
UNSUPERVISED 3D SEGMENTATION OF HIPPOCAMPUS
IN BRAIN MR IMAGES
Sandeep S. Kaushik and Jayanthi Sivaswamy
Center for Visual Information Technology, IIIT-Hyderabad, Hyderabad, India
Keywords:
Hippocampus, MRI segmentation, Water flow, Deep brain structure, Surface evolution, Region growing, 3D
segmentation, Hippocampal volumetry.
Abstract:
The most widely followed procedure for diagnosis and prognosis of dementia is structural neuroimaging of
hippocampus by means of MR. Hippocampus segmentation is of wide interest as it enables quantitative as-
sessment of the structure. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for hippocampus segmentation that is un-
supervised and image driven. It is based on a hybrid approach which combines a coarse segmentation and
surface evolution. A coarse solution is derived using region growing which is further refined using a modified
version of the physics based water flow model (Liu and Nixon, 2007). The proposed method has been tested
on a publicly available dataset. The performance of this method is assessed using Dice coefficient against the
ground truth provided for 25 volume images. It is consistent across volumes and the average Dice values are
comparable to a multi-atlas based method reported on a subset of the same dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dementia is a clinical syndrome that affects memory
and cognitive ability of a person. It is known to be
caused due to traumatic brain injury, neurodegenera-
tive diseases, bacterial infections, prolonged epilep-
tic seizures, and so on. Some common types of de-
mentia are mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or incip-
ient dementia, Alzheimer disease (AD) or dementia of
the Alzheimer type (DAT), dementia with Lewy bod-
ies (DLB) and fronto-temporal dementia (FTD). De-
mentia is usually diagnosed based on clinical obser-
vations, presence of characteristic neurological and
neuropsychological features. Onset of dementia is
difficult to diagnose with these methods. Therefore,
along with clinical diagnosis, structural neuroimag-
ing is used to enable early diagnosis so that it can
be treated at the onset. Apart from diagnosis, struc-
tural neuroimaging helps to distinguish between dif-
ferent types of dementia, to differentiate between nor-
mal aging and dementia and in differential diagnosis.
Some of the methods to assess change in brain vol-
ume by means of structural neuroimagingare volume-
try, voxel based morphometry(VBM), cortical pattern
matching and brain boundary shift integral measure-
ments. Hippocampus is the structure responsible for
long term memory in the brain and its atrophy is an
early and specific marker of dementia. The severity
of hippocampal atrophy is directly related to progress
of the underlying disease and hence reflects the extent
of cognitive impairment. Although atrophy rates have
been observed to be larger in entorhinal cortex than
in hippocampus, difficulty in unambiguously defining
this structure makes its measurement highly variable.
Thus, hippocampus is the region of interest in differ-
ential diagnosis of AD and mild cognitive impairment
(MCI).
Manual labelling by experts is considered as gold
standard of hippocampal segmentation. But this is
laborious, time consuming, prone to inconsistency
and inter-expert labelling variability. Advanced im-
age analysis techniques have been used to minimise
these problems by developing semi-automatic hip-
pocampal segmentation methods or further, by ob-
taining reliable initialisation, fully automatic segmen-
tation methods. From medical imaging viewpoint,
research in segmentation of deep brain structures in
general and hippocampus in particular is motivated
by various factors like i) development of computer
aided diagnosis solution by methods. The attraction
here is the potential for high precision and consis-
tency over manual segmentation which in turn offers
reliable volumetry (Bernasconi et al., 2003); ii) study
of the characteristic pattern of a particular disease or
normal aging (Chupin et al., 2008); iii) development
of generalised segmentation algorithm applicable to
182
S. Kaushik S. and Sivaswamy J..
UNSUPERVISED 3D SEGMENTATION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN BRAIN MR IMAGES.
DOI: 10.5220/0003145401820187
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2011), pages 182-187
ISBN: 978-989-8425-35-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

various structures (Morra et al., 2008); iv) accelera-
tion of drug trials and population study of diseases.
In general, the hippocampus, with weak edges and in-
homogeneity, acts as a good test case for a neuroseg-
mentation algorithm in both 2D and 3D (Morra et al.,
2010). Given the focus of this paper on hippocampus
segmentation, next section reviews the existing meth-
ods for the same in some detail.
1.1 Related Work
The existing methods can be classified broadly based
on the approach taken to include the domain knowl-
edge as follows: i) atlas and cohort atlas based, ii)
pattern classification and machine learning methods
based and iii) deformable models or template based.
Segmentation via registration to a brain atlas is
class of methods followed in (Akhondi-Asl et al.,
2010; Ltjnen et al., 2010). In these methods, a neu-
roanatomic atlas is registered, i.e., spatially aligned
with the given subject image to delineate the bound-
ary of the region of interest. The registration is carried
out after geometric transformation to correct align-
ment and enhancement to correct intensity variations.
Atlas-based approaches have the advantage that ad-
vances in registration techniques can be exploited.
Thus, most of the available standard registration al-
gorithms and packages can be used for segmentation.
Standard atlases available are Harvard whole brain
atlas and MNI-Talairach atlas. They contain the la-
belled structures of the whole brain and hence can be
used to segment any structure without prior knowl-
edge about the structure. However, if the subject im-
age varies largely from the atlas in terms of age of the
subject or physical dimensions of the voxels, segmen-
tation performance suffers. To overcome this issue, a
cohort atlas is built. In cohort atlas, experts manually
segment the structure of interest on one or more sub-
ject images selected from a set of reference images.
Each or combination of these labelled data (image)
can be used as an atlas. The disadvantage of using
cohort atlas is the requirement of an expert and one or
more labelled data. Both of these methods have the
common issue of inability to handle variation in data
over larger sets. Hence, atlases are more suitable for
initialisation than for complete segmentation.
An alternative way to use domain knowledge is
with pattern classification and machine learning tech-
niques. Statistical and anatomical prior knowledge
are learnt and used to localise and segment hippocam-
pus. Appearance based features are used to build a
context model in (Morra et al., 2010), while segmen-
tation is posed as an expectation maximisation prob-
lem in (Sabuncu et al., 2009). Prior information from
an atlas and segmentation via likelihood has been
adopted in (Akselrod-Ballin et al., 2007). Most of the
techniques depend upon the shape of hippocampus
varying within a given margin. Furthermore, since
these techniques are largely supervised, the choice of
features and modelling of the problem is critical.
Template and deformable models help use domain
knowledge in a more flexible way. These methods are
derived by using prior anatomical knowledge. The
structure to be segmented is modelled and parame-
terised using shape knowledge and then deformed to
segment the structure. Minimising an energy function
via iterated conditional modes (ICM), initialised by
prior information from probabilistic atlas is described
in (Chupin et al., 2008). Although these methods have
been observed to perform well, their design and im-
plementation are very complex. Shape encoding for
segmentation has to consider all possible variations of
shape of the structure. This requires a large amount
of supervision to train the model. In some of these
methods, anatomical information derived depends on
landmark detection.
In general, while prior knowledge about brain
structures can aid the segmentation problem, there are
some costs involved in acquiring this knowledge and
obtaining a good and consistent segmentation perfor-
mance: i) adequate amount of labelled data for train-
ing, ii) age, race and disease-specific matched infor-
mation. An alternative is to use an unsupervised, hy-
brid approach. A combination of region growing and
deformable model or curve evolution is one such op-
tion. Region growing is a relatively fast algorithm
which can extract all parts of the region like curves
and narrow parts. In most of the imaging modali-
ties like optical, CT and MRI, with appropriate fea-
tures used for determining homogeneity criteria, re-
gion growing proves to be one of the simplest meth-
ods of segmentation. However, this alone does not re-
sult in an exact boundary as region growing is vulner-
able especially to weak edges and non-homogeneous
regions. The second curve evolution stage is em-
ployed to address this problem. The resulting surface
is taken as input to surface evolution. This is more ac-
curate than the conventional simple geometric surface
initialisation and much faster than manual surface ini-
tialisation. Surface evolution merely needs to adjust
the surface to exact boundaries which results in quick
convergence. An image foresting transform (IFT) for
coarse segmentation together with an active surface
solution has been proposed for liver segmentation in
CT (Pohle et al., 2003).
In this paper, a non-parametric, hybrid method
is proposed for hippocampus segmentation which
utilises only local image information. The method
UNSUPERVISED 3D SEGMENTATION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN BRAIN MR IMAGES
183

follows the coarse segmentation and surface evolution
framework with the key differences being: the surface
is not parameterised and is evolved using a physics
based water flow model (Liu and Nixon, 2007). The
water flow model has been applied to 2D image seg-
mentation of synthetic images. It has been demon-
strated (but not rigorously assessed) on some 2D real
cases such as grey-white matter interface, femur from
MRI, carotid artery in MR angiogram and retinal ves-
sels; and 3D lateral ventricles. Most of these struc-
tures are homogeneous with well defined boundaries.
In this paper, it is demonstrated how the water flow
model can be adapted to a relatively inhomogeneous,
partially weak edged hippocampus. It is demon-
strated that, in spite of its simplicity, our hybrid algo-
rithm yields results comparable to a recently reported
method. The following section describes this method
in detail.
2 HYBRID SEGMENTATION
The water flow model directs the progress of a water
front based on local image properties derived from re-
gion and edge based forces. In this paper, this model
is chosen because of the following features: i) it is a
physics based model which does not depend on image
topology and ii) it makes use of both gradient forces
and region based forces which is attractive given the
weak edged boundary of the hippocampus.
Since the water flow algorithm acts on a water
front, one of the simplest methods to obtain a front
is by coarse segmentation via region growing. The
coarse segmentation stage works on intensity features
which are sensitive to intensity variation due to a bias
field that can be present. In order to address this prob-
lem, the image volume is pre-processed for bias field
correction. A modified fuzzy C-means algorithm pro-
posed in (Ahmed et al., 2002) is used for this pur-
pose. Here, the intensity inhomogeneity is estimated
using fuzzy logic and used to correct the slowly vary-
ing shading artefact over the image.
2.1 Coarse Segmentation
This stage begins with few seeds initialised by the
user. The protocol of choosing multiple seeds, in-
stead of one, is used so that longitudinal extremes
of hippocampus can be approximated and an initial
modelling of intensity variation can be obtained. In
the process of region growing, these seeds are used
to check for homogeneity in their immediate neigh-
bourhood and decide whether or not to include those
voxels into the region. The parameters used in ho-
mogeneity verification are: deviation of a candidate’s
voxel value from the mean voxel value of the region
and the gradient magnitude at the candidate voxel’s
location.
2.2 Fine Segmentation
The original water flow algorithm (Liu and Nixon,
2007) computes a resultant force on a voxel due to
its neighbouring voxels and decides the flow action.
Three types of image forces, namely, field, potential
and statistical forces aid or oppose the flow, based on
their direction with respect to the resultant field force.
The Field force experienced by a voxel at position
r
i
due to its neighbourhood W is given by the force
field transformation (Hurley et al., 2005) as
F
f
(r
i
) =
∑
j∈W, j6=i
L(r
j
)
(r
j
− r
i
)
|r
j
− r
i
|
3
(1)
The elements of L matrix are set to −1 when a
voxel is filled with water (it is inside the region) and
set to the gradient magnitude (edge strength) other-
wise. This results in a force which is always directed
away from the region. In a cross-sectional area A (set
to unity), the flow velocity gained by a voxel is
v =
F
f
(r
i
)
AR
(2)
where R is the flow resistance given by
R = e
kE(r
i
)
(3)
where E(r
i
) is the edge strength (magnitude of the
gradient) at location r
i
and k is the resistance control-
ling factor. Higher values of k leads to higher sensi-
tivity to edges.
In addition to the static field force F
f
(r
i
), image
forces such as potential force, statistical force con-
tribute to the element flow. The potential force is cal-
culated based on the gradient of the edge map E. This
force is largely concentrated around the edges in the
image and hence acts as a barrier to the water flow.
In the known direction of flow i, given a target posi-
tion r
t
, the potential force experienced by the flowing
element is given by
F
p,i
= ∇E(r
t
) (4)
Water flow model also uses a region based statistical
force based on the Mumford-Shah functional. It re-
flects the change in internal and external intensities of
a closed region and its surroundings. When the target
voxel intensity deviates largely from the equilibrium,
this force turns negative and hence checks the flow.
BIOSIGNALS 2011 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
184

Statistical force due to a target voxel at position r
t
is
given by
F
s,i
=
n
ext
n
ext
+ 1
(I(r
t
) − µ
ext
)
2
−
n
int
n
int
+ 1
(I(r
t
) − µ
int
)
2
(5)
where I(r
t
) is the intensity value at voxel position r
t
,
n is the number of voxels and µ is the mean of inten-
sity of the internal and external regions denoted by the
subscripts int and ext respectively. To maintain a bal-
ance in the simultaneous contribution of these forces
in the element flow, they are added by a convex equa-
tion as
F
i
= αF
p,i
+ (1− α)F
s,i
(6)
In the original water flow algorithm, the flow of an in-
dividual waterfront voxel is not constrained explicitly
by other voxels in the front. However, its movement
should be dependent on the mobility of its surround-
ing voxels on the surface and the tension between
these voxels. Hence, a new tensile force component is
introduced which has the effect of opposing the flow.
This force controls the stretching of the surface and
ensures a continuous surface without holes. The ten-
sile force experienced by a voxel at r
i
is calculated
using the umbrella operator approximation of Lapla-
cian given by (McInerney and Terzopoulos, 1999) as
F
t,i
=
1
n
∑
j∈N
(r
j
− r
i
) (7)
where r
j
is the position of the j
th
surface voxel within
N neighbourhood of r
i
and n is the total number of
voxels in that neighbourhood.
The work done by a voxel under the influence of
all the forces combined is given by
J =
m|v
i
|
2
2
+ (F
i
− ηF
t,i
)S (8)
where m is mass of the element analogous to inten-
sity of the voxel and S is the preset displacement. If
work done is positive, the element moves in the direc-
tion of the resultant force for a predetermined (fixed)
distance. η controls the influence of the tensile force
experienced by the surface.
3 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
User initialised seed points (minimum 1 per slice)
are collected along the length of hippocampus in the
coronal view of a brain MR volume image. Based
on the extreme points, with reasonable margin on all
sides, a sub volume is extracted for faster processing.
To make sure the surface evolves properly to match
both these shapes, two sets of parameters of surface
evolution - α, η and S are used, one to suit head re-
gion and one to suit the body-tail region.
The proposed method is tested on a publicly avail-
able brain MR dataset (Jafari-Khouzani, 2010). It
consists of 25 volumes of training data with as-
sociated ground truth and 25 volumes of testing
data without any ground truth. The first (train-
ing) set has been chosen as the test data. This
set consists of 15 volumes of T1-weighted MR im-
age data of each slice 256x256 pixels with voxel
size 0.781x0.781x2.00mm
3
and 10 volumes of T1-
weighted MR image data of each slice 512x512 pix-
els with voxel size 0.39x0.39x2.00mm
3
. Assessment
is done by computing the Dice coefficient.
Table 1: Comparison of performance with and without ten-
sile force.
Dice’s coefficient
Water flow model Min. Max. Avg.
With tensile force 0.63 0.72 0.68± 0.03
Without tensile force 0.49 0.68 0.62± 0.06
Figure 1: Comparison of performance with and without ten-
sile force.
Since a new tensile component was introduced in
the water flow algorithm, in order to assess its effec-
tiveness, the Dice coefficient was calculated for the
proposed method with and without this component.
Table 1 shows the maximum, minimum and the av-
erage Dice coefficient for 50 hippocampi in the test
set. It can be observed from the table that the tensile
force component plays a positive role in segmenta-
tion and contributes to 6% improvement, on average,
in the Dice coefficient. The dataset (Jafari-Khouzani,
2010) has also been used for assessment of a multi-
atlas (derived from 10 subjects) based method pro-
posed in (Akhondi-Asl et al., 2010) which reports the
UNSUPERVISED 3D SEGMENTATION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN BRAIN MR IMAGES
185
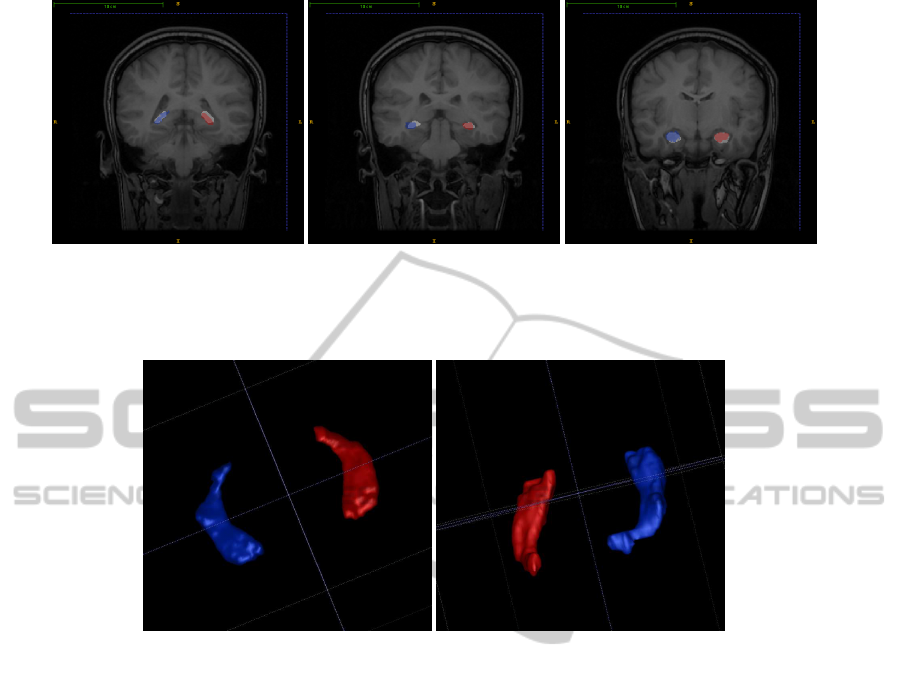
(a) Tail. (b) Body. (c) Head.
Figure 2: Overlay of algorithm output with manual label. Red and Blue translucent regions correspond to algorithm output
and white opaque regions correspond to manual label.
(a) 3D view from hippocampus head. (b) 3D view from hippocampus tail.
Figure 3: 3D surface view of the algorithm output.
average Dice coefficient for the testing part of the
dataset as (0.72± 0.09). This is comparable to that
(0.68 ± 0.03) obtained on the training subset by the
proposed method despite the major difference in the
approaches behind the two methods: multiple atlases
based versus unsupervised method.
Figure 1 provides a graphical comparison of the
Dice coefficient for every volume. The trend of the
two plots is approximately similar. This trend is con-
sistent with the fact that, by design, the tensile force
plays only a moderating role as per (8). In general,
it was observed that the segmentation performance
drops when, even in absence of atrophy, size of hip-
pocampus was very small. In such cases, the corti-
cal walls surrounding the hippocampusand the neigh-
bouring amygdala make the true boundary difficult to
detect resulting in an over-segmentation.
Figure 2 shows some sample extracted hip-
pocampi overlaid over the ground truth. The translu-
cent regions of red and blue denote segmented left
and right hippocampus respectively by the proposed
method. The opaque white region under these corre-
sponds to manual label which is used as the ground
truth. Figure 3 shows the 3D surface view of seg-
mented hippocampi as seen from head of the hip-
pocampus in Figure 3(a) and as seen from its tail in
Figure 3(b).
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a new method for segmentation of hip-
pocampus in MR volume images is proposed. The
advantage of this method is that it does not require an
atlas or template and is free of parameterisation and
supervision. In spite of its simplicity, this method’s
performance is comparable to existing methods. The
tight variance in the Dice coefficient is particularly
encouraging. These results demonstrate that the
framework of hybrid segmentation can successfully
tap advantages of each of the two stages.
The improvement in segmentation performance
with the addition of the proposed tensile component
to the water flow model indicates that the surface
evolution is constrained yet yields more accurate sur-
BIOSIGNALS 2011 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
186

faces. A shortcoming of the proposed methods is that
since the water flow model always evolves from in-
side the region to outside, the coarse segmentation
output has to be within the target boundary of the hip-
pocampus. This limitation can be addressed by de-
signing techniques which permit a two-sided evolu-
tion of the water front.
Overall, it can be concluded that the obtained re-
sults show promise and pave way for applying of
the water flow model for segmenting other (partially)
weak-edge structures as well. Future work will be
targeted at complete automation of this method by
reliable automatic initialisation of seed points or re-
placing the region growing with any other method for
coarse segmentation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Dr. D.Ravi Varma,
DM, KIMS hospital, Hyderabad for his input towards
anatomical structure of hippocampus and qualitative
analysis of results.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, M., Yamany, S., Mohamed, N., Farag, A., and Mo-
riarty, T. (2002). A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm
for bias field estimation and segmentation of mri data.
Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on, 21(3):193 –
199.
Akhondi-Asl, A., Jafari-Khouzani, K., Elisevich, K., and
Soltanian-Zadeh, H. (2010). Hippocampal volume-
try for lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: Auto-
mated versus manual methods. NeuroImage, In Press,
Corrected Proof:–.
Akselrod-Ballin, A., Galun, M., Gomori, J. M., Brandt,
A., and Basri1, R. (2007). Prior knowledge driven
multiscale segmentation of brain mri. MICCAI 2007,
4792/2007:118–126.
Bernasconi, N., Bernasconi, A., Caramanos, Z., Antel,
S. B., Andermann, F., and Arnold, D. L. (2003).
Mesial temporal damage in temporal lobe epilepsy: a
volumetric MRI study of the hippocampus, amygdala
and parahippocampal region. Brain, 126(2):462–469.
Chupin, M., Cuingnet, R., Lemieux, L., Lehericy, S., Be-
nali, H., Garnero, L., and Colliot, O. (2008). Fully au-
tomatic hippocampus segmentation discriminates be-
tween alzheimer’s disease and normal aging - data
from the adni database. In MICCAI Workshop on
CAPH.
Hurley, D. J., Nixon, M. S., and Carter, J. N. (2005). Force
field feature extraction for ear biometrics. Computer
Vision and Image Understanding, 98(3):491 – 512.
Jafari-Khouzani, K. (2010). Mri data set for hip-
pocampus segmentation by department of di-
agnostic radiology at henry ford hospital.
http://www.radiologyresearch.org/HippocampusSeg
mentationDatabase/.
Liu, X. U. and Nixon, M. S. (2007). Image and volume
segmentation by water flow. In ISVC’07: Proceed-
ings of the 3rd international conference on Advances
in visual computing, pages 62–74, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer-Verlag.
Ltjnen, J. M., Wolz, R., Koikkalainen, J. R., Thurfjell, L.,
Waldemar, G., Soininen, H., and Rueckert, D. (2010).
Fast and robust multi-atlas segmentation of brain mag-
netic resonance images. NeuroImage, 49(3):2352 –
2365.
McInerney, T. and Terzopoulos, D. (1999). Topology adap-
tive deformable surfaces for medical image volume
segmentation. Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions
on, 18(10):840 –850.
Morra, J., Tu, Z., Apostolova, L., Green, A., Toga, A., and
Thompson, P. (2008). Automatic subcortical segmen-
tation using a novel contextual model. MICCAI.
Morra, J., Tu, Z., Apostolova, L., Green, A., Toga, A., and
Thompson, P. (2010). Comparison of adaboost and
support vector machines for detecting alzheimer’s dis-
ease through automated hippocampal segmentation.
Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on, 29(1):30 –
43.
Pohle, R., Behlau, T., and Toennies, K. D. (2003). Segmen-
tation of 3d medical image data sets with a combi-
nation of region-based initial segmentation and active
surfaces. Medical Imaging 2003: Image Processing,
5032:1225–1232.
Sabuncu, M. R., Yeo, B. T., Leemput, K., Fischl, B., and
Golland, P. (2009). Supervised nonparametric im-
age parcellation. In MICCAI 2009, pages 1075–1083,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
UNSUPERVISED 3D SEGMENTATION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN BRAIN MR IMAGES
187
