
CONTINUOUS ANALYSIS OF REPOLARIZATION
CHARACTERISTICS DURING INSULIN INDUCED
HYPOGLYCEMIA
J. A. Lipponen, P. A. Karjalainen, M. P. Tarvainen
Department of Physics and Mathematics, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
J. Kemppainen, H. Mikkola, T. K¨arki
Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Turku University Hospital, Turku, Finland
T. Laitinen
Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland
Keywords:
ECG, Hypoglycemia, QT-time, Principal component regression.
Abstract:
Hypoglycemia has been shown to affect ECG. Reported changes are prolongation of QT-interval and increased
R/T amplitude ratio. These ECG changes are suggested to be connected to so-called dead in bed syndrome.
Continuous analysis of ECG changes and blood glucose values, during insulin induced hypoglycemia is pre-
sented. Altogether 22 subjects were analyzed in three different groups; 1) healthy group 2) diabetic patients
diagnosed less 5 years ago and 3) chronic diabetics diagnosed over than 5 years ago. The results showed that
20 of 22 subjects’ QT-time was prolonged during hypoglycemia. In addition, in group 3 changes were smaller
than in groups 1 and 2.
1 INTRODUCTION
The dead in bed syndrome which refers sudden death
in type 1 diabedic patients have been widely studied
in past decades. Earlier studies have shown that hypo-
glycemia affects somehow on the autonomic nervous
system and cardiac repolarization. It have been hy-
pothesized that these hypoglycemia related changes
could be connected to dead in bed syndrome. Thus
cardiac repolarization characteristics have been stud-
ied and QT time prolongation and T-wave flattening
during hypoglycemia have been reported (Laitinen
et al., 2008). In addition a connection between hy-
poglycemia and vector electrocardiogram parameters
such as QRS-T-angle has been found (Koivikko et al.,
2008).
Repolarization characteristic have been estimated
by averaging T-waves during few minutes period
(Murphy et al., 2004) and then averaged T-wave sec-
tions are annotated by hand. Because normal varia-
tion of ECG parameters is very large, averaging can
remove some information and thus disturb results.
We used an advanced principal component regres-
sion (PCR) based method (Lipponen et al., 2010) to
analyze repolarization characteristics. By using the
PCR method we can analyze ECG parameters beat-
by-beat, and this enables the compararison of repo-
larization characteristic parameters such as QT-times
and blood glucose values in given time instant.
Hypoglycemia may result in seizure or unaware-
ness, and can thus be fatal e.g. in driving conditions
(Cox et al., 1993). Since hypoglycemia seems to af-
fect ECG, were there have been some studies which
tries to predict hypoglycemic events using these ECG
changes (Nguyen et al., 2008). However, in almost all
studies euglycemic and hypoglycemic clamps are an-
alyzed separately, and thus, the key information; how
long hypoglycemic event should last before remark-
able ECG changes occur have not yet been reported.
We used continuous measurements and beat-by-beat
analysis, which gives us the opportunity to compare
estimated repolarisation parameters with blood glu-
cose values continuously, and thus, hopefully answer
the question is it possible to predict hypoglycemic
107
A. Lipponen J., A. Karjalainen P., P. Tarvainen M., Kemppainen J., Mikkola H., Kärki T. and Laitinen T..
CONTINUOUS ANALYSIS OF REPOLARIZATION CHARACTERISTICS DURING INSULIN INDUCED HYPOGLYCEMIA.
DOI: 10.5220/0003122201070111
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2011), pages 107-111
ISBN: 978-989-8425-35-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
events using ECG changes.
Many of the earlier studies have used diabetic
or/and healthy test subjects (Laitinen et al., 2008;
Koivikko et al., 2008). However, it is known chronic
diabetics who have suffered from diabetes for a long
time have lower autonomic response to hypoglycemia
than subjects with sorter history of diabetes. In this
reason our dataset contains three different groups of
subjects: 1). healthy normal subjects, 2). diabet-
ics who have suffered diabetes less than 5 years and
3). chronic diabetics who have suffered from diabetes
over 5 years.
2 METHODS
Advanced PCR based method was used for analyzing
repolarization characteristics beat-by-beat (Lipponen
et al., 2010). In the PCR method each T-wave was
modeled using three optimal orthogonal basis vec-
tors. These basis vectors were obtained as the most
significant eigenvectors of correlation matrix com-
puted from 1000 previous T-wave segments. Use of
such a large number of T-wave segments was possi-
ble because no remarkable heart rate or morphology
changes where present in used measurements, and on
the other hand such a large amount of prior infor-
mation maximize the denoising effect of the model.
Similar PCR approach was applied to model the QRS
complexes.
From each estimated waveforms, Q-wave onset,
R-wave peak, T-wave peak and T-wave offset were
then extracted. From these extracted time points QT
interval, RR interval adn R/T-wave amplitude ratio
time series weere then formed. In addtition, heart
rate corrected QTc time series was formed by using
Friedricia’s method.
For time series trend estimation, smoothness pri-
ors method was used (Tarvainen et al., 2002). Before
the trend estimation each time series was transformed
evenlly sampled time series by using 4Hz cubic spline
interpolation. Used trend estimation method reflects
time-varying lowpass filter with adjustable cutoff fre-
quency which can be changed by using a smooth-
ing parameter α. Because in these time series the
effects due to off the glucose concentration changes
are shown in very low frequency range, relatively low
cutoff frequency was used.
Glucose values were measured at 5 minute inter-
vals, but values were then interpolated such that sam-
ple rate was 4 Hz, same as for all time series. Al-
though second order and seven point Savitzky-Golay
smoothing was done to beforehand to reduce mea-
surement errors, because it is highly presumable that
blood glucose value doesn’t change rapidly during 5
minutes such a smoothing is recommended.
3 MATERIALS
ECG measurements were recorded in Turku Univer-
sity Hospital and altogether 27 subjects participated
test sessions. Continuous measurements of biosig-
nals such as ECG and EEG were acquired during the
test, along with the blood glucose measurements at 5
minute intervals. In this paper, we consentrate only
on analyzis of ECG signal. ECG was recorded using
a modified chest lead V5 with sample rate 128 Hz.
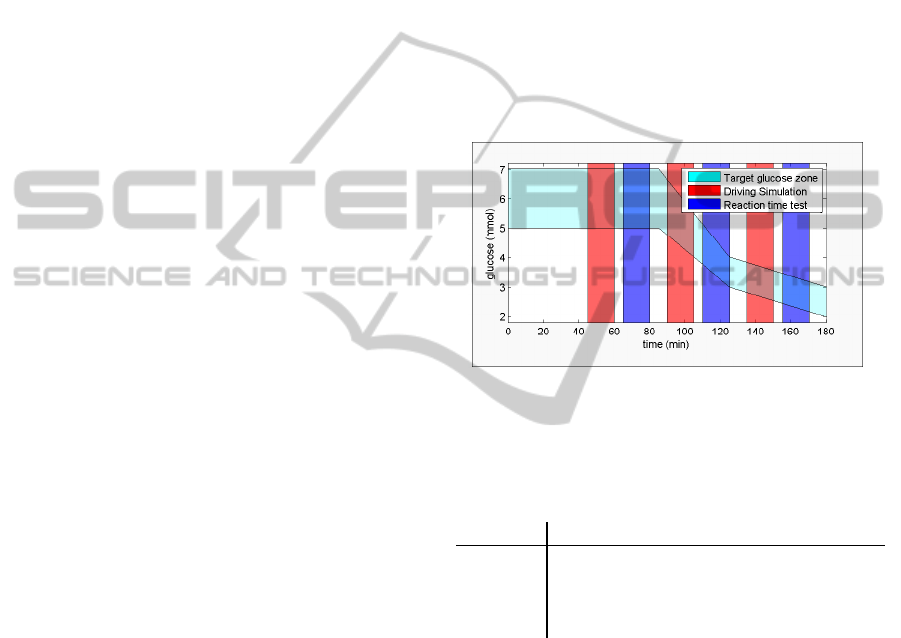
Figure 1: Measurement protocol. Target glucose zone is
presented by light blue, driving simulation by red and reac-
tion time tests by dark blue.
Table 1: Ages, sexes and mean duration of diabetes (years)
of test subjects in different groups.
Healthy T1DM T1DMc
number 9 6 7
age 43.0 ± 8.9 40.5 ± 9.8 49.4 ± 11.1
sex f/m 2/7 0/6 0/7
dignosis - 3.2 ± 2.3 22.7 ± 12.7
Subjects were divided into three groups: 1) 9
nondiabetic healthy subjects (Healthy), 2) 6 diabet-
ics whose diabetes were diagnosed less than 5 years
ago (T1DM), 3) 7 chronic diabetics, diagnosied over
5 years ago and who have suffered hypoglycemic
events repeatedly (T1DMc). Characteristics of dif-
ferent groups are presented in table 1. Unfortunately
T-wave was almost invisible in five subjects ECG and
results of repolarization characteristics were not reli-
able so those measurements were removed from final
analysis.
Protocol of the measurement is presented in Fig-
ure 1. Firstly, blood glucose value was adjusted
range of 5-7 mmol to normoglycemic section. Nor-
molglycemic section lasted approximately85 minutes
and during this period first driving and reaction time
BIOSIGNALS 2011 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
108
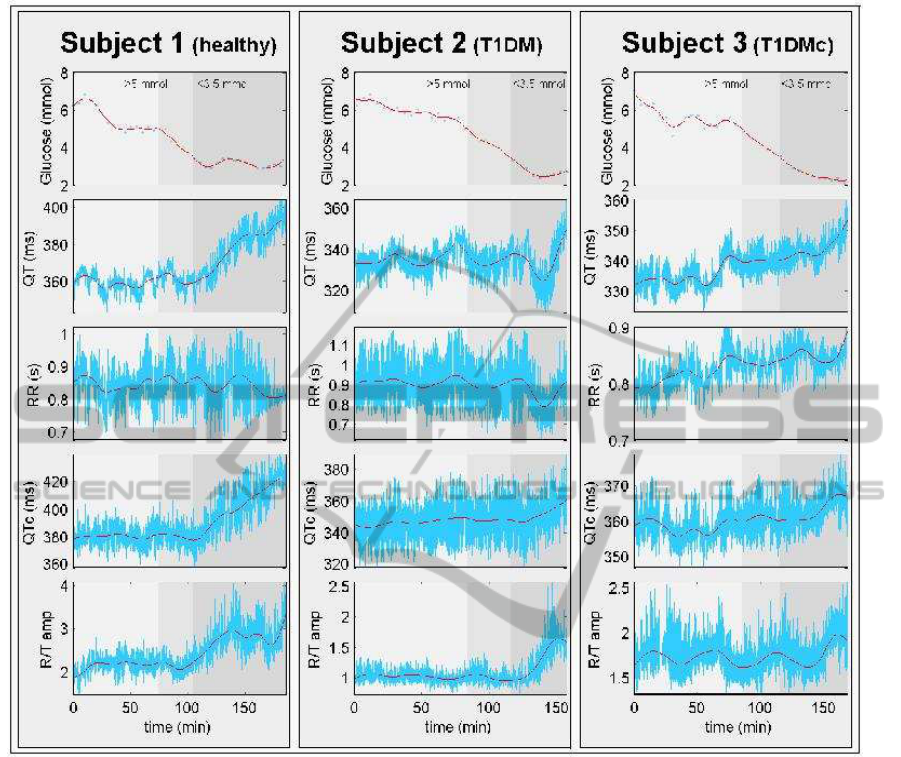
Figure 2: Representative time series of three different subjects. Subject 1 is from healthy group, subject 2 is from T1DM group
and subject 3 is from T1DMc group. In uppermost axes there are glucose values and timeseries are presented in four lower
axes. Original timeseries are presented by blue line and trend is as red line. Time series from top to bottom are QT-interval,
RR-interval, heart rate corrected QT-time (QTc) and R/T amplitude ratio (R/T amp).
tests were done. Secondly insulin infusion was in-
creased and blood glucose concentration started to de-
crease (decreasing state), are the period second driv-
ing and reaction time tests were made. During the de-
creasing state blood glucose value was 5 - 3.5 mmol
and it lasted approximately 40 minutes. However,
reactions to insulin infusion differ between individ-
uals, and thus, this section time differs between in-
dividuals. After the decreasing state blood glucose
was in hypoglycemic state and third driving and reac-
tion time tests were made. Third stage lasted approx-
imately 55 minutes and target blood glucose concen-
tration was below 3.0 mmol.
4 RESULTS
In Figure 2, representative time series from each
group are shown. First subject is from healthy group,
second subject is from T1DM group and third subject
is from T1DMc group. In uppermost axes there are
subject’s glucose values and different time series are
presented in lower axes. Time series are QT-interval,
RR-interval, heart rate corrected QT-interval and R/T
amplitude ratio. In addition also the trends of each
timeseries are presented by red solid line. Trend was
calculated by using a smoothing parameter α = 10
6
which means a cutoff frequency 0.001 Hz.
In Figure 3 mean glucose values and mean QTc-
CONTINUOUS ANALYSIS OF REPOLARIZATION CHARACTERISTICS DURING INSULIN INDUCED
HYPOGLYCEMIA
109
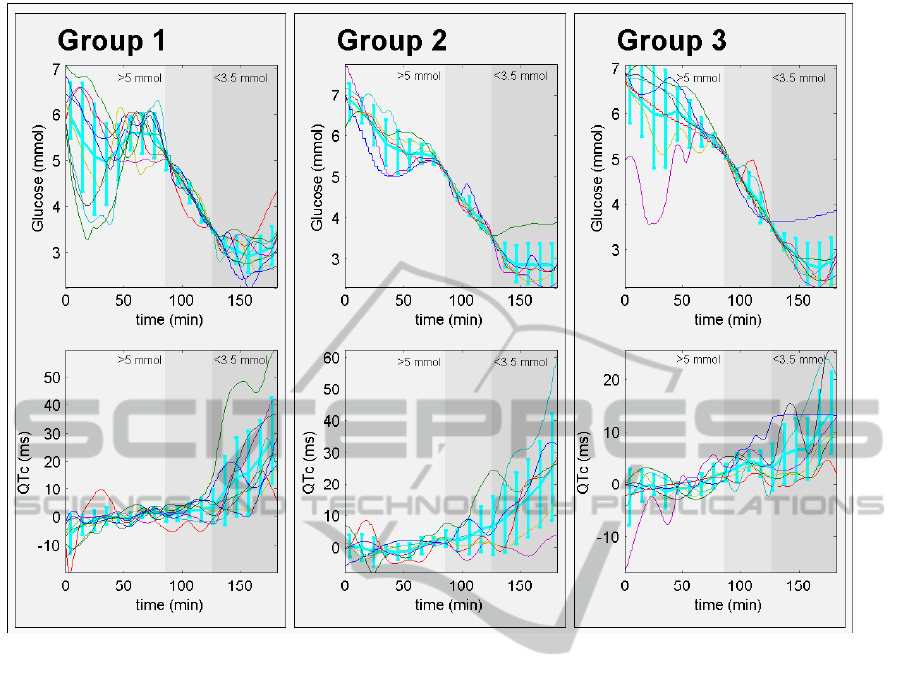
Figure 3: Glucose values and change of QTc-times during the measurement, for the three groups. Upper axes there are each
individual subjects glucose values by thin line and group mean and standarddeviations of thick blue line. Lower axes there
are trends of QTc-times form each subjects by thin line and group mean values and standarddeviations by thick blue line.
times for each group are presented as thick blue line.
Each subject s glucose values and trend of the QTc-
times are presented as thin lines. QTc times are pre-
sented as changes from baseline, where the mean of
he normoglycemic section was taken as the baseline
value. Reaction to insulin infusion is highly vari-
able between individuals and thus QTc time series are
timescaled using measured glucose values and mean
section lengths. That is, time when blood glucose was
last time more than 5 mmol was set to end of the sec-
tion 1 (i.e. 85 minutes), time when blood glucose was
first time lower than 3.5mmol was set to end of the
second section (i.e. 125 minutes) and rest of the data
is scaled to section 3 which lasts 55 minutes.
5 DISCUSSION
Time series analysis of repolarization characteristics
have been presented. As can be seen in Figure 2 nor-
mal variation of QTc and R/T amplitude ratio time
series is quite large and thus changes affected by glu-
cose concentration might be hard to find without beat-
to-beat analysis. Especially diabetic groups changes
are only visible in low frequency trend component
and normal variation is much bigger than changes
affected by hypoglycemia. In Figure 3 group anal-
yses of QTc time series are shown. Although mea-
surements were made by using scripted protocol, glu-
cose variation between individuals, is so large, that in
group analysis we have to scale time series using glu-
cose values. Time scaling was done so that the end
of the section one glucose was 5 mmol and end of the
section 2 glucose value was 3.5 mmol in all subjects.
Without the time scaling time series between the sub-
jects cannot be compared in time domain.
In healthy normal group QTc time increased over
10 ms during hypoglycemia when comparing to nor-
moglycemic section. In diabetic groups (T1DM,
T1DMc) QTc time was not increasing by one sub-
ject/group. However, in both groups mean value
was clearly higher than baseline value which can be
clearly seen in Figure 3. When comparing differences
between the tree groups it can be seen that largest re-
BIOSIGNALS 2011 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
110

sponses were in healthy group and lowest in T1DMc
group. Subjects in T1DMc group have suffered from
diabetes for a long time and they might be habituated
to hypoglycemic events and thus autonomic response
are lower than other in groups.
Prediction of hypoglycemic events by using ECG
parameters seem to be quite challenging, because
changes originating from glucose are delayed so that
they occur normally more than 10 minutes after the
glucose value has decreased below 3.5 mmol, which
can be seen in Figure 3. Furthermore, changes are
most intensive in healthy group and lower in dia-
betic groups were glucose prediction is needed. How-
ever changes are visible and thus some intelligent al-
gorithms might recognize hypoglycemic events early
enough to prevent some dangerous situations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by Academy of Fin-
land (project 126873, 1.1.2009-31.12.2011; project
123579, 1.1.2008-31.12.2011)
REFERENCES
Cox, D., Gonder, L., and Clarke, W. (1993). Driving
decrements in type i diabetes during moderate hypo-
glycemia. Diabetes, 42:239–43.
Koivikko, M., Karsikas, P., Salmela, P., Tapanainen,
J., Ruokonen, A., Seppnen, T., Huikuri, H., and
Perkiomaki, J. (2008). Effects of controlled hypogly-
caemia on cardiac repolarisation in patients with type
1 diabetes. Diabetologia, 51:426–435.
Laitinen, T., Lyyra-Laitinen, T., Huopio, H., Vauhkonen,
I., Halonen, T., Hartikainen, J., Niskanen, L., and
Laakso, M. (2008). Electrocardiographic alterations
during hyperinsulinemic hypoglycaemia in healthy
subjects. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 13:97–105.
Lipponen, J., Tarvainen, M., Laitinen, T., Lyyra-Laitinen,
T., and Karjalainen, P. (2010). A principal component
regression approach for estimation of ventricular re-
polarization characteristics. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng,
57:1062–1069.
Murphy, N., Ford-Adams, M., Ong, K., Harris, N., Keane,
S., Davies, C., Ireland, R., MacDonald, I., Knight,
E., Edge, J., Heller, S., and Dunger, D. (2004). Pro-
longed cardiac repolarisation during spontaneous noc-
turnal hypoglycaemia in children and adolescents with
type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia, 47:1940–1947.
Nguyen, H., Ghevondian, N., Nguyen, S., and Jones, T.
(2008). Detection of hypoglycemic episodes in chil-
dren with type 1 diabetes using an optimal bayesian
neural network algorithm. In 30th Annual Inter-
national IEEE EMBS Conference Vancouver, British
Columbia, Canada.
Tarvainen, M., Ranta-aho, P., and Karjalainen, P. (2002).
An advanced detrending method with application to
hrv analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 49:172–175.
CONTINUOUS ANALYSIS OF REPOLARIZATION CHARACTERISTICS DURING INSULIN INDUCED
HYPOGLYCEMIA
111
