
PROCON
A Tool for Curricula Accreditation
Dainis Dosbergs
Faculty of Computing, University of Latvia, 19 Raina blvd., Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Accreditation, ABET, EQANIE, ACM CC, PROCON.
Abstract: Compliance with the set requirements is controlled by curricula accreditation. Though curricula is managed
and prepared to meet the accreditation requirements, problems with control over accreditation requirements
and demonstrating the performers of accreditation compliance to those are quite common. This article
describes a system developed by the author – PROCON, which provides control over curricula content,
study result and other curricula indicators for accreditation purposes by utilizing a compliance matrix.
1 INTRODUCTION
The role of curricula accreditation varies throughout
the world. There are countries with mandatory
curricula accreditation and countries where
accreditation is optional and higher education
institutions may chose their way. There are areas
where the role of State accreditation becomes less
important while the role of international
accreditation increases, for instance, information and
communication technologies (ICT). International
accreditation is required to be able to compare
curricula in different countries and even different
regions, and considering the student mobility
tendencies as well. Such allegation is supported by
the fact that various accreditation organizations
strive to harmonize the accreditation criteria, and
had signed the Seoul Accord (Reif and Mathieu,
2009).
The higher education institutions must use their
efforts to analyze curricula content and demonstrate
its compliance with requirements of the industry.
For instance, in ICT field, compliance of curricula
with ACM Computing Curricula (ACM CC, 2006)
or SWEBOK (2004) is assessed.
The achieved learning outcomes are analyzed
during curricula accreditation, too. The issues of
learning outcome analysis and meeting the ABET
accreditation requirements have been analyzed by
Booth (2006) and Booth, Preston and Qu (2007).
The issues of learning outcomes control have been
researched by Abunawass, Lloyd and Rudolph
(2004).
This article describes research made by the
author on control of accreditation requirements by
analyzing curricula content from concept
classification standpoint and analyzing
correspondence of learning outcomes achieved to
accreditation requirements by developing
requirement matrix. The article describes a tool
developed by the author, PROCON, which includes
the above three activities for curricula analysis and
practical application of which is planned for 2011
during reaccreditation of ICT curricula according to
state requirements as well as during curricula
accreditation for EQANIE label.
2 ACCREDITATION
REQUIREMENTS
The importance of accreditation is different in
different countries and regions. When curricula
accreditation is mandatory, it is seen as measure of
curricula quality, a quality threshold, a tool for
attracting the best students, an assistant to students
for choosing quality curricula, an assistant to
employers for choosing next employees (Reif and
Mathieu, 2009).
Parallel to state mandatory curricula
accreditation the higher education institutions may
opt to accredit the curricula according to various
accreditation systems popular throughout the world
to assess the quality of such curricula as well as raise
its prestige. To achieve this, it is necessary to meet
316
Dosbergs D..
PROCON - A Tool for Curricula Accreditation.
DOI: 10.5220/0003305403160322
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2011), pages 316-322
ISBN: 978-989-8425-50-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the different accreditation requirements. For
instance, it is possible to accredit ICT curricula
according to requirements of EQANIE, ABET.
2.1 EQANIE
Accreditation Requirements
European Quality Assurance Network for
Informatics Education (EQANIE) organization was
established in Europe some years ago. One of the
aims of this organization is to develop a unified
standard and accreditation requirements for
informatics program accreditation (EQANIE, 2009).
Accreditation requirements include separate listing
of learning outcomes for First and Second Cycle
degree programs as well as guidelines for program
assessment.
Curricula assessment guidelines include program
educational objectives, academic and support stuff,
facilities, financial resources, agreements with
industry, management system. During preparing
curricula to accreditation for EQANIE label it is
necessary to ensure both analysis of learning
outcomes in the program and get ready for
inspection of assessment criteria.
2.2 ABET
Accreditation Requirements
Curricula accreditation is optional in United States
of America. Applied Science, Computing,
Engineering and Technology curricula use
Accreditation Board for Engineering and
Technology (ABET) curricula accreditation in their
battle for students, and to demonstrate the quality of
programs. ABET accreditation requirements involve
the following subjects: Objectives and Assessment;
Student Support; Faculty Curriculum; Laboratories
and Computing Facilities; Institutional Support and
Financial Resources; Institutional Facilities (ABET,
2009).
ABET requires that program objectives must be
measurable. That is, for any objective written for a
program, there must exist some practical way to
examine whether it is achieved over the graduates of
the program. (ABET, 2004)
ABET requirements may be divided into three
groups:
General requirements.
Requirements for learning outcomes.
Requirements for topics reviewed within the
curricula.
3 REQUIREMENTS
FOR CURRICULA CONTENT
The experts, during curricula accreditation, are
controlling the extent to which the curricula follow
the requirements of the industry. Such requirements
may vary between the industries. In ICT industry,
significant role is played by requirements for IT
curricula content summarized by leading
organizations of the industry – ACM, AIS and
IEEE-CS, the ACM Computing Curricula (ACM
CC, 2006). Particular disciplines may have their own
requirements developed, for instance, the Guide to
the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge
(SWEBOK) developed by IEEE-CS discusses one
particular ICT discipline – software engineering.
In due course of developing and managing the
curricula content, attention should be paid to the
extent to which the curricula meets the requirements
of external curricula content. At the moment of
curricula accreditation the experts may aim at
examination of review of particular topics within the
curricula.
3.1 ACM Computing Curricula
Requirements
As there is a very large number of IT curricula
around, it is important to understand the IT specifics
and its relation to study directions. Thus, the
Computing Curricula proposed by ICT industry
organizations ACM, AIS and IEEE-CS summarizes
the information on advisable curricula content in
directions of Computer Engineering, Computer
Science, Information Systems, Information
Technology and Software Engineering (ACM CC,
2006).
Computing Curricula describes the computing
topics to be reviewed within five kinds of degree
programs by indicating minimum and maximum
review volume for each topic. Non-computing topics
are described in a similar way. A sample of topic
listing is provided further in Table 1.
Degree outcomes are another thing described in
Computing Curricula. The report lists approximately
60 various performance capabilities and sets an
expectation indicator for each of them (values from
no expectation to the highest relative expectation).
Sample of such requirements is provided in Table 2.
When curricula content is controlled, it is
necessary to identify the extent to which the curri
cula content meets the ACM CC computing topics
and performance capabilities.
PROCON - A Tool for Curricula Accreditation
317

Table 1: Comparative weight of computing topics across the five kinds of degree programs (ACM CC, 2006).
Knowledge area
CE CS IS IT SE
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Programming Fundamentals 4 4 4 5 2 4 2 4 5 5
Integrative Programming 0 2 1 3 2 4 3 5 1 3
Algorithms and Complexity 2 4 4 5 1 2 1 2 3 4
Computer Architecture and Organization 5 5 2 4 1 2 1 2 2 4
… … …
Table 2: Relative performance capabilities of computing graduates by discipline (ACM CC, 2006).
Area Performance capability CE CS IS IT SE
Algorithms
Prove theoretical results 3 5 1 0 3
Develop solutions to programming problems 3 5 1 1 3
Develop proof-of-concept programs 3 5 3 1 3
Determine if faster solutions possible 3 5 1 1 3
Application
programs
Design a word processor program 3 4 1 0 4
… … …
3.2 SWEBOK Requirements
Individual disciplines may have their own standards
or guidelines developed. Thus, for instance, there is
a guidebook developed for Software Engineering
which is one of the IT disciplines, describing the
boundaries of Software Engineering discipline –
Guide to the Software Engineering Body of
Knowledge. (SWEBOK, 2004) The Body of
Knowledge is subdivided into ten software
engineering Knowledge Areas: Requirements,
Design, Construction, Testing, Maintenance,
Configuration Management, Engineering
Management, Engineering Process, Engineering
Tools and Methods, Quality. Each of the areas is
detailed further, even reaching the fourth detailing
level in some areas.
When correspondence of curricula content to
requirements of the industry is demonstrated during
curricula accreditation, it is necessary to demonstrate
the correspondence of curricula content to
requirements of SWEBOK.
4 PROCON
A relevant tool of support is needed to ensure
control over accreditation requirements discussed in
previous paragraphs above as well as to provide
control over curricula content. Performance of
control activities is much easier by using such
support tool, thus ensuring obtaining the results of
curricula analysis quicker. The PROCON tool
developed by the author is described in this chapter.
The tool is intended to be used both in everyday
work and during curricula accreditation. This tool
provides for input of curricula information, input of
various accreditation requirements for analysis of
curricula content, learning outcomes and other
curricula indicators, analyzing functions for control
over meeting the accreditation requirements.
4.1 Requirements
for Curricula Content
Analysis of curricula content is important for
curricula analysis as well as for comparing various
curricula. Research performed by DeLorenzo,
Kohun and Wood (2006) revealed that not all of
IS2002 study courses were included in US TOP 19
IT curricula, as well as different study courses not
mentioned in IS2002 were present. During curricula
accreditation, the experts need to obtain
confirmation that curricula cover particular
concepts.
In PROCON tool, the analysis of curricula content
requirements is granted by utilizing the concept
classification described in research of Dosbergs and
Borzovs (2010). Concept classification helps to 1)
describe the concepts of the respective science field,
2) identify the topics covered by curricula study
courses, 3) list the external curricula content
requirements, for instance, ACM Computing
Curricula computing topics, SWEBOK topics or
requirements for curricula content analysis brought
forward by accreditation commission experts.
Figures 1 and 2 present a screenshots of the
PROCON tool, showing an example of control of
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
318
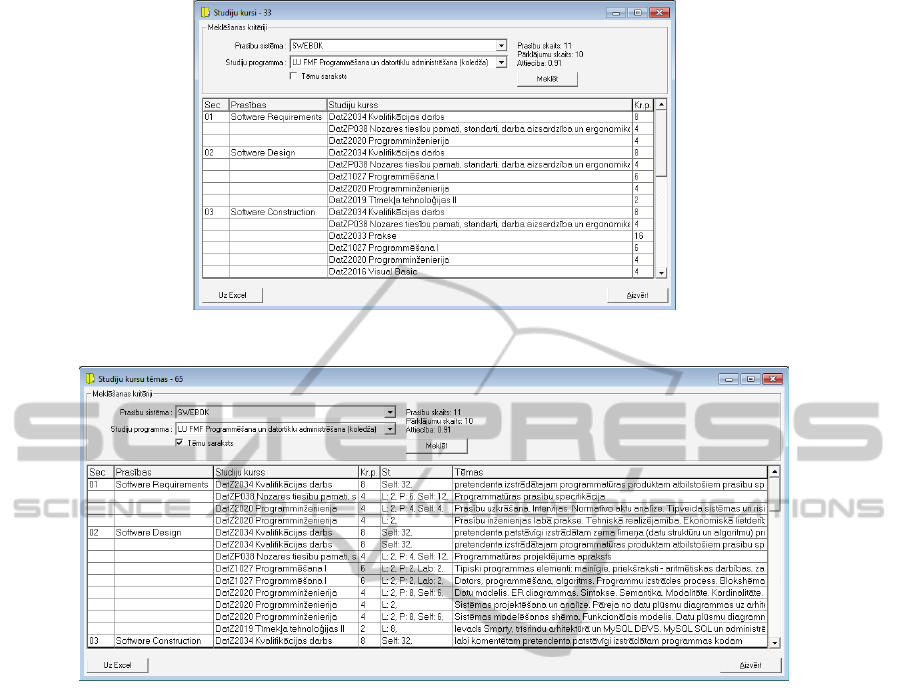
Figure 1: SWEBOK knowledge areas covered by study courses.
Figure 2: SWEBOK knowledge areas covered by topics of study courses.
requirements for curricula content: figure 1
illustrates report at the study course level, figure 2 –
at the level of the study course topics. In the left two
columns SWEBOK knowledge areas are included.
In the 3
th
and 4
th
column are included appropriate
study course code, name and amount of credit points
of evaluated study program. The last two columns in
figure 2 show study course topics description and
amount of contact and individual work hours planed
for each topic.
4.2 Requirements
for Curricula Learning Outcomes
Accreditation requirements demand achieving
particular learning outcomes in study courses. It is
necessary to demonstrate those during accreditation.
Indication of what results demanded by accreditation
requirements are achieved within each study course
is needed for such demonstration. This kind of
approach, with compliance matrix, is used also by
Yao, Liu, Grubb and Williams (2007) to describe
correspondence between study course learning
outcomes, program objectives, CC2001 standards
and CAC ABET criteria.
Requirements for achieving learning outcomes
are imposed by EQANIE also, requiring indication
of how program outcomes are met within curricula
and how the Relative performance capabilities of
computing graduates by discipline described in
ACM Computing Curricula are imposed.
For the sake of ensuring compliance with
accreditation requirements, PROCON provides for
listing the curricula study courses with a possibility
to indicate learning outcomes to achieve for each
study course. It is possible to define various
accreditation requirements with respect to learning
outcomes within the tool and connect the outcomes
to be achieved by study courses to accreditation
requirements towards learning outcomes. Also, it is
possible to generate reports on how accreditation
requirements are met by the audited curricula to
perform the accreditation requirement control, or on
the contrary, assist the curricula responsible ones in
PROCON - A Tool for Curricula Accreditation
319
preparations for the audits by reviewing study
courses that do not achieve the accreditation
requirements.
Figure 3: Control of learning outcomes in the PROCON
tool.
Figure 3 presents a screenshot of the PROCON
tool, showing an example of curricula learning
outcome control. In the left column are included
ACM Computing Curricula requirements for
curricula learning outcomes. In the 2
nd
and 3
th
column are included appropriate study course code,
name and amount of credit points of evaluated study
program. The last column shows study course
learning outcomes of evaluated study program.
4.3 General Requirements
PROCON is intended not only for analysis of
curricula content and learning outcomes, but also for
accumulation and processing of general
curricula information that is required for curricula
control and accreditation purposes. The tool allows
accumulating different types of information in a
universal data structure and ensures processing of
these data and their connection to external
requirements. The tool provides the option of
generating various voluntary reports from curricula
data accumulated by the system as well, for instance,
professor number ratio, number of students to one
professor ratio, number of students to one lecturer
ratio.
Universal data structure used for the tool
provides the option of defining new values to be
accumulated within the tool and indicate the data
type for such values. The tool allows accumulating
data with number, text, date and similar values as
well as employing classification or data selection
SQL request values definable within the tool. The
data selection SQL values provide for broader
opportunities to apply the tool because the user
familiar with data structure of the tool may generate
various reports on accumulated data without
changing the tool functionality.
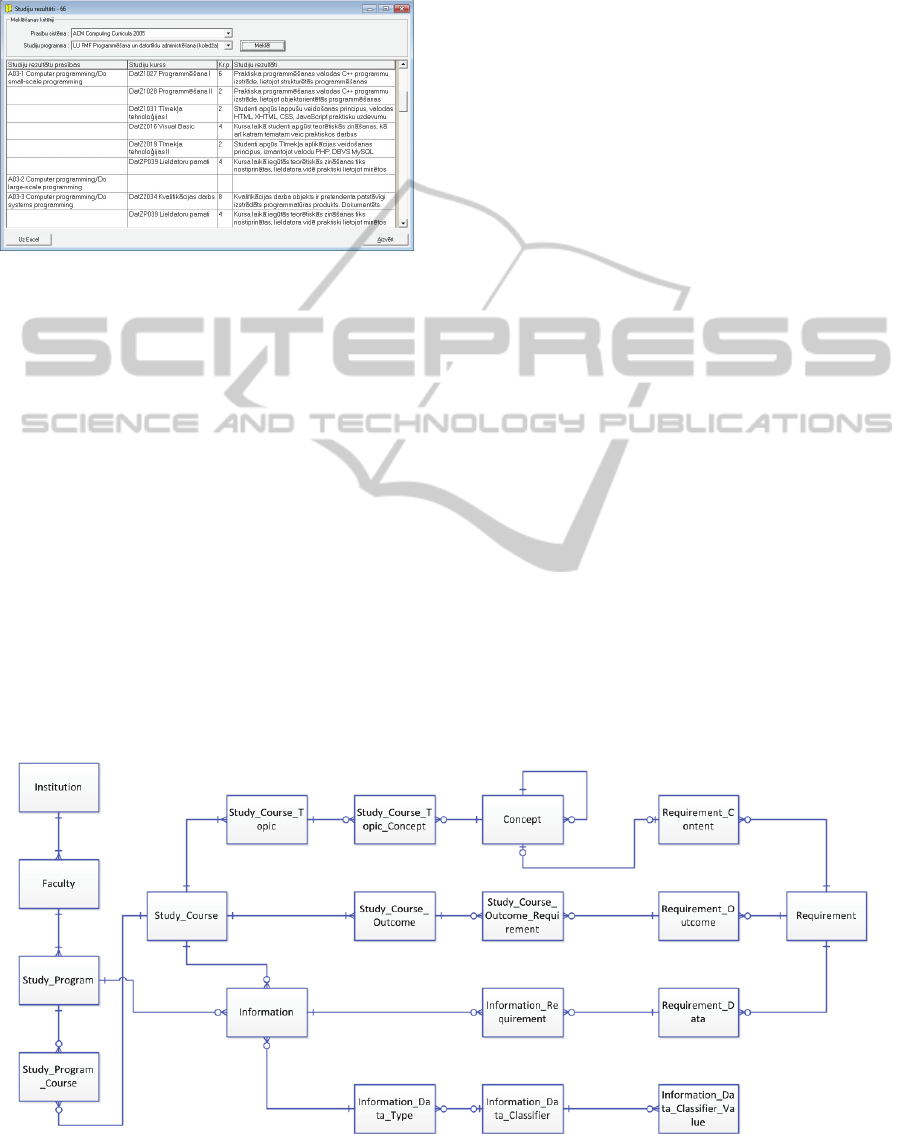
4.4 Technical Implementation
This chapter describes the part of PROCON
technical implementation related to curricula
content, learning outcome and curricula information
control discussed in this article. Data structure is
illustrated in Figure 4. Implemented curriculum
architecture corresponds to a simplified model
where the course has several topics attached
(Study_Course_Topic), but each topic has a
knowledge unit attached, to be discussed within the
topic (Study_Course_Topic_Concept).
Figure 4: Data structure of PROCON tool.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
320

Several learning outcomes have been adjusted to
the course (Study_Course_Outcome). Recording of
voluntary information (Information) on a curricula
or particular study course is possible also.
Universal data structure of information
accumulation is developed in a way that various
curricula or study course data types are defined
(Information_Data_Type), it is possible to define
voluntary classifiers applicable within the tool
(Information_Data_Classifier) and fill in these
classifiers with classifier values
(Information_Data_Classifier_Value).
The tool provides for listing of various
accreditation requirements and connection to
curricula indicators. Accreditation requirements are
defined (Requirement) and accreditation content
requirements (Requirement_Content), accreditation
requirements towards achievement of learning
outcomes (Requirement_Outcome) and accreditation
requirements for revealing information on curricula
or study course (Requirement_Data) are listed.
Compliance with accreditation requirements
within particular curricula is ensured by filling in
adequacies between curricula study course learning
outcomes and accreditation requirements for
learning outcomes to be achieved
(Study_Course_Outcome_Requirement) and filling
in correspondence of curricula information to
accreditation requirements (Information_Require-
ment).
5 FUTURE WORK
Continuation of research foresees practical
application of the developed PROCON tool in state
accreditation and EQANIE accreditation for IT
curricula.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Maintaining curricula information for accreditation
requirement purposes is a time consuming process.
It is not always possible to simply obtain
acknowledgements required for accreditation from
curricula data. Gathering of such data sometimes
requires analysis of curricula information. The
situation in curricula content analysis is made
complicated by the fact that it is possible to accredit
the curricula according to requirements of various
external accreditation systems.
The article describes a tool developed by the
author, PROCON, that is intended for accumulating
and analysis of curricula information during
preparation of curricula to various accreditations as
well as for supporting the curricula responsible ones
during accreditation. The tool supports control over
curricula content requirements, learning outcome
control and listing and control of curricula
information indicators.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research is supported by a grant from the
European Social Fund (ESF) operational program
“Support of doctoral studies at the University of
Latvia”.
REFERENCES
ABET (2004). Selfstudy questionaire for review of the
computer science program. Retrieved from
http://www.abet.org/forms.shtml.
ABET (2009). Criteria for Accreditating Computing
Programs. Retrieved from http://www.abet.org/forms.
shtml#For_Computing_Programs_Only.
Abunawass A., Lloyd W. and Rudolph E (2004).
Compass: A CS Program Assessment Project. ACM
SIGCSE Bulletin, 36(3), 269-269. Retrieved from The
ACM Digital Library.
ACM CC (2006). The overview report covering
undergraduate programs in Computer Engineering,
Computer Science, Information Systems, Information
Technology and Software Engineering. Retrieved
from http://www.acm.org/education/curric_vols/CC2
005-March06Final.pdf.
Booth L. (2006). A Database to Promote Continuous
Program Improvement. Proceedings of the 7th
conference on Information technology education, 83-
88. Retrieved from The ACM Digital Library
Booth L., Preston J. and Qu J. (2007). Continuous
Program Improvement: A Project to Automate
Record-keeping for Accreditation. Proceedings of the
8th ACM SIGITE conference on Information
technology education, 155-160. Retrieved from The
ACM Digital Library.
DeLorenzo G., Kohun F. and Wood D. (2006). ABET-
CAC is Accreditation: Curricular Standards and
Program Rankings, Issues in Information Systems,
7(1), 182-187.
Dosbergs D. and Borzovs J. (2010). Concept classification
for Study programs quality evaluation. Proceedings of
the 2nd international conference on computer
supported education, 441-445.
PROCON - A Tool for Curricula Accreditation
321

EQANIE (2009). Framework Standards and Accreditation
Criteria for Informatics Programmes. Retrieved from
http://www.eqanie.eu/pages/quality-label.php.
Reif H. and Mathieu R. (2009). Global Trends in
Computing Accreditation. Computer, 42(11), 102-104.
SWEBOK (2004). Guide to the Software Engineering
Body of Knowledge. Retrieved from
http://www.computer.org/portal/web/swebok.
Yao J., Liu Y., Grubb A. and Williams G. (2007). Course
Assessment Framework that Maps Professional
Standard and ABET Accreditation Criteria into Course
Requirements. Journal of Computing Sciences in
Colleges, 23(2), 128-136.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
322
