
PROPOSAL FOR OPEN DISCUSSION
Informatics Challenges for Next Generation Sequencing Metagenomics
Experiments
Folker Meyer
1,2
and Nikos Kyrpides
3
1
Argonne National Laboratory, 9700 S. Cass Avenue, Argonne, IL, 60439, U.S.A.
2
University of Chicago, 5801 South Maryland Avenue, Chicago, IL 60637, U.S.A.
3
DOE Joint Genome Institute, 2800 Mitchell Drive, Walnut Creek, CA 945987, U.S.A.
Keywords: Metagenomics, Next gen Sequencing, Democratization of Sequencing.
Abstract: With DNA sequence data production no longer the bottleneck in microbial studies, a rapidly increasing
number of researchers from diverse areas of interest can now use metagenomic tools to study their environ-
ment of interest. The large quantities of sequence data becoming available are posing significant challenges
to the existing analysis tools and indeed to the community providing analysis portals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Direct sequencing of environmental DNA (aka “me-
tagenomics”) has been ongoing for several
years(Tyson et al., 2004), (Bentley et al., 2008),
(Venter et al., 2004), (Margulies et al., 2005),
(Williamson et al., 2008). These types of experi-
ments were enabled by breakthroughs in DNA se-
quencing technology that lowered the cost for ob-
taining large quantities of DNA reads. Similar to the
sequencing cost for the human genome costs for
sequencing metagenomic DNA have been dropping
dramatically since the early 2000s. Data analysis for
complex microbial assemblages has proven to be
one of the key component of any metagenomic ex-
periment, leading to the development of a number of
software packages and several portals offering anal-
ysis, data integration and visualization (McHardy et
al., 2007), (Yooseph et al., 2007).With the advent of
next generation sequencing (Wilkening et al., 2009),
(Stein, 2010) data analysis for metagenomic data
sets became even more difficult. Existing tools are
not efficiently working since reads got shorter and
more abundant (see e.g.(Qin et al., 2010)) and com-
putational requirements grew dramatically (Meyer et
al., 2008). The length of reads went from an 700-
900bp of Q20 reads with Sanger sequencing to 75-
150bp for Illumina reads or about 450bp for 454
reads.
While only five years ago, data sets of several
million base-pairs (MBp) were considered disruptive
(take as an example the debate (Bentley et al.,
2008)). Data sets of this size can now be created
with a single instrument run of e.g. a Roche 454
instrument (see Figure 1 for data set sizes). With
sequencing no longer the bottleneck it used to be
both in financial terms and by the fact that few cen-
ters were capable of creating “large” data sets, the
metagenome analysis ecosystem undergoing change.
2 METAGENOME DATA
Data Set Sizes grow rapidly (see Figure 1) and are
outpacing the growth of computing equipment. As
stated frequently by many authors, the growth trajec-
tories of computing equipment and sequencing tech-
nology show dramatic differences, computing capa-
bilities doubling every 18 month and sequencing
roughly doubling every 5-6 months (for a recent
discussion see:(Seshadri et al., 2007)).
The Number of Data Producers Grows as well.
The long discussed democratization of sequencing
has finally arrived, allowing new individual insti-
tutes and universities to generate large scale se-
quencing data that just recently could be produced
only from large sequencing facilities.
If 10 sequencing machines could be dedicated to
global metagenomic sequencing, with the current
state of the art technology of 200 gigabases (Gb) in
around 10 days, we will be able to get 200 Gb of
metagenomics sequences per day.
363
Meyer F. and Kyrpides N..
PROPOSAL FOR OPEN DISCUSSION - Informatics Challenges for Next Generation Sequencing Metagenomics Experiments.
DOI: 10.5220/0003334203630366
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (Meta-2011), pages 363-366
ISBN: 978-989-8425-36-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Data set sizes grow exponentially. Over time for Illumina Solexa platform (red) and stay stable for the Roche 454
platform.
An influx prior to the advent of metagenomic data
of that magnitude is likely to overwhelm the arc-
hives (SRA and Genbank and their international
companions), which are struggling to keep up with a
few big centers submitting large data quantities, it
also represents demands on the analysis providers
mentioned above that are beyond their capabilities.
Even to this day the current analysis portals do
not provide an integration of the data from the Me-
tahit project (Qin et al., 2010). Published in early
2010, the MetaHit project produced 500 GBp of
metagenomic data for gut microbial communities
that will be an important resource for other research-
ers studying the human gut. However integrating
even one single large experiment is proving to be a
major challenge to the existing systems.
With the advent of the latest generation of se-
quencing instruments, even smaller centers have the
ability to produce data sets of that size within two
weeks. It is just the analysis bottleneck that prohibits
widescale adoption of large shotgun metagenomics
projects for many areas of research.
The argument made here is speculative in that we
predict a certain number of sequencing instruments
to be dedicated to running metagenomics experi-
ments, however past submission history of our exist-
ing analysis portals MG-RAST and IMG/M can
serve as evidence for the growing adoption of next
generation sequencing (see Figure 2 below).
Figure 2: Number of data sets is growing fast (red) and the
number of groups submitting is also rising (blue).
Analysis Cost Dominates the overall experimental
costs. As shown by (Meyer et al., 2008) the cost of
running sequence analysis is significantly higher
than the cost of sequencing.
Multiple Analysis Providers Re-run the initial
sequence analysis results using slightly different
tools and parameters. Driven by historical factors,
not by actual scientific need the various groups pro-
viding data portals for the metagenomics community
((Meyer et al., 2008), (Seshadri et al., 2007), (Mar-
kowitz et al., 2008)) each run separate analysis pipe-
lines, sharing significant parts of the value add
process.
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
364
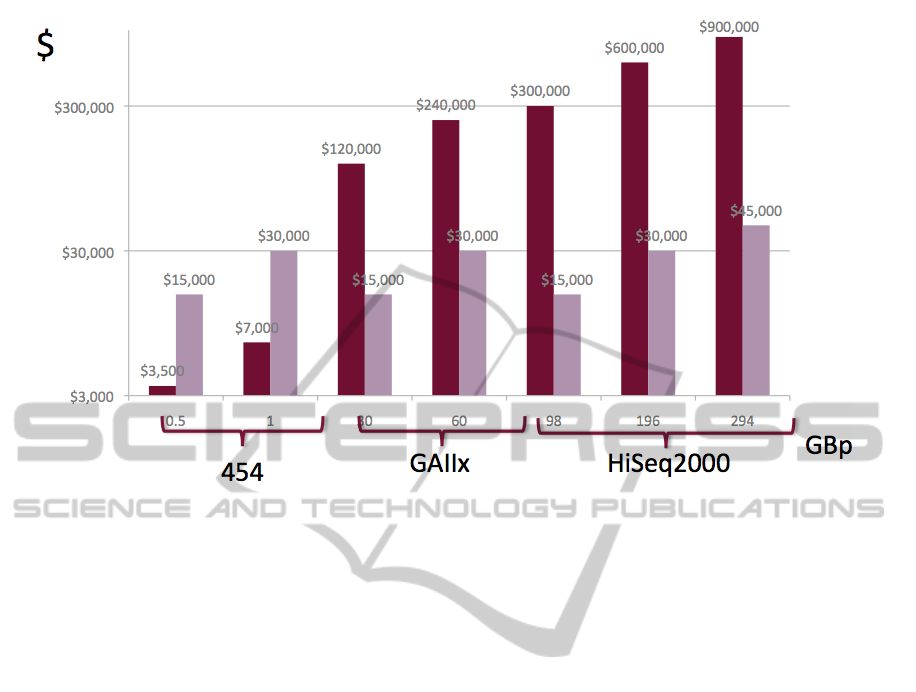
Figure 3: Computing cost dominate sequencing costs. While sequencing costs remain almost identical across platforms, the
analysis costs vary with data set sizes. The cost of sequencing compared to the cost of running BLASTX analysis. Data
from (Meyer et al., 2008) using the Amazon EC2 cloud machine as a cost model.
Given the cost of computing almost identical
analysis, sharing of results would be very desirable
at a time when significantly more data sets are being
created. However due to the aforementioned imple-
mentation details, sharing the computational results
is currently not possible.
In the current state of metagenomics, no single
tool can provide all the answers to researchers, so
submissions of data sets to multiple portals are the
norm rather than the exception. This frequently leads
to a multiple months wait time for researchers due to
the need to re-compute the basic similarity analysis.
3 METAGENOME STANDARDS
Data Standards are required to allow sharing of not
only sequence sets but also computational results. If
present these data standards would allow “instant”
access to the metagenomic views and analysis tools
provided by the other portals without incurring the
extensive cost for re-computing the analysis.
However at the current state of development
analysis provides lack the ability to even identify
data sets that have been submitted to other portals
before. The lack of experimental metadata, or better
the universal adoption of metadata standards by the
various communities producing metagenomes leads
to more or less anonymous data sets. While efforts
like GOLD (Liolios et al., 2007) provided an invalu-
able service to the community using Sanger se-
quencing to produce complete microbial genomes in
the past., the widespread adoption of metagenomic
sequencing have led to a situation where only a
subset of metagenomes is registered with GOLD.
Adoption of Metadata Standards by the com-
munity is ongoing, but the existing standards pro-
posed by the Genomics Standards Consortium (Field
et al., 2008), (Kottmann et al., 2008) are only slowly
being accepted. However with analysis providers
updating their tools to enforce metadata standards
compliance, the community of users will be guided
towards metadata standards compliance.
The standards proposed by the GSC include mi-
nimal checklists that are required of about a dozen
terms and the ability to create environmental pack-
ages that comprise many more parameters. With
these packages, specific communities e.g. medical,
soil or marine metagenomics can establish their
specific metadata sets.
Machine Readable Metadata is absolutely re-
quired in a data ecosystem that contains several
thousand data sets today and will contain several
hundred thousand metagenomic data sets in the near
future. The need for metadata goes beyond the de-
scription of sampling location and informatics anal-
ysis. While the recent discussion on the “rare bios-
PROPOSAL FOR OPEN DISCUSSION - Informatics Challenges for Next Generation Sequencing Metagenomics
Experiments
365

phere” (Huse et al., 2010), (Sogin et al., 2006),
(Reeder and Knight, 2009) has shown that informat-
ics analysis plays a significant role and can in fact
lead to significant false understanding of microbial
diversity in a given sample, a similar discussion is
already on the way regarding biome appropriate
strategies for DNA isolation and handling (Martin-
Laurent et al., 2001), (Lauber et al., 2010). Sampling
strategies and the need for appropriate biological and
technical replicates (in short statistically sound sam-
pling) are likely next-in-line discussions that the
community will have, now that the sequencing cost
are no longer prohibiting the creation of replicates.
Report Metagenomic Data Analysis is another
area that will require significant community input.
While a discussion about the pan-genome (Bentley,
2009) has clearly shown that the existing data stan-
dards are inadequate for reporting pan-genome vari-
ation. Even reporting more or less complete micro-
bial genomes extracted from metagenomic data sets
will proof to be a difficult task given the current
community standard operating procedures.
REFERENCES
Tyson G. W., Chapman J., Hugenholtz P., Allen E. E.,
Ram R. J., et al. (2004) Community structure and
metabolism through reconstruction of microbial
genomes from the environment.
Bentley D. R., Balasubramanian S., Swerdlow H. P.,
Smith G. P., Milton J., Brown C. G., et al. Accurate
whole human genome sequencing using reversible
terminator chemistry. Nature 428: 37-43.. 2008;
456(7218):53-9. PMCID: 2581791.
Venter J. C., Remington K., Heidelberg J. F., Halpern A.
L., Rusch D., Eisen J. A., et al. Environmental genome
shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science.
2004;304(5667):66-74
Margulies M., Egholm M., Altman W. E., Attiya S., Bader
J. S., Bemben L. A., et al. Genome sequencing in
microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature.
2005;437(7057):376-80.
Williamson S. J., Rusch D. B., Yooseph S., Halpern A. L.,
Heidelberg K. B., et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean
Sampling Expedition: metagenomic characterization
of viruses within aquatic microbial samples. PLoS
ONE 2008:3: e1456.
McHardy A. C., Martin H. G., Tsirigos A, Hugenholtz P,
Rigoutsos I. Accurate phylogenetic classification of
variable-length DNA fragments. Nature methods.
2007;4.
Yooseph S., Sutton G., Rusch D. B., Halpern A. L.,
Williamson S. J., et al. (2007) The Sorcerer II Global
Ocean Sampling expedition: expanding the universe of
protein families. PLoS Biol (1):63-72.
Wilkening J., Wilke A., Desai N., Meyer F., editors. Using
Clouds for Metagenomics: A Case Study IEEE
Cluster; 2009; New Orleans: IEEEE.
Stein L. D. The case for cloud computing in genome
Informatics. Genome Biology. 2010;11(5.):207.
PMCID: 2898083.
Qin J., Li R., Raes J., Arumugam M., Burgdorf K. S.,
Manichanh C., et al. A human gut microbial gene
catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing.
Nature. 2010;464(7285):59-65.
Meyer F., Paarmann D., D'Souza M., Olson R., Glass E.
M., Kubal M, et al. The metagenomics RAST server -
a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and
functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC
Bioinformatics BMC bioinformatics [electronic
resource]. 2008;9: 386. PMCID: 2563014.
Seshadri R., Kravitz S. A., Smarr L., Gilna P., Frazier M.
CAMERA: A community resource for metagenomics.
PLoS Biol. 2007;5(3):e75. PMCID: 1821059.
Markowitz V. M., Ivanova N. N., Szeto E., Palaniappan
K., Chu K., Dalevi D., et al. IMG/M: A data
management and analysis system for metagenomes.
Nucleic Acids Res . 2008;36: (Database issue):D534-
538.8. PMCID: 2238950.
Liolios K., Mavromatis K., Tavernarakis N., Kyrpides N.
C. The Genomes On Line Database (GOLD) in 2007:
status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their
associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;
36(Database issue):D475-9. PMCID: 2238992.
Field D., Garrity G., Gray T., Morrison N., Selengut J.,
Sterk P., et al. The minimum information about a
genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nature
biotechnology. 2008;26(5):541-7. PMCID: 2409278.
Kottmann R., Gray T., Murphy S., Kagan L., Kravitz S.,
Lombardot T., et al. A Standard MIGS/MIMS
compliant XML Schema: toward the development of
the Genomic Contextual Data Markup Language
(GCDML). Omics. 2008;12(2):115-21.
Huse S. M., Welch D. M., Morrison H. G., Sogin M. L.
Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through
improved OTU clustering. Environmental micro-
biology. 2010;12(7):1889-98. PMCID: 2909393.
Sogin M. L., Morrison H. G., Huber J. A., Mark Welch D.,
Huse S. M., Neal P. R., et al. Microbial diversity in the
deep sea and the underexplored "rare biosphere". Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(32):12115-20. PMCID:
1524930.
Reeder J., Knight R. (2009). The 'rare biosphere': A reality
check. Nat Methods Nature methods. 2009;6: (9):636-
637.
Martin-Laurent F., Philippot L., Hallet S., Chaussod R.,
Germon J. C., et al. (2001). DNA extraction from
soils: old bias for new microbial diversity analysis
methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 2354-2359.
Lauber C. L., Zhou N., Gordon J. I., Knight R., Fierer N.
(2010). Effect of storage conditions on the assessment
of bacterial community structure in soil and human-
associated samples. FEMS Microbiol Lett 307: 80-86.
Bentley S. (2009) Sequencing the species pan-genome.
Nat Rev Microbiol 7: 258-259.
BIOINFORMATICS 2011 - International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
366
