/Atern practitioners.
DSDM/Atern is characterised by: (i) The initial
formulation of requirements in terms of the business
objectives to be met by a development; (ii) the
division of the product delivery into increments,
each of which should achieve the deployment of
usable system components generating user benefits
and (iii) the prioritisation and allocation of
requirements to increments with fixed deadlines.
The second Agile approach to be considered will be
Scrum (Schwaber 2007), which, like DSDM/Atern,
is not focussed exclusively on software code
development. Scrum appears to emphasise the
behavioural aspects of projects, compared to the
DSDM/Atern concern with process. The
examination of more than one approach encourages
the development of more generic and robust research
outcomes.
2 RESEARCH QUESTIONS
We propose that CCMs enriched by ontological
modelling can support more effective decision-
making by those planning and managing IT projects,
particularly projects that use an Agile approach. To
confirm this, we believe the following research
questions will need to be addressed:
R1. How can project processes be most
effectively represented as ontologies?
R2. Can ontological models effectively capture
cause-and-effect relationships?
R3. Can ontological models be created which
clarify the perceptions of a project captured by a
CCM?
R4. To what degree can ontological models
usefully support tools and operations at the level of
practical project planning and management?
These four questions will be discussed in turn in
the next four sections.
2.1 How can Project Processes be Most
Effectively Represented as
Ontologies?
A methodology contains a set of recommended
(sometimes mandatory) steps for carrying out a
procedure. It may be a codification of good practice
or be mandated by an authority (as with the
PRINCE2 project management standard in UK
government projects). Any method will inevitably
have to be ‘fine-tuned’ for local use (Fitzgerald et al.
2003). We have already established the feasibility of
representing project processes in an ontological
model (Hughes 2010). We now need to find a way
of not only modelling core work practices in an
ontology, but also variations on that core.
We believe that Höfferer (2007) provides
valuable guidance on deriving ontologies for
processes. Processes can be modelled for an instance
of a project (level M
0
), e.g. a plan. At the next
highest level (M
1
), activities and other project
characteristics can be generalised to cover a class of
projects – e.g. as a software development lifecycle.
A metamodel (M
2
) can further generalise to
superclasses – for example, ‘design’, ‘build’ and
‘test’ can be generalised as instances of ‘activity’.
This procedure will be applied to the two Agile
process models DSDM/Atern and Scrum, with
separate level M
1
models for the two approaches,
and then an attempt at a level M
2
model of a general
Agile project model. The resulting models will be
validated by populating them with sample instance
(level M
0
) data from specific project scenarios.
These procedures implement the process to class
mapping transition from process model at the
Diagram/Concept level in Figure 3 to the Process
Model Ontology at the Classes level.
2.2 Can Ontological Models Effectively
Capture Cause-and-effect
Relationships?
Although we often generalise the idea of causality,
different cause-and-effect relationships involve
different processes. Some are physical processes,
e.g. ‘fire destroys data centre’, others matters of
human motivation, e.g. ‘better job opportunities
cause staff departures’. These differences are
noticeable when trying to combine the different
influences on a particular concept variable: in some
cases both A and B are needed to cause an effect
(e.g. a reliance on external resources and a shortage
of those resources), in other cases either A or B (e.g.
an increase in costs or a decrease in income).
Our experience with CCMs leads us to believe
that the types of causality identified in CCMs need
to be more carefully analysed. Some guidance on
this may clearly come from the literature on
causality – one obvious source is Pearl (2000). Our
aspiration is to create a causal taxonomy to be
incorporated into the process-oriented ontologies
identified above. This is part of the concept to class
transition from CCMs to Cognitive Causal ontology
in Figure 3, but relates only to the categorisation of
KEOD 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
322

linkages at CCM Concept level and equivalent
properties at Class level.
2.3 Can Ontological Models be Created
which Clarify the Perceptions of a
Project Captured by a CCM?
The successful construction of the envisaged
ontologies depends on effective modelling of
stakeholder perceptions. Existing ontological
modelling tools are usually not designed primarily
for easy communication with subject specialists. We
need a way of identifying and eliciting the
information needed to obtain a clear understanding
of the influences on a project. Ultimately some form
of online collaborative development of ontologically
enhanced CCMs would be desirable, but to achieve
this we need ways of establishing ontological
commitment, that is, agreement on the terminology
to be used and the way that a project is to be viewed.
Established methods (see Al-Shehab et al 2005)
will be used to create preliminary CCMs capturing
overall project objectives, environmental factors and
policies. A ‘straw man’ Project World ontology will
be created from existing sources such as PROMONT
(Abels et al 2006) which will describe the generic
classes of object that would be expected in the
context of a project. Classes in this ontology will be
mapped to concepts in the CCM ontology. Chauvin
et al (2007) describe a way of enriching CCMs with
contextual information which provides a basis for
this work. The initial prototype will be evaluated and
modified through a series of test-analyse-modify
iterations. Once again populating the resulting model
with data from real world projects will form the
basis of the validation. This would implement the
class to instance transition in Figure 3.
2.4 To what Degree can Ontological
Models usefully Support Tools and
Operations at the Level of Practical
Project Planning and
Management?
The research questions above address the feasibility
of representing processes and what are effectively
ontologically-enhanced causal maps as ontological
models. It remains to establish the actual usefulness
of these. We need to know if it is possible to adapt
existing tools and techniques, or develop new ones,
that use knowledge captured in the ontologies to
support typical project planning and control tasks.
The extent to which guidance on decision-making –
for example the selection of methods to execute the
project – can be provided needs to be assessed.
The starting point for this is the identification of
tasks and key decisions involved in planning a
project, initially by examining existing practitioner
and academic literature. Recognised guidelines
supporting project method configuration need to be
analysed to assess the extent to which the knowledge
held in the project ontologies, in conjunction with
heuristics, can offer useful advice the optimal
configuration of an Agile method for a particular
project. Karlsson’s and Ågerfalk’s (2009) work
which uses goal-modelling as a basis for Agile
method configuration provides a guidance on a
possible way forward. We need however to be aware
that each development project that claims to be
guided by a particular process model, may interpret
the model in a different way or may modify it to fit a
particular context.
3 CONCLUSIONS
This proposal is not just an engineering project to
create a prototype artefact that might then be
‘commercialised’. Rather it is the development and
integration of a set of interlocking techniques –
many of which already exist although some are in a
rudimentary or fragmentary form – and, where
appropriate, supporting prototype tools.
It can be envisaged that a potential user might
have difficulty simply plugging in such a tool and
then trying to use it effectively. The use of the
techniques and tools by a wider community would
depend on the acquisition of means-end reasoning
skills. It could be argued that the promotion of such
skills would itself be beneficial in many fields
including planning.
Some researchers will find that the ontological
modelling of processes by itself can be usefully
applied to a broad range of process scenarios beyond
the Agile development methods that are the subject
of the proposed work. The practical application of
contextualised CCMs is of use to researchers in
broad range of social science and other applications
who wish to document their theories in a structured
way which is sensitive to context. Software
engineers may be particularly interested in the
greater opportunities for informed method tailoring
that this work promises.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The development of many of the ideas in this paper
were developed as part of the University of Brighton
ProposalNet initiative. We would like to thank
ONTOLOGICAL MODELLING TO SUPPORT THE PLANNING OF IS DEVELOPMENT PROCESSES - A Position
Paper
323

fellow participants and the facilitation of the events
by Professors Jacqueline Reilly and Howard Rush.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Hamid T. K. 1988. Understanding the '90% syndrome'
in software project management: a simulation-based case
study, in Journal of Systems and Software. vol. 8, pp.
319-330.
Abels S., Ahlemann F., Hausman K., and. Strickman J. 2006.
PROMONT - A project management ontology as a
reference for virtual project organizations," in OTM
Workshops, pp. 813-823.
Al-Shehab A 2007 Causal and cognitive mapping methods
for the identification of risk in information development
projects: PhD dissertation. Brighton: University of
Brighton.
Al-Shehab A., Hughes R. T., and Winstanley G. 2005
Facilitating organisational learning through causal
mapping techniques in IS/IT project risk management .
Lecture Notes in Computer Science Lecture vol.
3782/2005 145-154,Springer-Berlin, pp. 145-154.
Al-Shehab A., Hughes R. T., and Winstanley G 2006
CorMod: a causal mapping approach to identifying
project development risk. Proceedings of European and
Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems
(EMCIS).
Axelrod R. 1976 Structure of decisions: the cognitive maps of
political elites. Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press,.
Fitzgerald B., Russo N. L., and O'Kane T. 2003 Software
development method tailoring at Motorola, in
Communications of the ACM. ACM, vol. 46: pp. 65-70.
Babar A., Cox K., Tosic V., Bleistein S. and Verner, J. 2008
Integrating B-SCP and MAP to manage the evolution of
strategic IT requirements. Information and Software
Technology. Elsevier. vol. 50. pp. 815-831.
Beck K. and Andres C. 2005. Extreme programming
explained: embrace change 2nd ed. Boston, MA, USA:
Addison-Wesley
Bleistein S., Aurum A., Cox K., and Ray P. (2004). Strategy-
oriented alignment in requirements engineering: linking
business strategy to requirements of e-business using the
SOARE approach. Journal of Research and Practice in
Information Technology. vol. 36. no. 4. pp. 259-76.
Bleistein S., Cox K., and Verner J. 2006a Validating strategic
alignment of organizational IT requirements using goal
modelling and problem diagrams. Journal of Systems and
Software. vol. 79. no. 3. pp. 362-78.
Bleistein S., Cox K., Verner J., and Phalp K. 2006b B-SCP: a
requirements analysis framework for validating strategic
alignment of organizational IT based on strategy, context
and process, in Information and Software Technology.
vol. 48. no. 9. pp. 846-868.
Boehm, B. W. 1991. Software risk management:
principles and practices. IEEE Software. : IEEE vol. 1 pp.
32-41.
Chauvin L., Genest D., Loiseau S.2007 Le modèle des cartes
cognitives contextuelles Annals du LAMSADE no 8
pp 285-292
De Nicola A., Missikoff M., and Navigli R.2009 A software
engineering approach to ontology building. Information
Systems. vol. 34: Elsevier, pp. 258-275.
DSDM, 2007. DSDM Atern Pocket Book Ashford: DSDM
Consortium
Eden C. 2004 Analyzing cognitive maps to help structure
issues or problems. European Journal of Operational
Research. vol. 159, pp. 673-686.
Gil Y. and Blythe J. 2000 PLANET: A shareable and
reusable ontology for representing plans. Proceedings of
AAAI Workshop on representational issues for real-world
planning systems at 17th National Conference on
Artificial Intelligence Austin, Texas, USA.
Gruber T. R. 1995. Toward principles for the design of
ontologies used in knowledge sharing. Int. J. Human-
Computer Studies. Academic Press, vol. 43 pp. 907-928.
Hendy, J., Reeves B. C., Fulop N., Hutchings A., and
Masseria C. 2005. Challenges to implementing the
national programme for information technology (NPfIT):
a qualitative study.British Medical Journal. Britisth
Medical Association vol. 331 pp. 331-4.
Höfferer, P. 2007 Achieving business process interoperability
using metamodels and ontologies , in H. Sterle, J. Schelp,
R. Winter, eds Proceedings of the 15
th
European
conference on information systems (ECIS2007) pp 1620-
31 Univerity of St. Gallen, Switzerland
Hughes R. T., Al-Shehab A., and Winstanley G.
2006.Obstacles to the modelling of the causes of project
success and failure systems. European Conference on
Research Methods in Business and Management. Trinity
College, Dublin: MCIL,
Hughes, R.T. 2010. Project management process ontologies: a
proof of concept. Proceedings of the 15
th
annual
conference of the UK Academy of Information Systems,
Oriel College, Oxford 23-24 March
Karlsson F. and Ågerfalk P. 2009 Exploring agile values in
method configuration . European Journal of Information
Systems. vol. 18, Palgrave Macmillan,.pp. 300-316
Kim J. and Gil Y. 2001. Knowledge analysis on process
models. Proceedings of International Joint Conference
on Artificial Intelligence pp. 935-942.
Marshall N. 2009. Cognitive and practice-based theories of
organisational knowledge and learning: incompatible or
complementary? Management Learning. Sage
Publications. vol. 39. no. 4. pp. 413-435.
Montibeller G., Belton V., Ackermann F., and. Ensslin L.
2007. Reasoning maps for decision aid: an integrated
approach for problem-structuring and multi-criteria
evaluation Journal of the Operational Research Society.
vol. 59, pp. 575-89.
Pearl, J. 2000 Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference.
Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
Schwaber K. 2007 The Enterprise and Scrum. Redmond,
Washington: Microsoft Press.
Stach W. and Kurgan L. 2004.Modelling software
development projects using fuzzy cognitive maps.
Proceedings of 4th ASERC Workshop on quantitative and
software engineering Banff AB
Winter M., Smith C., Morris P., and Cicmil S. 2006.
Directions for future research in project management: the
main findings of a UK government-funded research
network, International Journal of Project Management.
Elsevier, vol. 24 pp. 638-649.
KEOD 2010 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
324
