
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS’
BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR ENERGY
MANAGEMENT
Ayesha Kashif
1,2
, Xuan Hoa Binh Le
2
, Julie Dugdale
1
and Stéphane Ploix
2
1
LIG – Laboratoire d'Informatique de Grenoble, 110, Av de la Chimie, 38400, Saint Martin d'Hères, France
2
G-SCOP; ENSGI – INPG, 46, Avenue Félix Viallet, 38000, Grenoble, France
Keywords: Multi agent system, Inhabitants’ dynamic behaviour, Energy efficiency & management.
Abstract: Inhabitants' behaviour is a significant factor that influences energy consumption and has been previously
incorporated as static activity profiles within simulation for energy control & management. In this paper an
agent-based approach to simulate reactive/deliberative group behaviour has been proposed and
implemented. It takes into account perceptual, psychological (cognitive), social behavioural elements and
domestic context to generate reactive/deliberative behavioural profiles. The Brahms language is used to
implement the proposed approach to learn behavioural patterns for energy control and management
strategies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Europe’s energy consumption within buildings is
40% of the total energy (two-thirds of this is in
heating and cooling), however a major portion up to
90% is needlessly wasted (heel, 2009). By the year
2030, 70% (6 billion) of the world’s population will
live in urban areas resulting in huge sustainable
housing and energy demands. Hence the associated
energy loss from buildings is emerging as a potential
crisis (world urbanization prospects, 2007). A
solution to address this problem is energy efficiency
(saving from current energy waste) which is
cheapest, cleanest and immediately available, cost-
effective energy (ogilvie, 2009).
Energy control and management for heating and
cooling and lighting, etc. is an active research area.
The focus is for new buildings to comply with low
energy consumption standards and for renovated
buildings to improve energy efficiency as proposed
by the Euro ACE and European National Strategy
(Jensen et al., 2009). Centralized and distributed
approaches in buildings for power management
solutions have also been proposed to improve energy
efficiency, (Ha et al., 2006), (Abras et al., 2006). We
argue that understanding inhabitants’ behaviour is
the key for energy consumption and saving.
Inhabitants’ behaviour can either optimise energy
utilization, taking into account comfort needs, or it
can needlessly waste energy. Energy waste related to
human behaviour is not yet fully explored for energy
efficiency. The literature suggests that behaviour
strongly influences energy consumption patterns and
is an important factor for energy waste reduction in
buildings (Raaij and Verhallen, 1982), (Andersen et
al., 2009). Various surveys, studies and energy
audits have been conducted to analyze how
behaviour is affected by certain factors and how it
affects energy consumption (Seryak and Kissock,
2000), (Ouyang and Hokao, 2009), (Masoso and
Grobler, 2009). (Mahdavi and Proglhof, 2009)
conducted a study in order to find the user control
actions taking into account indoor/outdoor
environment. (Bourgeois et al., 2006) developed a
sub-hourly occupancy-based control model
(SHOCC) to track individual instances of occupants
and occupant controlled objects to investigate
lighting energy use in a single occupancy building
using ESP-r
1
. (Dong and Andrews, 2009) developed
an event based pattern detection algorithm for
sensor-based modelling and prediction of user
behaviour. They connected behavioural patterns
(Markov model) to building energy and comfort
management through EnergyPlus simulation tool for
energy calculations.
1
ESP-r is an integrated modelling tool for the simulation of the
thermal, visual and acoustic performance of buildings and the
assessment of the energy use and gaseous emissions.
190
Kashif A., Binh Le X., Dugdale J. and Ploix S..
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS’ BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR ENERGY MANAGEMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003150301900199
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 190-199
ISBN: 978-989-8425-41-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
The models discussed above focus on user
behaviour in non-domestic spaces such as offices
and they concern single users rather than group
reactive/deliberative behaviour. Simulations based
on static profiles or single user behaviour are limited
in extending results to real life. A better
management that coordinates and orchestrates the
use of all kinds of energy according to inhabitant’s
needs and comfort remains an important progress
factor. In this paper we focus specifically on
domestic situations and model dynamic
(reactive/deliberative) group behaviour which we
believe is the key for reliable simulation in energy
efficiency. The purpose of the proposed approach is
to identify the sensitivity of behaviour for energy
control and management which shall help in
developing the smart environments as well as testing
the design of new buildings or houses more suited to
humans according to their behaviour. A smart
environment is one that is able to acquire and apply
knowledge about environment and its inhabitants in
order to improve their experience in that
environment (Cook et al, 2007). A simulation has
been run in order to access human behaviour with
energy consumption which otherwise cannot be
done without some experimentation.
The conceptual framework proposed in this
article includes two components: (i) a logical
component for inhabitants’ dynamic group
behaviour (reactive/deliberative) simulation and (ii)
a physical component for energy calculations. An
agent based approach is used to model humans
interacting with their environment in the proposed
logical component. An agent based approach is well
suited since agents are a natural and intuitive way to
model humans and their characteristics and are a key
towards implementing group behaviour. Agents like
humans evolve in the environment, perceive it and
act accordingly.
The research objectives of this work are to
dynamically simulate user behaviour in domestic
settings, and further identify the context, beliefs and
facts that impact energy related behaviour. The
proposed framework will help in developing energy
efficient strategies to be implemented through social
campaigns, ubiquitous computing or centralized/
distributed approaches.
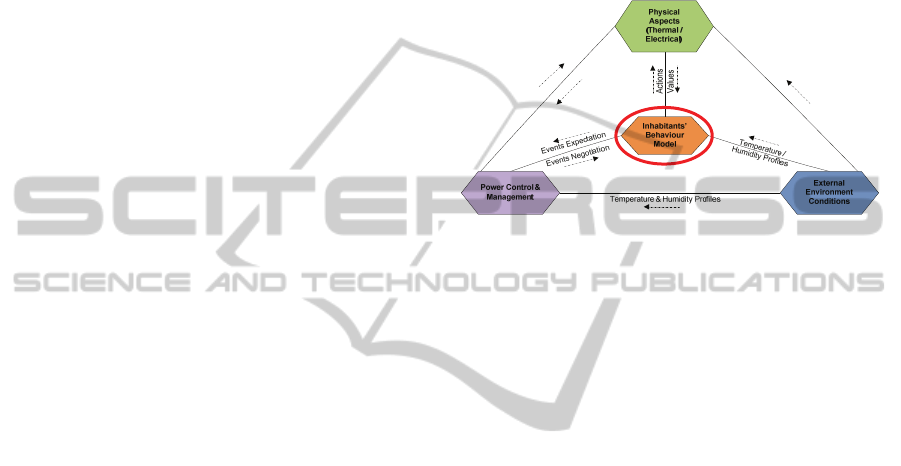
This work is part of the SIMINTHEC
(SIMulation and INteroperable software tools for the
management of THermal and EleCtrical energy in
buildings) project. The goal of SIMINTHEC is to
design a multi-simulation environment to improve
energy management in buildings by validating and
improve energy-saving policies and programs. It
includes five modules: 2 modules concerned with
thermal and electrical aspects, 1 module on energy
saving policies and control algorithms, 1 module on
inhabitants’ behaviour simulation and 1 module for
predicting the outdoor environment. Proposed agent
based framework to simulate dynamic group
behaviour, supports the “inhabitants’ behaviour
simulation” module, circled in Fig.1 with
interoperability among all modules.
Ev
ent
s
Set Points
T
emperat
u
re & H
um
idit
y
Prof
iles
P
hysical Values
Figure 1: Interoperability between modules in
SIMINTHEC.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The following section covers three aspects:
behaviour influence on energy consumption, home
context and Human Behaviour Representation
(HBR) models for possible integration in reactive/
deliberative group behaviour simulation.
There are multitude of factors of human
behaviour that influence energy consumption. For
example public information on the energy problem,
energy supply and energy efficiency, energy related
personal interests, economical differences, home
characteristics (no of rooms, degree of insulation),
lifestyle consciousness about energy saving and
environmental problems, social norms and lack of
knowledge about energy use (Raaij and Verhallen,
1982, Ouyang and Hokao, 2009).
A survey conducted by (Andersen et al., 2009)
showed that window opening, heating, lighting and
solar shading behaviour of occupants is affected by
gender, perceived illumination, noise level and air
quality. (Seryak and Kissock, 2000) conducted a
study on university residential houses and showed
that the same house occupied during 2 academic
years by different occupants show different energy
consumptions because of behavioural differences.
(Masoso and Grobler, 2009) conducted an energy
audit on six randomly selected buildings in Africa.
The results showed that more energy is consumed
during non working hours than during working
hours because of the occupant's behaviour of leaving
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS' BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
191

lights and other equipment on at the end of the day.
(Ueno et al., 2006) presented an on-line energy
consumption information system to make the
occupants aware of the impact of their energy
consuming behaviour of different appliances, power
and gas consumptions of the whole house, room
temperature, comparison with other houses and
comparison with past data. The system helped in
reducing power consumption of houses by 18% at
the end of the study.
In addition to behaviour, context is another
important factor affecting the energy related
activities of occupants. “The context of a task is the
set of circumstances surrounding it that are
potentially of relevance to its completion”
(Henricksen, 2003). In context aware systems the
contextual elements necessary to represent
behaviour are categorized as individuality (state),
activity (human needs expressed as ‘what’ and
‘how’), location (spatial arrangements) and time
(current time or any virtual time, working hours,
weekends, intervals) and relations (social relations
and functional relations) (Zimmermann et al., 2007).
In the home environment user behaviour is
considered as one of the most important contextual
factor amongst others including time, space,
environment and object (Ha et al., 2006). These
authors presented a user behaviour modelling
approach (5W: what, when, where, why & who and
1H: how) by mapping it in a home context (user,
time, object, space & environment) (
Fig.2).
Figure 2: 5W1H approach to map user behaviour in the
home.
It is evident from the above studies that human
behaviour is the most important factor affecting the
energy utilisation in buildings. In an urge to study
this most important factor in more detail, to find out
its different aspects affecting energy related
activities directly or indirectly and to find a way to
represent it for energy control and management, a
study of existing human behaviour representation
models has been conducted.
HBR models capture the covert and overt human
behaviour patterns and represent them in some way
using some representation mechanism. Most of the
HBR models share the aspects of both cognition and
performance. HBR models were analysed to find
those that could represent reactive/deliberative and
group behaviour including context elements. Atomic
components of thought (ACT) (Anderson et al.,
2004) focuses on cognition (thought processes),
perception and motor elements. (Freed, 1998) &
(Firby, 1989), suggested Architecture for procedure
execution (APEX) to model human behaviour in
complex, dynamic environments, but focus only on
individual tasks. (Sloman, 2001) presented
Cognition and affect project (CogAff) that captures
the reactive, deliberative & reflective mechanisms.
Cognition as a network of tasks (COGNET)
(Zachary et al., 1998), mainly focuses on cognitive
behaviour of humans, assuming that humans are
capable of doing multiple tasks simultaneously.
(Card et al., 1983) and (Kieras and Polson, 1985),
proposed cognitive complexity theory (CCT) which
is a simple model of cognition as it represent human
performance only on the sequential tasks and show
how humans use their task knowledge to interact
with the devices. Concurrent activation-based
production system (CAPS), (Thibadeau et al., 1982)
and (Just et al., 1999), is a production system where
a declarative knowledge base consists of facts
having a numerical activation value. Production is
fired when an element is matched with the condition
and the activation value exceeds a specific threshold.
(Eggleston et al., 2000) presented the Distributed
cognition (DCOG) model, according to which
cognition is distributed across the environment.
Agents having different skilful behaviour use
different strategies to accomplish the same task and
environment does affect individual performance.
Executive process/interactive control (EPIC),
(Kieras and Meyer, 1995), focuses on perceptual,
cognitive and motor processes that represent the
procedures required to perform complex tasks. It
also captures multitasking. Man-machine integrated
design and analysis system (MIDAS), (Corker and
Smith, 1993), focuses on human system interactions.
It makes an assumption that the “human operator
can perform multiple, concurrent tasks, subject to
available, perceptual, cognitive and motor
resources” (Pew and Mavor, 1998). Micro systems
analysis of integrated network of tasks (Micro
Saint), (Pritsker et al., 1974), include task as a basic
element, divided in subtasks until an elemental level
is reached. It also uses operator oriented concepts to
accomplish tasks as a mission. However it does not
capture the psychomotor element of human
behaviour. (Deutsch et al., 1997) and (Young and
Deutsch, 1997), suggested Operator model
architecture (OMAR) with an assumption that
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
192

human behaviour is proactive and reactive where
tasks occur concurrently within and among multiple
operators. State, operator, and result (SOAR) (Laird
and Newell, 1983), states that behaviour is captured
as a search or movement through the problem space
at a particular time and a goal state which represents
a solution for the problem. The knowledge is
modelled in terms of goals, states and operators,
where operators are used to change or transform the
state of the system. Business redesign agent-based
holistic modelling system (Brahms), (Sierhuis et al.,
1999), (Sierhuis et al., 2007), (Clancey et al., 1998)
& (Seah et al., 2005) is a modelling/simulation
environment to analyze work practices in
organizations and represents people, things, places,
behaviour of people over time, tools and artefacts
used, when they are used. It focuses on
communication between co-located and distributed
people to support social behaviour.
Brahms supports social and behavioural elements
necessary for dynamic group behaviour, however the
objective for logical simulation as presented in
section-1 is to find a model which can map human
behaviour process for reactive/deliberative group
behaviour and the context. The mapping between
user behaviour elements, context and Brahms is
presented in
Fig.3 below:
Figure 3: 5W&1H approach mapped to Brahms.
Workframes (activity model) and throughtframes
(knowledge model) are key elements in Brahms.
Thoughtframes are used to model the reasoning
behaviour of agents and are represented as
production-rules creating new beliefs of agents or
objects whereas workframes (rule-based) perform
agents and objects activities (simple or composite).
Brahms includes an agent model that represent
agents along with group hierarchy, and a
communication model to exchange beliefs about
agents and objects. It also provides means to model
locations and objects (geographical and object
models), that are important to establish the
environment in which agents operate. Brahms can be
used to model human beings interacting with a
complex habitable environment as powerful, active,
intelligent agents rather than passive participants for
energy efficiency and it can represent the
complexities found in real world human-
environment interaction scenarios. The literature
shows that behaviour inclusion within energy
control and management is focused on either static
profiles or predictive models (sensor based
inhabitants’ occupancy detection). However they
are based on single user interactions and do not
embed reactive/deliberative decision making. In this
paper inhabitants perception, cognition and
reactive/deliberative group behaviour is simulated
using home context (5W1H) and mapping it to
Brahms. It provides an opportunity to learn context,
beliefs and activities that influence energy
consumptions and could play significant role in
energy efficiency within domestic settings. Our
proposed approach is different from the existing
research to the extent that we have demonstrated
dynamic behaviour simulation and results obtained
shall be applicable to the real life situations.
3 PROPOSED FRAMEWORK
To simulate inhabitants’ reactive/deliberative group
behaviour an integrated definition (IDEF) model
with three levels of abstraction
(Fig.4, Fig.5 and Fig.6)
is proposed:
Figure 4: Behaviour simulation for energy efficiency.
IDEF models processes as functions with inputs
(left arrows), outputs (right arrows),
controls/constraints (top arrows) and means/methods
(bottom arrows) at different levels of abstractions.
Function A0 (
Fig.4) represents the highest level of
abstraction where 5W1H (domestic context) and
initial beliefs serve as input, comfort/cost criteria as
control, user behaviour and power management as
output and behaviour base, Inhabitant’s behaviour
and physical components and connector to
interoperate the outputs of these two components as
means/methods. Inhabitants’ in the 5W1H model fed
as input to function “A0” correspond to the agents
and their surrounding environment.
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS' BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
193

Sub-functions A1 (simulate dynamic inhabitants’
behaviour) and A2 (calculate energy performance)
as presented in
Fig.5. These represent the conceptual
framework of the abstract function A0. It is the
second level of functional abstraction towards
learning context and beliefs/facts from energy
related group behaviours within domestic settings:
Figure 5: Conceptual framework for behaviour simulation.
(i) Simulate dynamic inhabitants’ behaviour
(A1):
The ‘Simulate dynamic inhabitant’s behaviour’
component is the core element to simulate
reactive/deliberative group behaviour using an agent
based approach. 5W1H (context), initial beliefs and
facts (single user activity profiles) are inputs. “A1”
is implemented and simulated using Brahms
language/environment for dynamic group behaviour
scenario as presented in section 4 and its output
(dynamic user behaviour) serves as input to sub-
function A2 for energy calculations.
(ii) Calculate energy performance (A2):
The Physical component uses cost/comfort criteria
and the inhabitants’ behaviour/physical component
connector to calculate cost integrated with
behaviour. The Behaviour base serves as a data
structure to store dynamically generated behaviours.
The objective is to identify the context, beliefs and
facts that influence energy consumption patterns to
formulate energy control and management
strategies. This part is under implementation and is
not presented in this article.
The functional description of sub-function “A1”
as reactive/deliberative inhabitants’ group behaviour
is detailed below along with the sub-functions in
Fig.6. Since our approach is based on Belief Desire
Intention (BDI) agents, we can keep track of the
initial and changing beliefs of agents about
contextual elements, such as the state of objects
(what), inhabitants (who), physical location of
inhabitants (where) and current activities (how).
(i) Get context information (A1):
This function gets the information of three important
context elements i.e. inhabitant (who), object (what)
and location (where). The inhabitants are
represented by agents and it captures their beliefs
and facts, e.g. who is the inhabitant/agent, what are
the different characteristics of the inhabitants/agents
and how they perceive the environment around them
etc. The second important context element is the
‘physical location’ of inhabitants/agents and objects
(physical objects and appliances) in domestic
settings. The third context element ‘object’ provide
information about the appliance in use by the
inhabitant or that are involved in some activity along
with its state (on/off etc.). Output from this function
serves as input to the function ‘Update knowledge
base’.
(ii) Update knowledge base (A2):
This function takes ‘Knowledge base’ as its mean
which corresponds to memory where all the beliefs,
facts and context information is stored and updated.
It takes initial beliefs, facts and context information
from the ‘Get context information’ function.
Changed beliefs and facts are updated every time
some activity is performed by the ‘Perform activity’
function or based on some new beliefs from the
function, ‘Generate psychological state’. Output of
updated beliefs and facts serve as input to functions
‘Generate psychological state’, ‘Compute activity’
and ‘Calculate energy and save context’.
(iii) Generate psychological state (A3):
This function corresponds to human psychology
which varies from individual to individual based on
certain beliefs and facts. The psychological state is
generated based on the beliefs and facts and context
elements available to it from the “Update knowledge
base” function. It also captures two important
aspects of humans i.e. “feel and want”. For example
based on the fact that the temperature rises slowly in
the room, a person starts feeling hot when a certain
amount of temperature is reached and may want to
open the window based on his belief that the
temperature is very high. This belief will further
influence the “Compute Activity” function for the
selection of appropriate activity. It takes the social
behaviour from the function ‘Compute social
behaviour’ as control/constraint to generate changed
beliefs based on some social influence. For example,
having a belief that temperature is very high,
inhabitant does not open the window due to the fact
that other people present in the room don’t feel as
much hot and do not want him to open the window.
Every time the beliefs are changed, they are updated
in the “Update knowledge base” function.
(iv) Compute activity (A4):
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
194

Compute activity function represents a reactive
behaviour and is associated with the selection of an
appropriate activity like single user activity without
deliberation, single user activity with deliberation or
group activity with or without deliberation based on
the changed beliefs and facts as input from ‘Update
knowledge base’ function and psychological
influence as control from ‘Generate psychological
state’ function.
Since the inhabitants select some activity to be
performed based on the context under the
psychological influence, this function selects which
activity (single user/group) is to be performed. It
takes as input the beliefs, facts and context
information from the “Update knowledge base”
function and inhabitant who will be involved in the
activity from the “who” model. The ‘why/how’
model serves as means which contains the
information about activity. If selected activity is a
single user activity and does not require deliberation,
it is directly fed to the ‘Compute activity time’
function otherwise it is submitted to the ‘Compute
deliberative behaviour’ function. In case of group
activity it is always fed to the function ‘Compute
social behaviour’ for group agreement. The ‘why’
model depicts the reason or cause of computing
some activity. There could be certain causes to select
some activity which affect the energy consumption
patterns of inhabitants. These causes can be
categorized into primary and secondary causes. For
example a primary cause to turn on the electric lamp
in the corridor is that the inhabitant is passing by
there and it’s dark, whereas the secondary cause may
be some aesthetic sense.
(v) Compute social behaviour (A5):
Social behaviour of inhabitants significantly affects
the energy consumption patterns in domestic
settings. For example inhabitants having dinner
together may consume less energy than everybody
going to the kitchen and turning on the light and hot
plate at different times. This function takes input
from the ‘Compute activity’ function in case of a
group-activity and uses ‘who’ model as input which
will let this function know about the inhabitants who
will be involved in the group activity to perform
group agreement. Output in case of group agreement
could be fed to the function ‘Compute activity time’
if deliberation is not required otherwise it serves as
input for the function ‘Compute deliberative
behaviour’. The psychological state of inhabitants
affects the social behaviour which corresponds to
some group agreement or no group agreement.
Similarly the social rule of having dinner together
which is stored as agent beliefs can be bypassed by
some agent or all of them upon the perception of
some new facts and beliefs.
(vi) Compute deliberative behaviour (A6):
The deliberative behaviour of an agent is caused due
to some changed beliefs and facts which influence
the performance of the selected activity. This
function captures deliberation on different elements
like cost, comfort etc. for the selection of an
appropriate alternative activity. Deliberation is a
reasoning mechanism where an inhabitant decides
which activity to be performed keeping in view the
consequences of all possible choices. Deliberative
behaviour affects energy consumption e.g. having
multiple options to lower the temperature in the
room as it’s very hot inside, one of the inhabitants
believes that opening window can be a good solution
and moves to open the window. He then realizes a
storm outside. This new perception of a bad weather
outside by the agent at the ‘Compute activity’
function will update the changed beliefs and facts in
the “Knowledge base”. Based on the changed facts
and beliefs in the “Knowledge base” which serves as
means to this function or the past experiences which
are saved in the “Behaviour base” an inhabitant may
change his mind to turn on the air conditioning
system instead. The choice of alternative actions
based on cost, comfort, information etc. is stored in
a database called ‘behaviour base’ which could help
the inhabitant for future choices where he could
maximize the comfort while minimizing cost if he
likes to do so.
The selected activity after deliberation is finally
sent to ‘Perform activity’ function.
(vii) Compute activity time (A7):
This function computes the time when some activity
is to be performed by the inhabitants, e.g. the start
and end time etc. It computes activity duration and
sends this information to ‘Perform activity’ function.
It receives activity information as input from the
‘Compute activity’ or ‘Compute social behaviour’
functions and the timing information from the
“when” model, however activity time is computed
only upon the receipt of the activity information.
(viii) Perform activity (do/how) (A8):
Based on the single, group, reactive, deliberative
behaviour the activity is performed by this function
and the information is used to calculate the energy
consumption of this activity. It takes as input, a
single/group activity and its associated time from
‘Compute activity time’ function and outputs the
changed beliefs and facts to ‘Update knowledge
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS' BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
195
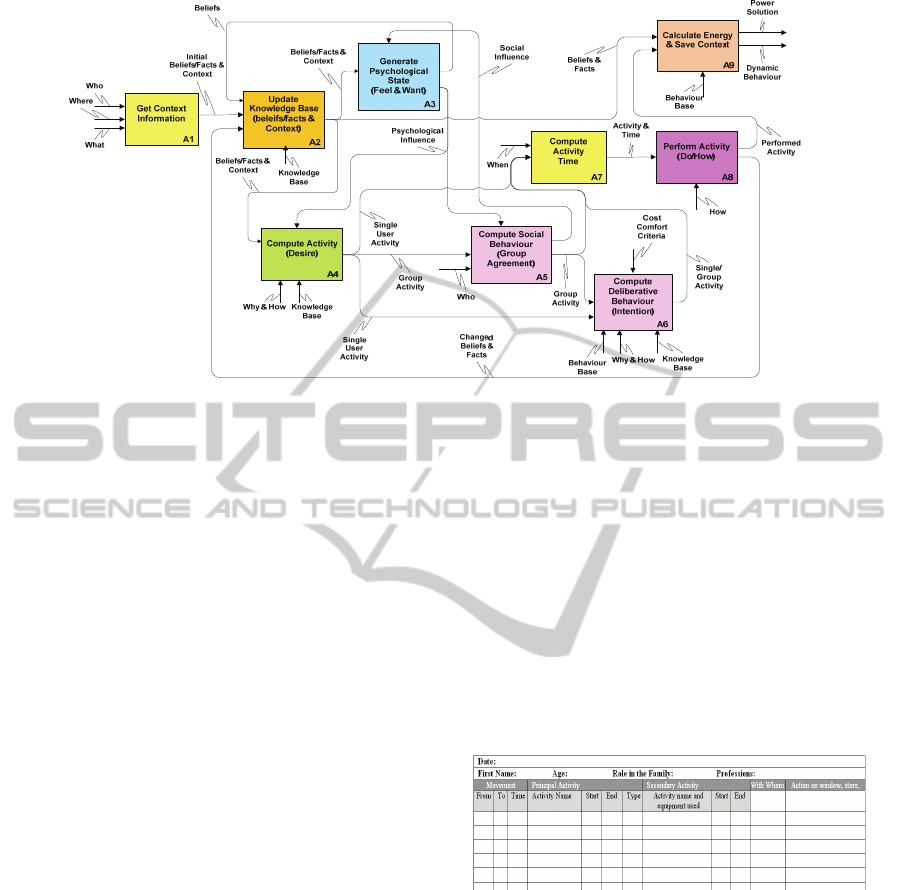
Figure 6: Functional model for dynamic behaviour simulations.
base’ and activity completion information to
‘Calculate energy and save context’ functions
respectively.
It is important to note here that activity
performed is not physically executed but simulated
for execution and is represented as start and end
time. Upon completion of the activity i.e. end time,
outputs are further submitted as respective inputs.
(ix) Calculate energy and save context (A9):
This function collects information about the
performed activity and other context elements
(beliefs and facts) from ‘Perform activity’ and
‘Update knowledge base’ functions and calculates
the energy consumed after performing the activity.
Information about the activity performed, context
elements and energy consumed is also saved in the
behaviour base which could further be utilized to
make choices based on cost/comfort criteria. Finally
the dynamic behaviour and power solution is
provided as output. The power solution will provide
a series of calculated energy requirements on
varying dynamic group behaviour within domestic
settings. It will help in identifying min/max energy
demand to balance the supply and demand equation
as well.
Activity information fed from ‘Perform activity’
function consists of name, start time and end time.
‘Calculate energy cost and save context’ function in
the presence of this information and beliefs and facts
calculates energy using activity duration and
appliances with associated energy costs. This
function calculates energy performance based on
theoretical and actual energy costs, theoretical
energy cost is computed based on static activity
profiles and actual energy cost represent the cost
computed based on dynamically simulated
behaviour profiles. The difference between the
theoretical and actual energy cost gives energy
performance. This function outputs complete
behaviour profile generated dynamically and its
associated power management solution.
4 SCENARIOS’ DESCRIPTION
We have collected a workday activity profile (24h)
of a family in France through an activity journal
(
Fig.7) with contextual information.
Figure7: Activity journal for data collection.
To demonstrate reactive/deliberative group behaviour
a simple scenario from the collected profile is
implemented using the Brahms language following
the model proposed in section 3:
“Stephan (father) comes back home from LAB at
19h48 and walks through the corridor to the kitchen
for dinner. Anna (daughter) and Erik (son) are
watching television in the lounge. They walk to the
kitchen for dinner at 19h50. Katherine (mother) is
already in the kitchen and is preparing the table for
dinner and is interacting with the fridge in parallel.
Stephan drinks water from the refrigerator. They
have dinner together from 19h50 till 20h30. Stephan,
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
196
Katherine and Anna move to the living room after
finishing the dinner and start watching television
there. Erik moves to the study room.
The temperature increases slowly due to the
presence of all family members in the living room.
Stephan feels hot and wishes to open the window to
reduce the temperature. Before opening the window
he asks Katherine and Anna. They agree and Stephan
goes to the window to open it. He realises that there
is a storm outside and opening window is not safe, so
he evaluates between two options to identify the most
comfortable (i) turn the AC on using the remote
control, (ii) open the door which is linked to the study
room. He decides to turn on the AC as opening door
might disturb Erik“.
To implement the above scenario we need to model
human cognition, reactive/deliberative behaviour
(group agreement), context (5W1H) and dynamism
(temperature increase slowly). Results from the
simulation represent human behaviour at multiple
levels of detail and interactions between agents and
objects. Sub-functions “A1 to A9” (Fig.6) are
implemented and simulated in Brahms with results
in section 5. Sub-function “A9” will be deve loped
as a plug-in to be integrated with the Brahms
simulation for energy calculation.
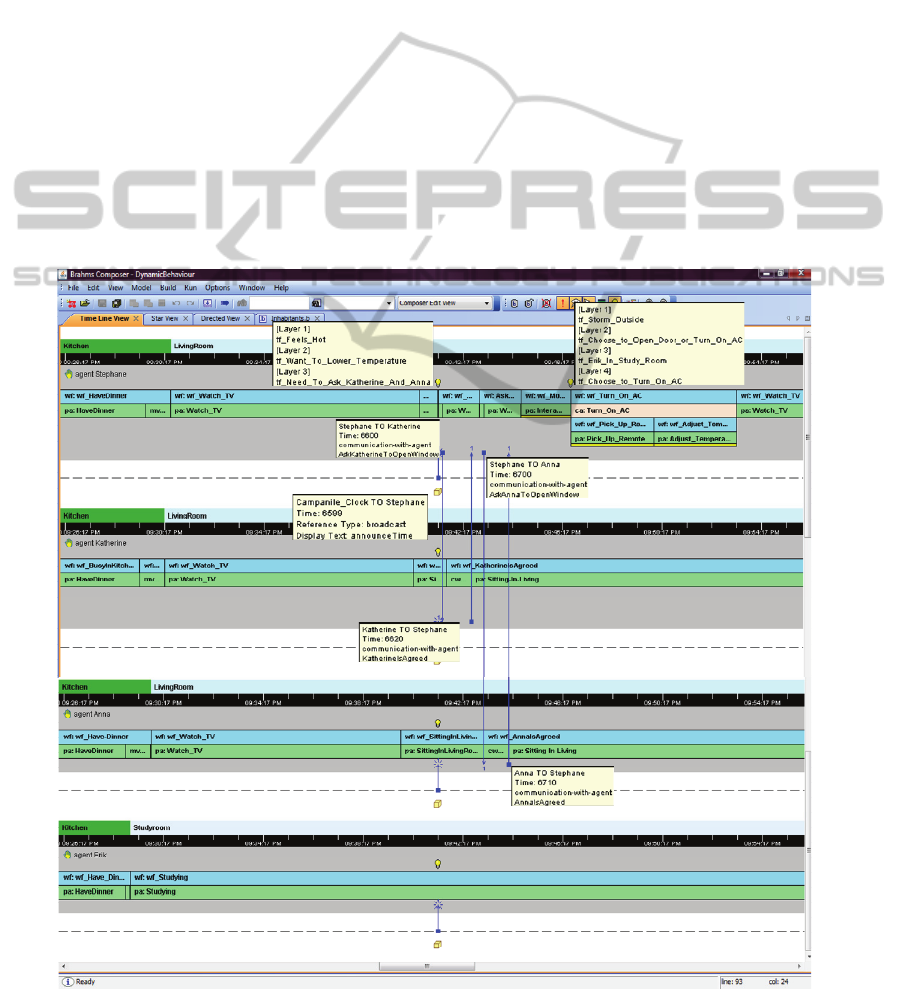
5 SIMULATION RESULTS
The scenario in section 4 is implemented and
simulated using the model (section 3) with the
Brahms language. It starts with Brahms code (using
composer), compiled (using builder) to create ‘.xml’
files and simulation results are generated as a text file
using the Brahms simulation engine. The simulation
text file is converted into a MySQL database by agent
viewer in order to graphically analyze the simulation
results as presented below in
Fig.8. Only a part of the
simulation results is shown here that takes into
account the reactive, deliberative and group behavi-
Figure 8: Communication and Group reactive/deliberative behavior.
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS' BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
197

our. Communication activities taking place between
agents Stephan, Anna and Katherine are represented
by vertical lines and the bulb represents the Brahms
throughtframe (tf).
It is evident from the Fig. 8 that agents Stephane,
Katherine and Anna have moved to the living room
after having dinner in the kitchen. The first
throughtframe with reference to the agent Stephane
highlights the temperature increase in living room
beyond 30 degrees and Stephane feels hot and want
to lower the temperature. In order to establish
dynamic group behaviour in the presence of
Katherine and Anna, Stephane decides to go for
group agreement and to establish this he starts
communication with other agents.
This belief gives rise to the deliberative
behaviour and now he wants to choose between
opening the door or turning on the air conditioner
based on Erik’s presence in the study room.
However, changing the parameter with no storm
outside will not trigger the thoughtframes used for
further reasoning and the simulation results will be
different. Horizontal lines beneath the primitive
activities (pa) show the interaction with some
appliance/object.
6 CONCLUSIONS
From the results, we have demonstrated the
simulation of reactive/deliberative group behaviour
within domestic settings (complex scenario).
Perception, cognitive, social and psychological
elements are dynamically simulated to generate
behaviour of inhabitants’ over time. We are working
on a Java plug-in to connect to the behavioural
pattern generated from Brahms for energy
calculations and learning context, beliefs and facts
that influence energy consumption within the
domestic environment. We are also working on the
sub-function “A9” to calculate energy related to the
dynamic behaviour profiles generated from
simulation and build a database (behaviour base) of
context, beliefs, facts and activities having strong
influence on the energy consumption. During
simulation, agents are provided with potential
consequences of possible actions learned from
previous simulations in anticipation to find energy
efficient behaviour and savings.
7 FUTURE WORK
In this article dynamic behaviour is demonstrated
with data collected from a single family, however
future work will include data collected from a set of
reference households. Dynamic behaviour
simulation could be extended to model patterns for
different classes of household behaviours and
analysis of energy impact due to correct behaviour
(ergonomy). Simulation results as presented in
section 5 start with the initialization of beliefs and
facts as static values; hence based on fixed initial
values we could have one behavioural pattern;
however adjusting the list of beliefs and facts
dynamically after each simulation within parametric
space could be interesting to identify generalized
energy related behaviour. Design of experiment
(DOE) and data mining techniques if employed
would help to reduce the number of possible
combination of facts and beliefs to start simulations
and optimize the computational time in terms of
reduced number of experiments.
REFERENCES
Abras, S., Ploix, S., Pesty, S., and Jacomino, M. A.
(2006). Multi-agent home automation system for
power management, In Proceedings of the 3rd
International Conference in Control, Automation, and
Robotics.
Anderson, J. R., Bothell, D., Byrne, M. D., and Lebiere, C.
(2004). An integrated theory of the mind, Int. Journal
of Psychological Review.
Andersen, R. V., Toftum, J., Andersen, K. K. and Olesen,
B. W. (2009). Survey of occupant behaviour and
control of indoor environment in Danish dwellings,
Energy and Buildings 41, 11–16.
Bourgeois, D., Reinhart C. and Macdonald I. (2006).
Adding advanced behavioural models in whole
building energy simulation: A study on the total
energy impact of manual and automated lighting
control, Energy and Buildings Vol. 38, pp. 814-823.
Card, S. K., Moran, T. P., and Newell, A. (1983). The
psychology of human-computer interaction. Hillsdale,
NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Clancey, W. J., Sachs, P., Sierhuis, M. and Van Hoof, R.
(1998). Brahms: Simulating practice for work systems
design, International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, 49, 831–865.
Corker, K. M. and Smith, B. R. (1998). An
architectureand model for cognitive engineering
simulation analysis: Application to advanced aviation
automation. In Proceedings of the AIAA Computing
in Aerospace: American Institute of Aeronautics and
Astronautics
Cook, D. J. and Das, S. K. (2007). How smart are our
environments? an updated look at the state of the art.
Journal of Pervasive and Mobile Computing.
Deutsch, S. E., Cramer, N. L., and MacMillan Jean (1997),
Operator model architecture: Software functional
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
198

specification, Technical Report by United States Air
Force Armstrong Laboratory.
Dong, B. and Andrews, B. (2009). Sensor based
occupancy behaviour pattern recognition for energy
and comfort management in intelligent buildings, 11th
International Building Performance Simulation
Association (IBPSA) Conference.
Eggleston, R. G., Young, M. J. and McCreight, K. L.
(2000). Distributed cognition: A new type of human
performance model, In M. Freed (Ed.), Simulating
human agents, AAAI Fall Symposium (pp. 8–14).
Firby, R. J. (1989). Adaptive execution in complex
dynamic worlds, Doctoral Dissertation, Yale
University, USA.
Freed, M. A. (1998). Simulating human performance in
complex, dynamic environments, Doctoral
Dissertation, Northwestern University, IL USA.
Ha, D. L., Ploix, S., Zamai, E. and Jacomino, M. (2006). A
home automation system to improve household energy
control, 12th IFAC Symposium on Information
Control Problems in Manufacturing.
Ha Seung, Jung Hong, and Oh Yong (2006). Method to
analyze user behaviour in home environment, Personal
Ubiquitous Computing. 10, 110–121.
Heel Eelco Van (2009), Climate and Environment 2009,
The Rockwool Group Denmark, Retrieved from:
http:/www.rockwool.com/environment/environment+r
eport.
Henricksen Karen (2003). A Framework for Context-
Aware Pervasive Computing Applications, PhD thesis,
School of Information Technology and Electrical
Engineering, University of Queensland.
Jensen Ole Michael, Wittchen Kim B. and Thomsen
Kirsten Engelund (2009). Towards very low energy
buildings, Danish Building Research Institute, Aalborg
University
Just, M. A., Carpenter, P. A., and Varma, S. (1999).
Computational modelling of high-level cognition and
brain function, Journal of Human Brain Mapping, 8,
128–136.
Kieras, D. E. and Meyer, D. E. (1995). An overview of the
EPIC architecture for cognition and performance with
application to human-computer interaction, (EPIC
Report No. 5). MI: The University of Michigan.
Kieras, D. E. and Polson, P. G. (1985). An approach to the
formal analysis of user complexity, International
Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 22, 365–394.
Lehman, J. F., Laird, J. E., and Rosenbloom, P. S. (1996).
A gentle introduction to Soar, an architecture for
human cognition. Sternberg and Scarborough, editors,
An invitation to Cognitive Science, vol. 4. MIT Press.
Mahdavi, A, Pröglhöf, C. (2009). Toward empirically-
based models of people’s presence and actions in
buildings, Proceedings of Building Simulation,
Scotland 9, 537-544.
Masoso, O. T. and Grobler, L. J. (2009). The dark side of
occupants’ behaviour on building energy use, Energy
and Buildings.
Ogilvie Trent (2009). Environment 2009, Roxul Inc.,
Retrieved from: http://www.roxul.com/files/RX-NA-
EN/pdf/ROXC2004_EnviroReport_Singles_L R.pdf.
Ouyang Jinlong and Hokao Kazunori (2009). Energy-
saving potential by improving occupants’ behaviour in
urban residential sector in Hangzhou City, China,
Energy and Buildings 41, 711-720.
Pew, R. W. and Mavor, A. S. (Eds.) (1998). Modelling
human and organizational behaviour: Applications to
military simulations, Washington, DC: National
Academy Press.
Pritsker, A. B., Wortman, D. B., Seum, C., Chubb, G., and
Seifert, D. J. (1974). SAINT: Systems Analysis of an
Integrated Network of Tasks (Aerospace Medical
Research Laboratory).
Raaij, W. F. Van and Verhallen, T. M. M. (1983). A
behavioural model of residential energy use, Journal
of Economic Psychology 3, 39–63.
Seryak J. and Kissock K. (2000), Occupancy and
behavioural affects on residential energy use,
Proceedings of annual conference on American solar
energy society.
Sierhuis, M., Clancey, W. J., and Van Hoof, R. (1999).
BRAHMS: A multiagent programming language for
simulating work practice, Retrieved from:
http://www.AgentiSolutions.com.
Sierhuis, M., Clancey, W. J., and Van Hoof, R. (2007).
BRAHMS A Multi-agent Modelling Environment for
Simulating Work Processes and Practices.
International Journal of Simulation and Process
Modelling.
Sloman, A. (2001). Varieties of affect and the CogAff
architectural scheme, Symposium on Emotion,
Cognition, and Affective Computing, Society for the
Study of Artificial Intelligence and Simulation of
Behaviour (AISB).
Thibadeau, R., Just, M. A., and Carpenter, P. A. (1982). A
model of the time course and content of reading,
Cognitive Science, 6, 157–203.
Ueno T., Inada R., Saeki O. and Tsuji K. (2006).
Effectiveness of an energy-consumption information
system for residential buildings, Applied Energy 8,
868–883.
World Urbanization Prospects (2007). United Nations
Department of Economic and Social Affairs/
Population Division.
Young Michael J. and Deutsch Stephen E. (1997).
Integrating human performance into the design
process: The operator model architecture, IEEE sixth
annual human factors meeting, Florida USA.
Zachary, W. W., Ryder, J. M., and Hicinbotham, J. H.
(1998). Cognitive task analysis and modelling of
decision-making in complex environments. In J. Canno
Cannon-Bowers and E. Salas (Eds.).
Zimmermann Andreas, Lorenz Andreas, and Oppermann
Reinhard (2007). An Operational Definition of
Context, B. Kokinov et al. (Eds.): Context 2007, LNAI
4635, pp. 558–571.
12
AGENT BASED FRAMEWORK TO SIMULATE INHABITANTS' BEHAVIOUR IN DOMESTIC SETTINGS FOR
ENERGY MANAGEMENT
199
