
SCHEDULING BASED UPON FREQUENCY TRANSITION
Following Agents Agreement in a NCS
O. Esquivel-Flores
1
and H. Benitez-Pérez
2
1
Posgrado en Ciencia e Ingeniería de la Computación, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, México D.F., México
2
Departamento de Ingeniería de Sistemas Computacionales y Automatización
Instituto de Investigación en Matemáticas Aplicadas y en Sistemas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
Apdo. Postal 20-706 Del. A. Obregón, México D.F., C.P. 01000, México
Keywords: Distributed systems, Agents, Frequency transmission, Control.
Abstract: This paper provides a strategy to schedule a kind of real-time distributed system base upon changes on
frequency transmission of agents included into a distributed system. Modifications on frequency
transmission (sensing periods) of system’s individual components impact on system quality performance
due to limited computing resources In this work we propose a dynamic linear time invariant model based
upon frequency transmission and compute times of agent’s task which constitute a networked control
system (NCS). Schedulability could be reached by controlling frequency transmission rates into a region
bounded by minimum and maximum rates besides satisfy compute times. This idea is reinforced through a
simulated case study based upon a helicopter simulation benchmark. It provides a good approximation of
system response where main results are perform under a typical fault scenario for demonstration purposes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays distributed systems are widely used in the
industrial and research. Current applications on
Distributed Systems under time restrictions are
Networked Control Systems (NCS) whose
implementations consist of several agents which
realize a part of control process and sensor/actuator
activities work on a real time operating system and
real time communication network. In order to
achieve overall objectives of all tasks performed, it
is necessary for all agents to exchange their own
information through communication media properly.
Therefore communication mechanisms play an
important role on stability and performance (Lian,
et. al., 2006). In a real-time system deterministic
time requirements have to be scheduled. A task is
periodic if it is time-triggered, with a regular release.
The length of time between releases of successive
jobs of task
is a constant,
, which is called the
period of the task. The deadline of each job is
time units after the release time. For a sporadic task
there are constants
and
such that the sum of the
compute times of all the jobs of
released in any
interval of length
is bounded by
. In many cases
is an upper bound on the compute time of each
job and
is the minimum time between releases.
(Sha, et. al., 2004) mentions that Serling et. al.
showed that a task is feasible if
∑
≤2
−1.
Moreover, network scheduling is a priority in the
design of a NCS when a group of agents are linked
together through the available network resources. If
there is no coordination among agents, data
transmissions may occur simultaneously and
someone has to back off to avoid collisions or
bandwidth violations. This results in time delays or
even failure to comply task’s deadlines. A good
scheduling control algorithm tries to minimize this
loss of system performance (Branicky, et. al., 2003),
nevertheless there isn’t a global scheduler that
guarantees an optimal system performance
(Menéndez and Benitez, 2010). The use of a
common-bus communication channel produces
different forms of time delays uncertainty. (Lian et.
al. 2001), (Lian et. al. 2002) have designed
methodologies for networked agents to generate
proper control actions and utilize communication
bandwidth optimally. The effectiveness of the digital
control (Figure 1) system depends on the sampling
rate . A region which networked control
389
Esquivel-Flores O. and Benitez-Pérez H..
SCHEDULING BASED UPON FREQUENCY TRANSITION - Following Agents Agreement in a NCS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003153303890393
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 389-393
ISBN: 978-989-8425-41-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
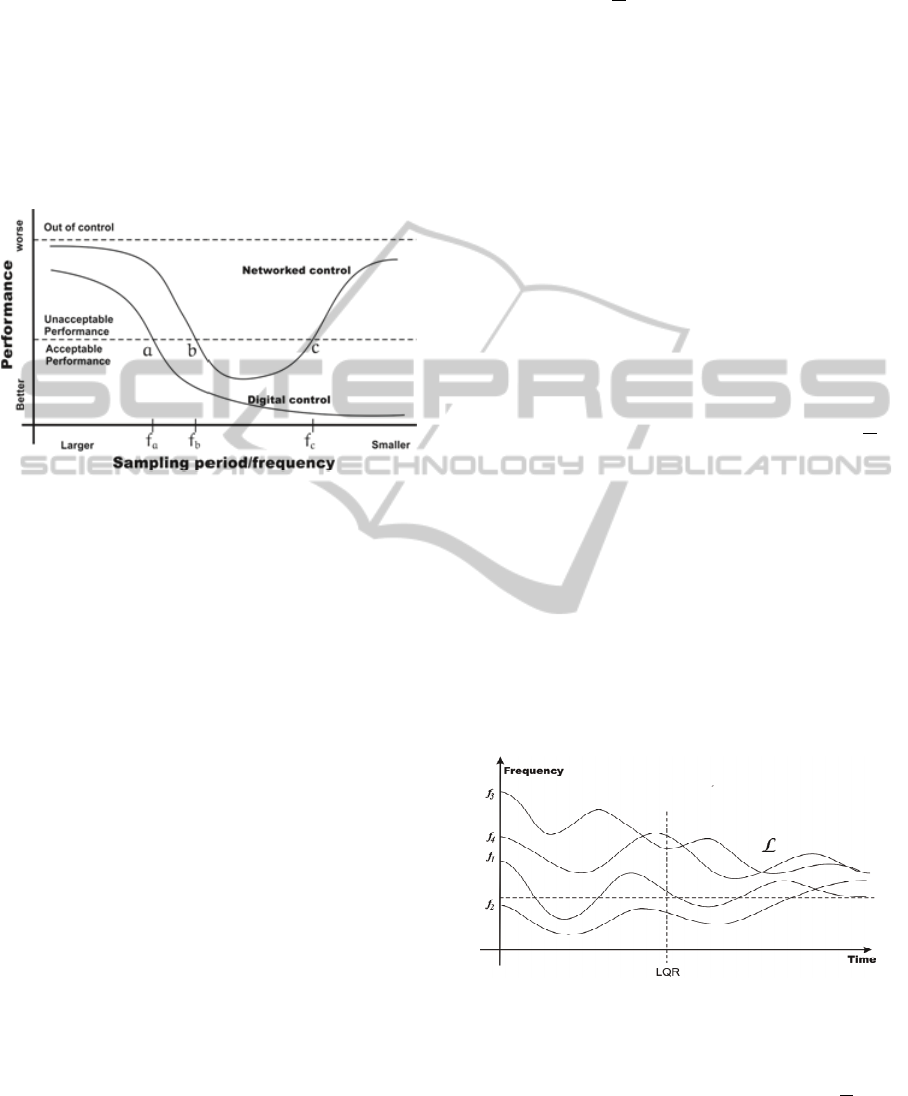
performance is acceptable deals with two points
and associated to use of
and
sampling rates
respectably which can be determined by
characteristics an statistics of networked induced
delays and device processing time delays. implies
that a certain level of control performance and it
could be determined by case of study, as the
sampling period gets smaller, the network traffic
load becomes heavier and data loss increase in a
bandwidth-limited network, time delays are longer.
Figure 1: Digital and Networked control performance.
Hence it’s very important to consider either
sampling periods or frequency transmission to
obtain better system performance.
This paper shows a way to control the frequency
of transmission among agents in a NCS based on
their frequency transmission relations. The authors
propose a lineal time invariant model in which the
coefficients of the state matrix are the relations
between the frequencies of each agent using a LQR
feedback controller that modifies transmission
frequencies bounded between maximum and
minimum values of transmission in which ensures
the system’s schedulability The rest of this paper is
organized as follow, in section 2 authors show a
frequency transmission model and a proposal to
matrix coefficients of the model, section 3 presents a
particular NCS as case of study, section 4 shows
numerical simulations of the model presented and
the performance of LQR controller. Brief
conclusions are presented at the end.
2 FREQUENCY TRANSITION
MODEL
Let a distributed system with agents that perform
one task
with period
and consumption
each
one, =1,2,…,. Network scheduling can be
modeled as a linear time-invariant system whose
state variables
,
,
…,
are the frequencies of
transmission
=
of agents involved on it. The
authors assume that there is a relationship between
frequencies
,
,
,…,
and external input
frequencies
,
,…,
which serve as coefficients
of the linear system:
=
+
=
(1)
∈ℝ
is the matrix of relationships between
frequencies of the agents, ∈ℝ
is the scale
frequencies matrix, ∈ℝ
is the matrix with
frequencies ordered, ∈ℝ
is a real frequencies
vector, ∈ℝ
is the vector of output frequencies.
The input =ℎ
−
∈ℝ
is a function of
reference frequencies and real frequencies of the
agents in the distributed system. It is important to
note that relations between the frequencies of the
n
agents lead to the system (1) is schedulable with
respect to the use of processors, that is, =
∑
.
Therefore it is possible to control the system
through the input vector such that the outputs
are in a region non-linear where the system is
schedulable. This is that during the time evolution of
the system (1) the output frequencies could be
stabilized by a controller within the schedulability
region This region could be unique or a set of
subregions
i
L
in which each
i
y
converges. Figure 2
shows the dynamics of the frequency system and the
desired effect by controlling it through a LQR
controller and defining a common region
L
for a set
of frequencies.
Figure 2: Frequencies controlled by a LQR controller into
a schedulability region.
All agents of the system start with a frequency
and the controller modifies the period
=
of
each task into a schedulable region. The real
frequency
of the agent is modified to
, it means
that
in time
changes to
at time
to
converge in a region where the system performance
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
390

is close to optimal. The objective of controlling the
frequency is to achieve coordination through the
convergence of values.
2.1 Matrix Coefficients Proposal
Let a
∈ given by a function of minimal
frequencies
of node and
∈ given by a
function of maximal frequencies
, this is,
=
,
,…,
and
=
,
,…,
. The
control input is given by a function of the minimal
frequencies and the real frequencies of agent , it
means =ℎ
−
=
−
. Then, the
system (1) can be written as:
=
+
=
+
−
(2)
3 CASE OF STUDY
The case of study is a prototype of a helicopter
system integrated to a CanBus network with two
propellers that are driven by DC motors. A
description of of the helicopter can be found in
(Quanser, 2006). Several Simulink models and
Matlab scripst are used to build the helicopter
dynamics model and it runs a simulation of the
closed-loop response using the position controller.
Figure 3 shows closed-loop system simulation
subsystem. Authors included a distributed system
which performs a control close loop dynamic system
based upon: sensor-controller-actuator and a
centralized scheduler. Figure 3 shows the networked
control system which consists of 8 processors with
real-time kernel, connected by through a network
type CSM / AMP (CAN) with a rate of sending data
of 10000000 bits / s and not likely to data loss.
Figure 3: Networked Control System included in
helicopter model.
These blocks of real-time kernel and network are
simulated using Truetime (Ohlin, et. al., 2007). The
first agent in the model, on the extreme left is the
controller agent (Figure 3) that uses the values from
sensors and compute control outputs. Sensor agents
sample the analog signals. Two actuator agents
located to the far right below (Figure 3) receives
signals. Finally scheduler, main agent, above far
right agent (Figure 3) organizes the activity of others
7 agents and it is responsible for periodic allocation
bandwidth. 4 signals are measured to control
helicopter fly: the pitch angle, the yaw angle,
pitch derivative,
yaw derivative.
(Tipsuwan and Chow, 2003) use optimal PI
controller gains scheduled in real-time with respect
to the monitored IP networked traffic conditions in
order to maintain the best possible system
performance.and tries to capture changes in network
traffic conditions.
In this work the authors focus on sensor agents
and the objective is to control through system (1) the
data frequency transmission. Each agent has a real
transmission frequency and sets the minimum
frequencies and maximum between which each
agent could transmit.
Elements of the matrices for system (1) are
defined as follows:
=
,
,…,
=
=
=
0
=
1=
0
̅
,
,…,
is the greatest common divisor of
the minimum frequencies, we are going to write only
λ
. It is very important to consider the compute time
of the task of each node as an additional state.
Using (2) we can write (1) as:
=
̅
0
̅
0
̅
0
̅
0
1
+
SCHEDULING BASED UPON FREQUENCY TRANSITION - Following Agents Agreement in a NCS
391

1
0000
0
1
000
00
1
00
000
1
0
11111
0000
0
000
00
00
000
0
0000
−
=
10000
01000
00100
00010
00001
thus
=
̅
0
̅
0
̅
0
̅
0
1
+
−
0000
0
−
000
00
−
00
000
−
0
00000
=
10000
01000
00100
00010
00001
4 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS
Numerical simulations were performed of the
system (1) without control and using LQR controller
for values of maximum, minimum and real
frequencies taking in account the compute time, the
values used were:
Table 2: Values of minimal, maximal and real frequencies
and compute time.
Agent Maximum. Minimum Real Consum
1 60 40 55 0.001
2 50 30 50 0.001
3 50 10 25 0.001
4 45 25 30 0.001
The coefficient matrix A is:
=
0.125 0.750 0.250 0.625 0
1.333 0.166 0.333 0.833 0
4.000 3.000 0.500 2.500 0
1.600 1.200 0.400 0.500 0
0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 1
with eigenvalues
=1.0000 ,
=3.3308,
=−0.8556,
=−0.6835,
=−0.5000.
The system is unstable
4.1 LQR Control
We chose weight matrices
44
,
x
RQ ℜ∈
as follows:
=
100000
010000
001000
000100
000010
=
10000
01000
00100
00010
00001
the gain and
=
−
are:
=
231.34 175.16 63.59 158.61 −0.26
189.95 14400 52.23 130.28 0.07
−72.73 −55.10 −19.81 −49.95 2.22
192.52 145.82 52.90 132.25 0.05
−222.43 −168.49 −61.15 152.60 3.44
=
−3.73 −2.16 −0.80 −2.01 0.004
−2.46 −2.71 −0.71 −1.77 −0.001
5.45 4.10 0.89 3.49 −0.044
−2.67 −2.04 −0.77 −2.43 −0.001
−31865 −241.38 −87.76 −21859 −4.5374
and eigenvalues
=−7.141
=−3.330,
=−0.507,
=−0.857,
=−0.687.
Figure 4 shows the dynamics of the controlled
system. The LQR controller modifies frequency
transmission rate into schedulability region.
Figure 4: Frequency response controlled by a LQR
controller.
Figure 5 shows the effect of to modify
transmission rate using frequency transmission
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
392
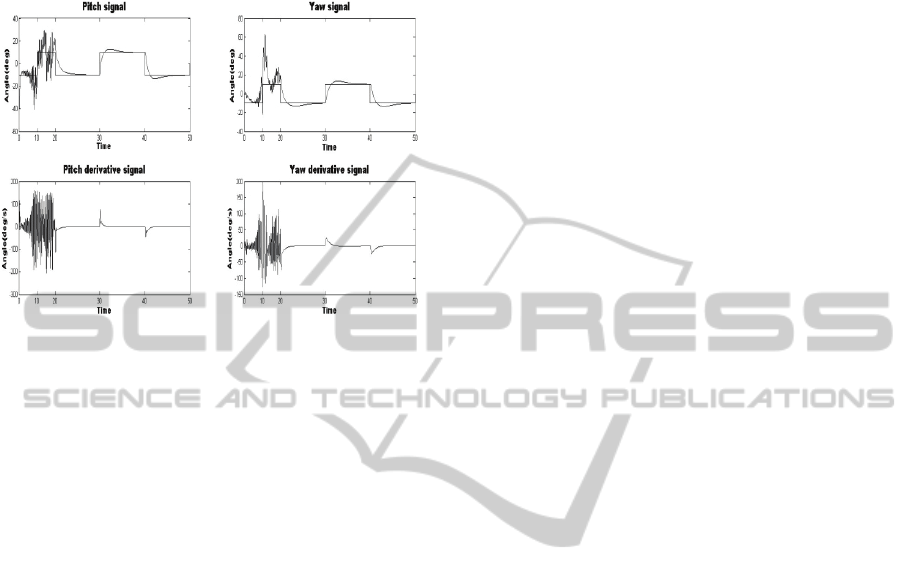
model during 50 seconds. At the beginning sensor
task periods are out of better performance interval,
once passed 20 sec the model modifies dynamically
frequency transmission of sensors.
Figure 5: Helicopter response using frequency transition
model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we have present a linear time invariant
model of agent’s frequency transmission involved
into a distributed system. The significance of control
the frequencies stem from the system schedulability
through information interchange between agents of
distributed system. The key feature of LQR control
approach is a simple design with good robustness
and performance capabilities let to modify the
frequencies easily. Authors have shown via
numerical simulations the performance of the
proposed control scheme using a helicopter
prototype.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The financial support given by grants PAPIIT-
UNAM 103310 and CONACYT is really
appreciated.
REFERENCES
Branicky, M., Liberatore, V., Phillips, S., 2003.
Networked control system co-simulation for co-design.
Proc. American Control Conf., 4:3341–3346, Denver,
June 4–6.
Lian, F., Moyne, J. Tilbury, D., 2006. Network
architecture and communication modules for
guaranteeing acceptable control and communication
performance for networked multi-agent systems, IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics, Vol. 2, No. 1.
Lian, F., Moyne, J. Tilbury, D., 2001. Time delay
modeling and sample time selection for networked
control systems, Proceedings of ASME-DSC, Vol.
XX, New York, USA.
Lian, F., Moyne, J. Tilbury, D., 2002. Network design
considerations for distributed networked for
distributed control systems, IEEE Transactions on
Control Systems Technology, Vol. 10, No. 2.
Menéndez, A., Benitez, H., 2010. An interaction amongst
real time distributed systems performance & global
scheduling, JART, August, Vol. 8.
Ohlin, M., Henriksson, D., Cervin, A., 2007. TrueTime 1.5
Reference Manual, Department of Automatica
Control, Lund University.
Quanser: 2006. 2-DOF Helicopter User and Control
Manual. Quanser, Speciallity Experiments:2-DOF
Helicopter.
Sha, L., Abdelzaher, T., Arzen, K., Cervin, A., Baker, T.,
Burns, A., Butazzo, G., Caccamo, M., Lehoczky, J.,
Mok, A., 2004. Real Time Scheduling Theory: A
Historical Perspective, Real time systems, Kluwer
Academic Publishers.
Typsuwan, Y., Chow, M., 2003. On the Gain Scheduling
for Networked PI Controller Over IP Network,
Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/ASME International
Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics.
SCHEDULING BASED UPON FREQUENCY TRANSITION - Following Agents Agreement in a NCS
393
