
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST
Anna Gambin
1,2
, Sławomir Lasota
1
, Michał Startek
1
, Maciej Sykulski
1
1
Institute of Informatics, University of Warsaw, 2 Banacha, 02-097 Warsaw, Poland
2
Mossakowski Medical Research Centre Polish Academy of Sciences, 5 Pawinskiego, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland
Laurent No
´
e
3
, Gregory Kucherov
3,4
3
LIFL/CNRS/INRIA, B
ˆ
at. M3, Campus Scientifique, 59665 Villeneuve d’Ascq C
´
edex, France
4
J. -V. Poncelet Lab, Bolshoy Vlasyevsky Pereulok 11, 119002 Moscow, Russia
Keywords:
Sequence alignment, Protein BLAST, Subset seed, DFA, Genetic algorithm.
Abstract:
The seeding technique became central in the theory of sequence alignment and there are several efficient tools
applying seeds to DNA homology search. Recently, a concept of subset seeds has been proposed for similarity
search in protein sequences.
We experimentally evaluate the applicability of subset seeds to protein homology search. We advocate the use
of multiple subset seeds derived from a hierarchical tree of amino acid residues. Our method computes, by an
evolutionary algorithm, seeds that are specifically designed for a given protein family. The representation of
seeds by deterministic finite automata (DFAs) is developed and built into the NCBI-BLAST software. This
extended tool, named SeedBLAST, is compared to the original NCBI-BLAST and PSI-BLAST on several
protein families. Our results demonstrate a superiority of SeedBLAST in terms of efficiency, especially in the
case of twilight zone hits.
SeedBLAST is an open source software freely available http://bioputer.mimuw.edu.pl/papers/sblast. Supple-
mentary material and user manual are also provided.
1 INTRODUCTION
Motivation. Since the time complexity of the opti-
mal alignment problem is quadratic (e.g., the Smith-
Waterman algorithm (Smith and Waterman, 1981)),
thus too large for everyday tasks, most of sequence
aligning is done using heuristics, typically with the
ubiquitous BLAST software (Altschul et al., 1990;
Altschul et al., 1997). It runs in three phases, and the
first of which finds short initial alignments, so called
hot spots. Theory of seeds may be applied here, trying
to answer the question: which short aligned segments
are relevant for the indication of a true global align-
ment?
In the case of nucleotide sequences, spaced seeds
have been intensively investigated and have success-
ful applications: an improvement of BLASTN (Bre-
jova et al., 2004), sensitive alignment tools like Pat-
ternHunter (Ma et al., 2002; Li et al., 2004) and
Yass (Noe and Kucherov, 2005), automaton based
theory for modeling and analyzing seeds (Kucherov
et al., 2006; Buhler et al., 2005). The idea of using
multiple seeds is also widely recognized (Li et al.,
2004; Brejov
´
a et al., 2005; Sun and Buhler, 2004;
Kucherov et al., 2005). In this paper we attempt to
achieve similar results for protein homology search.
However, techniques based on spaced seeds seem not
to apply directly to protein sequences, as the alphabet
size is bigger (20 amino acids) and strict letter identity
is much less relevant.
Related Research. The first phase of BLAST is a
search for hot spots, i.e., short initial alignments of
a query and a subject. Quite different methods are
applied to define a hot spot for DNA and protein se-
quences. In the case of DNA, a hot spot is a short
sequence of identically matching nucleotides. Ap-
plication of seeds enables the consideration of non-
identical matchings as well, and thus finding out pre-
viously overlooked good initial alignments. The re-
ported increase of the efficiency of homology search
is therefore quite expectable (Kisman et al., 2005;
Shiryev et al., 2007).
In the case of protein sequences, a hot spot is
149
Gambin A., Lasota S., Startek M., Sykulski M., Noé L. and Kucherov G..
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST.
DOI: 10.5220/0003147601490158
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2011), pages 149-158
ISBN: 978-989-8425-36-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

defined through a cumulative contribution of amino
acid matches, not necessarily identical. A short se-
quence of such matches is considered a hot spot if
their additive contribution (score) exceeds a prede-
fined threshold. It is thus not clear whether seed-
based approaches may measure up with the cumu-
lative scores in expressibility and effectiveness. A
first attempt to compare the two approaches has been
done in (Roytberg et al., 2009), with the conclusion
that subset seeds (Kucherov et al., 2006) may of-
fer an attractive alternative to the “cumulative” ap-
proach of BLAST (cf. also discussion and references
therein concerning expressibility of different classes
of seeds). It is also argued that the algorithmic cost
may thus be reduced, as application of seeds allows
the use of a direct indexing scheme based on hash-
ing. In addition, a comparison of subset seed tech-
nique with the vector seed approach (Brown, 2004)
has been reported.
A fundamental notion in seed theory is an align-
ment alphabet, whose letters correspond to matching
two residues. In the case of nucleotide sequences, the
alignment alphabet has 6 (or 12, if directional) let-
ters. In the case of amino acid sequences, however,
the alignment alphabet has at least 200 letters, which
makes exploration of even medium length sequences
costly and difficult. A way of approaching the prob-
lem is to reduce the alignment alphabet, exploit-
ing similarities among various amino acids (Royt-
berg et al., 2009). By applying the subset seed the
complexity of alignment description may be reduced,
while maintaining the biological information content.
The idea of subset seeds (Kucherov et al., 2006), can
be viewed as an intermediate concept between ordi-
nary spaced seeds and vector seeds. In this approach
different types of matches (or mismatches) are dis-
tinguished, as a seed letter corresponds to a subset
of matches. In the case of protein sequences, for
instance, it might be beneficial to distinguish muta-
tions inside some predefined amino acid groups (like
aliphatic, aromatic, tiny, etc. (Livingstone and Barton,
1993)) from mutations between these groups.
Deterministic finite automata (DFAs) find many
applications related to homology search and seed
theory. Early BLAST implementations investigated
two hashing methods (Altschul et al., 1990) to effi-
ciently manipulate the dictionary of hot spots. One
of these was a dictionary organized as a DFA; this
method was preferred until it has been abandoned
in 1997 in NCBI-BLAST (Neuwald, 1998). DFAs
are also known to be useful in constructing a per-
fect hashing function, in computing the value of a
hashing function, or retrieving a value from a dictio-
nary (Hopcroft and Ullman, 1979; Aho and Corasick,
1975). In (Kucherov et al., 2006) a special type of
DFA called probability transducer was used for com-
putation of seed sensitivity.
Recently the concept of hash seed for protein ho-
mology search has been proposed in (Li et al., 2009).
It also applies amino acid grouping (in this case based
on BLOSUM matrix) to designing good seeds that al-
low for a direct hashing scheme. The subset seeds, as
considered in this paper, can be regarded as another
(potentially more powerful) type of hash seeds.
Our Contribution. The overall aim of this paper is
to experimentally confirm the value of applying seed-
based hot spot search, using the approach of (Royt-
berg et al., 2009). It appears to be especially inter-
esting in cases when the search is restricted to a par-
ticular protein family, as this opens the possibility of
designing specialized seeds in order to increase the ef-
ficiency of the homology search. In short, as our tech-
nical contribution we propose a method of computing
a well-performing multiple space seed, and present an
implementation of a new seed-based hot spot search
routine. Furthermore, we advocate the use of deter-
ministic finite automata (DFAs) as a seed representa-
tion. Finally, we experimentally confirm a supremacy
of this new approach over the original NCBI-BLAST
hot spot search.
We investigate, and search for, reduced alignment
alphabets, called seed alphabets, that can be derived
from hierarchical trees of amino acids. Such trees
were designed, e.g., in (Li et al., 2003; Murphy et al.,
2000); for our purposes we compute, (by amino acids
clustering), a specific tree for a given protein family.
An advantage of using hierarchical trees is that the
alphabets are always transitive (i.e., each letter corre-
sponds to a transitive set of matching pairs) and thus
enable application of the direct hashing scheme.
We search for a well-performing alphabet and a
multiple subset seed over it with the use of an evolu-
tionary algorithm. The fitness evaluation is based on
computing the seed sensitivity and selectivity in the
way suggested in (Kucherov et al., 2006).
The multiple seed, represented as a DFA, is then
used in the hot spot search of BLAST. We have im-
plemented an extension to the NCBI-BLAST soft-
ware, called SeedBLAST, that accepts a multiple sub-
set seed as its input parameter. The extension is
written in C++, relies on the template mechanism,
and is prone to compiler optimizations (most func-
tions can be inlined). An important advantage of
our implementation is that being developed within the
NCBI-BLAST framework, it inherits all stable and
tested features of this implementation.
The first test results can be perceived as promis-
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
150

ing: although our multiple seed selection method is
rather simplistic, our tool returns more interesting hits
than the standard BLAST with comparable settings.
Some returned hits tend to be long although having
only medium E-value, the type of hits known to be
dimmed and not reported by BLAST. This kind of hits
is termed twilight zone after (Rost, 1999).
Furthermore, this methodology can be useful for
searching for particular type of alignments. Given a
set of alignments, one can construct a specific seed
automaton and perform database search for this cer-
tain type of alignments. Following this idea we in-
vestigated the ability to align known structurally ho-
mologous domains of the Rhodopsin family of G-
protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). The outcome of
our experiment showed a significant difference be-
tween NCBI-BLAST and SeedBLAST, in favor to the
latter: our method yielded much longer alignments
covering up to 70% of the entire domain, even for pro-
teins sharing low sequence identity (20-30%).
2 SUBSET SEED DESIGN
General Approach. Given a protein family, we as-
sume that a small representative subset of this family
has already been aligned well (for example manually
by experts), and is available as a training set. The
algorithm designing subset seed attempt to extract in-
formation about the structure of the family from this
set, and use it to produce alignments for the entire
family. In the first phase a hierarchical tree is con-
structed that represents similarities of amino acids.
Then, a seed alphabet is designed, along with a set
of seeds. This is a learning phase, and runs indepen-
dently of our BLAST enhancement. Next, the seed
alphabet along with the corresponding set of seeds is
used by the SeedBLAST algorithm to find hot spots.
Afterwards, the computation of SeedBLAST follows
the standard BLAST scheme.
Hierarchical Tree of Amino Acids. Let Σ =
{A,C,D,...} be the amino acid alphabet (|Σ| = 20).
A valid hierarchical tree of amino acids is a binary
tree whose leaves are labeled bijectively by elements
of Σ, and whose every internal (non-leaf) node has
two children. An example of such a tree is shown in
Figure 1. The specific tree used e. g. for Rhodopsin
family is presented in supplementary material. Such
a tree constitutes a parameter in our approach; we as-
sume that it corresponds to some biologically signif-
icant hierarchical clustering of amino acid residues,
c.f. (Murphy et al., 2000; Li et al., 2003).
Any non-leaf node v of T is represented by a set
of (labels of) leaves in the subtree rooted in v. This
set is denoted by Σ
v
. In particular, the root is labeled
by the whole set Σ. There are precisely |Σ| − 1 = 19
non-leaf nodes.
Our basic intuition is as follows. Think of a leaf
labeled by A ∈ Σ as a representation of the exact
match A—A. Then a node v represents all matches
A—B for A,B ∈ Σ
v
.
The tree is obtained from the training set of align-
ments in the following way: first, for each pair of
amino acids the number of times they have been
aligned one with another is counted, and then, using
those counts, the amino acids are hierarchically clus-
tered through neighbor-joining method.
Seed Alphabets and Seeds. From now on we as-
sume a fixed hierarchical tree T . The tree nodes are
partially ordered by a natural ordering induced by the
tree structure (we call it tree ordering). This coin-
cides with the inclusion ordering of the labeling sets:
v
1
≤ v
2
⇐⇒Σ
v
1
⊆ Σ
v
2
. We assume here for techni-
cal convenience that the leaves are labeled by single-
tons {A} instead of single amino-acids A ∈ Σ. Below
we consider sets of nodes of T, ordered by inclusion
as well. Certain sets of nodes will be seed letters (po-
tential elements of a seed alphabet).
A seed letter is defined as any subset α of nodes
such that:
(i) (maximality) α contains all leaves and
(ii) (downward closedness) whenever v ∈ α and
v
0
< v then v
0
∈ α.
Hence, a single seed letter α is defined as a lower
set of a maximal antichain wrt. the tree ordering. This
antichain contains the maximal elements of α wrt. the
tree ordering and may be visualized by a horizontal
cut through the tree T. Seed letters are naturally or-
dered by inclusion. The smallest one is the ”exact
match” seed letter #, containing only the leaves. The
largest one is the ”don’t care” seed letter , containing
all the nodes of T. One particular seed letter, denoted
by @, is obtained by removing from the root node.
We place an additional restriction on alphabets that
we use, that they must contain both # and .
The maximal elements of a seed letter α wrt. the
tree ordering form a partition of Σ. Thus α repre-
sents naturally an equivalence relation on Σ: A and B
are related iff they belong jointly to some node of α;
i.e., iff there exists some v ∈ α such that A ∈ Σ
v
and
B ∈ Σ
v
. We feel free to write (A, B) ∈ α in this case.
The induced equivalence is identity relation in case of
# and full relation in case of . The inclusion order-
ing of seed letters coincides with the inclusion of the
induced equivalences.
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST
151

CFYWMLIVGPATSNHQEDRK
CFYWMLIV
CFYW
C
FYW
FY
F Y
W
MLIV
ML
M L
IV
I
V
GPATSNHQEDRK
GPATS
G PATS
P
ATS
A
TS
T S
NHQEDRK
NHQED
NH
N
H
QED
QE
Q
E
D
RK
R
K
Figure 1: The hierarchical tree of amino acids proposed by (Li et al., 2003).
Certain families of seed letters will be allowed as seed
alphabets. Essentially, we forbid two letters α
1
,α
2
that are incomparable by inclusion. A seed alphabet
is a family A of seed letters totally ordered by inclu-
sion: for each α
1
,α
2
∈ A, either α
1
⊆ α
2
or α
2
⊆ α
1
.
Alphabets with this property are called hierarchical
in (Roytberg et al., 2009). We used this assumption as
it leads to a nice mathematical formalization, namely
the family of seed alphabets forms a constrained inde-
pendence system (Korte and Hausmann, 1978; Cheng
and Xu, 1995). We show that even with this restric-
tion very efficient seeds can be obtained. Thus, in this
paper we will not consider non-hierarchical alphabets.
Note that, again, the seed alphabets may be naturally
ordered by inclusion as well.
We define a seed over a seed alphabet A as a finite
word over A. A multiple seed is a pair consisting of a
seed alphabet and a set of seeds over that alphabet.
We say that a seed s = s
1
s
2
...s
n
aligns two amino
acid sequences a = a
1
a
2
...a
n
, b = b
1
b
2
...b
n
, if and
only if for all i ∈ {1, 2, ..., n}, (a
i
,b
i
) ∈ s
i
.
Foreground sensitivity (or just sensitivity) of a
multiple seed M, denoted by sens
F
(M), is the num-
ber of positions in the training set of alignments
matched by at least one of the seeds from M, divided
by the total number of positions. Foreground sensitiv-
ity is computed directly from the training set.
Background sensitivity of a seed corresponds to
the probability of matching two aligned random se-
quences. We assume that the background model for
amino acid sequences is given as a Markov chain.
For our experiments, the Markov chain models of
orders 1,2 and 3 were learned from the TrEMBL
database (Boeckmann et al., 2003) using GenRGenS
Java tool (Ponty et al., 2006). The background sensi-
tivity of a seed was computed with the use of Marko-
vian probability transducer as described in (Kucherov
et al., 2006). Background sensitivity of a multiple
seed M, denoted by sens
B
(M), is estimated from
above by the sum of background sensitivities of each
of the individual seeds in M (the estimation is sharp
only if seed occurrences are independent).
Evolutionary Approach. Optimizing multiple
seeds is recognized as a highly non-trivial task (Yang
et al., 2004; Buhler et al., 2005; Ma and Yao,
2008). In the case of hierarchical subset seeds the
combinatorial structure of seed alphabets suggests
hardness of the optimization problem (see (Roytberg
et al., 2009) for details). Therefore we decided to use
an efficient heuristic algorithm.
In the proposed approach seed alphabets and seeds
are simultaneously chosen through an application of a
genetic algorithm. The genetic algorithms are used to
solve various optimization problems (Mitchell, 1996).
They work by first generating a random multiset (ini-
tial population) of potential solutions, evaluating the
function being optimized (fitness function) for each
one of them, culling a percentage of them with low
values of such function, cloning and slightly altering
(mutating) the rest at random – and repeating this pro-
cess until a satisfactory solution is obtained.
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
152

In our case, the potential solutions are pairs: a
seed alphabet, and a set of seeds. A mutation applies
thus either to the alphabet, or to one of the seeds. Mu-
tating the alphabet is one of the following: deleting a
randomly chosen letter (except for the top # and bot-
tom one), altering a letter (by adding a tree node to
it, or removing a tree node – but only if that would
not violate the constraint that the alphabet must be
hierarchical), or adding a random (non-conflicting)
letter. While modifying the letter one has to respect
its definition, i.e. the (i) maximality and (ii) down-
ward closedness conditions. Mutating the set of seeds
means either deleting one of the seeds, adding a ran-
dom seed, or replacing a random letter in a random
seed by one of its neighbors in the alphabet. Algo-
rithm 1 explains the details.
A multiple seed may contain individual seeds of
different lengths in general. However to simplify and
speed-up the computations we have decided to fix the
length; all individual seeds computed by the evolu-
tionary algorithms have the same length W = 5.
Algorithm 1: Genetic Algorithm.
Input: Protein family F
Output: A multiple seed for family F
begin
Population ←a multiset of 100 randomly
chosen multiple seeds (the initial
population);
while Not Run Out Of Time do
foreach multiple seed M ∈ Population
do
f ←fitness
F
(M);
Randomly, based on f, choose one
of the following:
• Population ←Population \ {M};
- with increasing probability for
low values of f
• Population ←Population \ {M}∪
{Mutate(M)};
• Population ←Population∪
{Mutate(M)}; - with increasing
probability for high values of f
end
end
return the member of Population that
maximizes fitness
F
end
The most important aspect of every optimization
algorithm, a genetic algorithm being no exception, is
the fitness function chosen. Usually, what we want to
obtain is a seed that has as low background sensitiv-
ity as possible, while at the same time having as high
foreground sensitivity as possible. So, the first idea
might be to choose the following function:
fitness
1
(M) =
sens
F
(M)
sens
B
(M)
.
This, however, yields unsatisfactory results – the evo-
lution just results in a smallest multiple seed possible,
with minuscule foreground and background sensitiv-
ity.
The fitness function has to reflect the trade-off
between foreground sensitivity and background sen-
sitivity. It should be noted that both of these play
similar role to NCBI-BLAST ’-f’ parameter (i.e. the
threshold for the cumulative score of three hit posi-
tions). The ’-f’ parameter allows one to adjust the
length of computation, and the quality of results. With
SeedBLAST it has been split in two – the sens
F
(M)
part is responsible for the quality of results, while
sens
B
(M) is responsible for the length of computa-
tion. Keeping that in mind, we can select a fitness
function that can match our needs – using it, we can
in effect specify ’give me the best results you can
achieve within a given time-frame’ – or, the opposite
– ’give me results at least this good, and I don’t care
how long it takes to compute them’. Or everything
in-between.
An example of fitness function that adheres to the
first approach might be as follows:
fitness
2
(M) =
0 if sens
B
(M) > c
sens
F
(M) otherwise
The second approach is fulfilled by the following fit-
ness function:
fitness
3
(M) =
sens
F
(M) if sens
F
(M) < c
sens
F
(M)
sens
B
(M)
otherwise
Another appropriate fitness functions and their
evolution paths are presented in supplementary ma-
terial.
For further tests, described in the rest of the paper,
we have chosen the function fitness
3
, with c = 0.15;
except for the performance evaluation, where we pre-
fer to use fitness
2
(in order to make the fair compar-
ison with NCBI-BLAST ).
This decision was taken through trial and error -
there is no guarantee that this is the optimal choice.
The multiple seed that was computed and used for
further experiments exhibits foreground sensitivity
equal to 0.179906, and background sensitivity equal
to 0.01047971. The underlying alphabet is presented
in supplementary material; the whole multiple seed,
consisting of 3686 individual seeds, is not subject to
a concise presentation.
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST
153

3 SeedBLAST: EXTENSTION OF
NCBI-BLAST
Given a query, the goal of the first phase of the
BLAST algorithm is to index all subwords of length
W (chosen as a parameter). Not only exact subwords
are indexed but also their predefined neighborhoods,
with respect to a metric determined by the cumula-
tive score according to the BLOSUM matrix. With
each query, the occurrences of the neighborhoods are
stored in a dictionary-type data structure; current ver-
sion of NCBI-BLAST uses a hash table.
The size of neighborhood is crucial as it must be
stored in a dictionary. BLAST uses a threshold on the
BLOSUM score of an alignment of a segment pair.
The threshold represents the trade-off between sensi-
tivity and time and memory efficiency since it has a
direct impact on the number of analyzed hits. The
default threshold was adjusted experimentally by the
BLAST developers and currently equals 11 in protein
NCBI-BLAST.
We seek to describe the neighborhood using our
selected multiple seed. In principle, the method may
be applied to any multiple seed, possibly containing
words of different lengths. However, in the case study
described in the following section, all the seeds have
the same length W = 5. Moreover, all individual seeds
are constructed over the same alphabet. This assump-
tion greatly simplifies the seed design and allows to
construct a single automaton for looking for all hot
spots simultaneously.
3.1 Hot Spot Search using DFA
A trie, or a prefix tree, is a dictionary with a tree-
structured transition graph, in which the start node
is the root and all the leaves are final nodes (Liang,
1983). Tries are especially convenient when the keys
are short strings: the tree edges are labeled by letters,
and retrieving a value assigned to a given key w is
done by following the w-labeled path in the tree, thus
very efficient.
It is assumed that labels of edges outgoing from a
node are all different. A trie may be thus seen as an
acyclic DFA recognizing a finite language (the lan-
guage contains labels of all the paths going from the
root to a leaf). Upon acceptance, the automaton in ad-
dition returns the value assigned to a word read (being
a key). In our case, the value will be typically a set of
positions in a query.
In our algorithm, to be described below, we con-
struct a number of different tries (automata). To op-
timize for memory, on the implementation level we
always conform to the Mealy paradigm of keeping
values attached to transitions, not vertices.
In a preprocessing phase a trie S is constructed to
represent the multiple seed. Its input alphabet is the
seed alphabet A.
Next, we proceed with constructing a trie Q, over
the input alphabet Σ, that keeps all subwords of length
W from a given query. For each such word we store in
Q pointers to all positions in query where it appears.
This will reduce operations in the following phases. It
is worth noting that Q may be used to process jointly
multiple queries. Analogously, NCBI-BLAST also
permits many queries to be stored jointly in its hash
table.
As a consecutive step, a trie N is built to store
neighborhoods. Its alphabet is Σ, and language is
given by
N = Q ∝ S :=
{w | for some q ∈ Q and s ∈ S, s aligns q and w}.
The trie N is constructed by systematically traversing
a product of Q and S. The value assigned to a word w
in N denotes, similarly as in Q, a set of positions in
the query. It is given by the union of values assigned
to q in Q, for all q ranging over
{q ∈ Q | for some s ∈ S, s aligns q and w}.
On the implementation level, the union is represented
by a suitable pointer data structure.
Finally we construct an automaton H over the al-
phabet Σ, whose aim is to find hot spots in the sub-
ject sequences. Operation of H is similar to a pattern-
matching automaton. It is built on the basis of the au-
tomaton N, by adding additional edges outgoing from
the final (leaf) nodes. To easily explain the construc-
tion, we recall that each node of N is uniquely deter-
mined by the labeling of the path from the root to that
node. Fix a leaf determined by w and a letter a ∈ Σ;
the outgoing a-labeled edge will point to a node de-
termined by the longest suffix of wa that belongs to
N. Clearly, in contrast to all other automata, H may
have cycles.
Having constructed H, next BLAST phases re-
main unchanged. Each subject sequence is traversed
along, starting from the root of H. At each step, the
value assigned to the current node (state) of H informs
whether any hot spots are found at the current position
in a subject. If so, the hot spots are stored for further
processing in the following phases of BLAST.
4 EXPERIMENTS
Datasets. We used a dataset extracted from the
Pfam database, that contains expert-made pro-
tein structural families and their multi-alignments,
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
154
later extended to larger families using profile-
HMMs (Bateman et al., 2002; Finn et al., 2008).
A protein family, exhibiting low identity per-
centage, has been selected from Pfam (namely
PF00001). This family contains, amongst other G-
protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), members of the
opsin family, which have been considered to be typ-
ical members of the rhodopsin superfamily. They
share several motifs, mainly the seven transmembrane
helices (7tm 1 domain). This domain will be the main
focus of our experiment.
The rhodopsin-like GPCRs themselves represent
a widespread protein family that includes hormone,
neurotransmitter and light receptors, all of which
transduce extracellular signals through interaction
with guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins. Al-
though their activating ligands vary widely in struc-
ture and character, the receptors are believed to adopt
a common structural framework comprising 7 trans-
membrane helices.
The expert-made multi alignment of 7tm 1 do-
mains from 64 of the family members was down-
loaded (the whole family contains 16975 proteins),
and used as a training set to obtain a multiple seed.
The latter was subsequently used by the SeedBLAST
algorithm to compute pair-wise alignments of the
7tm 1 domain of all the family members. The results
were compared with those obtained by the standard
BLAST algorithm.
For a fair comparison, it had to be ensured that
both algorithms actually run with the same back-
ground sensitivity. Thus, the ’-f’ parameter of
NCBI-BLAST was adjusted in the course of the ex-
periment to obtain similar background sensitivity to
that of the multiple seed used by SeedBLAST. The
table shows typical values of the ’- f’ parameter to-
gether with the corresponding values of background
sensitivity:
f parameter of
NCBI-BLAST
SeedBLAST back-
ground sensitivity
11 (default) 0.002195
10 0.005342
9 0.00816
8 0.012276
7 0.018163
The background sensitivity of the seed used by
SeedBLAST was 0.01047971; this corresponds to
8 or 9 as the value of the ’-f’ parameter in the
NCBI-BLAST invocations.
As the alignment concerned only the domain frag-
ment of each protein, and the domain is already
known to be the same in each protein, every alignment
found should be considered biologically significant.
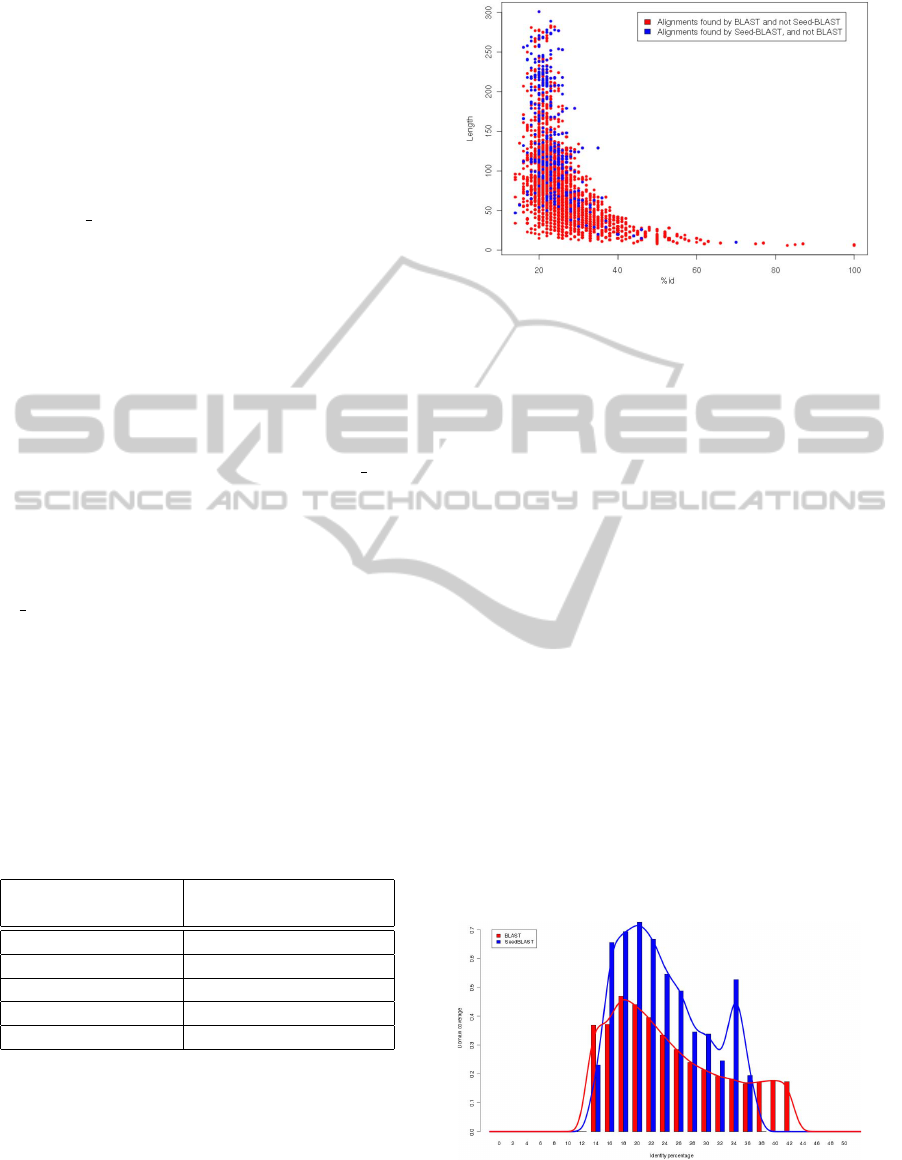
Figure 2: Symmetric difference between outputs of BLAST
and SeedBLAST.
Comparing Efficiency. Figure 2 shows the
symmetric difference between hits found by
NCBI-BLAST, and those found by SeedBLAST (that
is, alignments found by one of the algorithms but not
the other).
We observe that alignments found by SeedBLAST
are in general longer than those found by BLAST, and
thus provide better coverage of the domain. Espe-
cially many alignments that have not been found by
BLAST lie in the so-called twilight zone (Rost, 1999)
– namely long alignments with low identity percent-
age, and thus low E-value, that nevertheless are bi-
ologically significant. The reason why SeedBLAST
constructs longer alignments is that it detects much
more biologically significant hot-spots. A supremacy
of SeedBLAST becomes more apparent in view of
Figure 3. To obtain this diagram, pairs of domains
for which BLAST and SeedBLAST found different
alignments were chosen from the set of all align-
ments, and the coverage of domains by these align-
ments was computed. We conclude that SeedBLAST
is much more efficient in providing biologically sig-
nificant alignments than the standard BLAST algo-
rithm.
Figure 3: Domain coverage by alignments found by BLAST
and SeedBLAST.
The reason for SeedBLAST’s improved efficiency
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST
155

is the inclusion of subset seeds specifically tuned
for the domain under consideration. When one
aims at aligning different family of proteins appro-
priate multiple seed should be designed and used in
SeedBLAST. We conclude that SeedBLAST appears
much more efficient than BLAST in recognizing pro-
tein domains, as it is both more effective in covering
the entire domain as well as much less likely to cover
anything beyond the sought-for domain.
Table 1: f: -f Parameter of NCBI-BLAST c: correspond-
ing background sensitivity (parameter c) used in seed de-
sign, sens
B
(M): actual background sensitivity of the mul-
tiple seed SeedBLAST, NCBI-BLAST: running time of
NCBI-BLAST,SeedBLAST: running time of SeedBLAST.
f c sens
B
(M) NCBI-
BLAST
(sec.)
Seed-
BLAST
(sec.)
15 0.000306 0.00030564 1.20 0.45
11 0.002195 0.00211789 3.32 1.40
8 0.012276 0.01156471 12.17 4.74
5 0.026406 0.02622019 23.84 12.40
Comparing Running Time. In addition,
SeedBLAST and NCBI-BLAST were compared
with respect to their running time (preprocessing,
i. e. seed design phase is not included). For a
fair comparison, again, we had to ensure that both
algorithms actually run with the same background
sensitivity.
In case of SeedBLAST, we had to be able to con-
trol the background sensitivity of the multiple seed
used. This led us to choose the fitness function:
fitness
2
(M) =
0 if sens
B
(M) > c
sens
F
(M) otherwise
(cf. Section 2) that seems to suit best to this purpose:
the parameter c corresponds directly to the desired
background sensitivity of the multiple seed.
In case of NCBI-BLAST, its background sensitiv-
ity can be adjusted by the ’-f’ parameter. For the test,
we picked several different values of the ’-f’ param-
eter, and then calculated the background sensitivities
induced by these values. These background sensitivi-
ties were taken as the value of the c parameter in the
above fitness function, exploited in the computation
of multiple seeds used by SeedBLAST.
The results are summarized in the Table 1. In fact,
because of the unpredictable nature of multiple seed
evolution, we can’t control the background sensitivity
of a multiple seed exactly. This gives SeedBLAST a
slight advantage over the other, represented by the dif-
ference between the c parameter (equal to the actual
background sensitivity NCBI-BLAST runs with), and
the background sensitivity of an obtained multiple
seed. Still, even accounting for this slight difference,
the results show that SeedBLAST algorithm is over
two times faster than NCBI-BLAST on average. As
the SeedBLAST is an extension of NCBI-BLAST we
conclude, that the speed-up is achieved due to faster
hot-spot identification stage. We argue that the mul-
tiple seed approach enables to detect biologically sig-
nificant hot-spots, e.g. those corresponding to func-
tional residues (Oliveira et al., 1993).
It is worth mentioning here that the performance
of SeedBLAST (being the extension of standard
NCBI-BLAST implementation) is comparable with
the performance of subset seed based tools that use
parallel implementation or specialized hardware (Pe-
terlongo et al., 2008; Nguyen and Lavenier, 2008).
Comparison with PSI-BLAST. One can see the
close similarity between the seed approach and po-
sition specific scoring matrices used to improve ho-
mology search. Therefore we decided to compare the
selectivity and sensitivity of SeedBLAST to the effi-
ciency of popular PSI-BLAST algorithm. The experi-
ment was performed on two protein families (Surface
antigen - PF01617 and Globin - PF00042). The per-
formace of both algorithms on Globin family was al-
most identical (data not shown). On the other hand
on Antigen family SeedBLAST achieved much better
selectivity while keeping the same level of sensitivity
(c. f. Fig.4).
5 FURTHER RESEARCH
Further experiments using in-sample, out-of-sample
tests and larger families are needed. At this stage
the performance of SeedBLAST is comparable with
BLAST running with low threshold for hot spots. We
hope that this result can be improved if more ad-
vanced methods for construction of multiple seeds are
used, and longer seeds (i.e., of length > 5) are in-
cluded.
The remaining goal is to develop a method of seed
construction that would keep sensitivity high and im-
prove selectivity. That would eventually reduce the
running time and memory requirements for greater
seed lengths.
Protein homology search requires unavoidably
storing a large dictionary in memory. Hence it seems
to be worth pursuing ideas from (Kahveci and Singh,
2001), where a novel method of compression, based
on wavelets, was proposed for dictionaries of words.
Another possible improvement could be integration
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
156
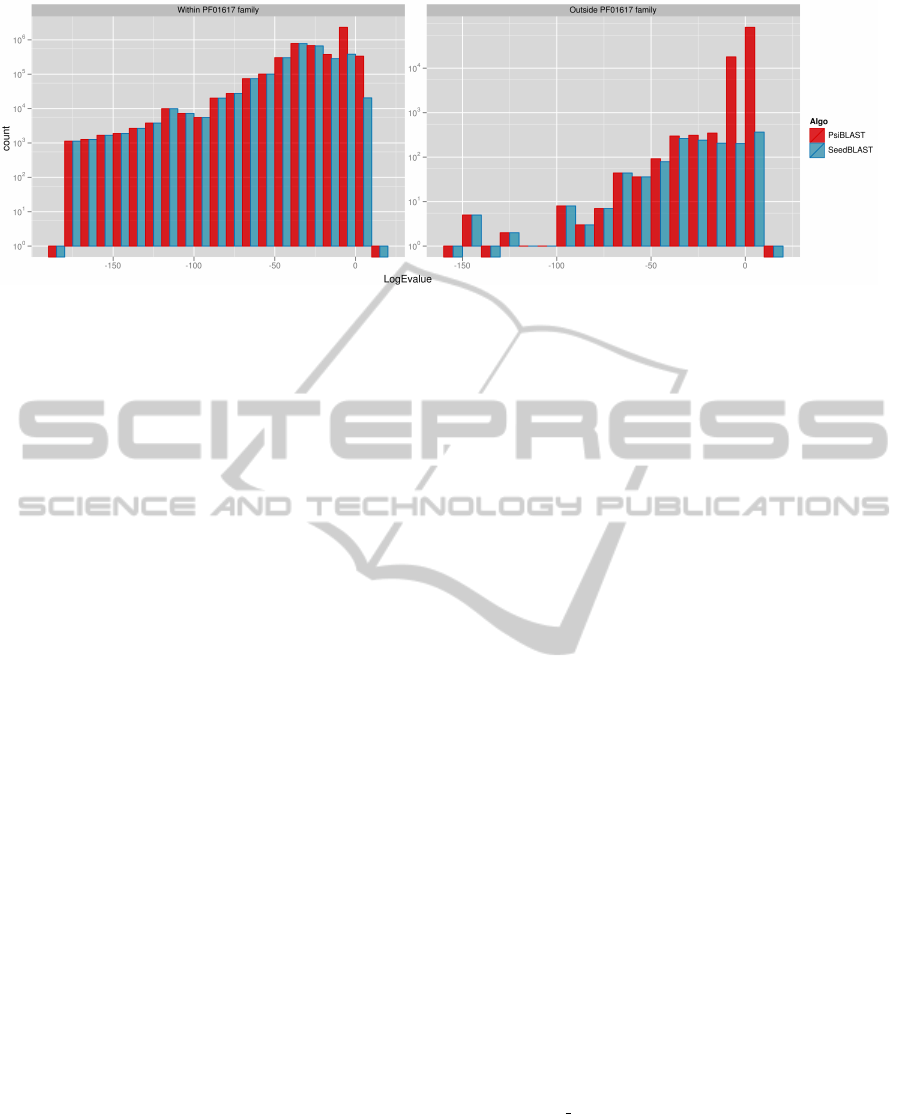
Figure 4: Histogram of found alignments grouped by logarithm of their E-value. We can observe that within the Antigen
family SeedBLAST finds all of the alignments that PSI-BLAST does (except for a small fraction of some non-significant
ones with E-values of 1 and more). Histogram on the right side shows results of alignment of proteins which we know
to be unrelated to Antigens with Antigens. We can see that SeedBLAST finds less non-homology-related alignments than
PSI-BLAST does.
of the cache-conscious hashing DFA to improve ef-
ficiency of page-swapping, as described in (Cameron
et al., 2006). However, we would like to recall here
that our overall goal of investigating the seed-based
hot spot search was to reduce the need for large infor-
mation storage by choosing only those hits that seem
important.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Parts of this work have been done during visits to
LIFL of AG and SL supported by the ECO-NET and
Polonium programs of the French Ministry of For-
eign Affairs. The research project was also funded
by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Educa-
tion grants no. N N301 065236 and N N206 356036
and European Social Fund (UDA-POKL.04.01.01-
00-072/09-00).
REFERENCES
Aho, A. and Corasick, M. (1975). Efficient string matching:
an aid to bibliographic search. Communications of the
ACM, 18(6):333–340.
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., and
Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search
tool. J. Mol. Biol., 215(3):403–410.
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schffer, A. A., Zhang, J.,
Zhang, Z., Miller, W., and Lipman, D. J. (1997).
Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation
of protein database search programs. Nucl. Acids Res.,
25(17):3389–3402. PMID: 9254694.
Bateman, A., Birney, E., Cerruti, L., Durbin, R., Etwiller,
L., Eddy, S., Griffiths-Jones, S., Howe, K., Marshall,
M., and Sonnhammer, E. (2002). The Pfam Protein
Families Database. Nucl. Acids Res., 30(1):276–280.
Boeckmann, B., Bairoch, A., Apweiler, R., Blatter, M.,
Estreicher, A., Gasteiger, E., Martin, M., Michoud,
K., O’Donovan, C., Phan, I., et al. (2003). The
SWISS-PROT protein knowledgebase and its supple-
ment TrEMBL in 2003. Nucl. Acids Res., 31(1):365–
370.
Brejova, B., Brown, D. G., and Vinar, T. (2004). Op-
timal spaced seeds for homologous coding regions.
Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biol-
ogy, 1(4):595–610.
Brejov
´
a, B., Brown, D. G., and Vinar, T. (2005). Vector
seeds: An extension to spaced seeds. J. Comput. Syst.
Sci., 70(3):364–380.
Brown, D. G. (2004). Multiple vector seeds for protein
alignment. In WABI, pages 170–181.
Buhler, J., Keich, U., and Sun, Y. (2005). Designing seeds
for similarity search in genomic DNA. J. Comput.
Syst. Sci., 70(3):342–363.
Cameron, M., Williams, H., and Cannane, A. (2006). A de-
terministic finite automaton for faster protein hit de-
tection in BLAST. J. Comput. Biol., 13(4):965–78.
Cheng, S. and Xu, Y.-F. (1995). Constrained independence
system and triangulations of planar point sets. In Com-
puting and Combinatorics, pages 41–50.
Finn, R. D., Tate, J., Mistry, J., Coggill, P. C., Sammut,
S. J., Hotz, H., Ceric, G., Forslund, K., Eddy, S. R.,
Sonnhammer, E. L. L., and Bateman, A. (2008). The
pfam protein families database. Nucl. Acids Res.,
36(suppl 1):D281–288.
Hopcroft, J. and Ullman, J. (1979). Introduction to au-
tomata theory, languages and computation. Mas-
sachusetts.
Kahveci, T. and Singh, A. (2001). An efficient index struc-
ture for string databases. Proceedings of the 27th
VLDB, pages 352–360.
SUBSET SEED EXTENSION TO PROTEIN BLAST
157

Kisman, D., Li, M., Ma, B., and Wang, L. (2005). tPat-
ternHunter: gapped, fast and sensitive translated ho-
mology search. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England),
21(4):542–544. PMID: 15374861.
Korte, B. and Hausmann, D. (1978). An analysis of the
greedy heuristic for independence systems. Ann. Dis-
crete Math., 2:65–74.
Kucherov, G., Noe, L., and Roytberg, M. (2005). Multiseed
lossless filtration. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol.
Bioinformatics, 2(1):51–61.
Kucherov, G., No
´
e, L., and Roytberg, M. (2006). A unify-
ing framework for seed sensitivity and its application
to subset seeds. Journal of Bioinformatics and Com-
putational Biology, 4(2):553–570.
Li, M., Ma, B., Kisman, D., and Tromp, J. (2004). Pattern-
Hunter II: Highly sensitive and fast homology search.
Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biol-
ogy, 2(3):417–439.
Li, T., Fan, K., and Wang, J. Wang, W. (2003). Reduction
of protein sequence complexity by residue grouping.
Protein Engineering, 16(5):323–330.
Li, W., Ma, B., and Zhang, K. (2009). Amino acid classifi-
cation and hash seeds for homology search. In BICoB,
pages 44–51.
Liang, F. M. (1983). Word hy-phen-a-tion by com-put-er.
Technical report, Departament of Computer Science,
Stanford University.
Livingstone, C. D. and Barton, G. J. (1993). Protein se-
quence alignments: a strategy for the hierarchical an
alysis of residue conservation. Computer Applications
in the Biosciences: CABIOS, 9(6):745–756. PMID:
8143162.
Ma, B., Tromp, J., and Li, M. (2002). PatternHunter: faster
and more sensitive homology search. Bioinformatics
(Oxford, England), 18(3):440–445. PMID: 11934743.
Ma, B. and Yao, H. (2008). Seed optimization is no easier
than optimal golomb ruler design. In APBC, pages
133–144.
Mitchell, M. (1996). An Introduction to Genetic Algo-
rithms. MIT Press.
Murphy, L., Wallqvist, A., and Levy, R. (2000). Simpli-
fied amino acid alphabets for protein fold recognition
and implications for folding. Protein Engineering,
13:149–152.
Neuwald, A. (1998). A probable solution to sequence-
analysis problems. Trends in Biochemical Sciences,
23(9):365–365.
Nguyen, V. H. and Lavenier, D. (2008). Speeding up subset
seed algorithm for intensive protein sequence compar-
ison. In RIVF, pages 57–63.
Noe, L. and Kucherov, G. (2005). YASS: enhancing the
sensitivity of DNA similarity search. Nucl. Acids Res.,
33(suppl 2):W540–543.
Oliveira, L., Paiva, A. C. M., and Vriend, G. (1993). A com-
mon motif in g-protein-coupled seven transmembrane
helix r eceptors. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecu-
lar Design, 7(6):649–658.
Peterlongo, P., No, L., Lavenier, D., illes Georges, G.,
Jacques, J., Kucherov, G., and Giraud, M. (2008). Pro-
tein similarity search with subset seeds on a dedicated
reco nfigurable hardware. In Parallel Processing and
Applied Mathematics, pages 1240–1248. Springer.
Ponty, Y., Termier, M., and Denise, A. (2006). GenRGenS:
software for generating random genomic sequences
and structures.
Rost, B. (1999). Twilight zone of protein sequence align-
ments. Protein Engineering Design and Selection,
12(2):85–94.
Roytberg, M., Gambin, A., No
´
e, L., Lasota, S., Furletova,
E., Szczurek, E., and Kucherov, G. (2009). On sub-
set seeds for protein alignment. IEEE/ACM Transac-
tions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics,
6(3):483–494.
Shiryev, A. S., Papadopoulos, J. S., S chaffer, A. A., and
Agarwala, R. (2007). Improved BLAST searches us-
ing longer words for protein seedin g. Bioinformatics,
23(21):2949–2951.
Smith, T. and Waterman, M. (1981). Identification of Com-
mon Molecular Subsequences. J. Mol. Biol., 147:195–
197.
Sun, Y. and Buhler, J. (2004). Designing multiple simulta-
neous seeds for DNA similarity search. In RECOMB,
pages 76–84.
Yang, I.-H., Wang, S.-H., Chen, Y.-H., Huang, P.-H., Ye, L.,
Huang, X., and Chao, K.-M. (2004). Efficient meth-
ods for generating optimal single and multiple spaced
seeds. In BIBE ’04: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Sym-
posium on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, page
411, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
158
