
THE USE OF ORANGE CANVAS PROGRAM TO ANALYZE
THE PERFORMANCE OF CHILDREN WITH CONGENITAL
BLINDNESS IN THE PLANNED CODES SUBTEST ADAPTED
Felipe Pulcherio
Neurolab, Instituto Benjamin Constant, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Carla Verônica M. Marques, Carlo Oliveira E. S. de Oliveira
Faculdade de Medicina, UFRJ, NCE -UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Maria M. D. Poyares, Eloisa Saboya
Neurolab, Instituto Benjamin Constant, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Lidiane F. Silva
NCE – UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Orange canvas, Planned codes, Congenital blindness, Neuropsychological assessment.
Abstract: At Laboratory of Cognitive Neuropsychology of the Benjamin Constant Institute (NEUROLAB-IBC) was
realized a study aiming at exploiting the cognitive component and a possible clinical guidelines of children
with congenital blindness from the adaptation of Planned Codes subtest of Das and Naglieri and the use of
artificial intelligence laboratory Orange Canvas of the University of Ljubljana. Due to the scarcity of
neuropsychological tests that assess brain function in congenital blind children in Brazil, Planned Codes
provided satisfactory scenery and needed to adapt to the reality of the applicator and children, containing,
therefore, features tactile, visual and translated into Portuguese. Moreover, the high-tech offered by Orange
Canvas program, favored the possibility of completely automating the entire subtest. The sample consisted
of 59 congenital blind children which are students of Specialized School, where 32 realized the whole
subtest being 2 of 7 years old and 28 from 8 to 12 years old. To validate this study, was made a clustering of
data inherent to the subtest with predictions drawn from behavioral analysis of children, through the Orange
Canvas, where it was confirmed the effectiveness of that procedure in clustering the data associated with the
predictions suggested. From the children performance, opens itself an intervention and creation field of
neuropedagogical strategies computerized to improve the cognitive processing of congenital blind children.
1 INTRODUCTION
The shortage of Brazilian studies related to human
cognition area in congenital blind children, makes
this field promising for psychological and
technology science to explore. The cognitive science
involves many disciplines and one thing in common:
the study of intelligence. As a consequence, after the
initiative of researching on human intelligence,
many theories have been produced including the
highlighting research of Alexander Luria Romanov
on the brain cognitive functions and organization. In
this work, published in 1973, he proposes three main
units of the brain function: the functional unit which
regulates the cortical tonus, the gait and mental
states, the functional unit to receive and analyze
information stored and the programming, regulation
and verification of the activity functional unit.
Okuhata and collaborators (2007), in the studies
based on the Electroencephalogram (EEG) results,
486
Pulcherio F., M. Marques C., Oliveira E. S. de Oliveira C., Poyares M., Saboya E. and Silva L..
THE USE OF ORANGE CANVAS PROGRAM TO ANALYZE THE PERFORMANCE OF CHILDREN WITH CONGENITAL BLINDNESS IN THE
PLANNED CODES SUBTEST ADAPTED .
DOI: 10.5220/0003128604860492
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2011), pages 486-492
ISBN: 978-989-8425-34-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

suggest that Luria has successfully captured the
brain activity in three distinct functional units, and
ultimately support the view that there are three
functional units working on cooperation for a variety
of activities.
Deriving from Luria studies, Das and Naglieri
developed a theory, where information processing is
seen as something dynamic, possessing different
cognitive skills. This theory suggests four processes
involved in the information processing: Planning,
Attention, and the Simultaneous and Successive
Processing called the (PASS) theory. Based on this,
the same authors created the Cognitive Assessment
System, CAS (Das & Naglieri, 1997). This test,
according to Das and Naglieri, 1997, measures
intelligence as a limited range of multiple skills, as
well as the Cognitive Abilities Woodcock-Johnson
Tests (Woodcock & Johnson, 1977), the
Intelligence Scale Stanford-Binet, Fourth Edition
(SB. IV, Thorndike, Hagen, & Sattler, 1986), the
Differential Abilities Scale (Das, Elliot, 1990), the
WISC-III (Wechsler, 1991) and the WAIS-III
(Wechsler, 1997).
The present study reports the cognitive
evaluation analysis in congenital blind children
according to their ability to create strategies for
problems presented, thus, setting the table that
occurs during the planning process. This process
works with the cognitive control, intentionality and
self-regulation to achieve a goal (Das & Naglieri,
1997). As a pioneer exploration of this type of class,
this work aims at developing of cognition
exploration in blind children with the help of the
artificial intelligence laboratory Orange Canvas
University of Ljubljana (2004) and the Planned
Codes subtest from the Das and Naglieri (1997)
Cognitive Assessment System battery test.
According to Das and Naglieri (1997), planning
is a mental process whereby the individual
determines, selects, applies and evaluates solutions
to problems, in what it is thought as a cause-effect
relationship between two actions within a specific
time window, inhibiting prepotent responses,
forming goals and performing activities. Moura and
Correa (1997) report that Alexander Luria proposes
a new brain organization and cognitive functions
model through of a study with brain injured patients.
Accordingly, Das (1980) points to the idea presented
by Luria, in which the brain could be divided into
three blocks. One of these blocks would be
responsible for developing plans and action
programs, beyond the regulation and control of
human behavior. He also reveals that this unit would
contain the frontal lobe.
An adjustment for the visually impaired of
Planned Codes subtest was used to assess this
construct of cognitive functioning. Thus, the use of
this subtest intends to measure and verify how the
child develops a plan of action, implements it,
considers whether their objectives were achieved
and how one modifies their action plans, should the
need arise (Das & Naglieri, 1997 apud Cruz, 2007).
This was possible, because this subtest allows the
children to decide how they want to accomplish the
task within the shortest time possible (Haddad,
2004).
The artificial intelligence laboratory Orange
Canvas is a machine learning and data mining, i. e.,
a collection of modules based on the Python
1
programming language which are located on a core
library and performs a feature in which the time
fulfillment is not crucial. Through this program, a
core objects library and programming sets
instructions designed to perform routines, it was
made a clustering of data inherent in the adapted
subtest and predictions obtained by the children`s
behavioral analysis.
Visually impaired population studies, offers two
new opportunities for the computer contribution
advance in the context of cognition and
neuropsychological assessment. In a first moment
the computing environments advance for processing
information allows the researchers easier access for
non-specialist meta-heuristic treatment (heuristic
method for solving general optimization problems)
database. A second opportunity lies in the possibility
of creating applications that allow automated access
of this population to a service evaluation and
prognosis of their cognitive ability.
In both cases, the visual deficient offers a
significant differential of the scientific research
property. That difference lies at the cognitive level
with morphogenetic channels preponderance which
are the means of organism transmission and
1
The Python language was chosen to develop this program,
because it is considered at high level and contains different
paradigms programming such as object-oriented programming,
structured programming and some elements of functional
programming, being possible the use of more appropriate
paradigm to solve the problem. This makes Python unique,
because the quality of the code is more readable, more compact,
easier to maintain and to reuse it. It requires fewer lines, does not
require prior declaration of the type of variables and neither a
cycle of build. This gives to the programme the possibility of
being executed immediately and still having portability. Many
programs developed in this language does not have any restriction
on Linux and Windows platforms. (http://www.python.org.br/
wiki, accessed in March of 2010).
THE USE OF ORANGE CANVAS PROGRAM TO ANALYZE THE PERFORMANCE OF CHILDREN WITH
CONGENITAL BLINDNESS IN THE PLANNED CODES SUBTEST ADAPTED
487

formation according to Seminério (1984). This
author gets to this theory through the English school
distinction in 20
th
century, where intelligence is
compared to energy and it is distributed in two areas,
the verb-educational area and practical performance
area. Based on this classical duality, Seminério
deepens this perspective and, based on
anthropological and psychophysiological data,
verified that in human nature, the proximity senses
(smell, touch and taste) show retraction signs while
sight and hearing accuse expansion when related to
their kinesthetic. It is also noted, that, throughout the
phylogeny, two channels involving afferent and
efferent pathways became specific to the superior
mental development activity, the visual-motor
channels and the audio-phonetic channels. The first
is the mean of transmitting and processing
information that connects visual perception and
motor action with their feedback executable on the
environment covered by the vision. The second is
the mean of transmitting information that links the
perception of the auditory environment and the
motor organization action to the speech phonemes
perception and motor production (Seminério, 1984).
The predominance of audio-phonetic channels in
visually impaired drives the heuristics to a faster
convergence, eliminating arising interference from
visual-motor channel. This same feature sets the
immediate automation process applicability of this
procedure, since this population will benefit from
the prognostics offered by the applicative towards
the cognitive evolution direction.
2 OBJECTIVE
This paper aimed to assess the congenital blind
children cognition in relation to cognitive valence,
planning and proposing a computerized process as a
whole and not just as statistical analysis. The use of
the laboratory Orange Canvas allowed not only
standardized evaluation, but also a prognostic
assessment, which enables, depending on the
prognosis confirmation, a cognitive disabilities
classification that have influenced in the child's
performance, as reported by Pendley, Myers and
Brown (2004 ) by claiming that CAS may indicate
Disorder Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
(ADHD). This allows a more objective and effective
treatment, besides allowing the advance in the
Planned Codes subtest administration as a whole, an
administration fully computerized to automate the
application and evaluation of subtest.
Therefore this study intended to classify visually
impaired children in possible clinical situations from
the results generated by laboratory Orange Canvas.
The researcher made prognostics based on
behavioral observation of each child generating a
total of seven forecasts. From this, the statistical
program grouped the data inherent to the Planned
Codes subtest with the prognostics generated by the
researcher. With the efficiency of such an analysis, it
also aimed a possible adaptation of the computerized
subtest as a whole so that more data were computed
with greater precision.
3 METHODS
3.1 Participants
The sample consisted in 59 visually impaired
children from 7 to 12 years old, in which 32 realized
the entire subtest. 19 boys (being 7 children from 7
to 9 years old and 12 children from 10 to 12 years)
and 13 girls (being 5 children from 7 to 9 years and
8 children from 10 to 12 years), students from
kindergarten to the 6th year of Elementary School,
who are attending the Specialized School of
Benjamin Constant Institute in Rio de Janeiro.
According to the information sheet of the children,
they belong to the underclass.
Figure 1: Sample Data.
3.2 Material
The Planned Codes subtest and its administration
were adapted to the reality of both the researcher and
the visually impaired. Therefore, it started
containing tactile and visual features, besides the
translation into Portuguese and the receipt to the
tested person.
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
488

The original subtest consisted of four pages, in
which two are referring to item 1 and two to item 2.
On the first page of each item there is an example
and a line for the child to practice before fulfilling
the activity. In the second page of each item, on the
bottom, there are seven rows and eight columns of
letters without their codes. The top of each page
contains the correlation between letters and the
corresponding encodings. Thus, in the first item the
correlation between letters and codes is A = OX, B =
XX, C = OO, D = XO, and in the second item the
correlation is A = XO, B = OO, C = XX and D =
OX. Another difference between the items is given
on the second page at the bottom of each item on the
arrangement of the boxes with the letters: while in
the first item all the letters (A, B, C and D) are
arranged vertically and there are eight ABCDABCD
columns, in the second item the letters are arranged
according a diagonal pattern, in which each diagonal
is formed by a sequence of the same letter.
The first step in the adaptation of the subtest was
the translation into Portuguese. Then, the visual
stimuli, as proposed in the original model were
replaced by tactile stimuli, so that the test would fit
to the children population with visual impairments.
The subtest Key Book leaves were transformed into
four plates (with the dimensions of 460 mm x 360
mm) containing a page of paper and another of
thermoform (pellicle PVC that has an elevation
which is detected tactually) on each plate. The
contours around the columns were partially
transformed into thermoform and in graphic printing
writing - "ink" - in the background visually
recognized). The letters (A, B, C and D) were both
converted to "ink", in the background, and in Braille,
on the surface. Codes present on the top of each
page (OX, OO, XX and XO), within the boxes they
were also printed in thermoform and in "ink".
This adaptation was made not only for blind
children, but also for the researcher to recognize the
letters or the symbols. In the paper part, there were
four boxes with letters and their codes in "ink" for
the applicator. Inside of each box there was a letter
on the top, right below it a horizontal line and once
again below it two codes separated by a vertical line.
In the PVC pellicle, there were the same four boxes
with their letters and respective codes, but in braille,
for the visual impaired, in which, within each box
represented by a square, at the top there was a letter,
right below it an elevation indicating an horizontal
line and below this line, the two symbols without the
division in the middle.
The test physical adaptation had two models, the
first was adequately reliable to the original test with
lumps in each row and column, but the children got
confused groping the last letter code with the first
code of the next letter. Also, in the first model, on
the second plate of every item, the bottom (in which
the children would have to grope the letters in
Braille and tell their codes), there were horizontal
lines in high embossed what would influence
children to a horizontal reading, from left to right
from top to bottom and there would be no formation
of strategies for solving the test. Therefore, it was
necessary to readapt the plates, in which the vertical
elevations located in the middle boxes and the
horizontal lines situated on the second plate of each
item, at the bottom were removed.
3.3 Procedures
The Planned Codes subtest was administered
individually to each one of the congenital blind
children. The subtest adaptation also occurred in the
application procedure, but without compromising
the original characteristics.
At first, there was the conduction of the child to
the room application, who set on a chair and answer
about some personal info (name, age, date of birth,
school level). Then, it was explained to the child in a
playful and detailed way, what she was doing there
and how to undertake the test. After that, it was said
to the child that he would play a game in which he
had to be as fast as possible. The first plate was
presented, the sample A, was picked up by the
child's hands, led him to explore the entire plate
asking him to say everything that was being
tactually perceived. When performing the Example
A and having identified that there were two codes
for each letter, they passed to item 1 and it was
repeated t the child to perceive all the plate and be as
fast as possible during the subtest, and at the end of
each item, to report what strategy did he used. The
same was done also during the Sample B and item 2,
drawing attention to the inversion of the symbols on
the second step.
Despite the guidelines, there were no cases of
timeout less than 180 seconds as the subtest for
children who sees. It was decided, then, for the no
stipulation of a time limit because of the study
pioneer and absence of previous parameters to fix an
average. The tactile perception is slower than the
visual and this is the main explanation for the fact
the children had presented a high rate in the timing.
3.4 Proposal Automation
With the goal of automating the entire process of
THE USE OF ORANGE CANVAS PROGRAM TO ANALYZE THE PERFORMANCE OF CHILDREN WITH
CONGENITAL BLINDNESS IN THE PLANNED CODES SUBTEST ADAPTED
489

neuropsychological assessment, two studies for a
new Planned Codes adaptation subtest were
developed. The first is based on input and output of
information via Augmented Reality (AR), in which
the computer acts as disseminator and receiver of
information via webcam from the perceived
movements. The second is via Augmented Reality
on input and output via voice command, where the
computer is the vector of information and receiver of
responses via verbalization. We opted for the first
method, because the technology is already under
construction and eliminates the process of training
voice, in other words, adequacy of the machine to
the vocal tone of each sample subject that is
necessary for the second method.
Therefore, the computed adaptation is idealized
as follows: the visually impaired will be exposed to
a wooden board containing subdivisions into several
squares. There will be a camera connected to this
object with the function of capturing the movements
made by the blind child on the board surface to the
computer. These movements will represent the codes
referents to each subtest letter. The visually impaired
have to touch the center of the square to find out
which letter matches it, because the camera will pick
up the position of the finger and will return, with
synthesized speech, the letter in question. The codes
for each letter will have specific senses and
direction, because there will be an internal
configuration in the software in which each square
vertex will receive an identification, i.e., when the
sense will be forward, top to bottom, left to right and
the direction will be the sum of a horizontal with a
vertical, has itself a diagonal to the right and this
will indicate the code "X"; when the felt will be
back, top to bottom, right to the left and the direction
will be the subtraction of a horizontal with a vertical,
has itself a diagonal to the left and this will indicate
the code "O". Figure 2 illustrates the structure of the
automated adaptation.
x = y + 1h + 1v (X)
o = y – 1h + 1v (O)
During the instructions, the original subtest
processes will remain, before each item there will be
an example so there is no doubt over the two
following items. And besides, in four squares
located above will be the four boxes with their
letters and their codes that, when touched, the
synthesized voice of the computer will say whatever
requested. This whole procedure will be reported, as
well as the explanation that the beginning of each
response should start by one of the edges above the
square and by putting your finger in the center of the
square, the computer will inform the corresponding
letter. That is, in the four boxes situated above,
which serve as an aid in case of forgetting the
answer. If you touch one of the upper extremities of
the square, the computer will tell what are next
directions, in order to obtain the correct answers.
Figure 2: Wooden board containing subdivisions into
several squares and a camera.
4 RESULTS
The analysis consisted in the grouping of raw scores,
weighted scores, times in the item 1, times in the
item 2 and prognostics, which the researcher
produced during the subtest application phase, with
the help of statistical program Orange Canvas. Such
predictions were categorized into seven levels:
standard (0), lack of attention (1), tiredness (2),
agitation (3), motor and speech difficulty (4)
difficulty of understanding (5), impatience (6) and
non-realization of the subtest (7); which received
numbers for statistical purposes.
Using the Orange Canvas program, it verified the
correlation between variables inherent to the subtest
and prognostics, in which their veracity was
checked. The scatterplot tool observed the linear
grouping of subjects in relation to the raw score
(abscissa axis) and the weighted score (ordinate
axis) according to the classified prognostics, figure
3. The results indicated the standard and lack of
attention prognostics had a cluster in specific regions
of tiredness, agitation, motor difficulty and on
speech, difficulty of understanding and impatience,
clustered between the two pertinent prognostics.
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
490
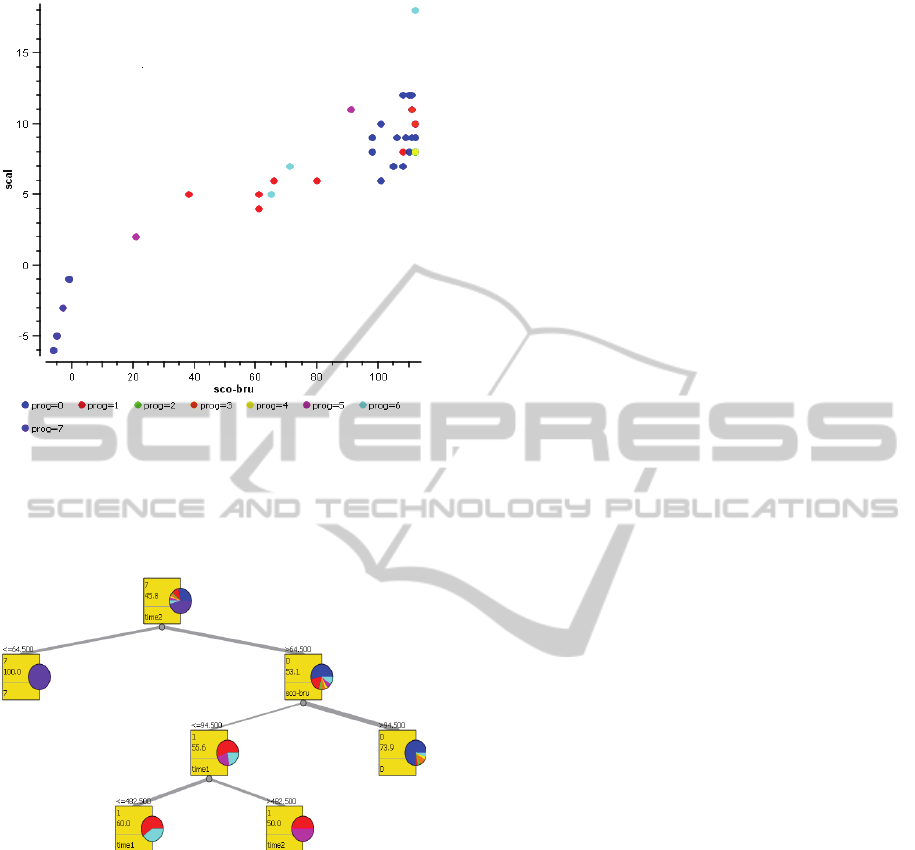
Figure 3: Scatterplot graph, where prog = 0 (standard),
prog = 1 (lack of attention), prog = 2 (tiredness), prog = 3
(restlessness), prog = 4 (motor and speech difficulty), prog
= 5 (difficulty comprehension), prog = 6 (impatience),
prog = 7 (absent).
Figure 4: Classification Tree Graph.
The Classification Tree Graph was also used, in
which a diagram was traced with the prognostic and
its relation with all the variables above. According to
figure 4, it was found that 23 of the 32 participants
are in a same classification (having a gross score ≥
94 500 and time in the item 2 ≥ 64 500), in which
there were 17 subjects classified as standard, one as
lack of attention, another as tiredness, two as
agitation, one as motor and speech difficulty and
another as impatience. The other nine participants
were a group in which five were in ratings of lack of
attention, 2 in difficulty of understanding and 2 in
impatience, where the raw score was ≤ 94 500 and
the time in the item 2 was ≥ 64 500. From this latter
group was derived two more, in which there were
three in lack of attention and two in impatience (raw
score ≤ 94 500, time in item 1 ≤ 482 500 and time in
item 2 ≥ 64 500), and the other had two of
inattention and 2 as lack of comprehension (raw
score ≤ 94 500, an item on time and time ≥ 482 500
≥ 64 500 in item 2).
5 DISCUSS
From these results it is noticed that the cognitive
planning of these children is to be encouraged for a
better utilization and better intellectual training.
Some of the points are to be used to substantiate this
assertion are the fact of conditioning in reading
(from left to right, top to bottom) and the excess in
the chronological count, even with the guidance to
be as fast as possible. However, according to
Haddad, F. A. (2004), Planned Codes subtest
measures, in fact, planning and not the processing
speed. E Naglieri, J. A. (1999) rejected the criticism
made to the planning subtests as speed tests, saying
that the data involving the use of strategies and do
no correlation with the conduct of speed tests such
as the task of having to be simple, involving little or
non thought and the fact that there was no use of
strategies or anything more than repeating the same
act as soon as possible. Therefore there was no
significant loss as to the original proceedings,
because the children continued having to develop
strategies of better resolution to identify letters and
their codes. This adaptation keeps maintaining the
characteristics of the subtest that is to measure the
cognitive valence, planning, because it does not take
away the need to develop strategies for its
resolution, i.e., to exploit the full spatial field for the
cognitive artifices formulation.
It can be concluded, also, that the prognosis
"lack of attention" was precise; which supports the
hypothesis that CAS can trace compatible profiles
with Deficit Disorder and Hyperactivity
(PENDLEY, MYERS & BROWN, 2004). Studies
on the relationship between CAS and the cognitive
dysfunction indication have been held. Van Luit,
Kroesbergen and Naglieri (2005) conducted a study
comparing performance of Dutch children with and
without ADHD with the performance of American
children with and without ADHD. The findings
showed that children with ADHD in both countries,
showed relatively low scores on Planning and
Attention scales of the CAS, although median scores
in the Simultaneous and Successive scales.
THE USE OF ORANGE CANVAS PROGRAM TO ANALYZE THE PERFORMANCE OF CHILDREN WITH
CONGENITAL BLINDNESS IN THE PLANNED CODES SUBTEST ADAPTED
491

6 CONCLUSIONS
The study demonstrates the weakness in researches
aimed at exploiting blind children's cognitive in
Brazil and a very prosperous area for research by
cognitive sciences such as psychology and
computing. This study reported a small but
significant, influence of both sciences in
neuropsychological development, in principle, and a
future investment in neuropsychological research
fully computerized for better coverage of data and
facilities provided by computation for the advance in
education cognitive and the formulation of possible
neuropedagogic interventions.
7 FUTURE WORK
The process of adapting the CAS to the public of the
visual impaired until the produced results showed us
how the adaptation of a test for a different audience
is laborious, because changes do not only occur in
the physical structure of the instrument, but also in
the language and method application. However, the
whole adaptive process can not detract from the
original proposal, and needs to be as reliable as
possible. From this conjecture, I suggest the
proposal for a future work, that is, to automate this
whole adapted subtest process , in other words, we
are proposing to develop a software, through which
the webcam, can capture the movements of the blind
student's finger on a concrete surface in high relief,
reproducing on the computer screen the circle and /
or 'X' shown by students in this area, giving a return,
on the synthesized voice, about what was run by
students, and this process will be stored internally in
database of the system to prepare the evidentiary
findings.
To develop this program, we are counting on
infrastructure (computers and space) of GINAPE
(Group Information Technology Applied to
Education) of NCE / UFRJ, Federal trainees of the
College Peter II and support of faculty of PPGI /
UFRJ. We will use the Python language and libraries
available on the website: www.hitl.washington.edu/
artoolkit/.
We are confident that this program will assist the
applicator in the production of systematic results, it
will also provide a larger sample and, finally, it will
be an encouragement for visually impaired people
performing the subtest in a dynamic, interactive and
better adapted to their needs.
REFERENCES
Blaz Z., Gregor L., Janez D., Tomaz C., 2004. Orange
Canvas: Data Mining Fruitful & Fun. Available at
http://www.ailab.si/orange/ (accessed April 12, 2010).
Cruz, V., 2007. O Cognitive Assessment System como
instrumento de avaliação psicológica. Revista de
Psicologia da Vetor Editora, v. 8, n. 1.
Das, J. P., 1980. Planning: Theoretical Considerations
and Empirical Evidence. Psychological Research, n.
41, p. 141-151.
Das, J. P. & Naglieri, J. A., 1997. Cognitive Assessment
System: Interpretative Handbook. Riverside
Publishing. Itasca, Illinois.
Luria, A. R., 1981. Fundamentos da Neuropsicologia.
Editora da Universidade de São Paulo. São Paulo.
Haddad, F. A., 2004. Planning versus speed: an
experimental examination of what Planned Codes of
the Cognitive Assessment System measures. Archives
of Clinical Neuropsychology, v. 19, n. 2, 313-317. doi:
10.1016/s0087-6177(03)00027-1
Moura, M. L. S. & Correa, J., 1997. Estudo Psicológico do
Pensamento: de W. Wundt a uma Ciência da
Cognição. Ed. UERJ. Rio de Janeiro.
Naglieri, J. A., 1999. How valid is the PASS theory and
CAS? The School Psychology Review, v. 28, n. 1, p.
145-62.
Owen, Adrian M., 1977. Cognitive Planning in Humans:
Neuropsychological, Neuroanatomical and
Neuropharmacologiacal perspectives. Progress in
Neurobiology, Great-Britain, v. 53.
Pendley, J. D., Myers, C. L., & Brown, R. D., 2004. The
Universal Nonverbal Intelligence Test with children
with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of
Psychoeducational Assessment, v. 22, 124-135.
Seminério, F. L. P., 1984. Infra-Estrutura da Cognição:
Fatores ou linguagens? Ed. Fundação Getúlio Vargas.
Rio de Janeiro, Cadernos do ISOP nº4.
Shiho, T. O., Okazaki, S., Maekawa, H., 2007. Differential
topographic pattern of EEG coherence between
simultaneous and successive coding tasks.
International Journal of Psychophysiology, v. 66, p.
66–80.
Silva, L. F., 2010. Geometrix : Ensinado conceitos
geométricos a deficientes visuais. Rio de Janeiro:
IM/NCE/UFRJ. Proposal of master’s thesis.
Van Luit, J. E. H., Kroesbergen, E. H., & Naglieri, J. A.,
2005. Utility of the PASS theory and cognitive
assessment system for Dutch children with and without
ADHD. Journal of Learning Disabilities, v. 38(5), p.
434-439.
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
492
