
LEARNING-ORIENTED ASSESSMENT OF WIKI CONTRIBUTIONS
How to Assess Wiki Contributions in a Higher Education Learning Setting
Emilio J. Rodr´ıguez-Posada, Juan Manuel Dodero, Manuel Palomo-Duarte
and Inmaculada Medina-Bulo
Superior School of Engineering, University of C´adiz, C/ Chile 1, 11002 C´adiz, Spain
Keywords:
Computer-supported collaborative learning, Wikis, e-Learning assessment.
Abstract:
Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning based on wikis offers new ways of collaboration and encourages
participation. When the number of contributions from students increases, traditional assessment procedures of
e-learning settings suffer from scalability problems. In a wiki-based learning experience, some automatic tools
are required to support theassessment of such great amounts of data. We have studied readily available analysis
tools for the MediaWiki platform, that have complementary input, work modes and output. We comment our
experience in two Higher Education courses, one using HistoryFlow and another using StatMediaWiki, and
discuss the advantages and drawbacks of each system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Collaboration between students is often limited by lo-
cation and time constraints, causing the task to be
divided into a number of almost independent work
packages that are later merged into a final handout.
The massive adoption of computers and Internet in
our life has reached the classrooms, where Computer-
Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL) offers new
ways of real collaboration. In this context, wikis are
appropriate tools to support the dynamic real-time
teacher-student and student-student interactions that
are required to facilitate collaborative learning ex-
periences (Jaksch et al., 2008). A wiki is a web-
site that eases the collaborativecreation of interlinked
web pages. This allows for a massive collaboration
process, where several students located in different
places can modify the same web site simultaneously.
Nowadays, work-group skills are one of the main
goals of e-learning processes. This work is motivated
by the increasing need to implement group-based col-
laborative e-learning experiences, specially in Span-
ish Higher Education institutions that are immersed
in the European Higher Education Area (EHEA), in
which courses aim at achieving transferable compe-
tences and skills for life-long learning (Fallows and
Steven, 2000). However, there are some issues that
emerge when such competences have to be assessed
or evaluated.
Most usual competence assessment procedures
and instruments are based on the detailed inspection
of a number of learning outcomes (i.e. assignments,
reports, deliverables, etc.) that are collaborativelycre-
ated and delivered by learners. Examples of assess-
ment instruments are rubrics, control lists, check lists
and so forth (Walvoord and Anderson, 2009). The
assessment procedure usually involves teachers and
learners in a guided interaction during which they
have to fill-in (or review) a number of evaluation
forms that hold the evaluation criteria, after inspect-
ing (or completing) each learning outcome. In these
procedures is pretty difficult to assess especial aspects
of collaboration such as, among others, the effort and
contribution degree from each learner, how individ-
ual contributions are distributed and how they add to
the overal group work, how efficient the resolution of
conflicts is as long as these happen, or what transfer-
able skills (e.g. analytic observation, authority and
leadership, thoroughness) can be elicited from learn-
ers’ contributions.
The main research question here is how a teacher
can assess an e-learning experience that produces a
large amount of data, in particular, when the students’
work is developed on or supported by a wiki. This
issue is known in Computer Science as scalability
(i.e. how well a system can adapt to increased de-
mands). Traditional assessment procedures do not
scale well if the number of students or groups of stu-
dents is too great, or if the number or complexity of
learning outcomes is not easy to handle. Usually,
evaluators’ workload is alleviated by extending the
assessment procedure so that students be part of it,
79
J. Rodríguez-Posada E., Manuel Dodero J., Palomo-Duarte M. and Medina-Bulo I..
LEARNING-ORIENTED ASSESSMENT OF WIKI CONTRIBUTIONS - How to Assess Wiki Contributions in a Higher Education Learning Setting.
DOI: 10.5220/0003308700790086
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2011), pages 79-86
ISBN: 978-989-8425-50-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

either through self-assessment or peer assessment of
learning outcomes (Barootchi and Keshavarz, 2002).
Not discussing the didactic advantage of these evalu-
ation procedures for the formative evaluation during
the learning process (Boud, 2007), the teacher might
sometimes miss important information for an eventual
summative evaluation (Falchikov, 2005).
From the analysis of contributions to a wiki, a
teacher (or even a student) can have worthwhile in-
formation to assess, self-assess or peer-assess the re-
sults of a collaborative learning experience (Cubric,
2007a). The scope of this paper is limited to experi-
menting with software-supported assessment of wiki-
based contributions for traditional teacher-based eval-
uation procedures. Our work is focused on Medi-
aWiki software, the most popular wiki system nowa-
days (it is used in Wikipedia and related projects, like
Wiktionary, Wikibooks or Wikisource).
The rest of this document is organized as fol-
lows: first, some techniques for the assessment of
wiki-based learning experiences are discussed and
some support tools are analysed. Third section deals
with two experiences, each one using a different tool,
namely StatMediaWiki and HistoryFlow, and shows
how their role is in the learning process. Finally, some
discussions about the experiences and conclusions are
provided, along with an outline of the future work.
2 WIKI-BASED
COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
EXPERIENCES
A great number of collaborative e-learning processes
are supported by wikis, including Higher Education
(Jaksch et al., 2008) and blended learning experiences
(Cubric, 2007b). Wikis are collaborative tools that
serve multiple purposes in Higher Education, spe-
cially for collaborative writing, assessment (Cubric,
2007a; Liu and He, 2008), software development
(Louridas, 2006) and project management (Trentin,
2008). In the following, a number of wiki-based pro-
cedures and tools are studied to analyse how well they
support the research issue, i.e. how they can help the
evaluator to assess an e-learning experience.
2.1 Assessment of Wiki-based Learning
Experiences
Initial proposals to support assessment in wikis tried
to generate question item models on a wiki for for-
mative assessment (Liu and He, 2008). Similar ap-
proaches have been provided with either formative
or summative evaluation purposes (Cubric, 2007a;
Cubric, 2007b). First proposals that evaluate learning
outcomes on the basis of individual students’ contri-
butions to the wiki define metrics in terms of generic
wiki-based log indicators (e.g. number and size of
contributions) (Trentin, 2008) or a set of pre-defined
categories for contributions (de Pedro, 2007). Al-
though such analyses are done on the basis of direct
observation and measurement of the wiki log values,
a number of useful tools have been provided to illus-
trate these in a more abstract fashion. Next, some of
these tools are summarized and described.
2.2 Wiki-based Contributions Analysis
Tools
After a bibliographical search, three tools supporting
MediaWiki wiki-based collaborative learning experi-
ences have been found:
HistoryFlow by the MIT Media Lab and the Col-
laborative User Experience Research Group in
IBM (Vi´egas et al., 2004). It is a data analysis
tool that retrieves the history of a given page of a
wiki. It produces diagrams as graphical represen-
tation of differences in sentences between consec-
utive versions of that page throughout time. This
is finer than usual behavior in Wikipedia, which
checks differences between paragraphs. Different
aspects of authorship can be highlighted with His-
toryFlow, i.e. contributions from all authors, con-
tributions from a single author, new contributions
from any author and content persistence.
WikiXRay by LibreSoft Research Group at the Uni-
versity Rey Juan Carlos (Ortega et al., 2007) is
a set of Python and GNU R scripts that makes a
quantitative analysis of public database dumps of
a MediaWiki website. WikiXRay builds an SQL
database with the data obtained from the dump
and creates additional tables with useful quanti-
tative information. A number of scripts are pro-
vided to generate many statistics and graphics,
and new ones can be created to obtained cus-
tomized output.
StatMediaWiki by the SPI&FM Research Group at
the University of C´adiz (Rodr´ıguez et al., 2010)
is a tool that collects and aggregates information
that help to analyze the status and development
of a MediaWiki installation. StatMediaWiki ver-
sion 1.0 generates CSV files and static XHTML
1.0 standard-compliant web pages including ta-
bles and graphics, showing timelines for the con-
tent evolution, activity charts for users and pages,
rankings, tag clouds, etc. The anonymous op-
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
80

Table 1: Summary of main features in wiki analysis tools (X: Yes, ✗: No).
Features HistoryFlow WikiXRay StatMediaWiki
Availability
Open source license ✗ X X
Free download X X X
Interaction
Command line ✗ X X
Graphical User Interface X ✗ ✗
Input modes
Connection to MediaWiki database ✗ ✗ X
MediaWiki database dumps ✗ X ✗
Histories exported with Special:Export X ✗ ✗
Analysis modes
Global ✗ X X
Page-by-page X ✗ X
User-by-user ✗ ✗ X
Content evolution X X ✗
Output modes
Optional anonymous ✗ ✗ X
(X)HTML X ✗ X
Tables ✗ X X
Charts (S: Static, D: Dynamic) D S S
CSV (Spreadsheet neutral format) ✗ ✗ X
tional feature allows to hide sensitive information
and the edit user patterns when desired.
All the technical information about these tools is sum-
marized in table 1.
3 CASE STUDIES
In this section we comment our experience using Stat-
MediaWiki and HistoryFlow in a Higher Education
setting. The case study of StatMediaWiki consisted
of two courses, while that of HistoryFlow was devel-
oped in a course.
3.1 Case Studies using StatMediaWiki
StatMediaWiki generates three kinds of analysis, i.e.
global, user-focused and page-focused. That helps in
understanding the dynamics of the wiki and allows to
know about each element in greater depth. The in-
formation is divided into sections, and it is presented
as graphs and tables. All the graphs (lines and bars)
use three different colours to split edits by MediaWiki
standard namespaces: all edits, only main edits (i.e.
edits in articles), and only talk page edits (i.e. discus-
sions about article contents). The delivered report is
a collection of HTML pages, in which every item is
linked to another page that holds more detailed infor-
mation and CSV files.
StatMediaWiki has been successfully applied to
the assessment of wikis developed in two courses dur-
ing the 2009/10 academic year: WikiHaskell
1
and
1
Available at http://osl.uca.es/wikihaskell
WikiRA
2
. They both used the same technologies, but
different working methodologies. As can be seen
in the StatMediaWiki output (StatMediaWiki, 2010),
this caused differences in results.
On the one hand, WikiHaskell is a wiki where 3-
member teams created Spanish-language documenta-
tion about libraries for the Haskell programming lan-
guage. Every month they had to do a presentation
showing the state of their assignment. That makes ef-
fort to be generally well-balanced during the course
time (see Fig. 1), so the work on the wiki had a very
positive influence in students’ final marks.
Figure 1: WikiHaskell progress timeline.
On the other hand, WikiRA contains lecture notes
about automated reasoning. The notes were freely
inserted by students during the course. Neverthe-
less, the scarce number of groups (that usually makes
2
Available at http://osl.uca.es/wikira
LEARNING-ORIENTED ASSESSMENT OF WIKI CONTRIBUTIONS - How to Assess Wiki Contributions in a Higher
Education Learning Setting
81
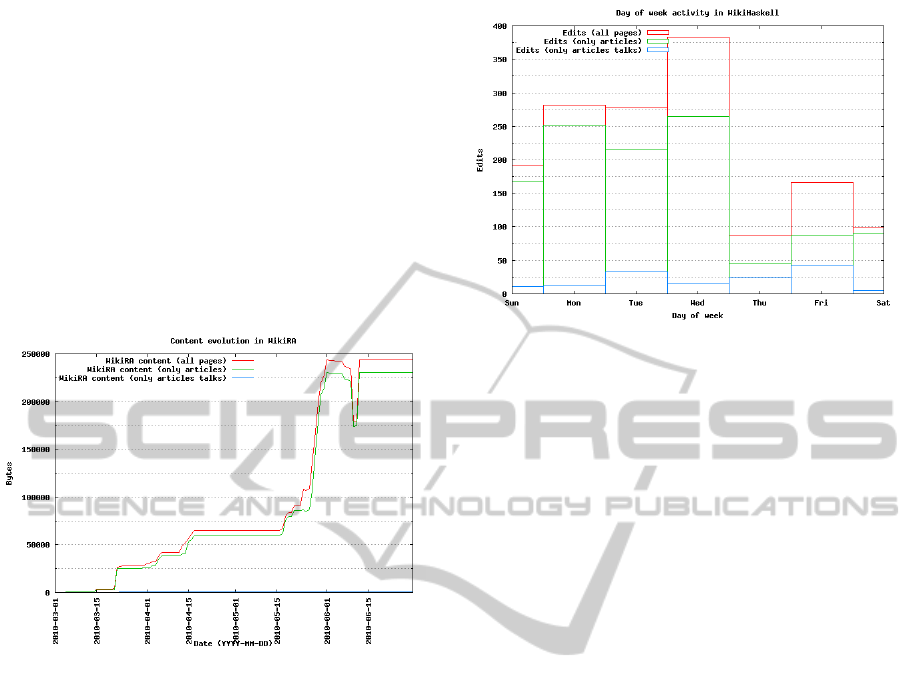
all members cooperate and work), the loose restric-
tions to their work (i.e. there were no intermedi-
ate presentations) and the hard topic of the course
(automated reasoning) caused not so positive results,
with many students only contributing near the end of
the semester, and other even abandoning the course.
We can see this in Fig. 2, where wiki content grows
sharply only a few days after the end of the chart.
Note that, in June, WikiRA suffered a spambot attack
where the content was blanked and replaced by some
spam links. Later, the admin restored the texts. That
explains the abrupt fall and growth. To preventsimilar
attacks the MediaWiki captcha extension was enabled
since then.
Figure 2: WikiRA progress timeline.
Using StatMediaWiki we have been able to derive in-
formation about the following items:
• The number of updates and what pages are af-
fected by updates. This information allows us
to know the average number of contributions per
student, besides identifying which sections of the
wiki suffered from a weaker development effort,
as well as providing valuable help when thinking
about how to foster this effort.
• A potential ranking of students. We can classify
our students by taking into account the number of
contributions, at what hours and days of the week
they do their work, and their participation level.
In the case of WikiHaskell, we have observed in
the global ranking of contributions that the 10
most prolific students (about 20% of the students
in the course) have added 50% of the contents to
the wiki. Also, students work harder on the previ-
ous days to the lecture (i.e. Wednesday), and the
edit rate falls abruptly on the next day (i.e. Thurs-
day), as seen in Fig. 3.
• The potential student work profiles. In particular,
Figure 3: WikiHaskell activity graph by day of the week.
both in WikiHaskell and WikiRA we have identi-
fied five different profiles:
– Continuous: This is the optimal profile. The
student is contributing continuously during the
whole project lifetime.
– Stepwise: This is still a good profile, though
unlike the previous there are some short regu-
lar periods when the student is not making any
progress.
– Early peak. This is the profile of abandonment.
A genuine effort is done right at the beginning,
but soon the number of contributions vanishes.
– Middle peak: This profile fits the behaviour of
a majority of our students. Most of the work
is done at the middle of the project. It seems
that one day, they realize that they do have to
contribute to the wiki to pass the course, decide
to do it as soon as possible and then forget about
it.
– Late peak: This profile reflects the common sit-
uation of some students trying to push forward
their contributions near the deadline.
Since StatMediaWiki analyses all the wiki, we
have had a wider comprehension of the dynamics of
the wiki and discovered unexpected patterns, such as:
how students work together in different pages; users
who usually fix errors, add improvements or leave
suggestions to other groups’ pages; how coordination
happens by using talk pages; pages that significantly
attract more attention, etc. For example, table 2 shows
the ranking of pages edited by one of the most active
students. We can see that she contributed to different
“Main” pages, so helping other groups. Additionally,
she also contributed to a “User talk” page, showing
communication with other student. There is also an-
other editing to a “Talk” page to provide a comment
about other group’s “Main” page.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
82

Table 2: Ranking of pages edited by a certain user.
# Page Namespace Edits
... ... ... ...
12 Biblioteca ... Gtk2Hs Main 4
13 Biblioteca ... Cabal Main 4
14 Primeros ... Gtk2Hs Main 3
... ... ... ...
42 User talk:...Jose User talk 1
43 Talk:Biblioteca ... Cabal Talk 1
3.2 Case Study using HistoryFlow
HistoryFlow provides a graphical view of users’ edit-
ing activity throughout several versions of a certain
wiki page. It enables visualizing cooperation and con-
flicts between wiki authors (Vi´egas et al., 2004). The
following HistoryFlow facilities can be used for that
aim:
• Display contributions of all authors in different
colors
• Highlight the contributions of a single authors
throughout all versions
• Highlight new text content in each page version
• Show the persistence of different contributions
over time
HistoryFlow diagrams are similar to Inserlberg’s
parallel coordinates (Inselberg and Dimsdale, 1990),
in which the horizontal axis represents a timeline for
all versions of a wiki page, and the lenght of each
vertical line is proportional to the page version size.
Each vertical line consists of a number of colored
parts that represent adjacent text passages, using a dif-
ferent color for each contributing user.
We have used HistoryFlow diagrams and visual-
ization facilities to illustrate competences drawn by
learners. The learning experience entails an 8-week
project-oriented learning course in which a number of
software projects are developed by 3-member teams.
All project-related documents and deliverables are
hosted in a single wiki page, so it can be eventu-
ally subject to analysis with the help of HistoryFlow.
Fig. 4 depicts some diagrams as they are generated
from a set of project-oriented learning wiki-based de-
liverables
3
. From these diagrams, we made the fol-
lowing considerations on some observable learning
competences:
• Overall effort: The amount of contributions
throughtout time can be observed as the growth
of vertical lines on the timeline. For instance,
Fig. 4 shows that activity of all projects occurs
3
Available at http://mediawiki.uca.es/
within the 8 weeks of the course, showing a con-
siderable amount of work (all timelines are quite
fine-grained). The curve shape indicates whether
such work has been equally distributed through-
out time (i.e. the curve is approximately straight,
as in Fig. 4(a)) or there have been work intervals
having intense or scarce activity —i.e. there are
sharp shapes or drops of the curve, as in Fig. 4(b).
A proportional spacing of the timeline representa-
tion can show up such intervals.
• Distribution of effort: since each learner’s contri-
bution is colored differently, the distribution of in-
dividual contributions to the wiki text is clear. Be-
sides, a numeric percentage for learners’ amount
of contributions is shown next to the user name.
For instance, the diagram of Fig. 4(c) shows a
balanced distribution of work (45%-27%-28%)
among the team members. Instead, the distribu-
tion of work of Fig. 4(a) is more biased towards
two members (11%-58%-31%).
• Work organization: Pieces of text can be writ-
ten and moved on a wiki page. Reorganization
and movements of text can be observed as slashed
line patterns that cross the diagram. For instance,
the Fig. 4(b) depicts this pattern in the middle of
the diagram; the same happens at the end of the
project on Fig. 4(a).
• Confict resolution: An interesting opportunity of
wikis is to check conflicts that might emerge dur-
ing text editing. This can be analysed on the wiki
logs, but then it is a hard task. HistoryFlow dia-
grams show editing conflicts as a zig-zag pattern
throughout the timeline. Unfortunately, such con-
flicts did not appear in our project-oriented learn-
ing experience.
• Other transferable skills: The analysis of Histo-
ryFlow diagrams may be indicative of some other
skills that learners demonstrate during the learn-
ing process. For instance, leadership can be seen
as first-mover events (i.e. to strike while the
iron is hot) when a text part that was early pro-
vided persists along older versions of the page.
HistoryFlow provides a special visualization that
plots older parts with darker colors, as depicted
in Fig. 4(a). The darker parts of the older (i.e.
righter) side of the timeline is provided by user
Mangel.vera. Along with the colored group con-
tribution view showing the provenance of text,
this user can be reasonably thought of behaving
as a leader of the team. Other transferable skills,
such as analytic observation abilities or thorough
attention to details can be analysed on these dia-
grams, as described in (Dodero et al., 2009).
LEARNING-ORIENTED ASSESSMENT OF WIKI CONTRIBUTIONS - How to Assess Wiki Contributions in a Higher
Education Learning Setting
83
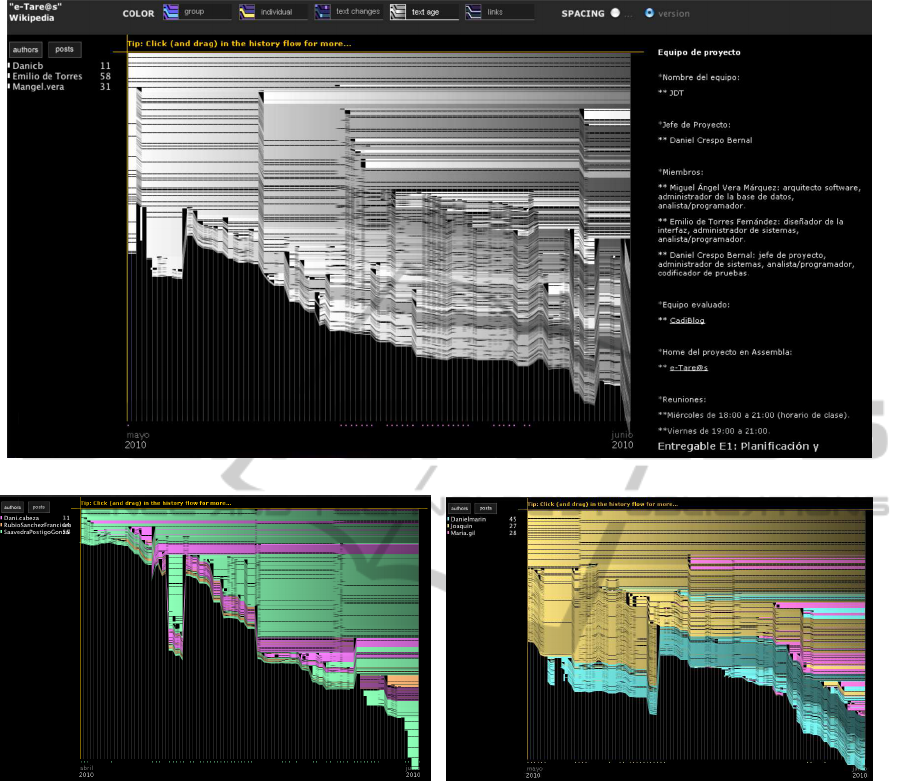
(a) Project e-Tare@s text age diagram
(b) Project LEARN group contribution diagram (c) Project CadiBlog group contribution diagram
Figure 4: HistoryFlow visual representation of wiki deliverables of different projects.
4 DISCUSSION
We have reviewed some e-learning applications of
available MediaWiki analysis tools. They are summa-
rized in table 3. Several conclusions can be extracted
from this study.
As for HistoryFlow and StatMediaWiki, both pro-
vide a simple user output, but their behavior is quite
different. On the one hand, HistoryFlow operatesonly
on single wiki pages. This limits its capability of ana-
lysis, as it does not consider the wiki interlinking na-
ture. Anyway, it is interesting for isolated analysis of
critical pages or learning outcomes that can take up
only one page. It focuses on changes to the page text
contents, not so deeply considered in StatMediaWiki.
It provides an usable graphical information but a lim-
ited numerical output.
Unfortunately, HistoryFlow remains the same
since 2005, therefore no future features are expected
to be added in the near future. This, coupled with the
lack of source code available, makes us not to rec-
ommend it as the only tool to support a course, as any
internal change in MediaWikiexport format can make
it obsolete.
On the other hand, StatMediaWiki quantitatively
analyzes the evolution of the whole wiki, providing
information on the overall content, contributions of
every user to the whole wiki and page-by-page ana-
lysis. This way, the information provides a wider
analysis of the work that a user has developed in the
whole wiki, not just one page. The information is
summarized in tables and charts and some options
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
84

Table 3: Summary of skills assessed by wiki analysis tools (X: Yes, ✗: No, i.p.: restricted to an isolated page of the wiki).
Skill / Tool HistoryFlow WikiXRay StatMediaWiki
Work effort X(i.p.) X X
Work distribution/collaboration X(i.p.) X X
Work organization X(i.p.) X ✗
Conflict resolution X(i.p.) X ✗
Transferable skills (e.g. leadership) X(i.p.) X X
are available like tag clouds, user rankings and anony-
mous output (which are specially interesting for pub-
lic wikis). Nevertheless, the analysis is quantitative,
so the software is not able to show some inner situa-
tions, such as conflict resolution.
Among the new features desirable for StatMedia-
Wiki, there is a categorical analysis feature on the
way. Using it, if a group of students works horizon-
tally in a set of properly categorized pages, the teacher
can obtain a better view of their work. Also adding
some dynamism to graphics (like those of History-
Flow), could improve its usability.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
RESEARCH
In this paper we have presented the main needs for
a correct assessment of wiki contributions and some
tools that support it. We have compared e-learning
applications of available MediaWiki analysis tools.
First, we can see a great difference between Wiki-
XRay and the other two tools. WikiXRay is by far the
most powerful tool, but requires specialized knowl-
edge to use it. It builds an SQL database with the
data from a MediaWiki dump and creates additional
tables with useful quantitative information. A num-
ber of default scripts can be used, or new ones be cre-
ated to generate customized analyses (but in this case,
GNU R and/or MySQL skills are desirable). Up to
date no information of any academic e-learning case
study has been found, so it remains as a future work.
Secondly, we can conclude that HistoryFlow and
StatMediaWiki can provide an acceptable support for
wiki contributions analysis in collaborative and co-
operative learning processes, specially if used com-
plementarily. StatMediaWiki gives a general picture
of the wiki, so students’ effort, work distribution and
other skills can be easily assessed. For critical pages,
HistoryFlow can provide a deeper look of some in-
ternal situations concerning content persistence, like
conflicts.
The analysis of these two case studies intent is not
to be comparative. Each of them present a different
scenario (problem-based versus project-based learn-
ing), but can share a common assessment method.
There is a long way ahead, but usual skills demanded
in collaborative and cooperative learning process can
be assessed, like work effort, distribution and collab-
oration, authority or conflict.
Next academic year, the two experiences will be
repeated again, developing new projects. We will try
to use StatMediaWiki to detect students with an early
peak in contributions and help them not abandoning
the course. Besides, a course on Operating Systems
Administration is planned to include a double-level
peer-assessment on a wiki (i.e., students assess each
other and those assessments are in turn assessed by
teachers). It is a compulsory course, so the number of
students can be quite high, and it can produce inter-
esting results.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded by the PAIDI programme
of the Andalusian Government, ASCETA project
(P09-TIC-5230); and Proyectos de Innovaci
´
on Ed-
ucativa Universitaria del Personal Docente e Inves-
tigador programme of the University of C´adiz and
the Andalusian Government, project “Empleo de tec-
nolog´ıas colaborativas Web 2.0 para fomentar el tra-
bajo en equipo del alumnado” (code PIE-101).
REFERENCES
Barootchi, N. and Keshavarz, M. H. (2002). Assessment
of achievement through portfolios and teacher-made
tests. Educational Research, 44(3):279–288.
Boud, D. (2007). Reframing assessment as if learning were
important. In Boud, D. and Falchikov, N., editors,
Rethinking Assessment in Higher Education. Learning
for the longer term, pages 14–25. Routledge, London.
Cubric, M. (2007a). Using wikis for summative and forma-
tive assessment. In Re-Engineering Assessment Prac-
tices (REAP) International Online Conference.
Cubric, M. (2007b). Wiki-based process framework for
blended learning. In Proceedings of the 2007 inter-
national symposium on Wikis, pages 11–24.
LEARNING-ORIENTED ASSESSMENT OF WIKI CONTRIBUTIONS - How to Assess Wiki Contributions in a Higher
Education Learning Setting
85

de Pedro, X. (2007). New method using wikis and forums to
evaluate individual contributions in cooperative work
while promoting experiential learning: results from
preliminary experience. In Proceedings of the Inter-
national Symposium on Wikis, pages 87–92. ACM.
Dodero, J. M., Rodr´ıguez-G´omez, G., and Ibarra-S´aiz,
M. S. (2009). An´alisis de las contribuciones a un wiki
para la evaluaci´on web de competencias. In I Confer-
encia Iberoamericana sobre Tecnolog´ıas del Apren-
dizaje.
Falchikov, N. (2005). Improving Assessment Through Stu-
dent Involvement. Practical solutions for aiding learn-
ing in higher and further education. RoutledgeFalmer,
London.
Fallows, S. and Steven, C. (2000). Building employa-
bility skills into the higher education curriculum: a
university-wide initiative. Education and Training,
42:75–82.
Inselberg, A. and Dimsdale, B. (1990). Parallel coordinates:
a tool for visualizing multi-dimensional geometry. In
VIS ’90: Proceedings of the 1st conference on Visual-
ization ’90, pages 361–378, Los Alamitos, CA, USA.
IEEE Computer Society Press.
Jaksch, B., Kepp, S., and Womser-Hacker, C. (2008). Inte-
gration of a wiki for collaborative knowledge develop-
ment in an e-learning context for university teaching.
In HCI and Usability for Education and Work, volume
LNCS 5298, pages 77–96. Springer, Berlin/Hidelberg.
Liu, B. and He, H. C. W. (2008). Wiki-based Collaborative
Learning: Incorporating Self-Assessment Tasks. In
Proceedings of the 2008 international symposium on
Wikis, pages 11–24.
Louridas, P. (2006). Using wikis in software development.
IEEE Software, 23(2):88–91.
Ortega, F., Gonz´alez-Barahona, J. M., and Robles, G.
(2007). The top-ten Wikipedias - A quantitative ana-
lysis using WikiXRay. In Filipe, J., Shishkov, B.,
and Helfert, M., editors, ICSOFT (ISDM/EHST/DC),
pages 46–53. INSTICC Press.
Rodr´ıguez, E. J. et al. (2010). StatMediaWiki.
http://statmediawiki.forja.rediris.es.
StatMediaWiki (2010). StatMediaWiki real-time demos.
http://osl.uca.es/statmediawiki.
Trentin, G. (2008). Using a wiki to evaluate individual con-
tribution to a collaborative learning project. Journal
of Computer Assisted Learning, 25(1):43–55.
Vi´egas, F. B., Wattenberg, M., and Dave, K. (2004). Study-
ing cooperation and conflict between authors with his-
tory flow visualizations. In Dykstra-Erickson, E. and
Tscheligi, M., editors, CHI, pages 575–582. ACM.
Walvoord, B. E. and Anderson, V. J. (2009). Effective Grad-
ing: A Tool for Learning and Assessment in College.
Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, CA, 2nd edition.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
86
