
AUGMENTED REALITY BASED INTELLIGENT INTERACTIVE
E-LEARNING PLATFORM
Héctor Martínez, Rafael del-Hoyo, Luis Miguel Sanagustín, Isabelle Hupont, David Abadía
Instituto Tecnológico de Aragón, P.T. Walqa Ctra. Zaragoza, N-330a, Km 566, Cuarte (Huesca), Spain
Carlos Sagüés
Departamento de Informática e Ingeniería de Sistemas, Universidad de Zaragoza, C/ Maria de Luna 1, Zaragoza, Spain
Keywords: Intelligent tutoring systems, Augmented reality, Adaptive systems, Virtual agents.
Abstract: e-Learning systems are continuously evolving in order to include new technologies that improve the
education process. Some of the technologies that are being incorporated to the e-learning systems are related
to virtual agents and Augmented Reality. The proposed architecture aims to offer a novel platform for non-
programming experienced users to develop intelligent Augmented Reality e-learning applications by an
intelligent fuzzy-rules-based framework. The applications consist of a series of interactive Augmented
Reality exercises guided by an intelligent adaptive virtual tutor to help the student in the learning process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, e-learning systems are focused on
including new emerging technologies that enhance
the learning process. The concept of Augmented
Reality (AR) refers to the representation of virtual
elements (such as 3D models or images) over a real
scene captured by a camera. AR has been proved to
be a useful tool in the learning process (Balog,
Pribeanu and Iordache, 2007; Chen, Su, Lee and
Wu, 2007; Kaufmann and Dünser, 2007). Students
find the concept acquisition more attractive and fun
when a virtual environment is mixed with the reality.
Opposite to other new technologies, AR usability
has a fast learning process. Even users who have
never used any AR application before have reported
a good feedback in the use of this technology for
education purposes (Sumadio and Rambli, 2010).
Some examples of AR applications for e-learning
purposes can be found in the literature such as the
MagicBook where a traditional book is augmented
to offer virtual content (Billinghurst, Kato and
Poupyrev, 2001), a book with finger marker used to
enhance the contents (Hwa Lee, Choi and Park,
2009) or an application to learn concepts related
with the human body (Juan, Beatrice and Cano,
2008). However, those applications do not show any
available kind of interaction or it is very limited. The
purposes of those works are mainly limited to show
virtual 3D contents to the users who can see some
objects under different angles and dimensions and
better understand how they work. The main gap
between AR applications and educators is the lack of
programming skills of the educators. Because of
that, the creation process involves computer science
experts and pedagogic professionals. Some user-
friendly authoring tools have arisen to help those
people who don’t have programming knowledge to
make some simple but powerful AR applications.
Some authoring tools examples can be ATOMIC
(http://www.sologicolibre.org/projects/atomic/en/ind
ex.php) and ZooBurst (http://alpha.zooburst.com/).
However, the created applications are limited to
show contents and the logic of the program is fixed
by the software creators.
The use of 3D environments opens the door to
the use of intelligent virtual agents. In the field of e-
learning, the benefits of using virtual humans able to
adapt the transmission of knowledge to each student
have been proved (Sklar and Richards, 2006). It is
important that the virtual agent shows intelligent
behaviours that respond accordingly to the evolution
of the interaction, like, for instance, offering help
when needed.
The proposed platform is a new intelligent
interactive e-learning platform based on AR. The
343
Martínez H., del Hoyo R., Sanagustín L., Hupont I., Abadia D. and Sagüés C..
AUGMENTED REALITY BASED INTELLIGENT INTERACTIVE E-LEARNING PLATFORM.
DOI: 10.5220/0003181503430348
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 343-348
ISBN: 978-989-8425-40-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

presented platform is oriented to create intelligent
AR applications for learning purposes. Instead of
just showing contents, the final applications are able
to offer a rich variety of interactive actions. The
platform uses an intelligent framework that enables
to define application logic using natural language.
Therefore, any non-programming expert person is
able to create interactive AR exercises for e-learning
with his/her mind as the only limitation.
One of the main features of the proposed
platform is the introduction of a virtual tutor. It is an
intelligent adaptive virtual agent who guides the user
through the learning process and evolves his
behaviour in function of the user’s actions, making
the exercises more interactive.
Thanks to the applications created with the
proposed platform, the traditionally acquired
learning concepts can be moved into practical
exercises. Due to the attractiveness of some of the
technological elements included in the platform,
such as AR exercises and virtual tutors, the learning
process becomes more interesting for students.
The rest of the text is organized as follows:
section 2 describes an overview of the proposed
platform architecture. In section 3, a practical
example is explained to show the potential of the
platform. Finally, in section 4 some conclusions and
future work are discussed.
2 PLATFORM ARCHITECTURE
OVERVIEW
This article presents an intelligent AR e-learning
platform. The main element of the architecture is the
intelligent framework in charge of the e-learning
process which also controls the virtual 3D
environment implemented to offer virtual content
(including a virtual tutor).
The control logic in the e-learning platform is
implemented inside of the intelligent framework
using natural language rules (fuzzy rules). This
framework is also responsible of the behaviour of
the virtual tutor. This intelligent e-learning platform
is able to evolve and adapt according to the actions
obtained from the user. During the learning process
parameters like the number of exercise repetitions or
increasing the level of difficulty of the exercise are
adjusted by means of a supervised learning.
Thanks to the rules-based intelligent framework,
the proposed platform is a powerful tool for general
e-learning purposes. The platform can be adapted
easily to any kind of subjects and contents, and the
exercises can be designed by any person even if he
or she does not have programming knowledge,
thanks to the natural language rules programming.
In order to study off-line the user’s progress and
his/her interaction with the exercises, the tutorial
stores some learning indicators in each session with
relevant data: time used to solve an exercise, number
of times he or she makes a mistake, history of
questions introduced in the help chat, trajectories
followed by the markers, etc in order to analyse the
e-learning interaction process by one expert.
Figure 1 shows the proposed architecture. The
user interacts with the platform through different
elements (webcam, keyboard and mouse,
microphone and markers). Those inputs are treated
to evolve the platform through the intelligent
framework called ISIS (Intelligent Support
Interaction System) which is the element in charge
of the logic of the platform control. ISIS
communicates with the virtual environment (a full
multimedia engine) which shows the final result in
the monitor.
2.1 The Intelligent Support Interaction
System (ISIS)
ISIS is the main element of the proposed application.
It is the evolution of a softcomputing-based
intelligent system called PROPHET that enables
real-time automatic fuzzy decision making and self-
learning over any kind of incoming inputs (from
sensors, video channels, audio channels, probes…).
The system has already been successfully used in
different domains such as logistics decision making
systems (del-Hoyo, Ciprés, Prieto, del Barrio, Polo
and Calahorra, 2007), real-time networking
management (del-Hoyo, Martín-del-Brío, Medrano,
Fernández-Navajas, 2009), virtual emotional agents
(Hupont, del-Hoyo, Baldassarri, Cerezo, Serón and
Romero, 2009) and natural language automatic
analysis (del-Hoyo, Hupont, Lacueva, and Abadía,
2009).
ISIS is the engine in charge of the logic of the
platform from the tutor point of view. It is also the
inference engine that makes the virtual tutor to react
to different inputs coming to the platform.
According to different inputs of the platform,
ISIS extracts knowledge and thanks to the use of
Neuro-Fuzzy techniques (Lin and Lee, 1996), the
module has the capability of self-extracting and self-
learning new fuzzy decision rules from historical
data.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
344
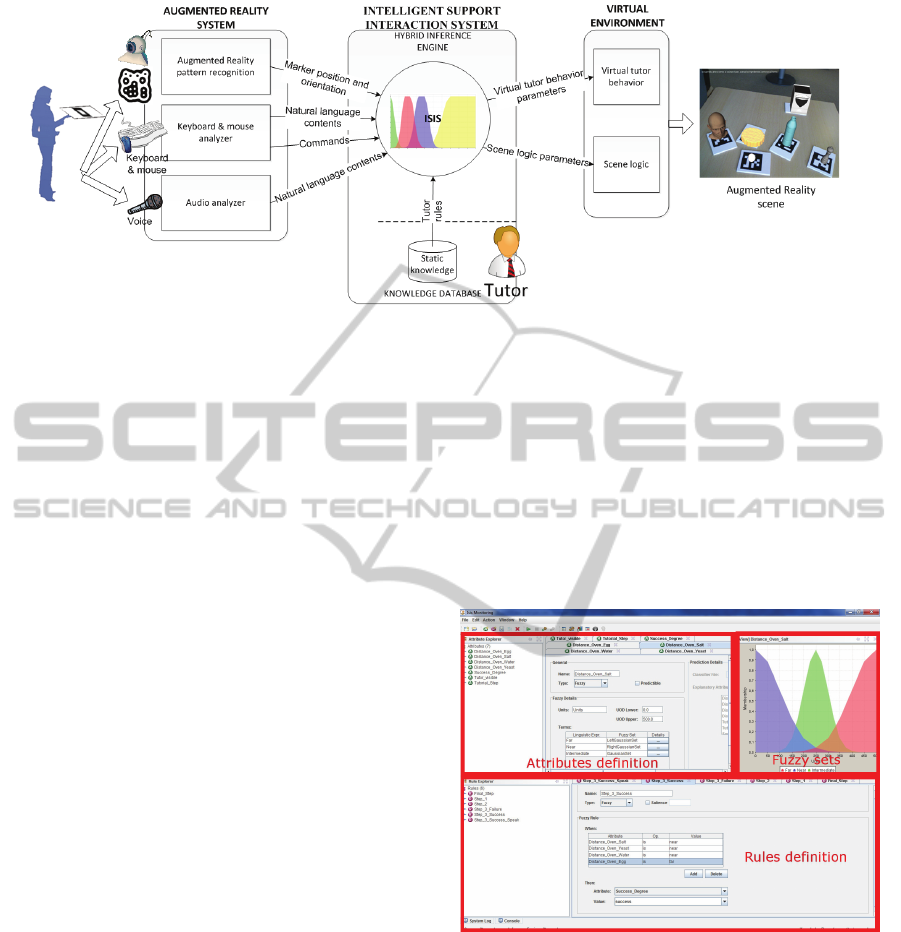
Figure 1: Proposed platform’s architecture.
ISIS consists of a set of modules for pre-
processing, integrating and extracting information
and making decisions in a flexible way under
uncertain contexts. The system is based on a state
machine in order to increase its scalability: each
module generates events that are treated
asynchronously inside the state machine. A brief
description of the different modules that compose
the system is presented in the following sections.
2.1.1 Information Pre-processing and
Integration Module
This module is in charge of inputs’ pre-processing,
integration and synchronization. The inputs come
from any source of information: webcam, keyboard
and mouse, microphone and markers. The system
has several pre-defined filters (e.g. data
normalization filters), but also allows the free
definition of any kind of expert pre-processing rules
(e.g. truncate an input value if greater than a given
threshold, accumulate data values…).
2.1.2 Automatic Knowledge Extraction and
Classification Module
This module extracts knowledge from input data, by
means of softcomputing-based algorithms. Thanks
to the use of Neuro-Fuzzy techniques, the module
has the capability of self-extracting and self-learning
new fuzzy decision rules from historical data.
2.1.3 Hybrid Rule Engine
The embedded rule inference engine is in charge of
rule-based decision making tasks in the e-learning
process. It is a hybrid rule inference engine since it
can both deal with crisp rules (applied to exact
inputs’ values) and execute inference from rules that
handle fuzzy concepts. Fuzzy rules can be defined
over the inputs whose fuzzy membership functions
have been previously configured in the system. The
elements in the inference engine’s Working Memory
are not only the rules pre-defined by an expert, but
also the set of automatically self-learned decision
rules created by the knowledge extraction and
classification module.
Figure 2 shows an example of fuzzy rules
definition using the interface of the ISIS framework.
Figure 2: Screenshot of the ISIS tool for Fuzzy rules
definition. The screen is divided in two parts. The first one
is used to define the attributes (the definition of fuzzy
attributes is accompanied of their fuzzy sets). The second
part is used to define the platform rules.
2.1.4 AIML inference Engine Module
The AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup
Language) inference engine module is in charge of
the virtual tutor dialogue. The module is full
communicated with the hybrid engine in order to
generate text events to the virtual tutor, modify
internal variable values or change the tutor dialogue
AUGMENTED REALITY BASED INTELLIGENT INTERACTIVE E-LEARNING PLATFORM
345

context (for example in which exercise is the
student).
2.2 Augmented Reality System
The Augmented Reality system used is based on
pattern recognition through computer vision
algorithms. In particular, the ARToolKit Plus has
been used. The ARToolKit Plus is an extension of
the popular and widely used ARToolKit library
(www.hitl.washington.edu/artoolkit). The original
ARToolKit is an open source library developed to
detect markers over the scene captured by the
camera. The detection of the markers is carried out
by pattern recognition being the detection algorithm
invariant to perspective and scale variations.
It requires a computer with a standard USB
camera to run. It is also necessary to have the
appropriated markers needed by the system which
are the patterns to be recognized. The camera
captures the motion of the scene and the system
detects the position and orientation of the visible
markers. Each marker has internally associated one
or more virtual elements (3D models, text,
images…) which are located in the scene according
to the marker position. The final result is a real time
compound motion of real and virtual elements that is
displayed on the computer screen.
The exercises consist of some 3D objects located
over the markers with which the user can interact.
The user is instantiated to take the objects needed to
carry out the exercise, interact with them, change
their properties, etc.
The output of the marker detection is a matrix
which represents the relationship between the
marker’s position and orientation and the camera.
This matrix is used to properly locate the 3D models
in function of the markers’ position. This
information is transmitted to ISIS.
An Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
system has been also integrated to make the virtual
tutor understand the user’s voice. Due to the lack of
open source Spanish ASR systems, the commercial
Loquendo system has been used. One of the features
of the system is to let the user to communicate with
the virtual tutor through a chat. Both communication
systems (voice and chat) send the text strings to the
ISIS system where the responses are obtained and
returned to the virtual environment. The
communication between ISIS and the virtual
environment is carried out with the XML-RPC
protocol.
2.3 Virtual Environment
The AR concept requires virtual elements to merge
with the image of the real scene. In order to obtain a
virtual environment where the virtual action takes
place, a powerful engine has been developed
integrating some libraries (most of them open
source). The 3D rendering engine used has been
Ogre 3D (http://www.ogre3d.org). Ogre is an open
source 3D graphic engine that enables to work with
3D objects and animations. The sound is an
important needed feature for the system proposed, so
an open source API called OpenAL has been
integrated in the system. A TTS (Text To Speech)
system to make the tutor talk is required. In the
presented engine, two TTS systems have been
included. The first one is an open source TTS called
Festival. The second one is the commercial solution
Loquendo. Finally, a WEB HTML 5 library has
been adapted to include HTML content in the 3D
virtual environment. Thanks to the library, any kind
of webpage content is properly located in the 3D
world. As it is a Chrome based browser, the same
features of the Google’s browser are implemented,
included some features available on the html5
specification, like the video tag.
One important figure in the platform is the
virtual tutor (a human look-like 3D model), who is
rendered in the virtual environment. He is the person
in charge of guiding the user through the exercises.
He also responds in an intelligent way to the actions
made by the user as wrong answers, help questions
and so on. The virtual tutor behaviour is controlled
by ISIS so he is able to interact with the user in an
intelligent natural way. There are different ways to
interact with the user. The most common way is by
reacting to the action of the user, such as showing
approval gestures or offering help if he thinks the
user needs it. In those cases, the tutor’s face may
change according to the user’s correct actions or
mistakes. Another possibility of interaction is the
chat mode. The user is able to chat with the virtual
tutor through the keyboard. In some cases, the
student will be offered to open a browser in order to
display a webpage or to play a video with more
detailed information. Apart from that, it is also
possible to communicate with the virtual tutor in a
conversational way using a microphone. In both
cases (chat and conversation), the tutor will search in
a question-answer engine and will answer as
accurately as possible attending to the student’s
needs.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
346

3 PRACTICAL APPLICATION
The platform has been used to develop a practical
tutorial in order to show its potential. The tutorial
consists of a series of practical exercises concerning
to the bread production in a bakery. It should be
mentioned that this is only an example, but the
platform can be used in any field.
The general procedure of the tutorial is as
follows. When the exercises begin, a welcome
message is showed on the screen and also is played
on the speakers. Every message is offered in both
formats (text and audio) to enhance the
comprehension of the information from the user.
After the welcome message, the tutorial asks the
user to locate the tutor’s marker on the scene. Once
the virtual tutor is visible, the exercise begins.
Depending on the exercise, the virtual tutor may ask
the user to locate a list of specific ingredients or
cooking tools. When every asked object is visible,
the virtual tutor indicates some actions to carry out,
such as taking the correct ingredients to the oven or
selecting the appropriate quantities of every
ingredient. When the exercise is completed, a
congratulation message is showed. Depending on the
exercise, some extra information is showed, like
some videos about the different processes of bread
cooking, and finally the exercise finishes.
During the process of the exercise, the virtual
tutor will help the user with his voice, but also with
nonverbal communication. For example, by smiling
to indicate approval or showing a sad face to
indicate disapproval. It is also possible to chat with
the virtual tutor through the keyboard to ask him for
help. To open the chat dialog, a specific key should
be opened.
At any moment, the user can ask the tutor for
help or tell him to repeat the instructions through the
microphone.
In Figure 3, an example of one of the exercises is
shown. As it can be seen, the virtual tutor
(represented as a human look-like head), an oven
and a variety of ingredients are displayed over a real
desk (Figure 3.a). The user is instantiated to locate
the appropriate ingredients next to the oven. The
quantity of the ingredients can be expressed using a
fuzzy set. The distances from every ingredient to the
oven are also fuzzy variables. An example of a fuzzy
rule definition is as follows:
if ((Distance_Oven_Salt is near) and
(Distance_Oven Yeast is near) and
(Distance_oven_water is near) and
(Distance_oven_Egg is far)) then
Success_Degree is success
When, according to the fuzzy rules system, the
wrong ingredients are located next to the oven, the
virtual tutor reacts with his gesture and voice (Figure
3.b). On the other hand, when the right ingredients
are near the oven, the cooked bread appears and the
virtual tutor smiles and congratulates the user
(Figure 3.c). Once the exercise has been successfully
completed, additional video information may be
displayed on a browser to reaffirm the acquired
concepts (Figure 3.d).
Figure 3: Example of one practical exercise. The user
interacts with the ingredients to get the necessary ones to
the oven. The tutor reacts to the user’s actions and a video
is displayed when the exercise has been successfully
solved.
Figure 4 shows another example of interaction in
the exercises. The platform offers virtual controls
(buttons and selectors) to manipulate the properties
of the 3D objects. In the image, the user is able to
change the quantities of the ingredients to obtain the
right mixture for the bread cooking. Those controls
allow the real tutor to create more advances types of
interaction, and adapt the exercises to the level of
knowledge needed in every case. For example, the
exercise showed in Figure 3 can be adapted to an
upper level of difficulty making the user not only to
include the right ingredients but also the right
quantities, modelling them as fuzzy variables:
if (Water_Quantity is high) then
Success_Degree is failure
Figure 4: The user can change the quantity of water
needed to cook the bread using the virtual controls.
AUGMENTED REALITY BASED INTELLIGENT INTERACTIVE E-LEARNING PLATFORM
347

4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
An intelligent interactive e-learning platform based
on AR has been presented. The platform allows
teachers to incorporate new virtual interactive
exercises to the traditional learning system by
defining natural language rules.
The user interacts with the platform by means of
AR markers, where the different 3D models are
represented. Moreover users can also interact with
other virtual components (such as buttons,
browsers…) in order to improve the user experience.
The user can also interact with a virtual tutor in a
variety of ways (listening to the instructions,
chatting, talking to him or receiving nonverbal
communication). The virtual tutor acts according to
intelligent framework, which is also responsible of
the logic of the platform.
The platform is now being evaluated with users.
The first evaluation results demonstrate that the
proposed AR exercises are a useful way to engage
the students in the learning process. It is an attractive
method for the students thanks to the multimedia
content offered and the possibility of interaction
beyond the traditional pen and paper.
Besides, the virtual 3D representation of
complex objects may be a help for the student to
assimilate the concepts because sometimes it is
difficult to visually image the objects.
In the future, the platform is expected to
automatically analyze the learning indicators
obtained in order to adapt the contents in real-time,
instead of the mediation of the real tutor. Emotional
detection for content adaptation is also a desirable
feature to obtain in the future.
The platform is expected to be integrated in a
standard Learning Management System. Another
aspect to develop in the future is to recognize more
user understandable patterns which have a visual
relation with the 3D object associated, creating a
new pattern recognition system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partly financed by the CETVI
project (PAV-100000-2007-307) and RA-IA-
LEARNING project (TSI-020302-2010-155),
funded by the Spanish Ministry of Industry, and the
Grupo de Ingeniería Avanzada (GIA) of the Instituto
Tecnológico de Aragón.
REFERENCES
Balog, A., Pribeanu, C., Iordache, D., 2007. Augmented
reality in schools: Preliminary evaluation results from
a summer school. International Journal of Social
Sciences, 2(3), 163–166.
Billinghurst, M., Kato, H., Poupyrev, I., 2001. The
MagicBook — Moving Seamlessly between Reality
and Virtuality. IEEE Computer Graphics and
Applications, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 6-8.
Chen, C. H., Su, C. C., Lee, P. Y., Wu, F. G., 2007.
Augmented Interface for Children Chinese Learning.
Seventh IEEE International Conference on Advanced
Learning Technologies, 268–270.
del-Hoyo, R., Ciprés, D., Prieto, J., del Barrio, M., Polo,
L., Calahorra, R., 2007. PROPHET: Herramienta para
la toma de decisiones en sistemas complejos. II
Simposio de Inteligencia Computacional, Zaragoza,
Spain.
del-Hoyo, R., Hupont, I., Lacueva, F.J., Abadía, D., 2009.
Hybrid text affect sensing system for emotional
language analysis. Proceedings of the International
Workshop on Affective-Aware Virtual Agents and
Social Robots, 2009, pp. 1-4.
del-Hoyo, R., Martín-del-Brío, B., Medrano, N.,
Fernández-Navajas, J., 2009. Computational
intelligence tools for next generation quality of service
management. Neurocomputing, vol. 72, pp. 3631–
3639.
Hupont, I., del-Hoyo, R., Baldassarri, S., Cerezo, E.,
Serón, F., Romero, D., 2009. Towards an intelligent
affective multimodal virtual agent for uncertain
environments. Proceedings of the International
Workshop on Affective-Aware Virtual Agents and
Social Robots, 2009, pp. 1-4.
Hwa Lee, S., Choi, J., Park, J., 2009. Interactive e-learning
system using pattern recognition and augmented
reality. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics,
vol.55, no.2, 883-890.
Juan, C., Beatrice, F., Cano, J., 2008. An Augmented
Reality System for Learning the Interior of the Human
Body. Eighth IEEE International Conference on
Advanced Learning Technologies. ICALT, 186-188.
Kaufmann, H., Dünser, A., 2007. Summary of usability
evaluations of an educational augmented reality
application. Virtual Reality, 660–669.
Lin, C. T., Lee, C. S., 1996. Neural fuzzy systems: a
neuro-fuzzy synergism to intelligent systems,
Prentice-Hall, Inc. Upper Saddle.
Sklar, E., Richards, D., 2006. The use of agents in human
learning systems. Proceedings of the Fifth
international Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents
and Multiagent Systems AAMAS '06. ACM, New
York, NY, 767-774.
Sumadio, D. D., Rambli, D. R. A, 2010. Preliminary
Evaluation on User Acceptance of the Augmented
Reality Use for Education. Second International
Conference on Computer Engineering and
Applications. ICCEA, vol. 2, 461-465.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
348
