
Norm-ML
A Modeling Language to Model Norms
Karen Figueiredo and Viviane Torres da Silva*
Computer Science Department, Universidade Federal Fluminense (UFF)
Rua Passos da Pátria 156, Bloco E, 24210-240, Niterói, Brazil
Keywords: Norm, Modeling, Validation, Metamodel.
Abstract: Norms in multi-agent systems are mechanisms used to restrict the behavior of system entities during a
period of time by defining what the entities are obligated, permitted or prohibited to do and by stating
stimulus to their fulfillment by defining rewards and discouraging their violation by pointing out
punishments. In this paper we propose a modeling language called NormML that makes possible the
modeling of the norms together with its main properties and characteristics.
1 INTRODUCTION
Norms are used to regulate the behavior of the
agents in open multi-agent systems (MAS) by
describing their obligations, permissions and
prohibitions. Norms can be defined at design time
together with the modeling of the system, or created
at runtime by agents that have the power to do so
(López y López, 2003). In this paper we focus on the
description of norms at design time. The modeling
of norms is an important part of the specification of
a system and should be treated as an essential task of
MAS design. Norms refer to actions and entities that
compose a system. So, the refinement of the system
may influence the norms and the definition of a new
norm will only be possible if the actions, agents and
roles being mentioned in the norm are being
considered in the system design.
Although there are many modeling languages
and notations, proposed by methodologies and
organizational models, that provide support to the
modeling of norms, there is still a need for an
approach that completely contemplates the main
properties and characteristics of a norm, i.e., the key
elements that compose a norm: deontic concept,
involved entities, actions, activation constraints,
sanctions and context.
In this paper we identify these elements by follo-
*The present work has been partially funded by the Brazilian research councils CNPq
under grant 135891/2009-4 and 303531/2009-6 and FAPERJ under grant E-
26/110.959/2009, and by the Spanish project “Agreement Technologies"
(CONSOLIDER CSD2007-0022, INGENIO 2010).
wing the premise that norms restrict the behavior of
system entities during a period of time and define the
sanctions applied when they are violated or fulfilled.
Such elements were found out after investigate ten
specification and implementation languages used to
describe and implement norms such as (García-
Camino et al., 2006; López y López, 2003; Silva,
2008; Vasconcelos et al., 2007).
It is the aim of the paper to present a normative
modeling language called NormML, which is an
extension of its preliminary version presented in
(Silva et al., 2010), to model the main elements that
compose the norms and to check the conflicts
between them. Due to the lack of space, in this paper
we focus only on the modelling of the norms.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 discusses the support given by the
modeling languages and the notations provided by
the methodologies and organizational models
analyzed to model the norm elements that we have
identified. Section 3 presents the normative
modeling language NormML. Finally, Section 4
concludes and presents some future work.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we analyze how MAS (i) modeling
languages: AML (Danc, 2008) and AORML
(Wagner, 2003); (ii) notations of methodologies:
Gaia (Zambonelli et al., 2003), O-MaSE (Garcia-
Ojeda et al., 2008), PASSI (Cossentino, 2005),
232
Figueiredo K. and Torres da Silva V..
Norm-ML - A Modeling Language to Model Norms.
DOI: 10.5220/0003179502320237
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 232-237
ISBN: 978-989-8425-41-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Prometheus (Padgham and Winikoff, 2002),
ROADMAP (Juan et al., 2002), Secure Tropos
(Giorgini et al., 2006) and SODA (Omicini, 2001);
and (iii) organization models: MASQ (Ferber et al.,
2009), MOISE+ (Hübner et al., 2002) and OperA
(Dignum, 2004) support the modeling of norms and
its elements.
Deontic Concept: In multi-agent systems, concepts
of deontic logic (Meyer and Wieringa, 1991) have
been used to describe behavior restrictions for the
agents in the form of obligations (what the agent
must execute), permissions (what the agent can
execute) and prohibitions (what the agent cannot
execute). Most of modeling languages and
methodologies make available the deontic concept
of obligation in order to describe the actions that
agents must execute. Methodologies such as Secure
Tropos, SODA, Prometheus and the organization
model proposed in MOISE+ do only offer the
concepts of obligation and permission since they
consider that everything that is not permitted is
automatically prohibited. In the Secure Tropos
methodology the concept obligation can be
represented by the delegation relationship and the
concept of permission by the ownership and trust
relationships. NormML, different from the majority,
includes all the three deontic concepts (obligation,
permission and prohibition) to the modeling of
norms.
Involved Entities: Since norms are always defined
to restrict the behavior of entities, the identification
of such entities whose behavior is being restricted is
fundamental. A norm may regulate the behavior of
individuals (i.e., a given agent, or an agent while
playing a given role) or the behavior of a group of
individuals (i.e., all agents playing a given role,
groups of agents, groups of agents playing roles or
all agents in the system). All languages,
methodologies and organization models analyzed
propose a way to describe the entities to which the
norm applies. The majority provides support to
describe a norm for a particular agent playing a role.
But Gaia, PASSI and ROADMAP methodologies
and the MOISE+ organization model do not allow
the description of norms that apply to a group of
individuals.
The Secure Tropos methodology also allows the
designer to describe the system itself as an entity and
to define norms that can be applied to the system as
a whole. By using NormML it is possible to describe
norms to individuals (agents or roles), groups of
individuals or all the entities of the system (see
Context).
Actions: Since a norm defines restriction over the
execution of entities, it is important to clearly
represent the action being regulated. Such actions
can be communicative ones, typically represented by
the sending and receiving of a message, or non-
communicative actions. In this paper we have not
taken into account norms applied to states. All the
modeling languages, methodologies and models
analyzed provide a way to restrict non-
communicative actions. In OperA, PASSI, MASQ,
Gaia and Secure Tropos it is also possible to restrict
communicative ones. NormML supports the
modeling of both kinds of actions, communicative
and non-communicative.
Activation Constraints: The norms have a period
during while they are active, i.e., during while their
restrictions must be fulfilled. Norms can be activated
by one constraint or a set of constraints that can be:
the execution of actions, the specification of time
intervals (before, after, between), the achievement of
systems states or temporal aspects (such as dates),
and also the activation/deactivation of another norm
and the fulfillment/violation of a norm. None of the
analyzed works supports the description of all the
kinds of activation constraints mentioned. By using
NormML all these activation constraints can be
modeled.
Sanctions: When a norm is violated the entity that
has violated this norm may suffer a punishment and
when a norm is fulfilled the entity who has followed
the norm may receive a reward. Such rewards and
punishments are called sanctions and should be
described together with the norm specification. A
small number of languages and methodologies
consider that norms can be violated, and only few of
them provide a way for describing sanctions. The
AORML language assumes that commitments (or
obligations) between entities of the system can be
violated, and, as consequence, a sanction should be
applied. But the language does not offer a way to
describe this sanction. The organizational models
OperA, MASQ and MOISE+ consider that norms
can be violated, and, excluding MOISE+, they have
mechanisms to describe sanctions. The O-MaSE
methodology group norms in two kinds of policies:
law policies and guidance policies. Only the
guidance policies can be violated but there is not a
way to define sanctions for such violations. The
Gaia and PASSI methodologies express norms as
organization rules that cannot be violated, and so
there is no need to define a sanction mechanism.
None of the analyzed languages or methodologies
allows the description of rewards in case of the
Norm-ML - A Modeling Language to Model Norms
233
fulfillment of a norm. However, NormML support
the definition of both punishments and rewards.
Context: Norms are usually defined in a given
context that determines the area of its application. A
norm can, for instance, be described in the context of
a given environment and should be fulfilled only by
the agents executing in the environment or can be
defined in the context of an organization and
fulfilled only by the agents playing roles in the
organization. All languages, methodologies and
organizational models only define the norms in an
organizational context. Besides describing norms in
an organizational context, NormML also provides
the environmental context.
3 THE NORMATIVE MODELING
LANGUAGE
NormML is a UML-based modeling language for
the specification of norms that constraint the
behavior of MAS entities. The choice for UML as
metalanguage allows for an easy integration of
NormML with other MAS modeling languages also
based in UML such as AUML (Odell, 2000), AML
(Danc, 2008) and MAS-ML (Silva et al., 2008).
NormML was designed with the view that norm
specification in MAS design and security policy
specification in role-based access control (RBAC)
(Ferraiolo et al., 2007) design are closely coupled
issues. RBAC security policies specify the
permissions that a user has under a given role, while
trying to access system resources. In MAS we
specify the norms that regulate the behavior (or
actions) of a role, an agent or an agent playing a
given role. The metamodel of the current version is
detailed in Section 3.1 and some of the invariants
that garantees the well-formedness of a norm are
presented Section 3.3.
3.1 Metamodel
A norm corresponds to an instance of the NormML
metamodel, i.e., it is defined by instantiating several
metaclasses and their relationships. In this section,
we present the NormML metamodel focusing in the
definition of the main elements that compose a
norm. The whole picture of the NormML metamodel
is available in http://www.ic.uff.br/~viviane/
normML/metamodel.pdf.
Deontic Concept: A norm is either an obligation
(represented by the metaclass NormObligation), a
permission (represented by the metaclass (NormPer-
mission) or a prohibition (represented by the
metaclass NormProhibition), as illustrated in Figure
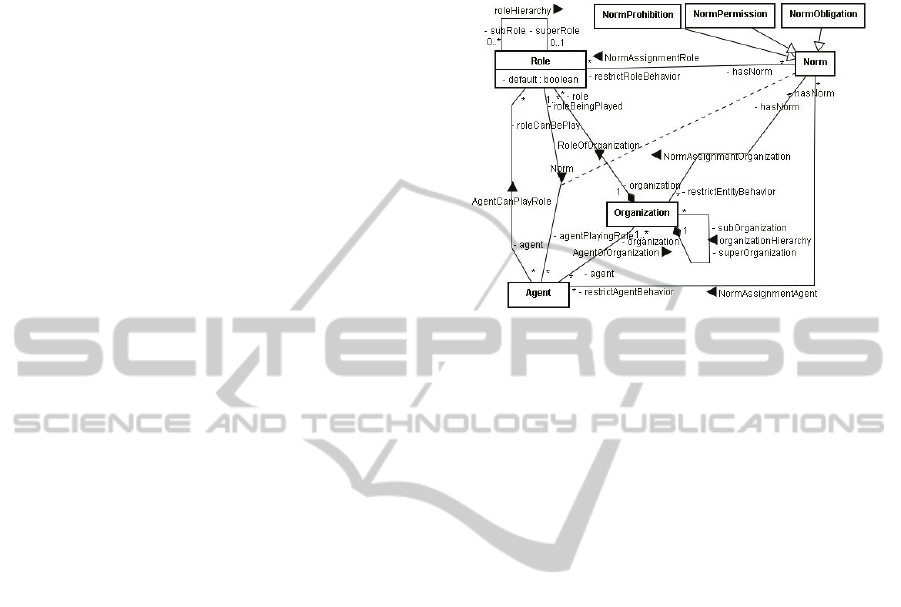
1.
Figure 1: Deontic concept and involved entities related
metaclasses at the NormML Metamodel.
Involved Entities: In the preliminary version of the
language, a norm could only be described to regulate
the behavior of Agents, the behavior of all agents
that play a given Role, or the behavior of a specific
agent when it is playing a given role, captured by the
Agent<->Role relationship. Nowadays, it is also
possible to define a norm to a group of agents by
using the metaclass Organization (as pointed up in
Figure 1).
Actions: NormML inherits four resource kinds from
SecureUML (Basin et al., 2009): Attribute, Method,
Entity and AssociationEnd. It extends the set of
resources with agent and roles’ actions represented
by the metaclass AgentAction and with roles’
messages represented by the metaclass Message that
is part of a communication protocol of a role
(Protocol metaclass).
Thus, it is possible to describe norms to control the
access to attributes, methods, objects and association
ends, to control the execution of the actions of
agents and roles, and also to control the sending and
the receiving of messages by roles (Figure 2). Each
resource kind has a set of actions that can be used to
control the access to the resource. For instance, in
the case of restrictions applied to actions of agents
and roles (AgentAction metaclass), the behavior that
must be used is the execution of the action
(AtomicExecute). Note that AgentAction is the
resource and AtomicExecute is the action being used
to control or restrict the access to the resource.
Activation Constraints: The preliminary version of
NormML allows for the specification of the time
period that a norm is active based on the execution
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
234
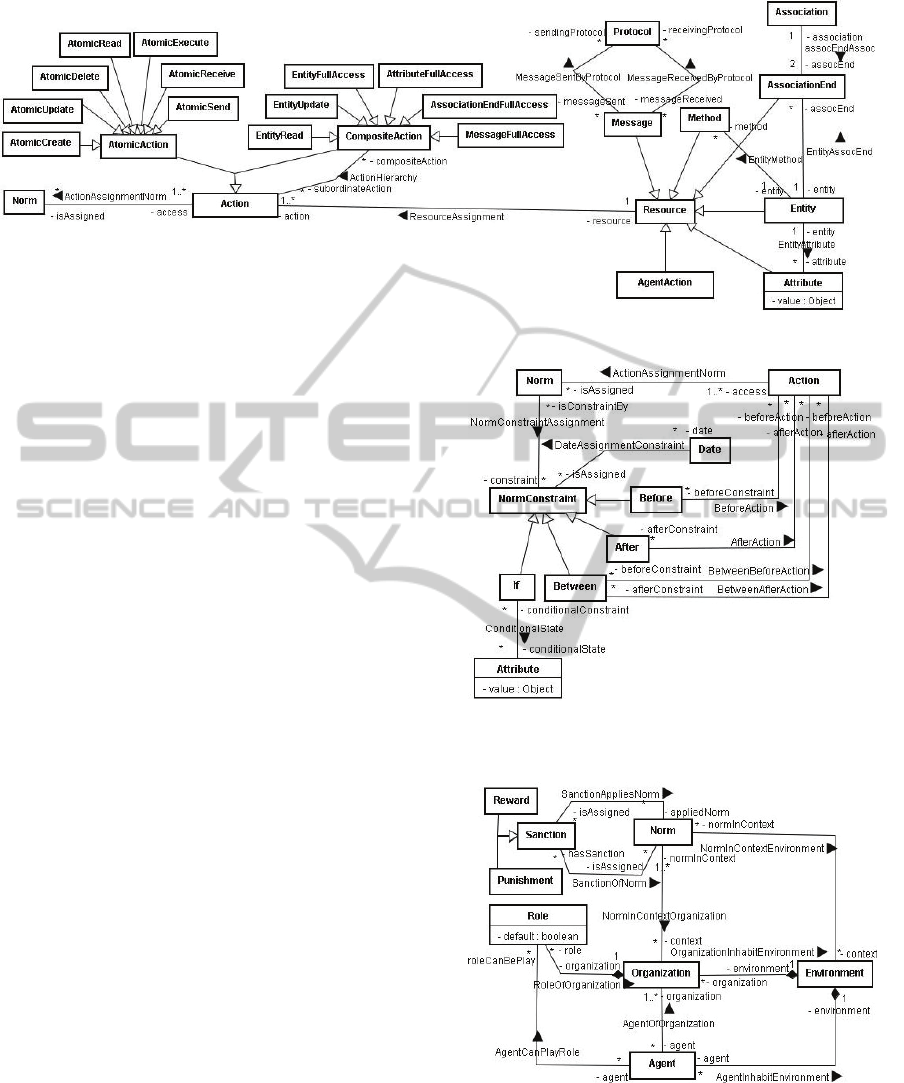
Figure 2: Actions related metaclasses at the NormML Metamodel.
of actions. The language was extended to define
activation constraints also based on the definition of
dates and predicates (i.e., values associated with
attributes), as shown in Figure 3. The activation
constraints are represented by the metaclass
NormConstraint.
If a norm is conditioned by a Before/After clause, it
means that the norm is active before/after the
execution of the action(s) and/or the achievement of
the date(s) described in the Before/After clause. In
the case of a Between clause, the norm is only active
during the period delimited by two groups of actions
and dates. In the case of a norm conditioned by an If
clause, the norm is only active when the value(s) of
the attribute(s) described in the If clause is (are)
achieved.
Sanctions: The current version of NormML
supports for the description of sanctions (Sanction
metaclass) to the norms, as shown in Figure 4. A
sanction may be a reward applied when the norm is
fulfilled (by instantiating the metaclass Reward) or a
punishment applied when the norm is violated (by
instantiating the metaclass Punishment). A sanction
can activate other norms to restrict the behavior of
some particular entities. For instance, in case an
agent violates a norm, another norm is activated to
prohibit the agent of executing a particular action
(see norms N1 and N2 in Figure 5 for an example).
Context: The recent version of NormML makes
possible the definition of norms in two different
contexts, as illustrated in Figure 4: Organization and
Environment. Organizations define roles played by
agents and both organizations and agents inhabit
environments.
Figure 3: Activation constraints related metaclasses at the
NormML Metamodel.
Figure 4: Sanction and context related metaclasses at the
NormML Metamodel.
3.2 Modeling Norms with NormML
In order to exemplify our approach, we define two
norms of a simplified version of a web store. The
Norm-ML - A Modeling Language to Model Norms
235

web store is being modeled as an organization that
inhabits the market place environment and defines
two roles to be played by the agents: seller or buyer.
The sellers of the web store can advertise goods
while the buyers can buy the goods that are
announced on the store by the sellers. Figure 5
shows the model of the norms N1 and N2 by
instantiating the classes of the NormML metamodel.
N1:
Sellers are obliged, in the context of the
organization WebStore that inhabits the environment
MarketPlace, to give the good to the buyer after the
given buyer pay for it. Norm N1 states an obligation
(deontic concept) to the sellers (involved entities) of
the organization WebStore (context) to give the
good to the buyer (an atomicExecute of an
AgenAction) after the given buyer pay for it
(activation constraint).
N2:
(Punishment) Sellers are prohibited, in the
context of the organization WebStore that inhabits
the environment MarketPlace, to advertise goods.
Norm N2 applies a punishment (sanction), if a seller
violates N1, N2 states to the given seller (related
entity) a prohibition (deontic concept) to advertise
goods (an atomicExecute of an AgenAction).
For the norm N1 we have specified a sanction (norm
N2) the seller should receive if it violates the norm.
Note that this sanction is also a norm that is
activated when the related norm N1 is violated.
3.3 Validating the Norms
The process of validating a norm encompasses two
steps. First, the norm, as an instance of the NormML
metamodel, is checked according to the invariants of
the metamodel. The invariants check if the norm is
well-formed according to the metamodel
specification. The second step checks if any given
two norms are in conflict. Second, it is important to
check for conflicts among norm. This paper focuses
on the first step.
The current version of NormML has a set of
operations described in OCL to check the invariants
of the norms. Not all the norms that can be
instantiated from the metamodel are well-formed.
Below we describe two examples of well-formed
rules of the NormML metamodel. Those were
chosen since they discuss some of the new elements
included in the actual version of the language.
WFR1:
The action to be executed by an entity that is
defined in the before clause of a between cannot also
be defined in the after clause of such Between to be
executed by the same entity in the same context. If
the actions in the before of a Between and in the
after of a Between are the same, are related to the
same entity (an agent, a role or an agent playing a
role) and executed in the same context, this situation
does not constitute a time period, but a moment in
the time.
WFR2:
If the norm applied to an entity is
constrained by an If whose condition is the value of
an attribute, the entity of the norm must have
permission to read this attribute. The entity related
to a norm that states an If constraint must be able to
read the attribute associated to the constraint (by a
permission of read or full access to the Attribute or
to the Entity which the attribute belongs), otherwise
the entity will not be capable of knowing when the
norm is active.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we presented the normative modeling
language NormML by emphasized the contributions
Figure 5: Norm N1 and N2.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
236

of the language when compared with other modeling
languages and notations used by methodologies and
organization models. With the preliminary version
of NormML (Silva et al., 2010) it was possible (i) to
model permissions, prohibitions and obligations; (ii)
to regulate the behavior of agents and roles; (iii) to
define norms that restrict the execution of non-
dialogical actions; (iv) to define activation
constraints based on the execution of actions. By
using the current version of NormML it is also
possible (i) to model norms associated with different
contexts; (ii) to regulate the behavior of groups of
individuals (or organizations); (iii) to define norms
that restrict the execution of dialogical actions; (iv)
to define activation constraints based on the
definition of deadlines and predicates (values
associated with attributes); and (v) to define
sanctions associated with the norms. We are in the
process of extending the language to define norms
that restrict the achievement of states. It is our aim to
develop a graphical tool for modeling and validating
norms using NormML.
REFERENCES
Basin, D., Clavel, M., Doser, J. and Egea, M. 2009.
Automated analysis of security-design models. Inf.
Software Technology, 51(5), pp: 815—831.
Clavel, M, Silva, V., Braga, C. and Egea, M. 2008. Model-
driven security in practice: an industrial experience. In
Proc. 4th European Conf. on MDA, pp: 326-337.
Cossentino, M. 2005. From requirements to code with the
PASSI methodology. In Agent-oriented Methods, Idea
group, pp. 79-106.
Danc, J. 2008. Formal specification of AML. Department
of Computer Science, Comenius University, Master’s
Thesis, Advisor: Mgr. Bratislava.
Dignum, V. 2004. A model for organizational interaction:
based on agents, founded in logic. PhD dissertation,
Universiteit Utrecht, SIKS dissertation series 2004-1.
Ferber, J., Stratulat, T. and Tranier, J. 2009. Towards an
integral approach of organizations: the MASQ
approach in multi-agent systems. In MAS: Semantics
and Dynamics of Org. Models, IGI.
Ferraiolo, D. F., Kuhn, D. R. and Chandramouli, R. 2007.
Role-based access control. Artech House Publishers.
García-Camino, A., Rodríguez-Aguilar, J., Sierra, C and
Vasconcelos, W. 2006. Norm-oriented programming
of electronic institutions. In Proc. 5th AAMAS, ACM
Press, pp. 670-672.
Garcia-Ojeda, J., DeLoach, S., Robby, O. and Valenzuela,
J. 2008. O-MaSE: a customizable approach to
developing multiagent development processes. In
AOSE VIII, LNCS 4951, Springer, pp.1-15.
Giorgini, P., Mouratidis, H. and Zannone, N. 2006.
Modelling security and trust with Secure Tropos. In
Integrating Security Soft.Eng.: Advances and Future
Vision.
Hübner, J. F., Sichman, J. S. and Olivier, B. 2002. A
model for the structural, functional and deontic
specification of organizations in multiagent systems.
In Proc. 16th SBIA, LNAI 2507.
Juan, T., Pierce, A. and Sterling, L. 2002. ROADMAP:
extending the Gaia methodology for complex open
systems. In Proc. 1st AAMAS, pp. 3-10, ACM Press.
Kagal, L. and Finin, T. 2005. Modeling Conversation
Policies using Permissions and Obligations. In van
Eijk, R., Huget, M., Dignum, F., eds.: Developments in
Agent Communication. Volume 3396 of LNCS.,
Springer (2005) 123–133.
López y López, F. 2003. Social power and norms: impact
on agent behavior. PhD thesis, Univ. of Southampton,
Department of Electronics and Computer Science.
Meyer, J. J. and Wieringa, R. J. 1991. Deontic logic in
computer science: normative system specification.
John Wiley and Sons.
Molesini, A., Denti, E. and Omicini, A. 2009. RBAC-
MAS & SODA: experimenting RBAC in AOSE
engineering societies in the agents world. LNCS 5485.
Odell, J., Parunak, H. and Bauer, B. 2000. Extending
UML for agents. In Proc. Agent-Oriented Information
Systems Workshop at National Conf. of AI, pp. 3-17.
Omicini, A. 2001. SODA: societies and infrastructures in
the analysis and design of agent-based systems. In
Agent-Oriented Software Engineering, LNCS 1957.
Oren, N., Luck, M., Miles, S. and Norman, T. J. 2008. An
argumentation inspired heuristic for resolving
normative conflict. In Proc. of The Fifth COIN
Workshop, 41–56, Estoril, Portugal.
Padgham, L. and Winikoff, M. 2002. Prometheus: a
methodology for developing intelligent agents. In
Proc. of Agent-Oriented Software Engineering
Workshop, pp. 174-185.
Silva, V. 2008. From the specification to the
implementation of norms: an automatic approach to
generate rules from norms to govern the behaviour of
agents. In IJAAMAS, Special Issue on Norms in Multi-
Agent Systems, (17)1, pp. 113-155.
Silva, V., Choren R. and Lucena, C. 2008. MAS-ML: a
multi-agent system modelling language. In IJAOSE,
Modeling Lang. for Agent Systems,(2)4, pp.382-421.
Silva, V, Braga, C. and Figueiredo, K. 2010. A Modeling
Language to Model Norms. In Workshop on
Coordination, Organization, Institutions and Norms in
agent systems (COIN 10) at AAMAS10, pp. 25-32.
Vasconcelos, W., Kollingbaum, M. and Norman, T. 2007.
Resolving conflict and inconsistency in norm-
regulated virtual organizations. In Proc. AAMAS’07.
Wagner, G. 2003. The Agent-Object-Relationship meta-
model: towards a unified view of state and behavior.
Information Systems, 28(5), pp. 475–504.
Zambonelli, F., Jennings, N. R. and Wooldridge, M. J.
2003. Developing multiagent systems: the Gaia
methodology. ACM TSEM, 12(3):417-470.
Norm-ML - A Modeling Language to Model Norms
237
