
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS
From Data- to Process-Orientation
Martin Schmollinger, Friedemann Iwanowski, Timo Kußmaul, David Schwarting, Julian Stark
School of Informatics, Reutlingen University, Alteburgstr. 150, Reutlingen, Germany
Eric Stricker, Marcus Rall
Tuebingen Centre for Patient Safety and Simulation, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine
University Hospital of Tuebingen, Silcherstraße 5, Tuebingen, Germany
Keywords: Process-integrated web applications, BPM, Methodology for healthcare-IT, Incident reporting, Healthcare.
Abstract: In recent years web applications have evolved from pure data-centric towards complex process-based
applications that involve multiple users, organizations and systems. Web applications in the area of
healthcare have been particularly affected by this evolution. New process-oriented technologies like
business process management systems were used for the development of such web applications. They
facilitate the implementation of the processes by providing tools for the process design, execution,
administration and integration and guarantee performance and scalability. However, most web applications
are implemented conventionally and therefore, cannot take advantage from these new technologies. What
they are lacking is a methodology for converting conventionally implemented, intrinsically process-oriented
web applications to process-oriented platforms. In the following article, a methodology is introduced that
shows how web applications may be re-engineered towards process-oriented platforms. Furthermore, the
relevance of this methodology to solve the challenges arising in a concrete web application in the area of
healthcare, specifically incident reporting in hospitals, is outlined.
1 INTRODUCTION
The web has become the major platform for business
processes involving multiple users, organizations
and systems. Healthcare has been particularly
affected by this trend because of the extensive and
complex nature of the corporation and collaboration
required between the employees of hospitals, the
pharmaceutical and medical engineering companies
and of course patients. The work is intrinsically
process-oriented and web applications are a useful
technology to integrate participants from different
organizations. The main driver for the general trend
towards process-orientation is business process
management (BPM). Although BPM has already
been an IT-related discipline for a long time, the
terminology is sometimes confusing. The present
paper uses the terms business process and BPM. The
slightly differences to the terminology “workflow”
or “workflow management (WFM)” are not
considered. A discussion and clarification of the
various BPM terminologies can be found in (Ko,
2009). BPM is defined as “supporting business
processes using methods, techniques and software to
design, enact, control and analyze operational
processes involving humans, organizations,
applications, documents and other sources of
information” (van der Aalst, ter Hofstede and
Weske, 2003).
According to van der Aalst these steps describe the
BPM life cycle as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Van der Aalst et al.’s BPM life cycle (van der
Aalst et al., 2003).
42
Schmollinger M., Iwanowski F., Kußmaul T., Schwarting D., Stark J., Stricker E. and Rall M..
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation.
DOI: 10.5220/0003135100420051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2011), pages 42-51
ISBN: 978-989-8425-34-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
While the first generation of web applications
dedicated to e-commerce, content publication and
management focused on data-centric user interaction
e.g. uploads or searches, process-oriented web
applications were developed to create a distinct
process, consisting of consecutive system and user
activities executed under consideration of a
predefined rule-based control flow. During the
execution, different user roles claim user activities
and different systems are integrated realizing the
system activities. The design and implementation of
process-oriented web applications make new
demands on implementation platforms and
methodologies (Brambilla, Ceri and Fraternali,
2006).
Therefore, many process-oriented platforms and
frameworks have emerged in the last years. Software
tools supporting the management of such operational
processes have become known as business process
management systems (BPMS) (van der Aalst et al.,
2003), (Brambilla et al., 2006).
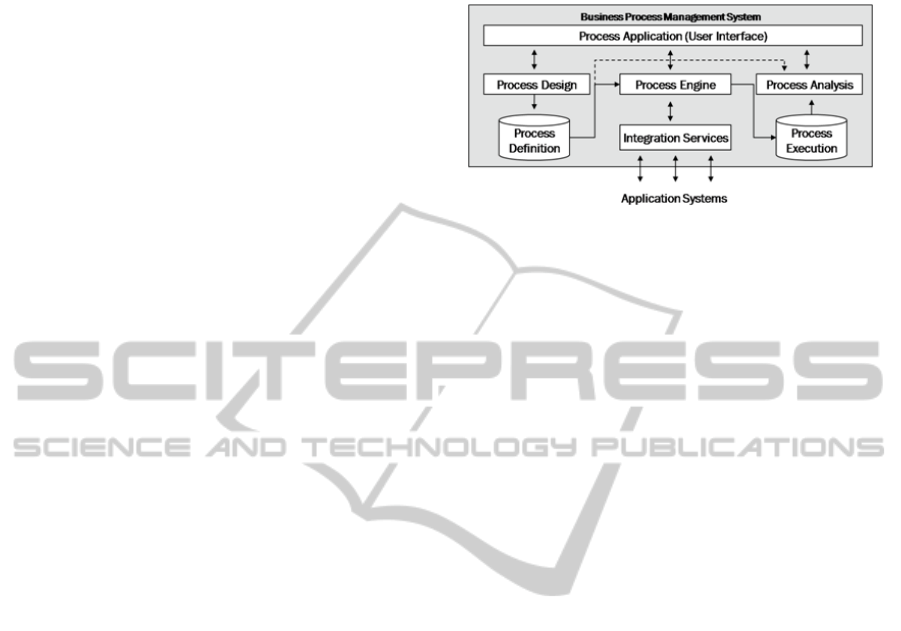
A BPMS in general consists at least of the
following components as depicted in Figure 2
(Strohmeier, 2008), (Chang, 2006).
─ Process Designer: Supports the design of the
business process and its technical realization
by graphical representations. Within the
designer it is possible to define user and
system activities and to define rules which
steer the process flow during execution.
─ Process Engine: Execution and steering of the
complete process involving all users and
systems. The engine uses an executable code
that was generated out of the graphical
representation of the modeled process.
─ Process Analysis: This component is necessary
to analyze the process definition and
execution. In particular it has the functionality
of process simulation, process monitoring and
business activity monitoring (BAM).
─ Process Application: Different User Interfaces
for different user roles e.g. administrators,
business analysts, process owners,
collaborators. By means of these interfaces it is
possible to start, interact, control and analyze
processes.
─ Process Persistence: The BPMS needs a
persistence layer for storing process definitions
(process repository) and the current states of
the executed processes (process execution).
─ Integration Services: The system activities of a
process integrate services and transaction from
different systems (data bases, legacy systems
and so on). BPM is the “killer application” of a
service-oriented architecture (SOA). Each
service of the SOA can be integrated for the
implementation of a business process.
Figure 2: The core components of a BPMS (Strohmeier,
2008), (Chang, 2006).
The main benefits embedding a BPMS into process-
oriented web applications compared to the
conventional web application development are:
─ Transparency of the processes within the
software due to the graphical process designer.
Hence, know-how is more easily transferred to
new developers. Transparency is the
assumption of agility and therefore is the
biggest advantage of embedding BPMS over
using conventional software development.
─ Integration of non-IT end users in the
development process. In dynamic web
applications new organizations have to be
integrated quickly by adapting their processes.
This can be done best by involving the end
user in the development process. BPMS enable
the incorporation of end-users by graphical
representations and simulations. A similar
approach can be found in Nussbaumer,
Freudenstein and Gaedke (2006).
─ Better maintainability, agility and easier
extensibility and faster development.
Individual processes can be created and
integrated faster and with less risk of side
effects due to graphical process modeling, less
coding and simulation.
─ Flexible change management. Due to long
running processes, there are situations where
the same process has to be supported in
different versions. This is a problem to
conventionally implemented applications, but
not for BPMS-based ones because the process
definitions are separated from the web
application and can exist in different versions
at the same time.
─ With respect to continual improvement,
BPMSs make it easy to administrate and
monitor running processes. This is the base for
optimizing the web application’s processes.
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation
43

Despite of this trend and the benefits of BPMSs,
most process-oriented web applications are
implemented conventionally. That means they are
developed using a standard web application
programming framework like PHP, ASP.NET or
JEE and the processes are implemented directly.
Reasons for this are:
─ In general, web applications have a history.
The development was started several years ago
when process-oriented platforms were in their
infancy. Therefore, with time and money
already invested in their web application, the
decision to migrate the application to a BPMS
is a big step and associated with new
investments.
─ BPMS technology is expensive. Many
applications do not justify the investment into
specialized process-oriented platforms.
─ Commercial BPMS technology is complex and
new to the casual web application developer.
Hence, the company must invest in BPMS
knowledge before it can take advantage of the
benefits. Only few Open Source products exist.
─ There is a lack of methodologies that describe
how to migrate a process-oriented web
application to a BPMS. There are few
experiences to follow for such projects which
increase the risk of failure.
Particularly in non-business domains like e.g.
healthcare these reasons are even more fatal. Public
services are always short on cash and IT-staff
capacity. Nevertheless there is the same need for
intra- and inter-organizational processes as in
business domains. The motivation and need for re-
engineering process-oriented web applications is
founded in the nature of non-business domains and
conventional web development. Together with the
success of a web application the number of new
requirements of the users is increasing quickly, too.
The result is a monolithic system that involves a lot
of special process branches. Transparency and
maintenance suffer. The web application know-how
is distributed among few software experts. The only
way out is to re-engineer the application and because
of its process-oriented nature the use of BPMSs is
preferable.
Gartner reported that as of 2006 the BPMS
market had reached nearly $1.7 billion dollar in total
software revenue and it was further estimated that
the BPMS market will have a compound annual
growth rate of more than 24% from 2006-2011 (Hill,
Cantara, Deitert and Kerremans, 2007).. Fortunately,
with the increase of commercial products, open
source projects have come along (e.g. JBOSS jBPM
by Red Hat Inc. (Red Hat, 2010).). Commercial
suites are more powerful but for the adoption in the
area of process-oriented web applications, the
existing open source platforms are powerful enough.
Open source BPMS products are complex. On the
other hand, they do rely on open standards and
popular programming languages. Hence, the effort
for the familiarization with the new technology is
justifiable and doable.
There are numerous web design and modeling
methods that cover different aspects of designing
data-centric web applications, e.g. Schwabe and
Rossi (1998), Ceri and Bongio, (2000), Gomez,
Cachero and Pastor (2001). None of these
methodologies addresses the design and
implementation of processes in web applications.
The missing link between existing conventionally
implemented process-oriented web applications and
process-oriented platforms is a methodology that
describes how to migrate these web applications to
the BPMS target platform. In Brambilla et al.
(2006), process modeling and process distribution is
incorporated into the design of process-centric web
applications. The authors propose to extend the
development process of such web applications in
line with Boehm’s classic spiral model and modern
web and software engineering methods by these two
steps. Unfortunately, the resulting method is too
abstract, does not cover the implementation of the
web application using a BPMS and is therefore not
yet complete. Another approach is to look at best
practices of BPM(Miers, 2006). The consecutive
steps of the BPM life cycle are refined in order to
make the procedure more concrete and practical.
Following the methodology helps realizing and
managing business processes in practice. The
approach does not discuss web applications and their
conversion to a BPMS and is therefore not sufficient
for our problem either.
In the following section, a methodology that
combines both approaches is presented. The idea of
Brambilla et al. (2006) is picked up and integrated in
the best practice approach from Miers (2006) and
van der Aalst et al. (2003) BPM life cycle. The
result is a methodology that enables the re-
engineering of a conventionally implemented,
intrinsically process-oriented web application by
embedding a BPMS. By means of the combination
of a theoretical web engineering method with a best
practice BPM method a new method arises that
claims to have a solid theoretical fundament.
Further, it is realistic enough to meet the
requirements of practical use. The potential of the
methodology for challenges in healthcare web
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
44

applications is sketched in section 3.
2 THE METHODOLOGY
The fundamental difference between the source and
the target architecture has first be understood.
Conventionally implemented web applications
create processes implicitly. That means the process
logic is implemented using the programming
language of choice and the state of each process is
stored in the data base used by the web application.
Process control- and data-flows are implemented
indirectly using the data base. For example, the logic
of a XOR-Gateway can be controlled by an if-clause
that stores a data set or attribute in dependence of
the evaluation of a condition in different data base
tables.
In contrast, embedding a process-oriented
platform separates the processes from the rest of the
web application. The processes are controlled
explicitly. Using the wording of object-oriented
programming, process models can be regarded as
classes that can be instantiated. Equivalent to objects
of classes, each process instance hides an internal
state. The state can be manipulated by user and
system activities (corresponding to methods in the
object-oriented scenario) until the process
terminates. Process models are designed using a
special process notation like OMG’s Business
Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) (OMG, 2010),
(White and Miers, 2008). The BPMS translates the
process model into an executable format like e.g.
BPEL (Alves, 2006) or XPDL (WfMC, 2010) that
can be executed by the embedded process engine
(Ouyang, Dumas, van der Aalst, ter Hofstede and
Mendling, 2009). The persistence of the internal
state of the processes is guaranteed by the BPMS
and its internal data base.
Hence, the main difference between the two
architectures is in the way the processes are
implemented. While in the conventional case the
processes are implemented implicitly, the new
architecture implements them explicitly by
embedding a process engine. The methodology for
re-engineering consists of four major steps that are
executed iteratively until the migration is
successfully finished. Each major step consists of
several minor steps that describe the concrete
activities more precisely and generate important
artifacts for a successful re-engineering. In the
following, the methodology will be explained in
detail and is depicted in Figure 3.
Discover an Understand: the re-engineering
starts with an analysis of the underlying web
application. The existing processes have to be
unsheathed. This step is an analogy for the work of a
business analyst in a company who tries to
understand and model a concrete business process.
The difference is that the process is not hidden in the
minds of the company’s employees, but in the
present web application. Due to the iterative nature
of the methodology, it is possible to start with a
subset of the embedded processes. In each iteration,
more and more processes can be added until the
complete set of processes is addressed. The best
practice is to start small but think big. Within this
step, several artifacts have to be generated.
First of all, a non-technical model of the considered
processes must be created documenting control and
data-flow complete with non-technical iteration to
iteration process map. This is an important output of
the step. Furthermore, the existing user roles and
their activities within the processes have to be stated.
Figure 3: Adopting the BPM-Lifecycle from Miers (Miers,
2006) for the reengineering of intrinsically process-
oriented web applications.
Design and Implementation: the next step
addresses the technical process model. In it an
executable model of the analyzed processes is build.
While the first step can be done by business
analysts, the second step is handled by process
engineers using general software. The process
engineers have to work tightly together with the
original web application developers. They augment
the non-technical business process model by
implementing the details. They have to design and
embed the forms to recognize for the user tasks.
They have to define and implement system activities
such as data base accesses or web service calls.
Further, they implement business rules for the
control flow of the processes. By separating the
processes from the rest of the web application, a
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation
45

redesign of the underlying data base scheme of the
web application is necessary doing such things as
eliminating redundant tables and attributes. The state
of the processes is considered in the present data
base scheme and is no longer needed. Moreover, an
architecture has to be build that describes how the
integration of the process engine in the web
application is arranged. Following this the technical
processes are integrated following this architecture.
In addition, the authentication and authorization
concept of the web application has to be mapped to
the BPMS. Ideally, it is possible to use the BPMS of
choice for the first two steps. Unfortunately, in
practice it is often necessary to use different
software tools for both steps. Hence, a lot of
discipline and manual work is necessary to align the
non-technical and the technical process model.
Deployment and Test: following the
development and implementation, the technical
processes have to be deployed to the process engine
and. Besides the casual test scenarios for software
applications, there are several aspects that have to be
tested because of the special target architecture. The
processes must be tested using the administration
console of the BPMS and the web application as
well. This test gives information about the quality
and correctness of integration. The tests have to
prove that the control- and the data-flow of the
process are implemented correctly. The process
analysis tools (e.g. business activity monitoring) of
the BPMS employed is very helpful. Such tools
allow an activity based debugging.
Further, user and system activities can be tested
individually. The functionality of forms and
correctness of service calls using the integration
services of the BPMS are subject to these tests.
Another special test affects the mapping of
authentication and authorization rules of the web
application to the defined user roles and activities in
the designed processes. The tests have to verify that
user activities are only claimed by the designated
users of the web application.
Evaluation and Review: this last step of the
iteration collects the results of the testing step. While
little errors are fixed directly in step 3, conceptual
problems are evaluated and reviewed in step 4.
These can either be technical or non-technical
problems such as where testing has detected
performance problems with a process. This technical
problem can be addressed by performance
measurements. Alternative implementations can be
inspected and simulated. It may be discovered that
some of the original processes of the web
application emerge to be (non-technically)
suboptimal. These processes can be optimized and
alternative process models can be simulated.
In terms of the continual re-engineering approach
the next iteration is started for missing processes or
processes that have to be optimized according to
step 4. If all processes of the web application have
been re-engineered and if the evaluation and review
step has been finished without any open issues then
the migration can be finished successfully. The new
process-oriented web-application can replace the old
production system. It is important to manage and
improve the resulting production system with a
concrete BPM life cycle as defined in Miers (2006).
3 RELEVANCE FOR HEALTH
CARE WEB APPLICATIONS
In many countries errors in medicine are estimated
to be among the ten leading causes of death (WHO,
2005), (Kohn, 2006). The number of adverse events
is about tenfold higher. Errors with no negative
outcome (incidents, near-misses) are much more
frequent. Cases with patient harm are only the tip of
the iceberg. If we look at “errors in medicine” as a
serious diagnosis, we do not know enough about the
methods of preventing, diagnosing and treating this
“illness”. Clearly, most errors are not due to a basic
lack of medical knowledge of health care
professionals, but problems of applying that
knowledge under the imperfect real world conditions
of patient care (Rall and Gaba, 2005). The IOM
(Institute of Medicine) concludes that identifying
and learning from errors by developing a nationwide
public mandatory reporting system and by
encouraging healthcare organizations and
practitioners to develop and participate in voluntary
reporting systems. Based on Lucian Leape’s
recommendations for incident reporting systems the
World Health Organization (WHO) published the
guidelines for safe and effective reporting systems as
shown in Table 1 (WHO, 2005).
“If reporting is safe and provides useful information
from expert analysis, it can measurably improve
safety.“ (Leape, 2002)
The Tübingen Center for Patient Safety and
Simulation (TüPASS) has the task to improve
patient safety in hospitals and was founded in 1997
and pursued several strategies. Besides simulation
training of clinical personnel, one of the main topics
is the web-based collection and analysis of incidents
and critical incidents (incident reporting system;
IRS). Our IRS PaSIS (Patient-Safety Information
System) is a web-application written in PHP that is
used
by more than 70 hospitals and over 30 rescue
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
46

Table 1: Characteristics of Successful Reporting Systems;
Adapted by Leape (2002) from Cohen, Conell.
Non-
punitive.
Reporters are free from fear of
retaliation against themselves or
punishment of others as a result of
reporting.
Confidential. The identities of the patient, reporter,
and institution are never revealed.
Independent. The reporting system is independent
of any authority with power to punish
the reporter or the organization.
Expert
analysis.
Reports are evaluated by experts who
understand the clinical circumstances
and are trained to recognize
underlying systems causes.
Timely. Reports are analysed promptly and
recommendations are rapidly
disseminated to those who need to
know, especially when serious hazards
are identified.
Systems-
oriented
Recommendations focus on changes
in systems, processes, or products,
rather than being targeted at individual
performance.
Responsive The agency that receives reports is
capable of disseminating
recommendations. Partici-pating
organizations commit to implementing
recommendations whenever possible.
helicopter bases in central Europe and has more than
3000 reports. All reports undergo an active
professional four-eye anonymization and de-
identification process by domain experts trained
in
incident reporting and using checklist protocols to prevent
any lapses in de-identification.
After de-identification, most reports can be read
in full text by all employees. This is meant to
sensitize all by reading all the cases and to stimulate
discussion about patient safety in the department and
to report your own cases. All reports are manually
tagged with key words for meaningful search results;
they are classified according to the U.K. NHS NPSA
contributory factors framework (Vincent, Taylor-
Adams and Chapman, 2000), (Vincent,
2004),(Vincent, 2003) and also categorized with the
CRM (Crisis Resource Management) key
points(Howard, Gaba and Fish, 1992), (Rall and
Dieckmann, 2005). The nature of an IRS is truly
process-oriented, and therefore faces several
challenges:
─ PaSIS is characterized by long running
processes (several weeks or months) that
involve various process participants in
different organizations, e.g. the report author,
medical experts, employees of medical
engineering or pharmaceutical companies.
Even patients report incidences to the system.
Finally, reports and solutions can be made
public after de-identification, analysis and
approval.
─ Furthermore, the application does not consist
of one standard process. Because of different
structures, the requirements of the participating
hospitals are very different and individual
processes have to be implemented. Moreover,
the system is open to new client hospitals and
grows continuously. At the moment,
customizing the system for new hospitals is a
complex and time-consuming task, because the
processes have to be implemented
conventionally.
─ Another challenge is to open the system for
new types of clients like e.g. medical practices.
Together with these new client types, new
processes with new user roles have to be
implemented and integrated from scratch in a
transparent and user-centric manner.
─ In this sense, it is profitable to involve new
clients in designing the individual processes. In
general, contact persons of new clients are
medical experts and not software engineers.
Therefore, a business process modeling
notation has to be used that is understandable
by medical employees.
─ Another aspect of the application is that
different versions of the processes have to be
executed simultaneously. This is necessary,
because processes change and process
instances of older versions are still in the
system. The challenge is to guarantee that the
instances of the old versions still run correctly
and are able to terminate. Sometimes the
update of instances to newer versions is
preferable.
─ Because of the big variety of incident cases,
the analyzing process is very complex,
extensive and has to be open to new
techniques. Even the number of stakeholders
connected to an incident case change with the
underlying and contributing factors.
Conventional web application development is
not capable of managing these requirements
satisfactorily. In contrast, embedding modern
process-oriented software architectures or platforms
following the introduced methodology has many
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation
47

benefits for the system’s implementation. Applying
the methodology assumes the choice of a process-
oriented target platform.
4 A PROCESS-ORIENTED
ARCHITECTURE
As stated earlier, the various BPMSs are complex
and diverse. Due to the embedding of the process
engine within the web application it is advisable to
choose a rather ligthweight system. Hence, the open
source system jBPM is adequate. jBPM is a java
based tool, which is easy to integrate into an existing
java based environment and it is also a framework,
that allows the user to implement the main stages of
BPM. Its focus is to provide a bridge between non-
technical business users and developers. To reach
this goal, jBPM consists of a powerful process
engine as well as a modeler provided by the
company Signavio (Signavio, 2010). jBPM also
offers an eclipse plug-in based tool to describe
processes in a formal language called jPDL. In
Version 4.3, the user can choose between jPDL and
BPMN 2.0 in order to model the processes. The
plug-in does not as yet provide BPMN 2.0. The
process engine also offers a configurable
environment to execute the predesigned processes.
In addition, it provides tools to analyze and audit the
history of process executions in order to improve
processes and make more accurate business
decisions (Salatino, 2009).
The jBPM target platform can be divided into
three main components. First, there is the
development environment. Here the developer
designs the business processes with designing tools
in a graphical notation (BPMN 2.0 or jPDL), creates
the required forms and embeds them into the
process. The second component is the administration
interface. It is an administration and monitoring
console that allows inspection and manipulation of
runtime instances and management of the deployed
processes. For these reasons, the JBoss-provided
GWT-based jBPM console will be used. Figure 4
sketches the resulting process-oriented architecture.
The main component of the architecture is still
the actual IRS web application where the IRS-
process is initiated and where incident reports are
composed, anonymized, analyzed and handled. But
this is done in a different way. The original web
application is extended by the communication with
the
jBPM-engine. The jBPM-engine itself is
Figure 4: Outline of our process-oriented architecture.
transparent to the user. The process-oriented part of
the web application is made visible and transparent
within the development process by realizing it
graphically with jPDL. Unfortunately, jBPM does
not yet provide an official, generic interface for non-
java environments (e.g. a rest interface); therefore,
the interaction of the web application with jBPM is
realized using JEE-technology. The PHP application
sends requests to a JEE web application that realizes
a seamless integration of jBPM into the PHP
application. The JEE web application interacts with
jBPM and responds to the PHP application. In our
architecture the XForms standard of the W3C (W3C,
2010) is used to design the different forms. The
forms are completed with process variables using
FreeMarker, a java template engine (FreeMarker,
2010). The forms are rendered by the java web
application Orbeon (Orbeon, 2010). Process data is
managed by the process instance. Access to data or
the state of running processes is possible using the
jBPM-API or using the management console of
jBPM. Before process termination, the relevant
process data (in our case the incident report, the
analysis, and so on.) have to be stored in the original
data base of the IRS web application.
5 TOWARDS A
PROCESS-INTEGRATED IRS
The detailed realization of the IRS processes for
more than 70 hospitals is a time consuming venture.
In order to verify the presented methodology and
process-oriented architecture, a default IRS process
was implemented successfully on our process-
oriented architecture using the suggested
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
48

methodology. This process features no exceptional
conditions, error conditions or special cases.
Although, the default process is not that complex as
the actual implementations, it is meaningful enough
and can be used as a proof of concept for the
architecture and the methodology. The methodology
allows refining the process step by step. Hence, the
default process can be used as a starting point for the
real processes of the several participating hospitals.
Only one iteration of our methodology was
necessary to create the default process. In the
following, we will outline some aspects of this
iteration.
The requirement for the first step of the
methodology was an instance of the original system
serving as a reference. By that we were able to
survey the view of the several process participants to
the system. Within this step, we had several
meetings together with the developers and users of
the system. We decided to use the BPMN. First, we
had to create a common understanding of the
system. The result is what we call a strategic process
model. This model describes the main participants
(user roles and systems) and the order of their main
activities (see Figure 5). In this phase, it is advisable
to disregard all the special cases and exceptional or
error conditions of the real process.
After creating a common understanding of the
IRS process, we started to model its operative
details. The result is an operational process model
that is needed for several reasons:
1. It helps process participants to orientate
during daily work.
2. Process analysts can use it as a base for
improvement.
3. The model is the starting point for the
process implementation.
The operational model even includes the role of
the process engine (see Figure 6). At this point, you
have to decide which degree of accuracy you want to
achieve in the first iteration of our methodology.
Although we had more detailed models as results of
our meetings, we decided to use the operational
model of the default process (also called “happy
path”) as input for the design and implementation
step. This is reasonable, because we wanted to use
the first iteration as a proof of concept for our
approach.
In the design and implementation step, we turn
the operational process model into a technical
process model that can be executed by the process
engine. We decided to realize the technical model
using jPDL. Unfortunately, the current version of
jBPM was not robust enough using BPMN 2.0.
Figure 5: The strategic process model of the IRS process.
Besides creating the technical process model
using jPDL, the following work had to be done:
1. Design of the forms for user interaction
using the XForms standard of the W3C.
2. Implementation of data base access tasks.
3. Integration of jBPM in the PHP application
using JEE technology.
After testing the resulting implementation
thoroughly in step 3 of our methodology, we
discussed the actual implementation in step 4. It is
obvious that the implemented process has to be
improved in further iterations, because we started
with a simplified default IRS process. Hence, we can
skip step 4. In the first iteration, most time was spent
for the first two steps of the methodology.
Obviously, with an increasing number of iterations,
the portion of time per iteration that is spent for step
3 and 4 will increase, while the portion for step 1
and 2 will decrease.
The resulting system is a web application with a
seamless integration of the default IRS process. The
task to realize the accurate IRS processes requires
just diligence in order to complete it.
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation
49

Figure 6: Extract of the default operative IRS process.
6 CONCLUSIONS
More and more, web applications are controlling
business processes. They have major advantages in
the field of healthcare where the work is typically
based on collaboration and cooperation between
employees of hospitals, companies and patients.
However, most web applications are implemented
conventionally using a typical web programming
language like PHP. As such, the necessary
transparency and agility for managing business
processes is limited by the implementation
technology and the surrounding classical software
engineering process. New process-oriented
technologies like BPMSs promise to overcome these
limitations. The present paper showed a
methodology to embed process engines of BPMSs
into conventionally implemented, intrinsically
process-oriented web application. Applying the
methodology separates the implicitly implemented
processes from the rest of the web application
allowing these processes to be controlled explicitly
by an integrated BPMS. Of course, a final
judgement of the proposed methodology cannot be
done until the new process-oriented implementation
has been deployed completely. Despite of this, the
methodology is promising and the whole web
application can benefit from the advantages of
process-oriented platforms and can then be managed
according to the BPM life cycle. This paper sketches
out how process-oriented techniques can solve the
distinctive challenges arising in healthcare web
applications, particularly in incident reporting for
hospitals. Moreover, a process-oriented target
architecture for embedding into web applications
was presented and used to verify the methodology
by controlling the main process of our incident
reporting system. Further iterations of the
methodology will lead to a process-integrated web
application that benefits of the advantages of BPM,
like e.g. to involve the hospital employees in the
modeling of the IRS processes within the software
engineering process. Ongoing research in the area of
BPM is very alive and dynamic. Especially the
adaption of the new version 2.0 of BPMN by the
several BPMS projects and vendors are very
promising for the future. Besides the mentioned
advantages, we also have to verify thoroughly if the
resulting process-oriented system with its increased
complexity (additional technologies and servers)
will still remain controllable like a classical web
application.
After defining and verifying the methodology for
migrating web applications to process-oriented
platforms presented in this paper, we will address
the methodology for managing the migrated web
applications. The support of both methodologies by
software tools will be surveyed. This is directly
related to technical issues like a suitable, complete
tool-chain and a reference architecture for the
integration of BPMS in web applications. Finally,
the complete incident reporting system will be
migrated to the process-oriented platform and
afterwards will replace the actual production system.
REFERENCES
Alves, A. e. a (2006), Web Services Business Process
Execution Language Version 2.0. Retrieved March 12,
2010, from http://docs.oasis-open.org/wsbpel/2.0/
wsbpel-specification-draft.html
Brambilla, M., Ceri, S., Fraternali, P. (2006). Process
Modeling in Web Applications. ACM Transactions on
Software Engineering and Methodology, 15, 360–409.
Ceri, S. F. P., Bongio, A. (2000). Web modeling language
(WebML). A modeling language for designing Web
sites. Computer Networks, 33, 137–157.
Chang, J. F. (2006). Business process management
systems. Strategy and implementation. Boca Raton:
Auerbach.
FreeMarker: Java Template Enginee (2010).
Retrieved July 23, 2010, from http://freemarker.
sourceforge.net/
Gomez, J., Cachero, C., Pastor, O. (2001). Conceptual
modeling of device-independent Web applications.
IEEE MultiMedia, 8, 36–39.
Hill, J. B., Cantara, M., Deitert, E., Kerremans, M. (2007).
Magic quadrant for business process management
suites.
HEALTHINF 2011 - International Conference on Health Informatics
50

Howard, S. K., Gaba, D. M., Fish, K. J. (1992). Anesthesia
crisis resource management training. Teaching
anesthesiologists to handle critical incidents. Aviation,
Space, and Environmental Medicine (ASEM), 63, 763–
770.
Karagiannis, D. (1995). BPMS: Business Process
Management Systems. ACM SIGOIS, 16, 10–13.
Ko, R. K. L. (2009). A Computer Scientist's
Introductionary Guide to Business Process
Management (BPM). ACM Crossroads, 15.
Kohn, L. T. (2006). To err is human. Building a safer
health system. Washington, DC: National Acad. Press.
Leape, L. L. (2002). Reporting adverse event. New
England Journal of Medicine, 347, 1633–1638.
Miers, D. (2006). Best Practice BPM. ACM Queue, 4, 42–
48.
Nussbaumer, M., Freudenstein, P., Gaedke, M. (2006).
Stakeholder Collaboration. From Conversation to
Contribution. In: Proceedings of the 6th international
conference on Web engineering, pp. 117–118.
Object Management Group / Business Process Managemnt
Initiative (n.d.). BPMN Specifications. Retrieved
March 12, 2010, from http://www.bpmn.org/
Orbeon: Web Forms for the Enterprise (2010). Retrieved
July 23, 2010, from http:// http://www.orbeon.com/
Ouyang, C., Dumas, M., van der Aalst, W.M.P., ter
Hofstede, A. H. M., Mendling, J. (2009). From
Business Process Models to Process-Oriented
Software Systems. ACM Transactions on Software
Engineering and Methodology, 19(2), Article 2.
Rall, M., Gaba, D. M. (2005).Human Performance and
Patient Safety. In: Miller, R. D. (ed.) Miller's
anesthesia, pp. 3021–3072.
Rall, M., Dieckmann, P. (2005).Safety culture and crisis
resource management in airway management. General
principles to enhance patient safety in critical airway
situations. Best Practice & Research Clinical
Anaesthesiology, 19, 539–557.
Red Hat, I (n.d.). JBoss jBPM. Retrieved March 12, 2010,
from http://www.jboss.com/products/jbpm/
Salatino, M.(2009). jBPM Developer Guide. Birmingham,
UK: Packt Publishing.
Schwabe, D., Rossi, G. (1998). An object oriented
approach to web-based application design. Theory and
Practice of Object Systems, 4, 207–225.
Signavio GmbH (n.d.). Signavio Process Editor - Software
as a Service. Retrieved March 12, 2010, from
http://www.signavio.com/en/products/process-editor-
as-a-service.html
Strohmeier, S. (2008). Informationssysteme im
Personalmanagement. Architektur - Funktionalität -
Anwendung ; [in german]. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag /
GWV Fachverlage GmbH Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden.
van der Aalst, W. M. P., ter Hofstede, A. H. M., Weske,
M.: Business Process Management: A Survey. In: van
der Aalst, W. (ed.) Business process management.
International conference, Eindhoven, The Netherlands,
June 26 - 27, 2003 ; proceedings. Springer, Berlin
(2003).
Vincent, C., Taylor-Adams, S., Chapman, E.J. (2000).
How to investigate and analyse clinical incidents.
Clinical risk unit and association of litigation and risk
management protocol. British Medical Journal, 320,
777–781.
Vincent, C. (2003). Understanding and responding to
adverse events. The New England Journal of
Medicine, 348, 1051–1056.
Vincent, C. A. (2004). Analysis of clinical incidents: A
window on the system not a search for root causes.
Quality and Safety in Health Care, 13, 242–243.
W3C: XForms Standard (2010). Retrieved July 16, 2010,
from http://www.w3.org/MarkUp/Forms/
White, S. A., Miers, D. (2008). BPMN modeling and
reference guide. Understanding and using BPMN ;
develop rigorous yet understandable graphical
representations of business processes. Future
Strategies Inc., Lighthouse Point, Fla.
WHO World Alliance for Patient Safety (2005). Draft
Guidelines for Adverse Event Reporting and Learning
Systems. From Information to Action. Retrieved
March 12, 2010, from hxxp://www.who.int/
patientsafety/events/05/Reporting_Guidelines.pdf
Workflow Management Coalition (WfMC) (2010): XPDL
Specification. Retrieved March 12, 2010, from
http://www.wfmc.org/xpdl.html
A CHALLENGE FOR HEALTHCARE WEB APPLICATIONS - From Data- to Process-Orientation
51
