
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
MEASURED USING CAPACITIVE TEXTILES ON A BED
Hong Ji Lee, Seung Min Lee, Kang Moo Lee
Interdisciplinary Program of Bioengineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
Kwang Suk Park
College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
Keywords: Electrocardiogram (ECG), Capacitive textile, Heart rate variability (HRV).
Abstract: Devices for Ubiquitous-Healthcare have been currently developed to monitor health state unconsciously.
Especially, measuring electrocardiogram (ECG) non-invasively on a bed has an advantage of long-term
monitoring. We developed a simple and easy-to-use ECG measurement system on the bed with conductive
textile sheets. It was arranged through experiments to monitor ECG more stable. Three male subjects
participated in our experiment to measure ECG with four postures; a supine, prone, right lateral, and left
lateral posture. Error rates of heart rate variability and correlation of RR-intervals were analyzed to evaluate
the performance of the designed system. The results showed that the performance of the developed system
was affected by environmental conditions, posture types and subjects.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ubiquitous-Healthcare (U-Healthcare) which is to
provide medical services whenever and wherever
people are has been popular and many researchers
have studied. Ishijima measured ECG signals using
conductive textiles on a bed (Ishijima, 1993).
Tamura gathered ECG from a bath (Tamura et al,
1997) and Andreoni showed a method of getting
ECG on a chair and steering wheel (Andreoni et al,
2000). However, the measured ECG morphology is
different from that of a conventionally used
measurement system such as Ag/AgCl, due to an
instinct property of capacitive electrode. Therefore,
it is necessary to find other elements to analyze the
measured ECG data rather than morphology of
capacitive ECG. On the other hand, heart rate
variability (HRV) is still remained as an evaluation
index because time index of R-peak seems very
similar to normally measured one. HRV provides
information of the interplay between the sympathetic
and parasympathetic nervous systems (Rajendra
Acharya et al, 2006) that autonomic nervous system
can be monitored.
Capacitive ECG measurement on the bed has
many benefits. What a subject does not move often
during sleep is the best merit, since capacitive ECG
is suffering from motion artifacts. Furthermore, as
we lie on the bed for one-third of our daily life, a
large amount of ECGs are measured. Especially, for
hospitalized patients, they attach electrodes to their
bare skin to monitor ECG on the bed that makes
them uncomfortable due to gel typed electrodes and
wires. For these reasons, RR-intervals and HRV
parameters using capacitive electrodes one the bed
should be verified to evaluate the diagnostic ability
of the developed system for U-Healthcare.
In our previous study, we proposed a 12-channel
capacitive-coupled-electrodes array to measure ECG
on the bed (Hong Ji et al, 2010). Even though a
performance of ECG signals obtained using the
array was enough good to use, it was uncomfortable
to monitor ECG for a long time, because it stuck out
on the bed and was designed with hard-typed
capacitive electrodes. Moreover, electrodes that
were not contacted to a body had noise, and even
electrodes contacted with the body showed different
ECG amplitudes for various body postures.
436
Lee H., Lee S., Lee K. and Park K..
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAM MEASURED USING CAPACITIVE TEXTILES ON A BED.
DOI: 10.5220/0003291604360439
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices (BIODEVICES-2011), pages 436-439
ISBN: 978-989-8425-37-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
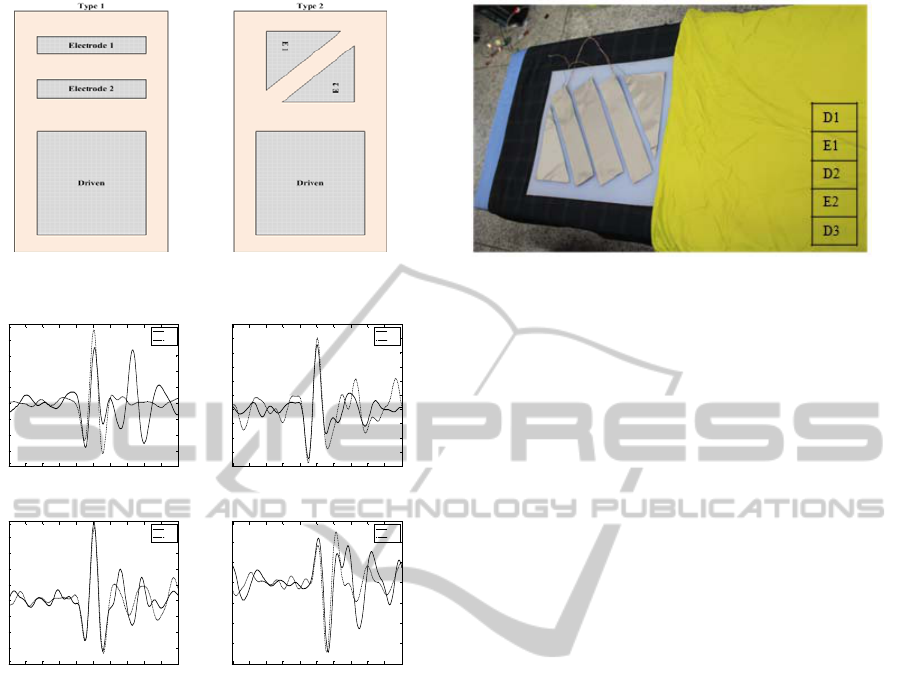
Figure 1: Two kinds of capacitive textile designs.
Figure 2: The amplitudes and ECG morphologies of two
models.
In this paper, we introduce capacitive electrodes
made of textile sheets with a modified shape and
contact areas to perform properly with easy to use.
We also verified the ability of the developed system,
focusing on the HRV analysis comparing capacitive
textiles with Ag/AgCl electrodes.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 A Design of Capacitive Textile
Electrodes
Capacitive textiles were employed for ECG
measurement electrodes and a driven electrode. Two
textile electrodes were placed on an upper area of
the bed in parallel as shown left in Figure 1. Driven
was put on a lower part of the bed to cancel common
noise of the body. The size of textiles for ECG
referred to a reference (Kin-fai et al, 2008).
Figure 3: The final design of capacitive textile (silicon
pad).
Figure 1 shows two kinds of electrode placement
designs. Left one (type 1) is a normally designed
measurement system and the other (type 2) is
designed based on the notation that heart electric
activity transmits obliquely to the body. To verify
two models, measured capacitive ECG signals were
averaged with Matlab 2008b to figure out which
design had an stable amplitude with four postures; a
supine, prone, right lateral, left lateral posture. The
amplitudes and ECG waveforms of two types are
shown in Figure 2.
Taken as a whole, type 2 showed stable R-peaks
compared to type 1. However, in the point of view
of usefulness and easiness to install, a whole
measurement system is too big that covers most of
the bed when including the driven sheet. To make
them more practical and easy to use, the shape of
two electrodes and a driven was redesigned to take
only the upper part of the bed. An improved model
of type 2 is shown in Figure 3. Driven was divided
into three parts to contact with the body as wide area
as possible. Capacitive textiles were fixed on silicon
to make it easy to install on the bed.
2.2 A Design of Driven Electrodes
Noise exists everywhere including electromagnetic
pulses from electrical apparatus, power line
interference, and static electricity. To reduce these,
common voltage of the body should be minimized.
Larger area of electrodes shows smaller impedance
between the body and the measurement system that
will minimize the common voltage (Winter et al,
1983).
With this reason, a driven electrode was
expanded as possible. Driven signals are obtained by
inverting the summated measured signal from two
capacitive electrodes.
-0.5 -0.4 -0.3 -0.2 -0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
300
400
500
second
amplitude
QRS morphology of supine posture
Type 1
Type 2
-0. 5 -0.4 -0. 3 -0.2 -0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
second
amplitude
QRS morphology of prone posture
Type 1
Type 2
-0.5 -0.4 -0.3 -0.2 -0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-400
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
300
400
500
second
amplitude
QRS morphology of right lateral posture
Type 1
Type 2
-0. 5 -0.4 -0. 3 -0.2 -0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-800
-600
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
second
amplitude
QRS morphology of left lateral posture
Type 1
Type 2
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAM MEASURED USING CAPACITIVE TEXTILES ON
A BED
437

Table 1: Results of HRV analysis in time domain and frequency domain. SDNN: The standard deviation of the RR-intervals.
RMSSD: The roof mean square successive difference of intervals. pNN50: The number of successive difference of intervals
which differ by more than 50 ms expressed as a percentage of the total number of ECG cycles (Rajendra Acharya et al,
2006). LF: Power in low frequency range. HF: Power in high frequency domain. nLF: LF Power in normalised units. nHF:
HF power in normalised units. LH/HF: Ratio LF/HF.
Error rate in time domain (%) Error rate in frequency domain (%) Correlation
of RR-
intervals
Subject Posture SDNN RMSSD pNN50
mean
of HR
LF HF nLF nHF LF/HF
1
Supine 1.06 2.38 17.65 <0.001 0.64 2.10 0.85 0.60 1.42 0.987
Prone 2.90 9.65 10.71 0 0.97 8.33 5.39 3.52 8.59 0.991
Right
lateral
0.71 0.35 35.07 0 0.77 3.51 1.49 1.19 2.63 0.925
Left
lateral
6.21 12.95 16.00 0 0.29 12.19 6.75 4.90 11.12 0.988
2
Supine 15.71 26.92 0 <0.001 4.79 37.54 44.64 13.78 67.77 0.948
Prone 1.32 12.15 133.33 <0.001 3.45 12.46 7.26 9.21 18.17 0.916
Right
lateral
0.79 1.66 0 <0.001 0.36 3.06 2.03 1.29 3.32 0.999
Left
lateral
2.83 6.80 18.18 <0.001 0.80 6.41 3.80 1.55 5.27 0.975
3
Supine 0.60 3.82 7.14 <0.001 0.68 2.86 0.52 1.70 2.25 0.995
Prone 0.93 6.73 28.79 0.001 0.17 2.44 0.94 1.65 2.54 0.974
Right
lateral
0.32 1.49 2.63 0 0.04 4.04 0.98 3.01 3.85 0.999
Left
lateral
0.58 1.78 21.95 0.005 1.08 4.58 1.97 3.66 5.41 0.996
Average 2.83 7.22 24.29 0.0008 1.17 8.29 6.38 3.84 11.03 0.974
2.3 Method
3 healthy male subjects participated in this
experiment, with 27.7 ± 2.5 years aged. Subjects lie
with four postures; a supine, prone, right lateral, and
left lateral posture. ECG was recorded for 5 minutes
in each posture with 500Hz sampling rate using
Biopac MP 150 (Biopac system Inc, USA). The
system was put on the upper part of a mattress and
Ag/AgCl electrodes were attached on both wrists for
reference. HRV parameters and RR-intervals were
calculated and we compared those of capacitive
ECG to those of reference ECG.
3 RESULTS
Differences of reference and capacitive ECG for
each parameter were calculated using error rate (1).
Error Rate = 100 ∗
(. . )
.
(1)
Calculated HRV error rates in time domain and
frequency domain are shown in Table 1.
Error rates of SDNN, RMSSD, and pNN50
showed 2.83, 7.22, and 24.29, respectively. Error
rates of LF, HF, nLF, nHF, and LF/HF were 1.17,
8.29, 6.38, 3.84, and 11.03, respectively. An average
value of heart rate (HR) for five minutes was almost
same between reference and capacitive ECG. An
average value of correlation of RR-intervals showed
0.97 that was a high correlation.
4 DISCUSSION
A correlation of RR-intervals showed 0.974 that
means the developed system can be used for heart
rate monitoring. However, HRV parameters showed
relatively low correlation between capacitive ECG
and reference. Especially for pNN50 with prone
posture, subject 2 showed very a poor error rate.
When measuring capacitive ECG from subject 2
with prone posture, the signal was a little noisy that
may affect the result value. However, even though
excluding this subject, pNN50 for prone posture
BIODEVICES 2011 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
438

showed poor performance. Subject 1 and 3 showed
good performances when they lie with supine
posture and subject 2 showed good error rates in
right lateral posture. In frequency domain,
performance abilities are differ from each subject
and each posture. This probably is due to the
differences in R wave transient path way (R axis) for
each subject.
Generally high correlation of RR-intervals
showed low error rate that implies a high signal
quality of the capacitive ECG tends to reveal
accurate HRV parameters. Therefore, to estimate
autonomic nervous system, the array, shape and size
of capacitive textiles should be needed to be
redesigned. Moreover, capacitive ECG with high
signal to noise is strongly required to measure HRV
correctly. We also found that ECG morphologies for
each posture are different from each other that could
be used for detection of sleep postures like a
reference (Hong Ji et al, 2010).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was supported by Seoul R&BD Program
(JP090968M0209721), Republic of Korea.
REFERENCES
Andreoni, G., Pienzo, MD. 2000. ECG monitoring
through environmental electrodes. On IEEE EMBS.
Gruetzmann, S., Hansen, S., Muller, J. 2007. Novel dry
electrodes for ECG monitoring. In vol. 28, pp. 1375-
1390 on Physiol. Meas.
Hong Ji, L., Seung Min, L., Kang Moo, L. 2010. Detection
algorithm of sleep posture using capacitive-coupled
electrodes. On u-Healthcare.
Ishijima, M. 1993. Monitoring of electrocardiograms in
bed without utilizing body surface electrods. In vol. 40,
pp. 593-594 on IEEE Trans Biomed Eng
Kin-fai, W., Yuan-ting, Z. 2008. Contactless and
continuous monitoring of heart electric activities
through clothes on a sleeping bed. On Information
Technology and Application in Biomedicine.
Marek, M. 1995. Heart rate variability. In vol. 17, pp. 354-
381 on European Heart Journal.
Rajendra Acharya, U., Paul Joseph, H., Kannathal, N.,
Choo Min, L., Suri, JS. 2006. Heart rate variability: a
review. In vol. 44, pp. 1031-1051 on Med Bio Eng
Comput.
Searle, A., Kirkup, J. 2000. A direct comparison of wet,
dry and insulating bioelectric recording electrodes. In
vol. 21, pp. 271-283 on Physiol. Meas.
Tamura, T., Yoshimura, T., Nakajima, K., Miike, H.,
Togawa, T. 1997. Unconstrained heart-rate monitoring
during bathing. In vol. 31, pp. 391-396 on Biomed
Instrum Technoll.
Winter, BB., Webster, JG. 1983. Reduction of interference
due to common mode voltage in biopotential
amplifiers. In vol. 30, pp. 58-62 on IEEE Trans
Biomed Eng.
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAM MEASURED USING CAPACITIVE TEXTILES ON
A BED
439
