
REAL TIME FALL DETECTION AND POSE RECOGNITION
IN HOME ENVIRONMENTS
Jerry Aertssen, Maja Rudinac and Pieter P. Jonker
Delft Biorobotics Lab, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands
Keywords: Action recognition, Motion detection, Shape descriptors, Home monitoring, Application in elderly care.
Abstract: Falls are one of the major obstacles for independent living of elderly people that can be severally reduced
introducing home monitoring systems that will raise the alarm in the case of emergency. In this paper we
present an inexpensive and fast system for fall detection and dangerous actions monitoring in home
environments. Our system is equipped only with a single camera placed on the ceiling and it performs room
monitoring based on the motion information. After background subtraction, motion information is extracted
using the method of Motion History Images and analysed to detect important actions. We propose to model
actions as the shape deformations of motion history image in time. Every action is defined with the specific
shape parameters taken at several moments in time. Model shapes are extracted in offline analysis and used
for comparison in room monitoring. For testing, we designed a special room in which we monitored in
various environmental conditions a total of four different actions that are dangerous for elderly people:
“walking”, “falling”, “bending” and “collapsing”. Obtained results show that our system can detect
dangerous actions in real time with high recognition rates and achieves better performance comparing to the
state of the art methods that use similar techniques. Results encourage us to implement and test this system
in real hospital environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
The amount of elderly people will strongly increase
during the next decennia. The strong increase of
elderly people has some social effects especially on
healthcare and elderly care. There is a large trend in
the displacement of elderly care from healthcare
institutes to healthcare at home. Prevent care on
elderly is done in order to keep elderly home and
independent as long as possible. Falls in elderly
population are large hazard for their health and
produce high costs for social system as well. Almost
half of the fall incidents occurre in elderly houses
and can be prevented by an adequate monitoring
system. There are lots of different factors that
increase the chance of fall incidents (Kannus et al,
2005
). Because of the decreasing muscle force and
movement speed due to the aging, it is harder to
keep the body balanced. Besides that, the reaction
time decreases which result in reduced ability of
elderly person to judge dangerous situations in time.
Current systems for fall detection and prevention
that are implemented in healthcare are not able to
detect multiple dangerous situations and falls
without the help of extra electronic devices mounted
on the person. And more problems arise when there
are multiple persons inside one room (Close et al,
1999).
The goal of our research is to design an
intelligent camera system able to detect multiple
actions and falls during day and nighttimes using
only one camera. The system must work real time
with the intended goal to implement this technique
into an embedded system. The monitoring system
should be designed in such a way that it warns an
elderly person on the dangerous pose or action that
he or she is performing and to alert the medical
services in the case that actual fall occurs. In this
paper, we propose such a system for action
recognition that uses a webcam mounted on a ceiling
pointing directly down, in order to create a top view
image. In this way cluttered scenes are brought back
to a minimum and there is a clear distinction
between different poses. For testing, we designed a
test room that will simulate house environment for
acquiring our data. The data used for this research is
captured during daytime with different illumination
conditions. In total we observed 4 actions
“Walking”, “Bending”, “Falling” and “Collapsing”
(very slow falling) that were performed by multiple
people differing in size and wearing different
409
Aertssen J., Rudinac M. and P. Jonker P..
REAL TIME FALL DETECTION AND POSE RECOGNITION IN HOME ENVIRONMENTS .
DOI: 10.5220/0003326504090414
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2011), pages 409-414
ISBN: 978-989-8425-47-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
clothing in order to create a realistic dataset. In
further text we will describe the methods that we
used to design our system.
In section two we discuss the related work which
already has been done in this field of work. Section
three describes the methods form motion detection
that we used to describe actions. Chapter four
explains how the actual system is working and how
the actions are detected while Chapter five shows
the results and gives the conclusion.
2 RELATED WORK
Several different techniques and systems were
proposed recently that detect dangerous poses or
falls of humans inside a room. Most of those
systems make use of accelerometers which detect
abnormal accelerations and trigger an alarm. One of
the approaches is based on the wearable systems
which are able to detect falls. (Zhang et al, 2006)
uses a non-negative matrix factorization method for
feature extraction. The major advantage of this
method is the accuracy of detecting a fall, but the
major disadvantage is the fact that people have to
wear these devices which results in discomfort. This
might cause that after some time the devices will be
left a side by the user and a fall will not be detected.
Recently, some researchers proposed to detect
falls using camera systems. They use single camera
to analyze moving object by background subtraction.
To detect a fall, the measurements of the length
width ratio of the bounding box are calculated. Their
results show that this approach works well and that it
is able to detect different poses when the camera is
placed sideways (Tao et al, 2005) and (Anderson et
al, 2006). However, such approaches experience a
lot of problems due to occlusions from objects inside
of the room.
Other researchers propose to use 3D cameras in
order to get specific coordinates of the human inside
of the room with respect to the floor (Diraco et al,
2010). This approach proved to have nice results but
because of the use of 3D cameras, it is very
expensive for the healthcare home environment
where you will need multiple cameras to cover all
the rooms. (Nait-Charif and McKenna, 2004)
proposed a system which uses only a single
omnidirectional camera with a wide angle lens
placed on the ceiling. This approach reduces the
cluttering scenes and can be used to detect multiple
objects in the room to define safe regions. Falls were
detected using the ratio between the bounding
ellipses. However the main drawback is that they
are using ratio information which is not sufficient
for multiple pose detection and multiple action
detection that we would like to perform.
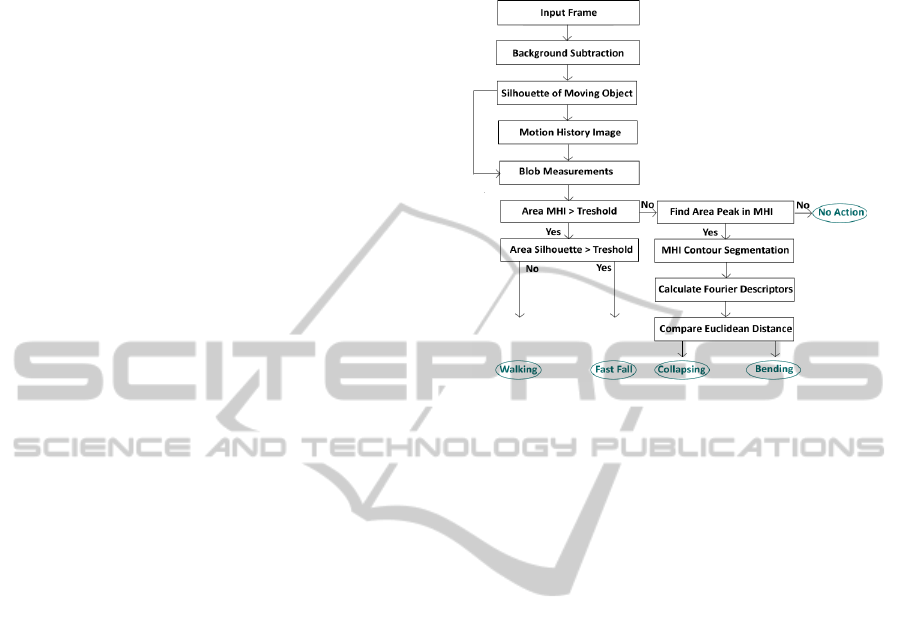
Figure 1: Proposed system for action detection.
3 MOTION DETECTION
We can define actions as the change of the motion in
time. In our method we propose to describe all the
events (or motion changes) belonging to a certain
action using only a single image, which can be
further modelled using a specific shape descriptor.
In that way every action is uniquely described with
its representative shape models. Such a method
requires several steps, and they are explained in
more detail in the next chapters.
3.1 Background Extraction
In order to analyze the action in a certain frame first
step is to detect the motion change by removing the
background information. There are many different
methods to segment the background but the easiest
way is to use Frame Differencing. The major
advantage of this method is its simplicity and fast
computation so it can be applied in real time
applications. Another advantage is that it does not
require any prior processing and it is independent of
the environmental conditions, such as the specific
room type or illumination conditions. However,
motion segmentation using this method is very
coarse and dependant on the shadows in the scene.
To eliminate these effects and acquire more accurate
results we applied Doubled Frame Differencing.
After capturing three successive frames in a video,
two separate difference images (‘t-1’ and ‘t’) and (‘t
VISAPP 2011 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
410

‘ and ‘t+1’) are generated. These difference images
are now binarized and summed up using the “and”
operation. The resulting image is now the binary
Double Difference Image (DDI). In order to further
improve segmentation results, morphological
filtering is performed on the DDI image. The
resulting image is called “Silhouette of moving
object” in further text.
3.2 Motion History Images
Now we need to capture the sequence of motion
change (DDI images) belonging to the one action in
a single image. For that we apply the method of
Motion History Images (MHI) (Bobick and Davis,
2001). Basic idea is to model the motion by
accumulating intensity changes of pixels. Now we
can define the intensity as a function of the temporal
history of motion at that point. The MHI at time t is
calculated according to Equation 1, where D(x,y,t)
represents DDI image at time t and pixel position
(x,y). The variable τ represents the duration of
movement, in consecutive frames, and MHIτ (x,y,t)
temporal history of motion at point (x,y,t) occurring
during the τ frames.
{
(, ,)
max( 0, ( , , 1) 1)
MHI x y t
MHI x y t
τ
τ
τ
=
−−
(, ,) 1fDxyt
Otherwise
i =…
(1)
Resulting MHI is now a scalar valued image where
more recently moved pixels appear brighter as can
be seen on Figure 3. Such MHI is useful for our
application since we only need to know the shape
and location of the motion change, not the direction.
3.3 Area Measurements
During movement the silhouettes generated from the
DDIs are changing. Therefore also the MHI changes
during time. We propose to describe the action by
analyzing this change of the MHI. We focused on
two different measurements, the area change and the
shape change.
In every moment t, we now define and measure
two parameters: the Area of the Individual
Silhouette (from DDI image) and the Area of the
MHI. Since both images are binarized, the area is
calculated as the sum of all positive pixels in that
image. Now we can measure the differences in the
area through time which proves to be very useful for
“fall” and “walking” detection. Detailed explanation
of the detection method follows in the section
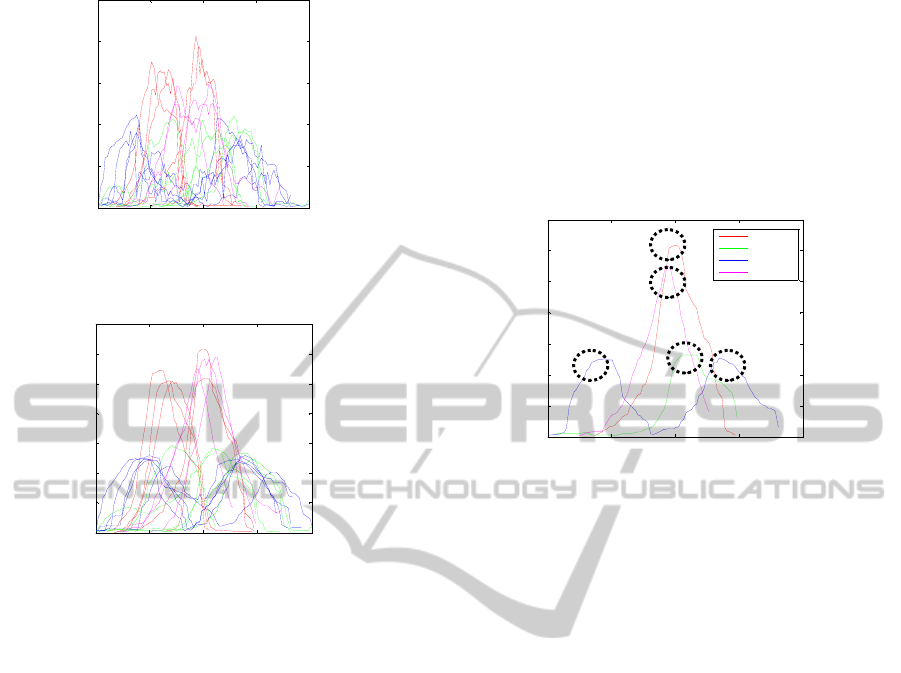
Action recognition. Results of the area changes for
specific actions are presented in Figure 2a and
Figure 2b.
3.4 Shape Measurements
As we already described, we measure the change of
the shape of the MHI. At first a contour of a MHI is
generated, and afterwards described using Fourier
Descriptors. The major advantage of using Fourier
Descriptors is because of their invariance on
translations, rotations and scale. The contour of a
silhouette is described in the frequency domain in
such a way that the lower frequencies describe the
general contour of the silhouette while the higher
frequencies describe the fine detail of the contour. In
our application fine details of the contour are not
useful for global contour discrimination. Therefore
only a subset of the Fourier Descriptors is sufficient
to describe the global contour of the silhouette. This
reduces the dimension of the descriptors and
increases the speed, which is a big advantage for
applying it real time.
For a given contour s(t) which is normalized to N
points, the discrete Fourier transform is given by
Equation (2)
2
1
0
1
( )e , 0,1,..., 1
jnt
N
N
d
t
Fst nN
N
π
−
⎛⎞
−
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
=
=
=−
∑
(2)
This results in a vector of complex numbers where
the magnitude of the descriptors is divided by the
magnitude of the second descriptor in order to apply
scale normalization. This results in:
1
2
11 1
3
, ,...
N
d
d
d
d
dd d
F
F
F
F
FF F
−
⎡
⎤
=
⎢
⎥
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
(3)
Scale invariance is now obtained by dividing the
magnitude values of FDs by the Fd
0
component.
After that the first descriptor Fd
0
is discarded since it
only gives information about the position of the
contour and it is not describing the contour itself.
(Zhang and Lu, 2001).
Shape descriptors are used to model the specific
actions by describing the change of the MHI of that
action. Detailed explanation of modelling and
detection of different actions follows in next section.
REAL TIME FALL DETECTION AND POSE RECOGNITION IN HOME ENVIRONMENTS
411
0 50 100 150 200
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
x 10
4
Frame Nr
Arrea of the Silouethe
Ac tion trigger peaks
Figure 2a: Change of the “Area of Silhouette” for different
actions in different conditions.
0 50 100 150 200
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
x 10
4
Frame Nr
MHI Area
Action Trigger Peaks
Figure 2b: Change of the “Area of MHI” for different
actions in different conditions where: “Red – falling”;
“Pink – walking“; “Green – collapsing” and “Blue –
bending”.
4 ACTION RECOGNITION
We now combined the methods described in section
3 in order to make a fast, reliable and efficient action
detection system. The scheme of this detection
system can be found in Figure 1.
4.1 Action Triggering
As can be seen in Figure 2, we first apply the
background subtraction using Double Frame
Differencing to obtain the Silhouette of moving
object. Using this image, we now calculate the Area
of the silhouette image and the Area of motion
history image, as explained in previous section.
When a person is performing one of the actions we
want to detect, we can observe a large increase of
both the Area of silhouette and the Area of motion
history image. Once the action is finished this area
will decrease, which results in area peaks of the
silhouette and motion history image. These peaks
define when an action has happened and when to
analyze it and are referred to as Action Trigger
Peaks and are shown in Figure 3.
The Action Trigger Peak is found by subtracting
the Area at time t and time t-1 checking the resulting
value. The positive or negative resulting value
corresponds to an ascending or descending slope, as
defined in Equations 4 and 5.
() ( 1)
() ( )
Area t Area t
Slope t MHI MHI
−
=−
(4)
(1)0& ()0Slope t Slope t Peak t
−
><→=
(5)
Figure 3: The Action Trigger Peaks.
4.2 Fall and Walk Detection
We generated our data in a home environment where
all actions are performed under different
illumination conditions and by multiple people
wearing different clothes. Analyzing the Action
Trigger Peaks of the MHI Area of the different
actions, we observed that the average maximum
“Falling” and “Walking” values exceed the
“Bending” and “Collapsing” values by 20% (Figure
2b) .This is used to define the Area MHI threshold.
Further analyzing the Action Trigger Peaks of the
Area of Silhouettes, we observed that the average
maximum values of “Falling” actions exceed the
average maximum “Walking” value with 15%
(Figure 2a). This is used to define the Area
Silhouette threshold. Combining these two
thresholds we can distinguish between “Walking”
and “Falling”. What is important to notice is that
both of these thresholds are learned from manually
labelled training data by comparing differences in
area values. These thresholds are then applied on
the testing data, to detect the “Fall” and “Walking”
actions.
4.3 Action/Pose Models
Another way to describe a change in the motion
history image is by shape descriptors. We now
model an action using an exact shape of the MHI
that occurs in the peak of that action. For every
0 50 100 150 200
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
x 10
4
Frame Nr
MHI Area
Action Trigger Peaks
Falling
Walking
Bending
Collapsing
VISAPP 2011 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
412
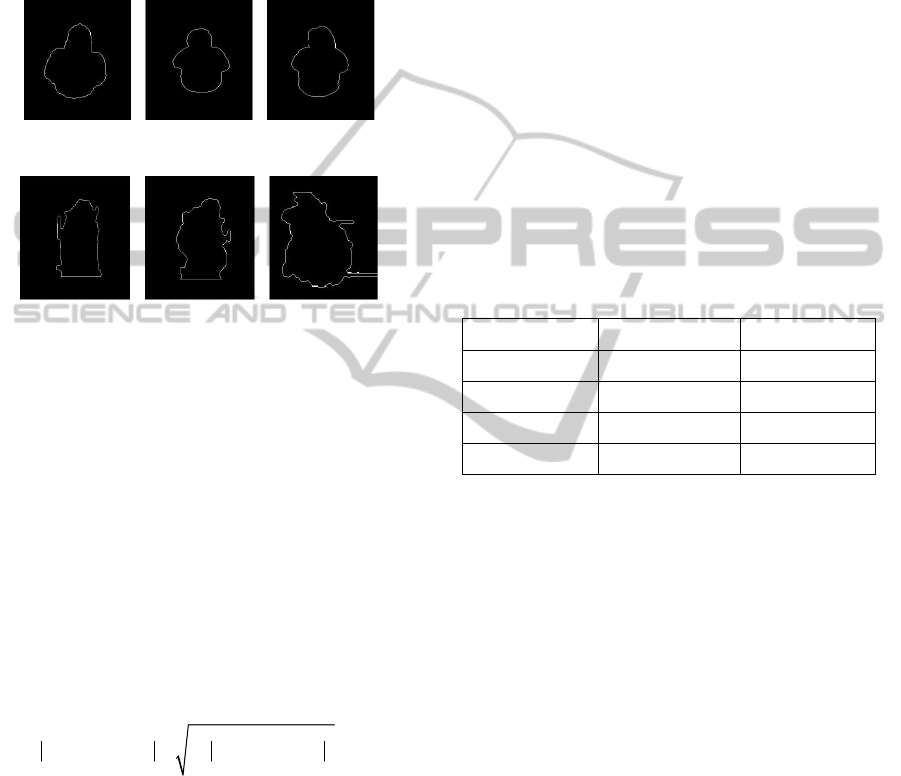
specific action the training data is analyzed and at
the Action Trigger Peak, a contour segmentation is
performed on the MHI. On this contour we calculate
the Fourier descriptors and save them as a model for
the specific action. Examples of such models can be
found in Figure 4, where is clearly visible that same
actions performed by different people in a different
conditions preserve same shape information.
Figure 4a: Models for the action “Bending”.
Figure 4b: Models for the action “Collapsing”.
4.4 Bend and Collapse Detection
For all the actions in the training data, we extracted
the action models in an offline step and formed the
database. In an online step, when we want to detect
certain action, we first search for an Action Trigger
Peak to detect the action culmination. Once it occurs
and the Area value is below the Area MHI threshold
(which eliminates “Walking” or “Falling” actions),
model of that action is extracted using the Fourier
Descriptors. Now to recognize which action it is, we
compare the extracted model (FD
contour
) with all the
models from the database. For comparison the
Euclidian distance is used. As defined in the
Equation (6).
2
mod mod
1
N
contour el contour el
i
dFDFD FDFD
=
=−= −
∑
(6)
Since Action Trigger Peak lasts several frames,
for the final classification of an action all the frames
from the specific Action Trigger Peak are compared
with the predefined models. At every frame the
votes for the two best matching models, with the
smallest distance are saved. We now apply the
voting scheme and the model (action) with most
votes is considered as detected.
5 TESTING AND RESULTS
For the purpose of this research we designed a
special testing room, with the web camera mounted
on the ceiling to generate a top view image. We used
this setting since it is independent of the motion
direction angle while providing visibility of the
entire room. We recorded in total 52 movies
containing all the dangerous actions that elderly
person can perform: Walking, Bending, Collapsing
and Falling. All data is recorded in a standard room
during daytime under different illumination
conditions. For the multiple action data another 16
movies were recorded using the same conditions. To
make our testing more robust, we used in total 4
different subjects who all differ in height and wear
different clothes. We trained our data on 5 randomly
selected movies with only single actions (or 10% of
all data) Results are presented for the testing data of
both single and multiple action movies.
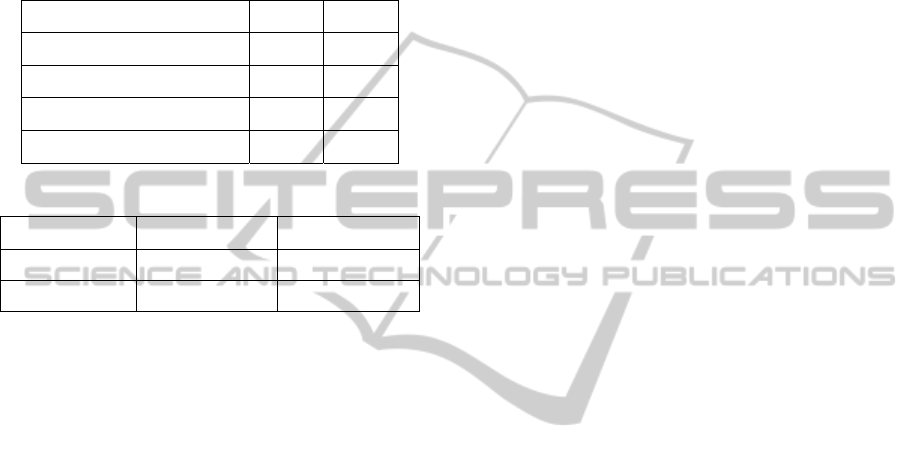
Table 1: Single Action Results.
Action Precision Accuracy
Walking 100,00% 100,00%
Falling 100,00% 100,00%
Collapsing 91,67% 95,83%
Bending 91,67% 95,83%
Table 1 shows the results of the data containing
only one single action. The actions “Walking” and
“Falling” are with all the data correctly classified
using only the Area information of the MHI and the
Area of individual Silhouette. The actions
“Collapsing” and “Bending” have a slightly lower
precision and accuracy. Confusion matrix shows that
these two actions are both misclassified with each
other. The reason for misclassification is the fact that
when a human collapses to the ground it sometimes
first bends over which will be classified as bending
and not as collapsing. Even though the bending
action shows some clear models constructed form
the Fourier Descriptors, there is a small chance that
“Bending” and “Collapsing” are misclassified.
In normal daily activity multiple actions can
happen after each other which might make
classification of an action a more challenging task.
Table 2 shows the results of these multiple task. The
results show that the action “Walking followed by
Falling” is classified correctly in all the data. This is
caused by the fact that the calculations of the MHI
Area and the Silhouette Area are very stable and
clearly distinguish from other actions. Combining
the other two action who make use of the models
REAL TIME FALL DETECTION AND POSE RECOGNITION IN HOME ENVIRONMENTS
413
from the Fourier Descriptors, the Precision seems to
drop to 83,33%. This is mainly caused by the fact
that the MHI contour during “Bending” still contains
information of the Walking silhouettes. This extra
information changes the contour of the MHI
contour. This change in contour deteriorates the
results compared with the predefined contours of the
“Bending” en Collapsing actions.
Table 2: Multiple Action Results.
Action Precision Accuracy
Walking -> Fall 100,00% 100,00%
Walking -> Bending 83,33% 91,67%
Bending -> Walking 91,67% 95,83%
Walking - > Bending -> Collapse 83,33% 91,67%
Table 3: Single Action results for (Tao, 2006) method.
Action Precision Accuracy
Walking 80% 88,89%
Falling 75% 85,71%
If we compare our results with the state of the art
we outperform other techniques based on the
bounding box ratio. Table 3 shows the results using
the bounding box ratio principle as used in (Tao et
al, 2005) and (Anderson et al, 2006) on our dataset.
The actions “Walking” and “Falling” are being
detected but with a drop in precision and accuracy,
while the actions “Bending” and “Collapsing”
couldn’t be detected on our dataset at all. Using only
the bounding box ratio proved not to be successful
on our dataset, but since it shows that in some cases
falling and walking can be detected, the combination
of using the bounding box ratio together with our
method can be promising. If we look at the other
methods such as the wearable devices discussed by
(Zhang et al, 2006), we achieve slightly better
performance on a very similar dataset but these
devices have a drawback that patients need to wear
them all the time which is very uncomfortable.
Regarding speed, our system achieves real time
performance.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The research presented in this paper is related to
human fall detection and the detection of different
actions that can be dangerous for elderly people. Our
main goal was to design a system which can work in
real time applications and reduce the implementation
costs by using only one web camera. Our system is
able to detect and distinguish different actions by
using a size and shape information of the motion
history image that characterizes certain action. It
outperforms other methods based on background
subtraction and pose recognition using silhouette
information. It also gives very high fall detection
results, works in real time and is very inexpensive to
implement. For further development we plan to
implement it in an embedded system and test it in
different nursing home environments.
REFERENCES
Anderson, D., Keller, J.M., Skubic, M.; Xi Chen;Zhihai
He, (2006). Recognizing Falls from
Silhouettes. Engineering in Medicine and Biology
Society, EMBS '06, 28th Annual International
Conference of the IEEE , vol., no., pp.6388-6391
Bobick, A. and Davis, J. (2001). The recognition of human
movement using temporal templates. In IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, volume23, pages257–267.
Close, J. Ellis, M., Hooper, R., Glucksman, E., Jackson, S.
Swift C. (1999). Prevention of falls in the elderly trial
(PROFET): a randomised controlled trial. Department
of Health Care of the Elderly, Guy's King's, and St
Thomas' School of Medicine, King's College Hospital,
London, UK.
Diraco, G., Leone, A., Siciliano, P. (2010). An active
vision system for fall detection and posture
recognition in elderly healthcare. Design, Automation
& Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE),
vol., no., pp.1536-1541.
Kannus, P., Sievanen, H., Palvanen, M., Jarvinen, T.,
Parkkari, J. (2005). Prevention of falls and consequent
injuries in elderly people, The Lancet, Volume 366,
Issue 9500, Pages 1885-1893
Nait-Charif, H., McKenna, S.J. (2004). Activity
summarization and fall detection in a supportive home
environment, Pattern Recognition, 2004. Proceedings
of the 17th International Conference on Pattern
Recognition , vol.4, no., pp. 323- 326 .
Tao, J., Turjo, M., Wong, M. F, Wang, M., Tan, Y. P.
(2006). Fall Incidents Detection for Intelligent Video
Surveillance, Information, Communications and
Signal Processing, 2005 Fifth International
Conference on , vol., no., pp.1590-1594.
Zhang, D.S., Lu, J. (2001). Comparative study on shape
retrieval using Fourier descriptors with different
shape signatures, In Proceedings of the International
Conference on Multimedia and Distance Education,
Fargo, ND, USA, pp. 1–9.
Zhang, T., Wang, J., Xuetal, L. (2006). Using wearable
sensor and NMF algorithm to realize ambulatory fall
detection, Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
Advances in Natural Computation, vol. 4222, pp.488-
491.
VISAPP 2011 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
414
