
NOVEL APPROACH TO CHEST IMPEDANCE SIGNAL
ANALYSIS
Algimantas Krisciukaitis, Andrius Macas, Renata Simoliuniene
Robertas Petrolis and Zita Bertasiene
Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Eiveniu str. 4, Kaunas, Lithuania
Keywords: Chest impedance signal, Principal component analysis, Independent component analysis.
Abstract: New wave of development of more informative and reliable diagnostic methods substituting classical
Impedance Cardiography introduced by Sramek in the 1960's was inspired by rapid development of IT
based devices in medicine. We illustrate approaches of multivariate analysis of chest impedance signals in
aim to reveal parameters reflecting detail pattern of functions of cardiovascular system.
1 INTRODUCTION
The electrical resistivity of human body organs
varies about 100-fold from about 1.6 Ωm in blood to
about 170 Ωm in bone. Within the soft tissues the
variability is about 10-fold, with about 20 Ωm in the
lung and in fat (Malmivuo 1995). Physiological
processes in chest result in the permanent changes in
chest impedance. Activity of the heart and
respiratory movements play major roles.
The amount of blood in the thorax changes as a
function of the heart cycle. During systole, the right
ventricle ejects an amount of blood into the lungs
which equals the stroke volume. At the same time
blood flows from the lungs to the left atrium. The
effect of these changes in the distribution of blood in
the thorax as a function of the heart cycle can be
determined by measuring the impedance changes of
the thorax. The amount of air in the thorax is
changing as function of the respiratory cycle. It also
results in the impedance changes of the thorax.
Permeability of lung alveoli to the blood flow is
affected by air pressure in the lungs, i.e. it is
changing as a function of respiratory cycle. Taking
into account all mentioned facts we can state that
chest impedance changes reflect several interacting
processes and quantitative evaluation of the features
of it could be of great diagnostic importance.
Impedance cardiography has been introduced by
Sramek in the 1960's as a simple and non-invasive
measurement of cardiac output which is used till
nowadays. Very simple decomposition of the chest
impedance signal (ICG) or Z by determining of
first derivative (dZ/dt) of it extracts only the
component reflecting blood volume changes (BVC)
in the thorax caused by heart activity. Cardiac output
is proportional to the amplitude of dZ/dt. However,
measured data in some cases remain controversial.
This is highly expressed in the states causing low
cardiac output syndrome cardiogenic shock, severe
arrhythmias as well as in healthy obese patients.
Rapid development of devices of digital registering
of biomedical signals and availiability of
comparatively cheap computational resources for
their proccessing have inspired new wave of
development of methods for processing of such
signals. The aim of it is to reveal more informative
features of the signal and to elaborate more reliable
diagnostic methods. Extraction of other parameters
then ejected blood volume is reported in (Ernst
1999). Respiratory movements representing
component of the chest impedance signal was
reconstructed by integration of first derivative dZ/dt
of the ICG registered by means of standard
equipment. Acording to the biophysical models
(Malmivuo 1995) chest impedance signal carries
much more diagnostic information than it is used
today. Our previous studies have shown that
structural analysis of simultaneously recorded ICG
and ECG is able to separate two major components
of chest impedance signal – BVC and respiratory
movements reflecting component. Quantitative
estimates of the shape of cardiocycles of the
extracted BVC also correlate with blood volume
ejected by heart (Tamosiunas 2006). Moreover
component reflecting BVC reflects a result of left
526
Krisciukaitis A., Macas A., Simoliuniene R., Petrolis R. and Bertasiene Z..
NOVEL APPROACH TO CHEST IMPEDANCE SIGNAL ANALYSIS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003275705260529
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2011), pages 526-529
ISBN: 978-989-8425-35-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

and right ventricle outputs, so it is also a complex
signal. Decomposition of which could realize a
possibility to evaluate separately the efficiency of
functions of both ventricles. It could have a great
value for monitoring of cardiac output in acute phase
of myocardial infarction. Such decomposition could
be realized if additional blood flow reflecting signal
could be registered somewhere apart from the chest.
Then multivariate analysis methods applied for
simultaneously recorded signals from the chest and
e.g. limbs together with ECG leads could reveal
parameters reflecting detail pattern of functions of
cardiovascular system. The aim of this paper is to
present several illustrations of application of
advanced signal processing methods used to extract
parameters representing detail status of central
hemodynamics.
2 METHODS
2.1 Signal Registration
Clinical recordings of the signals for investigation
we performed during 24h follow up of the patients
hospitalized in the acute phase of myocardial
infarction in Cardiology Clinics of Kaunas
University of Medicine (Permission of Kaunas
Region Ethics Committee for Biomedical Research
Nr. 169/2004). Chest impedance signal together with
one lead ECG was recorded by means of Heartlab™
system (Dregunas 1999) (certificate No. LS.
08.02.1957) using 12 bit resolution A/D conversion
at 1000 Hz sampling rate. 250 recordings from
patients in various states of severity of myocardial
infarction were used in the study. Ten recordings we
made from healthy volunteers in addition
simultaneously recording spirogram by means of
spirometer “VMax-229” (Sensomedics USA).
Another 10 recordings we made also from healthy
volunteers in addition simultaneously registering
limb pulse wave.
2.2 Signal Processing
2.2.1 Chest Impedance Signal
Decomposition
Method for the ICG signal decomposition is based
on combined structural analysis of synchronically
registered ECG and ICG signals. The principle of
the method is illustrated on fig.1. Automatic
detection of fiducial point of every cardiocycle –
peak of ECG R-wave (marked with crosses on the
upper trace) is made in two steps. Preliminary
detection finds time points where filtered derivative
of the ECG signal exceeds certain threshold. Final
detection is made maximizing cross-correlation of
the sliding R-wave template with current ECG signal
in the region of preliminary detected point. R-wave
template is constructed from first 10 cardiocycles of
the recording and updated after every processed
cardiocycle. Fiducial time points are always pointing
to the same phase of the ICG signal component
reflecting blood flow (solid line of trace A on fig.1).
So respiratory movements caused component of the
signal is restored by means of cubic spline
interpolation between the samples of the ICG signal
at these time points (dotted line of trace A on fig.1).
Subtraction of this component (trace B on fig.1)
from the ICG signal gives the component reflecting
only blood volume changes in the chest vessels
(trace C on fig.1).
A
B
C
E
CG
A
B
C
E
CG
Figure 1: ICG signal decomposition: (A) cubic spline
interpolation between samples of ICG signal
corresponding to peaks of ECG R-wave, the fiducial
points of cardiocycles; (B) - reconstructed respiratory
movements reflecting component; (C) – extracted blood
volume changes reflecting component of the ICG signal.
The 180 samples of ICG signal starting from
fiducial point is considered as samples of one
cardiocycle and is used to construct a matrix
representing all cardiocycles of one recording.
2.2.2 Quantitative Evaluation of the Shape
of the Chest Impedance Signal
Samples of the extracted cardiocycles give
redundant but comprehensive representation of the
signal shape. We used Principle Component
Analysis (PCA) (Jollife 2002) to reduce the
dimensionality of the representations. Samples of
ICG cardiocycles formed two-dimensional array:
1,1 1,2 1,
2,1 2,1 2,
,
,
,1 ,2
...
...
... ... ...
...
n
n
ij
pn
pp
x
xx
x
xx
x
x
xx
X
,
(1)
NOVEL APPROACH TO CHEST IMPEDANCE SIGNAL ANALYSIS
527

where x
i,j
is the i
th
sample of the j
th
cardiocycle. The
PCA transforms the original data set into a new set
of vectors (the principal components) which are
uncorrelated and each of them involves information
represented by several interrelated variables in the
original set. Every vector x
i
representing ordinary
ICG cardiocycle or ECG T-wave is then represented
by the linear combination of the principal
components
k
multiplied by coefficients w
i,k
:
,
1
p
iikk
k
w
x .
(2)
The calculated principal components are ordered so
that the very first of them retain most of the
variation present in all original variables. Thus it is
possible to perform a truncated expansion of ICG
cardiocycles by using only the first several principal
components. We expected to get one or mostly
several principal components reflecting desirable
changes. We calculated the basis functions (principal
components) as eigenvectors of the covariation
matrix R
x
:
E
T
x
RXX .
(3)
Calculation of the covariation matrix was performed
using MatLab
TM
function “COV” which gave
mathematical expectation E after removing the mean
from each column. Variation or trend of coefficients
w
i,k
represents changes of the shape of evaluated
ICG cardiocycles. It is expected that the dynamics of
cardiac output will be reflected by the shape changes
of ICG cardiocycles and represented by changes of
one or several coefficients.
2.2.3 Extraction of Components
of Chest Impedance Signal by Means
of Independent Component Analysis
Independent component analysis is able to separate
independent source signals from the mixtures which
are linear combination of them. The minimal amount
of the mixtures given for ICA should be equal to the
number of independent source signals we want to
extract. Detailed description of the method of
Independent Component Analysis is given in
(Hyvärinen, 2001). BVC reflecting component of
chest impedance signal consists of two components
which reflect: a) pulmonary (lesser) blood
circulation; b) systemic (greater) circulation. It was
used as first mixture. Pulse wave signal
simultaneously registered from the limb, which
mainly reflects systemic (greater) circulation was
used as second mixture. ICA we used to extract two
independent components and afterwards we used
averaged cardiocycle excerpts of them as basis
functions for decomposition of every single
cardiocycle of BVC reflecting component of the
chest impedance signal.
BVC reflecting component of signal x is
represented as following:
2221212
2121111
2
1
2221
1211
,
,
x
sasax
sasax
s
s
aa
aa
As
,
(4)
Where x
1
and x
2
are two registered signals: chest
impedance and pulse wave from the limb. Then
estimated independent components will be:
s
1
=w
11
x
1
+w
12
x
2
, (5)
s
2
=w
21
x
1
+w
22
x
2
, (6)
where W=A
-1
.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Adequacy of Extracted Signal
Components
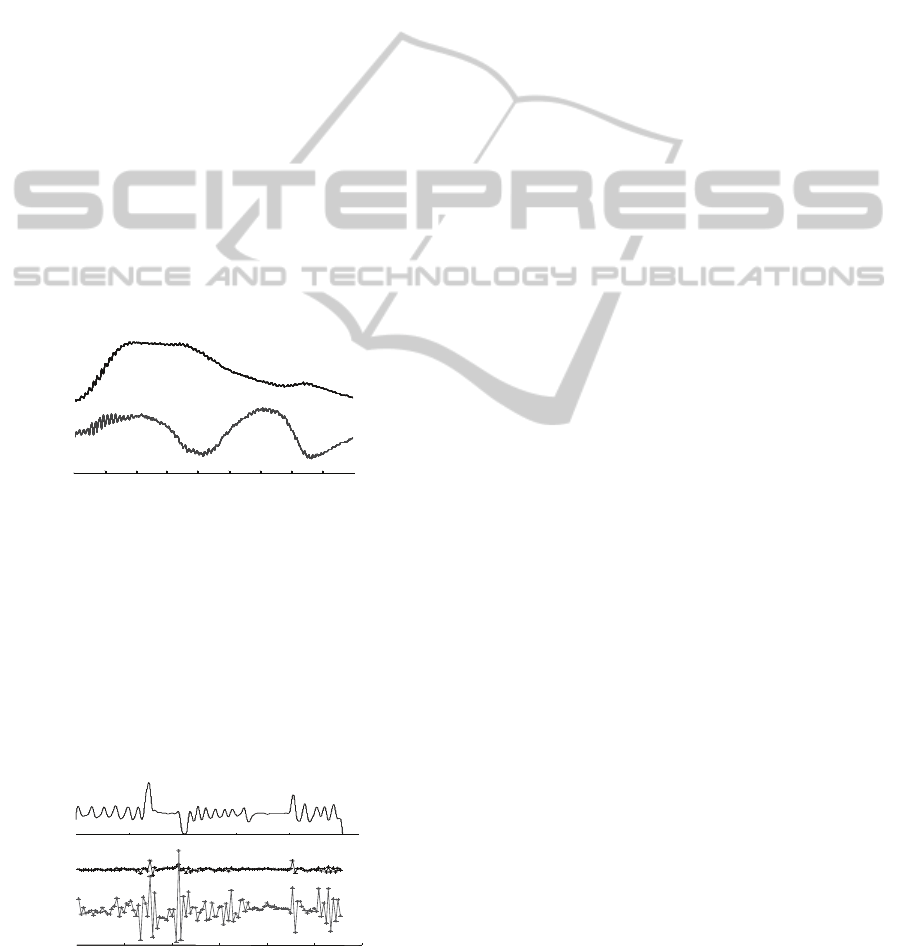
Result of the adequacy test of extracted respiratory
movement representing signal component is shown
on fig.2. The extracted signal is visually identical to
the signal registered by means of spirometer during
normal breathing. Limited frequency characteristics
of the ICG registering device caused inadequacy of
the respiratory component during forced and
sustained breathing. However such cases were
comparatively rear in analyzed recordings.
0102030405060Time
,
s
2
4
6
Volume, l
0102030405060Time
,
s0102030405060Time
,
s
2
4
6
Volume, l
Figure 2: Illustration of the adequacy test of respiratory
movement representing signal (dashed line). Control
signal (solid line) is registered by means of spirograph.
Forced breathing starts at 21 second of the test.
3.2 Chest Impedance Signal Shape
0 200 400 600
-4
-3.8
-3.6
-3.4
-3.2
Time, ms
Rel.units
0 200 400 600
-
-
-
-
-
0 200 400 600
-4
-3.8
-3.6
-3.4
-3.2
Time, ms
Rel.units
0 200 400 600
-
-
-
-
-
Figure 3: Variety of the shapes of the ICG component
reflecting blood flow during various phases of respiratory
movement. Full inhale – solid line, full exhale – dotted
line and medium position – dashed line.
BIOSIGNALS 2011 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
528
Variety of the shapes of the ICG component
reflecting blood flow during various phases of the
respiratory movement is presented in fig.3.
The quantitative estimates of shape of the
decomposed ICG signal component obtained by
means of PCA showed significant correlation with
reference cardiac output estimates obtained by
means of intermittent thermodilution. The most
important fact was that correlation coefficients of the
first and the second principal component showed
significant correlation (r= 0.6 p<0.001 and r= 0,75
p<0.001 respectfully) in cases when standard
method of the evaluation of the cardiac output by
means of first derivative of ICG failed.
3.3 Independent Component Analysis
of Chest Impedance Signal
Independent components calculated from the
cardiocycles of synchronically recorded chest
impedance signal and pulse wave from the limb are
presented on fig. 4. The linear combination of them
was used for representation of cardiocycles of
recorded chest impedance signal.
0 100 200 300 Time, ms
S
1
S
1
0 100 200 300 Time, ms
S
1
S
1
Figure 4: Independent components calculated from
cardiocycles of synchronically recorded chest impedance
signal and pulse wave from limb.
Coefficients of these basis functions reflect
shape changes of the signal during the whole
recording. We expected that changes of only one of
them will be correlating with respiratory
movements. If so, we can expect that especially this
component will be reflecting pulmonary (lesser)
circulation (changes in permeability of the lung
alveoli will affect it). Results on fig.5 illustrate that.
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
0 1 2 3 4 5
x 10
4
RESP
w
2
w
1
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
0 1 2 3 4 5
x 10
4
RESP
w
2
w
1
Figure 5: Coefficients of independent components (lower
traces) together with reference respiratory movements
representing signal.
4 DISCUSSION
AND CONCLUSION
Results presented in this article illustrate only the
preliminary investigations which already gave
promising results. A lot of investigations is needed
till estimates obtained by means of ICA or PCA will
give the conventional estimates of cardiac output for
clinicians. However even from these results we can
expect that at least dynamics of the estimates will be
shown what sometimes is of great diagnostic value.
We hope that novel approach to chest impedance
signal analysis started by (Ernst 1999) will be
continued including applications of advanced signal
processing methods. Hopefully the result will be less
invasive and more reliable methods for the
evaluation of detail pattern of functions of
cardiovascular system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work is supported by Research Council of
Lithuania (Grant: MIP-68/2010).
REFERENCES
Dregunas K, Povilonis E. Cardiac output and
hemodynamic monitoring system “Heartlab”.
"Biomedical engineering" (Proc.Int.Conf.), Kaunas
1999, p.100-105.
Ernst J. M., Litvack D. A., Lozano D. L., Cacioppo J. T.,
Berntson G. G. Impedance pneumography: Noise as
signal in impedance cardiography. Psychophysiology,
36 1999, 333–338.
Hyvärinen A, Karhunen J., Oja E. Independent
Component Analysis. Wiley, New York 2001.
Malmivuo J. and Plonsey R. Bioelectromagnetism:
Principles and Applications of Bioelectric and
Biomagnetic Fields. Oxford University Press New
York 1995. (http://butler.cc.tut.fi/ malmivuo/bem/
bembook)
Jollife I. T., Principal component analysis (Second
edition), (Springer New York, 2002) (ISBN 0-378-
95442-2).
Tamosiunas M, Macas A., Baksytė G., Krisciukaitis A.,
Brazdzionytė J. Monitoring of cardiac output by
means of chest impedance signal morphology analysis.
Proc. 6th Nordic Conference on eHealth &
Telemedicine NCeHT2006 Helsinki, Finland, 2006. p.
257-258.
NOVEL APPROACH TO CHEST IMPEDANCE SIGNAL ANALYSIS
529
