
SOFTWARE-ASSISTED IMPROVEMENT OF SURGICAL
MANAGEMENT AT CARLOS HAYA REGIONAL
UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MALAGA, SPAIN
Julio Díaz, Juan Cano
Hospital Regional Universitario Carlos Haya, Avda. Carlos Haya, s/n, Málaga, Spain
Adolfo Jiménez, Antonio Alonso
Hospital Regional Universitario Carlos Haya, Avda. Carlos Haya, s/n, Málaga, Spain
Keywords: Performance, Operating rooms, Surgery, Waiting lists, Management, Software.
Abstract: This paper reports the features of a computer program (AQuA) developed to improve surgical management
at the Carlos Haya Regional University Hospital in Málaga, Spain. Several factors have forced the devel-
opment of this digital solution: i) our hospital is made of four buildings some 5 km apart, ii) there are 41 op-
erating rooms attended by 319 surgeons and 72 anaesthesiologists and, most important, iii) some predefined
pathologies are protected by law in our region and have a guaranteed limited waiting time (LWT) before
surgery. In this complex milieu our program was conceived, developed and put to work. It has been running
for just over a year with progressive implementation in surgical departments. Some facts that seem to indi-
cate the usefulness of the program: the number of patients with diseases with LWT that have received op-
erations has increased in 14 months from 1,145 to 1,564 patients/month (36.59% increase) and surgical per-
formance has increased from 65.93% to 71.80% in the same period. Since all other conditions related to
surgical activity have remained unchanged the improvement seems to be attributable to the AQuA program.
AQuA is a comprehensive, flexible, friendly and open program capable of dealing with most hospital set-
tings.
1 INTRODUCTION
The arrival of Information Technologies has pro-
vided a very powerful tool in many areas of society.
In health services, where there is a permanent social
demand to improve its quality, the application of
information technology is one of the key elements
that can help improve management, optimize re-
source utilization, better control of health spending
and, consequently, offer better services to society.
(Informe SEIS, 2010).
In the past 15 years, the Spanish health institu-
tions have incorporated many experiences leading to
an improvement in the know-how in technological
terms. This strategy is just beginning to provide
results. (Gutiérrez, 2009).
A successful implementation of these technolo-
gies will enable institutions to make significant steps
towards achieving greater efficiency.
The hospital environment generates large
amounts of information of different nature (clinical,
administrative, management, etc.) which need to be
processed.
The trend is to manage that information in a way
that allows on one hand, increase process efficiency
and on the other, making it available securely from
any location. In addition, analysis of information is
particularly useful for improving medical knowledge
and making the most appropriate management deci-
sions. (Informe SEIS, 2007).
Surgical treatment is not only vital to the
achievement of the objectives of the hospital but is
also the centre of many inter-related activities.
In addition, the resolute character of surgery
makes it a first-rate care component being the oper-
ating room one of the more expensive and scarce
resources of a hospital. The operating room, with its
high concentration of technology and highly quali-
131
Díaz J., Cano J., Jiménez A. and Alonso A..
SOFTWARE-ASSISTED IMPROVEMENT OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT AT CARLOS HAYA REGIONAL UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MALAGA,
SPAIN.
DOI: 10.5220/0003112401310137
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2011), pages 131-137
ISBN: 978-989-8425-34-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

fied personnel, usually becomes the bottleneck of
clinical practice.
But the surgical activity also creates a great de-
mand and it is difficult to accommodate such de-
mand at the optimum level required by the user, so
the waiting lists generated must be controlled and
monitored.
In-depth knowledge of the surgical activity be-
comes, therefore, the key to the hospital manage-
ment. Two main elements form the backdrop: surgi-
cal waiting list and activity of operating rooms.
1.1 The Surgical Waiting List
In hospitals of the Andalusian Public Health System
a computerized record system is in use since 2001
called AGD. It is configured to monitor the proce-
dures covered by the “surgical delay time assurance
program". These delay times were established taking
into account the relative frequency of the relevant
processes in the local population and their clinical
relevance. Data recorded in this system is transpar-
ent for both the patients and the health authorities.
The AGD is therefore a list of users awaiting for
a surgical intervention. The time in the waiting list is
guarantied by regional laws to a maximum of 180
days. Meeting this deadline has proved to be a diffi-
cult task. (SAS, 2010).
1.2 The Activity of Operating Rooms
The operating rooms are one of the areas that gener-
ate the largest costs to a hospital as they consume
about 15 percent of the budget. (Quecedo, 2009).
It has been estimated that the optimal occupancy
rate of surgical block should be around 85 percent
and that every unit of percentage below 85 costs
€10,000 per operating room and year. In other words
the drop of surgical rate in one unit means loosing
11 surgical interventions per operating room per
year.
Therefore, the surgical block inactivity causes a
loss of considerable economic and social opportu-
nity, so it is essential to increase production capacity
and performance of the surgical block through
knowledge of the actual time of use of operating
room and their shortcomings for efficient manage-
ment.
1.3 The Need for a Change.
AQuA, not to Sink but to Float
Until recently the Carlos Haya Regional University
Hospital in Malaga was not supported by any com-
puter application that integrates the four key aspects
of the surgical schedule:
1. Waiting list (AGD) and some other processed
outside the AGD.
2. Management of operating rooms assigned by
the Medical Director.
3. Anaesthesiologists Planning.
4. Preoperative visit carried out by the
anaesthesiologist.
The computer application covered by this paper
aims to improve the efficiency of the operating
room, assisting the surgical schedule to sort out the
availability of operating rooms. This action will
prevent a bottleneck. (Ramolla, 1999).
We must also mention the point in time where
this program has been implemented. One of the
barriers that traditionally stood in the way of pro-
gress for implementation of information technology
was the health staff. (Riesgo, 2007). Currently, this
staff has evolved and is now more receptive to new
information technologies.
Among them, the "doctors", which have tradi-
tionally been the major obstacle, now show a more
positive disposition towards informatics. This posi-
tive attitude is a conditioning factor for the imple-
mentation of medical bioinformatics since they now
accept that their role goes beyond the cure.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 The Structural Complexity of our
Hospital
Carlos Haya Regional University Hospital is a pub-
lic institution belonging to the Andalusian Autono-
mous Community. For historical, reasons it is organ-
ised in four major buildings some 5 km apart from
each other, three of them with surgical activity. All 4
buildings are under the same management and cover
for the health needs of the east of Malaga (348,656
inhabitants). In addition it is “reference for the prov-
ince” (1,517,523 inhabitants) for obstetrics end pae-
diatrics matters and “reference for the region” in 5
surgical and 6 medical specialties, including trans-
plants.
The main building (A) has 590 beds, 15 operat-
ing rooms and 141 surgeons. It houses the most
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
132

15 operating rooms
141 surgeons
8,000+ operations/year
13 operating rooms
12 delivery rooms
98 surgeons
9,000+ operations/year
13 operating rooms
80 surgeons
10,000+ operations/year
21 surgeons
Figure 1: The complexity of our hospital complex.
complex medial and surgical specialties. Building B
(women and children) has 520 beds and 13 operating
rooms. Building C has 147 beds and 13 operating
rooms. The activity of this building focuses on alter-
natives to traditional hospitalization such as major
ambulatory surgery and short stay surgery. Building
D is a high-resolution outpatient service.
The name given to the program presented in this
paper is AQuA (Actividad QUirurgica Asistencial =
Surgical Care Activity) and its task is to facilitate the
flow of patients awaiting for surgical intervention
taking into account all these factors, allowing simul-
taneously complete freedom to clinicians to intro-
duce exceptions whenever necessary, as outlined in
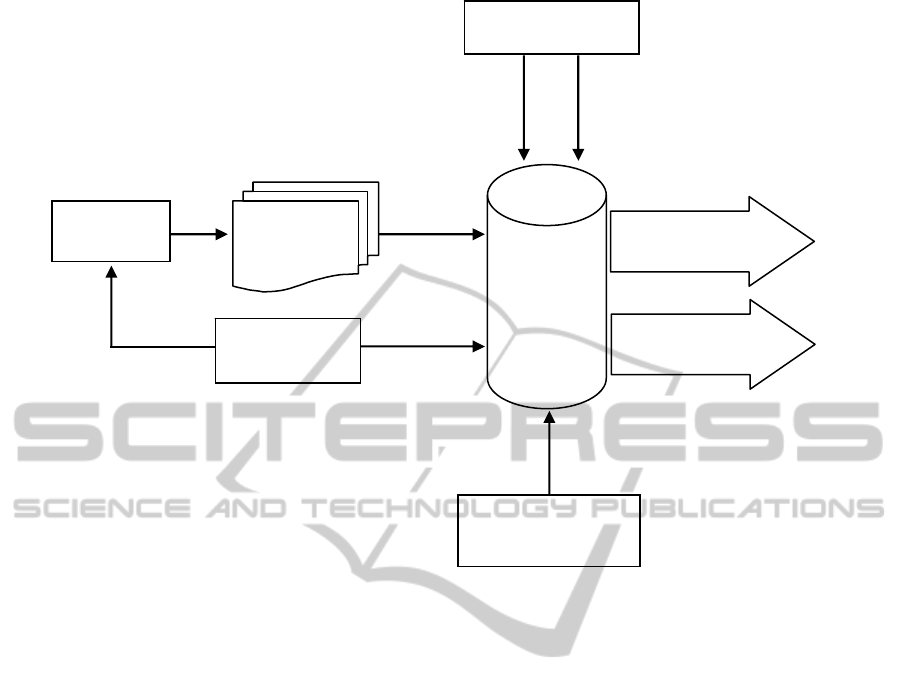
figure 2.
Once the relevant surgical specialist has decided
to operate the patients enter an unique waiting list
but with some privileges, i.e., some predefined pa-
thologies are protected by law in our Autonomous
Community and have limited waiting time (LWT)
before surgery.
Two categories of LWT exist, 180 and 120 days.
The system is so strict that if the public social
security hospital does not meet the corresponding
LWT the patient is free to seek care at a private
hospital and pass the cost to the Social Security
administration.
Needless to say the complexity of organising the
surgical activity in such a complex multi-building
hospital with the legal limitations of maximum LWT
for many pathologies.
In this setting AQuA was conceived, produced
and put to work with a great success as outlined
below.
2.2 The AQuA Program.
Applied Technology
AQuA has been designed for ORACLE database,
with client-server technology, and developed in a
modular programming in Object-Pascal language
under the Delphi platform, making the maximum
use of object-oriented paradigm, and the environ-
ment Fast Reports generator.
The general features of AQuA are:
1. Capture and transfer of data daily from the
patients’ waiting list, with control and error
correction, allowing automatic loading system
that coordinates the input and update of new
data on patients enrolled in the centralized
waiting list (AGD). This allows simultaneous
and permanent updating in AQuA of local
data.
Any discrepancies in patient identification,
diagnostic code, procedure or prescribing
physician, is detected and corrected immedi-
ately. In addition to CIE9MC encoding, si-
multaneous descriptions of diagnostic and
procedures with terminology of the relevant
department can be used.
2. Multifunctional management of waiting lists
by the relevant services.
Complete treatment in a single screen of pa-
Surgical
waiting lists
A B
AQuA
Hospital
management
72 anaesthesiologists
Clinical Laboratory
Radiology
Morbid anatomy and others
C
D
SOFTWARE-ASSISTED IMPROVEMENT OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT AT CARLOS HAYA REGIONAL
UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MALAGA, SPAIN
133
AQuA
Operating
rooms
assignment
Operatingrooms
schedule
Anaesthesiologist
assignment
Pre‐anaesthesia
checkup
Hospital
management
Anaesthesiology
Waitinglists
withlimited
waitin
g
time
Customer
service
Automatic
download
Operatingrooms
programming
Surgical
indication
Surgical
Departments
Surgical
reports
Figure 2: AQuA general’s scheme.
tients’ waiting list for every department, with
interactive upward and downward classifica-
tion of any column.
Classifications and searches can be done us-
ing multi-filters with more than 10 different
criteria simultaneously, that allow shortening
the list by physicians, diagnostic procedures,
anaesthesia and waiting times.
It includes two main choices:
Current status of approval by the an-
aesthesiologist
Date of appointment for the Pre-
Anaesthesia check.
The possibility of filtering and sorting data
provides a transcendental tool not only for
printing but also for exporting information to
spreadsheets for further internal or external
treatment.
At the same time, each patient record is in-
terconnected with the applications that pro-
vide their medical history, radiology and
laboratory tests and an intercom service be-
tween relevant hospital areas dealing with
major events related to that patient.
3. Control of pre-operative anaesthesia appoint-
ments.
Daily or periodical planner of pre-operative
anaesthesia appointment, (from where alloca-
tion is channelled approval of anaesthesia) or
any other important fact about the patient.
Access to patient history and tests is also al-
lowed from this position.
Scheduled assignment of anaesthesiologists to
relevant surgeries. It is carried out by the head
of department of anaesthetics. Through a
simple drag-and-drop system, anaesthesiolo-
gists are assigned to an operating room on any
date. Holidays, sick leaves, and others, are
taken into account by the program.
4. Management of surgical lists
This process allows a fast programming of
any surgery once the operating room features
and type of activity are configured.
The user just “captures” the patient from
the Department’s waiting list (or from any
other Dept, privileges necessary).
After that, simply assign the surgical team,
intervention order and any necessary en-
dorsement, as blood supply, reserve bed in in-
tensive care or preparation of special instru-
ments needed.
It allows the immediate transfer of the pa-
tient from an operating room to any other
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
134

available operating room, provided the cur-
rent user has the relevant privileges to access
it.
The surgical list is now ready for printing
and copies of it (hard or soft) will be distrib-
uted to the different areas involved: operating
rooms, general services, blood bank and hos-
pital management, amongst others.
5. Operating Room Module
It is a window that shows the surgical activity
scheduled for that current day. It allows navi-
gation between operating rooms and patients.
Information can be classified by both criteria
and reports permanently in a colourful fashion
of the situation of every patient.
This module is the gateway to the “Man-
agement of Surgical Intervention" or the form
based on the WHO’s “Surgical Safety Check-
list” (World Health Organization, 2008).
6. Management of surgery in all aspects and
professional areas: Medical, Nursing, Anaes-
thesiology.
It is a complete record of the events that occur
and actions taken during surgery.
Collects information produced by the an-
aesthesiologist, surgeons and nurses, allowing
a reconsideration of the original diagnoses
and procedures, as well as adding secondary
diagnoses and procedures.
The result is the dynamic creation of a re-
port that finally becomes the “discharge re-
port” in patient undergoing major ambulatory
surgery and the “surgery report” in the rest of
patients.
This report is supplemented with many aux-
iliary procedures: contextual help in drafting
parts of the report, issuing labels, generation
of department-specific documents, direct ac-
cess to the patient's history, processing of ur-
gent intra-operative biopsies, registration of
any prosthetic implants used, etc.
If circumstances had forced the depro-
gramming of an intervention the AQuA pro-
gram requests accurate information about the
causes involved enabling a later analysis of
the situation.
Every department involved can create a set
of complementary documents that can be re-
trieved from this screen in a privilege-
dependent fashion.
7. Patients’ module with full integration with the
relevant hospital applications.
A powerful search engine provides access to
the patient’s administrative data, from which
the medical history, the waiting list, addi-
tional tests, and others, can be accessed.
Some other documents can easily be gener-
ated within AQuA, i.e. the patient’s written
consent.
Urgent surgery can be directly entered indi-
cating the appropriate operating room. The
patient’s surgical history and the relevant re-
ports can be seen from this screen.
8. Management of patients already operated
AQuA is connected with the hospital central-
ized program dealing with “appointment for
surgery”. When surgical intervention is com-
pleted or a definitive deprogramming takes
place the patient is withdrawn from the wait-
ing list for that particular surgery. Other pos-
sible surgeries in the waiting list for the same
patient are not affected.
This process also allows for the gradual im-
plementation of the program because it will
temporarily close a surgical intervention to
provide statistical information immediately,
without having to fill in all the clinical infor-
mation of the intervention.
9. Total security management.
Management of events (logs) with users
maintenance, access profiles and access con-
trol to the program and/or each of the options
that have been considered necessary to con-
trol.
10. Statistics module
Large catalogue of statistical modules. Dy-
namic listings and 100% integrated exporta-
tion of data to Excel, Dbase, Paradox and text
formats.
2.3 Results
The AQuA program has been designed and devel-
oped to work in and within our hospital. Nonetheless
a great effort has been made to produce an open
program adaptable to a variety of settings. The aim
of presenting it in this HEALTHINF 2011 Confer-
ence is to seek suggestions to improve a final ver-
sion able to fully accommodate to any demands.
The program used has been implemented pro-
gressively in different hospital departments as it was
produced. Many changes, improvements and correc-
tions have been made along the way. It has been a
difficult task, not only by the intrinsic complexity of
surgical activity but also by the multi-building lay-
SOFTWARE-ASSISTED IMPROVEMENT OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT AT CARLOS HAYA REGIONAL
UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MALAGA, SPAIN
135
out of our hospital. But today we are proud of pre-
senting a comprehensive program covering any
possible aspect of surgical activity.
If there is a point that reflects the usefulness of a
program, beyond the obvious result, that is its ac-
ceptability. This program has spread along the hos-
pital with a tremendous avidity. Its easy friendly use
and the fact that many users had had the opportunity
to introduce or change an aspect concerning their
particular activity has paved the way to success.
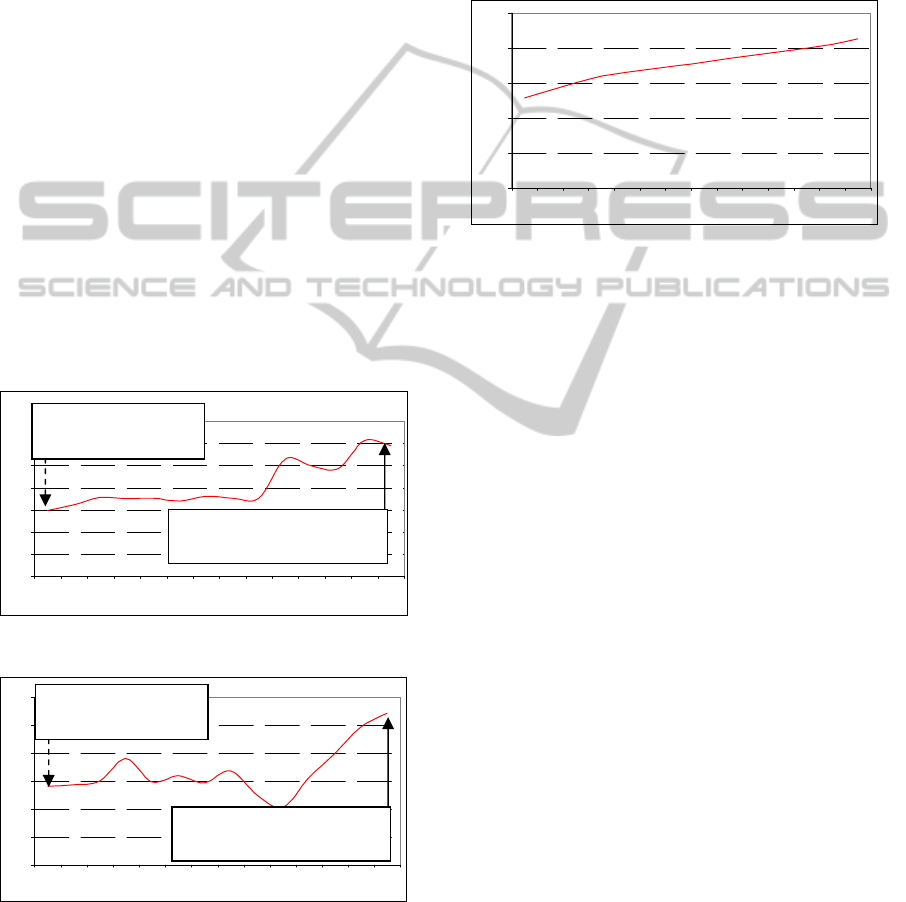
The operating rooms' performance has increased
progressively since the introduction of the program.
The vertical dotted arrow in figure 3 indicates the
point at which the program started running in two
surgical departments and the continuous arrow indi-
cates the point when 75% of the surgical activity
was under the control of AQuA. As a whole, from
launching in April 2009 to date the surgical per-
formance has increased from 65.93% to 71.80%.
Since any other conditions related to surgical activ-
ity have remained unchanged the improvement
seems to be attributable to the AQuA program.
Figure 4 shows the percentage of patients oper-
ated on before 90 days of waiting time, from April
2009 to May 2010. As can be seen the percentage
has increased from 54.06% to 67.13%.
60%
62%
64%
66%
68%
70%
72%
74%
ap
r
'
09
may'
09
j
u
n'
09
j
u
l'09
au
g
'
09
se
p
'
09
oct'
09
n
ov
'
09
dic
'
09
e
ne
'
10
feb'
1
0
ma
r'1
0
a
pr'10
may'10
Figure 3: Operating rooms performance.
40%
45%
50%
55%
60%
65%
70%
apr'09
may
'
0
9
jun'09
jul'09
a
ug
'
0
9
s
e
p'09
oct'09
nov'
0
9
dic
'
09
e
ne
'
1
0
feb
'
1
0
mar '10
a
pr'
1
0
m
ay
'10
Figure 4: Patients operated within 90 days from diagnosis
(%), from April 2009 to May 2010.
Finally, it is important to note that the number of
patients with diseases with guaranteed limited wait-
ing time, that have received operation, has increased
from 1,145 patients/month to 1,564 patients/month
in 14 months, representing a 36.59% increase, as
show in figure 5.
This result is complementary to those shown in
Figure 4 and is a valuable piece of information since
the surgical activity has been shifting gradually
toward patients with maximum waiting time limited
by law.
500
750
1.000
1.250
1.500
1.750
apr'09
may
'
0
9
jun'
0
9
jul'09
a
ug
'
0
9
s
e
p'09
oct'09
nov'
09
dic
'
09
en
e
'
1
0
feb
'
1
0
mar '10
a
pr'
1
0
m
ay
'10
Figure 5: Number of patients protected by the “Limited
Waiting Time law” operated from April 2009 to May
2010.
3 CONCLUSIONS
AQuA is a multitask computer program developed
to improve surgical management in our hospital. It is
running in all surgical departments in all 4 building
of our hospital.
It receives input from patient’s waiting lists,
availability of operating rooms, surgeons, anaesthe-
siologists, and many other concepts.
The program has shown to be very valuable in
the handing of patients on the waiting list with sur-
gical pathologies covered by law by certain privi-
leges i.e, depending upon the disease, some patients
have the right to seek private attention and pass the
bill to the social security administration after 120 or
180 days on the waiting list.
The introduction of AQuA in the Carlos Haya
Regional University Hospital in Malaga has intro-
duced a set of improvements in the management of
surgical activity that can be summarized as follows:
Real time monitoring of a set of quantitative
indicators, such as, total number of surgical
interventions carried out, operating room per-
formance and use, deprogrammed surgical in-
terventions, entries to, and exists from the
waiting lists, and so on.
Planning of operating rooms 15 days in ad-
vance.
AQuA started running in
two surgical departments
75% of the surgical activity was
under the control of AQuA
AQuA started running in
two surgical departments
75% of the surgical activity was
under the control of AQuA
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
136

Improved control of pre-operative studies
leading to a 20% reduction in the number of
studies that are due to expire.
The pre-operative anaesthesia appointment
may obtain lists of patients as they are ap-
proaching the date of surgery.
Surgical departments can perform a surgical
schedule with updated information of patients,
operating rooms, pre-operative anaesthesia
and others.
In addition, AQuA, has helped unify two impor-
tant aspects regarding the clinical documentation:
Surgical schedule forms are now the same for
all operating rooms of all 4 hospitals build-
ings. The change from the previous obsolete
procedure to the actual one, handled by
AQuA, was achieved in less than three
months.
Surgical reports have now the same format for
all surgical departments. This has been
achieved through the "intra-operating room
module" a flexible piece of the program that
allows adaptation of the report to different
needs in the context of a general layout.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to acknowledge all those related to
the development and the use of the program, spe-
cially the Medical Directors of all 4 buildings of the
hospital, the Informatics Department, Heads of Sur-
gical Departments and the general staff that has not
only facilitated the use of the program but also sug-
gested many of its present features.
REFERENCES
Informe SEIS, 2010. Líneas estratégicas en Tecnologías
de la Información y Comunicaciones para la Salud en
España. Sociedad Española de Informática de la Sa-
lud.
SAS, 2010. Manual de procedimiento administrativo.
Aplicación para la Gestión de la Demanda y Registro
de Demanda Quirúrgica, versión 4.1. Consejería de
Salud de la Junta de Andalucía.
Quecedo, L., 2009. La eficiencia del bloque quirúrgico:
perspectivas desde el sistema privado o público de sa-
lud. NETS, Red de Comunicación e Información Glo-
bal de Tecnología Aplicada a la Salud.
Gutiérrez, R., 2009. El papel de las e-TIC en la evolución
de los servicios de salud. Colección Fundación Tele-
fónica.
World Health Organization, 2008. Implementation manual
WHO surgical safety checklist. World Health Organi-
zation.
Riesgo, I., 2007. Los retos de la transformación digital del
sistema sanitario. V. JORNADA FORUM cis
Informe SEIS, 2007. La gestión de proyectos de Tecnolog-
ías de la Información y de la Comunicación en los
Servicios de Salud. Sociedad Española de Informática
de la Salud.
Ramolla, T., 1999. Die computerunterstützte Di-
enstplanorganisation. Anaesthesiologie und Intensiv-
medizin.
SOFTWARE-ASSISTED IMPROVEMENT OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT AT CARLOS HAYA REGIONAL
UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL IN MALAGA, SPAIN
137
