
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING
∗
Anandha Gopalan
Department of Computing, Imperial College London, 180 Queens Gate, London SW7 2RH, U.K.
Spyridon Karavanis
Hellenic Army, Athens, Greece
Thomas Payne
Omnifone Ltd., Island Studios, 47 British Grove, London, W4 2NL, U.K.
Morris Sloman
Department of Computing, Imperial College London, 180 Queens Gate, London SW7 2RH, U.K.
Keywords:
Virtual learning environment, Mobile learning, e-Learning, Voice-based framework.
Abstract:
Children often attend schools intermittently in rural areas in Africa and India due to socio-economic conditions
which make pupils augment their family income by working. An e-Learning solution could aid in raising the
level of education by making it easier for children to fit schoolwork into the day, acting as a complement
to when they are able to attend school. Traditional distance learning solutions based on computers are not
suitable due to lack of infrastructure support. In this paper, we evaluate both text and voice based smartphone
prototype environments which could provide the tools and services for pupils to download educational content,
interact with teachers as well as other pupils to discuss topics. These have been implemented as a proof-of-
concept and the initial evaluation feedback, although not from target users, was very promising. We intend to
re-implement the prototype and do a proper evaluation with rural-area school children.
1 INTRODUCTION
Access to education remains an impediment to-
wards economic development of rural communities in
Africa and India. The reasons include lack of infras-
tructure, lack of teachers, poor attendance and finally
cost; the main problem among these being the low
attendance rate – (Azim Premji Foundation, 2004)
states that the gap between enrolment and attendance
is significant. Due to the prevailing socio-economic
conditions, most pupils have to work to augment the
family income, thereby affecting their ability to at-
tend classes (Jean Dr
`
eze and Geeta Gandhi Kingdon,
2001). This paper presents an interactive e-Learning
environment that would allow pupils to learn in a col-
∗
We gratefully acknowledge support from EPSRC Grant
EP/EO251881 AEDUS2: Adaptable Environments for Dis-
tributed Ubiquitous Systems.
laborative manner without constant supervision. The
proposed system will deliver content in a manner that
takes into account restrictions such as poor IT infras-
tructure, high cost of bandwidth and poor knowledge
of electronics.
To achieve this goal, the high availability of more
affordable cellular mobile devices in these areas will
be leveraged to provide interactive content via mobile
phones (Marsden, 2003; Kam et al., 2009a; Parikh
and Lazowska, 2006). Mobile phones need very lit-
tle infrastructure, are low-power devices that can be
used in places where the availability of electricity is
not very reliable and are the fastest growing technol-
ogy platform in the developing world (CNN. Weapon
against epidemics: Cell phones, 2009). In addition,
mobile phones are inherently interactive in nature, as
compared to TV and radio, so are the most suitable
technology to use to access and share content in rural
161
Gopalan A., Karavanis S., Payne T. and Sloman M..
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING.
DOI: 10.5220/0003334901610170
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2011), pages 161-170
ISBN: 978-989-8425-50-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

areas.
Our proposed e-Learning environment will pro-
vide educational content in the form of lessons, sim-
ple tests or quizzes, as well as allowing pupils to in-
teract both with teachers and their peers as they would
in a normal school environment. Connectivity cannot
always be guaranteed so the system should support
downloading educational content for the pupil to read
at a later time, and recording input from pupils to up-
load when a connection is available.
A couple of Masters student projects were used to
implement proof-of-concept systems to evaluate suit-
able implementation technology. The first project - a
Virtual Learning Environment for Mobiles (VLEM)
used an iPhone and a fairly sophisticated open-source
web-based educational system called Moodle (Moo-
dle, 2010) as the back-end for management of text
documents. The second project explored the use of
an Android smartphone for a Voice-Based Framework
(VBF) for delivery of content and interaction with
teachers and peers. This was primarily because of in-
creased familiarity with voice systems in rural areas.
The proposed methods of educational delivery and in-
teraction were intended to act as a complement (and
not a substitute) to attending school. The emphasis of
the two projects was on evaluating technology for im-
plementing such a system rather than evaluating the
effectiveness of delivering educational content using
smartphones. No real educational content was used in
the project. Both implementations were evaluated by
a few volunteers to obtain some feedback on feasibil-
ity and usability. In the future, we plan to merge the
different implementations into one to provide a com-
plete solution. The evaluation results are very encour-
aging and prove that this is a viable means of provid-
ing distance education in rural areas. We plan to in-
stall the proposed system in a village in India and run
field tests to determine the effectiveness of the sys-
tem and gather valuable data that would help improve
the overall solution. Although smartphones can be
criticised as currently being too expensive for the tar-
get environment, their development environments are
much easier to use for a proof-of-concept implemen-
tation. Given the rise of the Android open platform,
it is very likely that these smartphones will be more
affordable in developing countries within a few years.
There has been research on using mobile phones
as a means of providing information and services in
rural areas (see related work), but as far as we know,
this is the first project of its kind to try and provide
a comprehensive solution that would allow pupils in
rural areas to be able to keep up with their educa-
tion while not forsaking their livelihood. According
to the World bank, “Despite growing hype, there are
still precious few widespread examples of the use of
[mobile] phones for education purposes inside or out-
side of classrooms in developing countries that have
been well documented, and fewer still that have been
evaluated with any sort of rigor” (World Bank, 2009).
The rest of the paper is organised as follows. Sec-
tion 2 gives an overview of the proposed environ-
ment and the requirements we have identified. Sec-
tion 3 describes the text-based Virtual Learning Envi-
ronment, while Section 4 describes the Voice-Based
Framework. Section 5 provides a detailed evaluation
of the two frameworks, while Section 6 outlines areas
of future work. Section 7 outlines the related work,
while Section 8 concludes the paper.
2 AN E-LEARNING
ENVIRONMENT USING
SMARTPHONES
2.1 Overview
Figure 1 shows the overall architecture of the pro-
posed e-Learning framework. It consists of (a) a sim-
ple user interface on the phone for displaying and
recording information and (b) technology and ser-
vices at the server for content management and dis-
semination. The required content is developed using
normal workstations connected to the internet, and
delivered by the content providers (schools, educa-
tors) to the content manager. The technology for de-
veloping the content will use off-the-shelf tools that
are readily available to educators and schools. Each
school will be connected to the central server. Pupils
will use phones to access content such as available
lessons and to collaborate with peers via a forum sup-
ported by an educational portal which can easily be
extended by adding additional capabilities, such as
announcements, tests etc. To show how the proposed
framework would work, an example scenario is de-
scribed in Section 2.2.
Figure 1: System Design.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
162

2.2 Example Scenario
A teacher updates the content system with the new in-
formation based on the lessons that were used in class
during the day and also deletes any obsolete informa-
tion. A pupil living in a remote village goes about his
errands in the morning and is unable to attend school
for the day. On returning home in the evening, he uses
a mobile phone to access his classs information. The
pupil checks for any update since last access and if
any, downloads the required content on to the mobile
phone. After completing required tasks, the pupil will
have caught up with some of the material covered in
school during the day. Some material may not be ap-
propriate for delivery to a mobile phone. Queries can
be sent to his teachers, and he can ask questions or
discuss issues with his fellow pupils via the phone.
2.3 Requirements
The following requirements were identified for an e-
Learning environment:
• Content management (addition, deletion, updates)
must be easy for non-technical educators. A
widely used content management system (CMS)
is preferable, as educators may already be famil-
iar with it and the system will be maintained and
developed to keep it upto date.
• The User Interface on the mobile phone must be
intuitive, simple and easy to use. For example,
having a very elaborate user menu on the phone
to access the system may increase its complexity
and make it hard for pupils to use the system.
• The system must enable downloading content for
offline perusal and offline recording of questions,
discussions etc. by pupils for uploading when a
connection is available.
• The system must facilitate peer-to-peer discussion
between pupils as well as with teachers to simu-
late the classroom environment.
• The system must take into account bandwidth us-
age. This requires recording “changes” to the
data; only the data changed since the last request
is transferred to synchronise the phone and CMS.
• The system should facilitate peer-to-peer sharing
of downloaded content between pupils when they
come into contact with each other, using bluetooth
or wifi to reduce usage of comparatively expen-
sive cellular networks. Note that neither of the
projects had time to implement this.
• The code-base developed must be modular and
easily extensible to incorporate future additions.
3 VIRTUAL LEARNING
ENVIRONMENT FOR
MOBILES (VLEM)
The VLEM system used an iPhone and evaluated
Moodle (Moodle, 2010) as the back-end software.
Moodle is a well known open-source Course Man-
agement System, with a large user community. The
functionality is thus continuously being enhanced and
the code is well maintained. Another advantage is the
ability to send bulk data which will help in bandwidth
reduction. The iPhone was chosen for its user inter-
face. The overall architecture along with the different
components is depicted in Figure 2.
3.1 Moodle Component
The Moodle component consists of a back-end for
content storage and a workstation interface for teach-
ers and administrators, which contains all the internal
functionality to facilitate registering users, creating
and updating lessons etc. Each teacher has an account
to access Moodle and is associated with a number of
courses. A teacher uses Moodle to create the lesson,
which is stored in a MySQL database. To access this
information from outside the Moodle domain, the sys-
tem was extended in the following ways to support re-
quirements identified in Section 2: (i) implement the
external functions used by Moodle using its naming
and development conventions, (ii) add functionality
required in the workstation to support web-based ac-
cess to Moodle back-end, (iii) create a table, called
firechanges in the Moodle database to manage the
changes. This table keeps a record for each user of
what changes he has received related to his lessons,
forums etc. by labelling them with 0 (clean) for re-
ceived and 1 (dirty) for not received, (iv) create the
triggers (Insert, Delete, Update). For every table of
interest in the Moodle database we have created trig-
gers to inform the firechanges table of any change that
has been made, and (v) create the webservice external
functions to retrieve the firechanges data. After the
retrieval of the data the tables are reset to 0 and a new
request is made to retrieve the changed data.
3.2 iPhone Application Component
The iPhone Application was implemented in Objec-
tive C and Figure 3 shows its architecture. The view
module contains a main view and many sub views.
The observer module monitors the network on the
mobile phone and informs the component of the net-
work’s “connectivity”. The action module is a virtual
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING
163
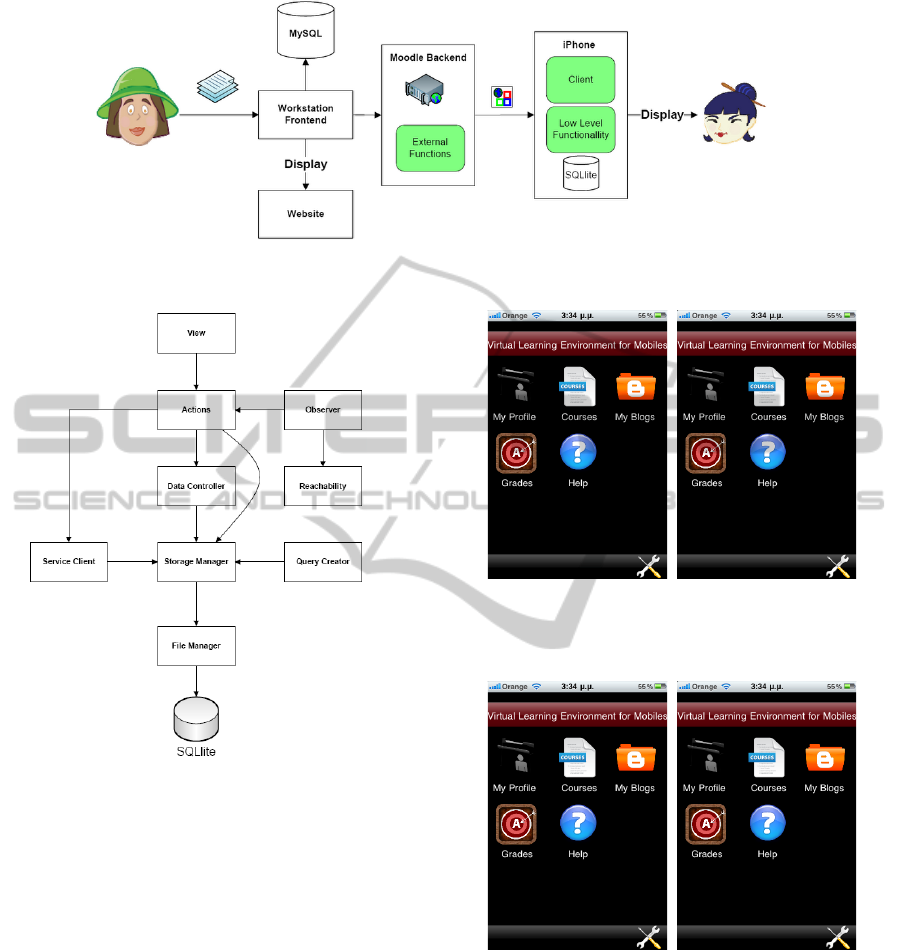
Figure 2: VLEM Architecture.
Figure 3: iPhone Application Architecture.
module that is included to ensure that proper empha-
sis is attributed to the actions performed during the
execution phase. The service client supports func-
tions to access the web service. The storage manager
sets up every database request and it uses the query
builder to create the appropriate query which needs to
be executed. All requests to the database are via the
file manager. In order to use VLEM, pupils have to
be authenticated using the iPhone application (due to
space constraints we do not go into detail).
Figures 4 and 5 show example application screens
on the iPhone. Figure 4(a) shows the starting screen
of the Virtual Learning Environment. Figure 4(b)
shows the help menu that explains the functionality of
each of the buttons. Figure 5(a) shows the list of avail-
able courses in the VLEM and choosing one of them
will bring the user to the interface shown in Figure
5(b), which gives the user the options that are avail-
able for that particular course.
(a) Main Screen. (b) Help Screen.
Figure 4: VLEM iPhone Screencaptures.
(a) List of Courses. (b) One Course.
Figure 5: VLEM iPhone Screencaptures.
4 VOICE-BASED FRAMEWORK
(VBF)
Unlike VLEM, the voice-based framework was not
meant to provide an entire e-Learning framework, but
to provide a means for pupils to gain some of the inter-
action that they are missing if they are studying from
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
164
home. The idea is for a forum where pupils will be
able to interact with their teachers and peers, asking
questions and finding out answers. Several studies
have discussed the success of voice-based mobile ap-
plications in rural areas of the developing world due
to the fact that they are so used to accessing informa-
tion and communicating orally (Parikh, 2010; Agar-
wal et al., 2009). For this reason, the forum was de-
signed and implemented as an asynchronous audio
space where pupils can post questions or comments
to teachers and listen to those of others.
While using the criteria stated in Section 2, the
available software and APIs that best suited our pur-
pose was the Android open-source OS for the mobile
phone and Django for the back-end. Android runs
on a wide variety of handsets, from top-of-the-range
devices to some at the lower end of the smartphone
market (Open Handset Alliance, 2010). Another key
reason for choosing the Android platform was the
availability of an API for sound recording. Django
was chosen since it’s a fast, extremely reliable open-
source framework that comes with a built-in modifi-
able administration interface.
4.1 Client Component
The aim of the client is to provide a simple interface to
the user that will allow them to access the information
involved in the system via the following methods: (i)
record the user’s voice as they ask their question and
save it as an audio file, (ii) browse other users’ ques-
tions and responses, (iii) filter these questions and re-
sponses based upon subject area or user, (iv) browse
responses to a particular question, and (v) post an au-
dio response to a particular question.
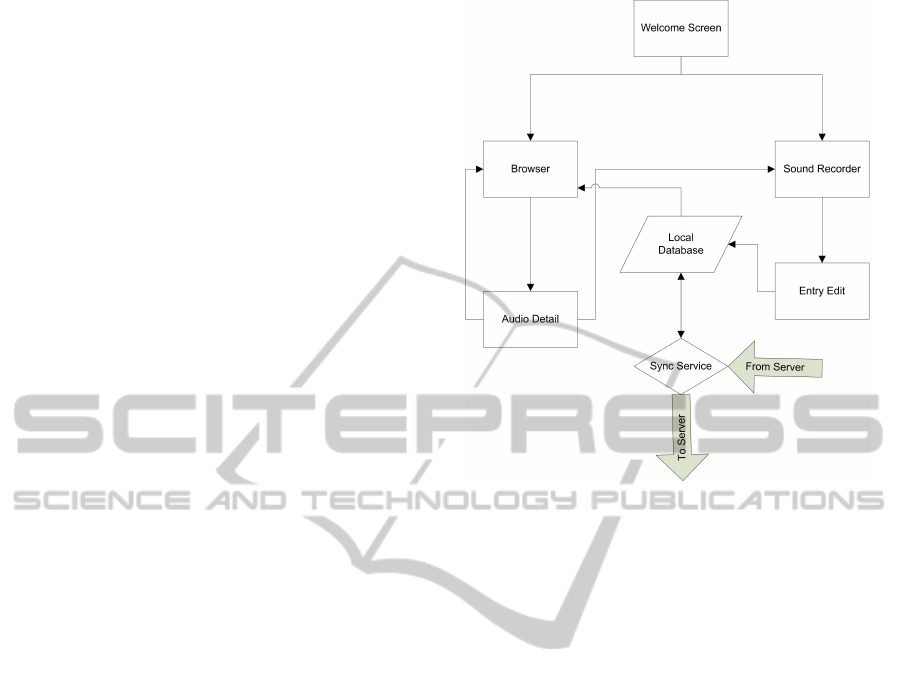
The diagram shown in Figure 6 represents a sim-
plified flow of control between the different compo-
nents of the client application. There are two main
flows from the welcome screen, either the user wants
to record a new question or they want to browse ex-
isting posts. The former takes the right-hand path
through the process of recording the audio for their
question and onto the Entry Edit activity which will
take in additional metadata from the user before sav-
ing everything to the Local Database and starting up
the Synchronisation Service. This is a background
service which synchronises the local database with
the master database on the server.
The left-hand path leads into a browser that lists
posts on the system; selecting one will take the user
into the Audio Detail activity showing more informa-
tion about the post and allowing playback. There is
an option to leave a response to the post, which takes
the user to the Sound Recorder activity.
Figure 6: Flow between components of the client.
The audio file is encoded using the Adaptive Multi-
Rate Narrowband codec, a data compression scheme
optimised for speech. It is recorded with a bitrate of
approximately 12kbit/s which is higher than the aver-
age telephone quality (8kbit/s), but still low enough to
ensure that the files will not be too large. An average
question is expected to last approximately 30 seconds
generating an audio file of roughly 45kB which even
on an early GSM network would upload in roughly
five seconds.
4.2 Server Component
The server stores and maintain all the necessary data
for the application via the following methods: (i) re-
ceive an audio file and metadata and store these in the
master database, (ii) provide metadata in a machine-
readable format about questions that are stored in the
master database, filtered by criteria such as subject
area and user, (iii) provide metadata about responses
to a particular question, and (iv) serve a specific audio
file after providing its URL.
The server has been designed to provide its func-
tionality through a RESTful (Representational State
Transfer) API above HTTP to enable it to be used by
a wide variety of potential clients. Interactions are
stateless, so any client submitting the same request
to a particular URL will receive the same response;
this means that these URLs can be bookmarked and
shared among users. This simplifies creating a new
audio post that can then be accessed and responded to
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING
165
by other clients, thus creating a thread of audio con-
versation.
The server-side components have been built based
on the model-view-controller principles, leading to a
completely modular environment with in-built sup-
port for being run in a variety of environments. The
built-in administration interface was also extended to
provide a robust web-based interface for the teacher.
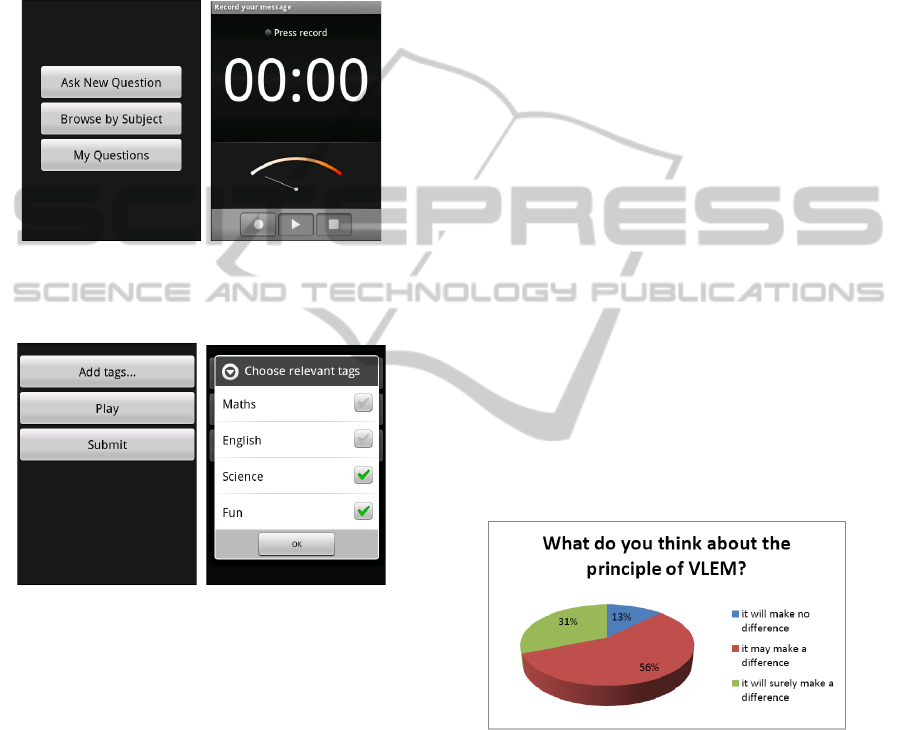
(a) Main Screen. (b) Recording Screen.
Figure 7: VBF Android Screencaptures.
(a) Options after Record-
ing.
(b) Available Tags.
Figure 8: VBF Android Screencaptures.
Figures 7 and 8 show some application screens on
the Android phone. Figure 7(a) shows the welcome
screen of the Voice-Based framework. If the user
wants to record a new question, they will be taken
to the recording interface that is provided by Android
(Figure 7(b)). After recording their question, the user
can either tag the question, play the question back or
submit it (as shown in Figure 8(a)). If the user chooses
to tag the question, a list containing the different sub-
jects is presented to them (shown in Figure 8(b)).
5 EVALUATION
5.1 VLEM
We evaluated VLEM using two approaches. In the
first approach, we conducted a survey, asking 16 users
to use the system and to fill in a questionnaire. 12%
of the users were in the age group 8-18, 63% were
between 19-35, while 25% were older than 35. In
order for the users to use the system, we created a
few lessons apriori. The users browsed the available
lessons and participated in the forums. Most of the
users were competent in the usage of a mobile phone.
The questionnaire contained personal as well as ques-
tions relating to the usability of the system. In the
second approach, we asked an educator (teaching sec-
ond grade in a school) to use and evaluate the system.
Due to the space constraints, we only present the re-
sults from the user survey, but the educator did say
“The convenience and support of the pupils is the pri-
mary goal of this application. I believe that ideas such
as this must be carried out because it will help pupils
and in general the whole education sector”.
To begin with, we wanted to evaluate the idea of
a VLEM before users actually saw the implementa-
tion. We asked users to indicate whether they thought
the concept of a VLEM was interesting or not. As
we can observe from the results in Figure 9, an over-
whelming majority thought that the idea would make
a difference in education.
Figure 9: Opinion on VLEM principle.
For the next part of the survey, we asked users to
use the application and fill in the questionnaire. Our
first concern was the impression the VLEM applica-
tion created on the users, especially after their opin-
ion about VLEM as a concept. Figure 10 shows that
the results were very promising with 25% saying that
they were very excited by the application and only 6%
saying that they were disappointed. This augurs well
for the functionality as well as the implementation.
Our next step was to find out how easy it was to
use the VLEM. Figure 11 shows that 13% found the
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
166
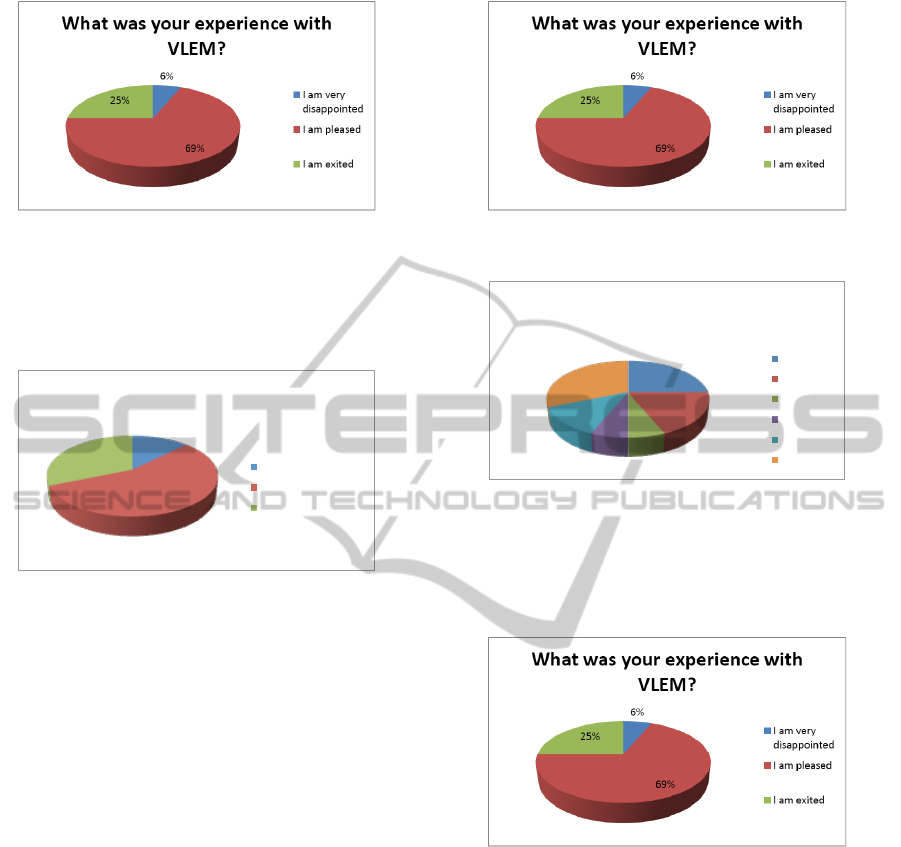
Figure 10: VLEM Experience.
application hard to use. Though this is not a very large
number, it is still not small enough to ignore. One of
the reasons for this higher number is revealed later.
13%$
56%$
31%$
How$easy$was$VLEM$to$use?$
it$was$very$hard$to$use$$
it$was$average$to$use$
it$was$excellent$to$use$$$
Figure 11: Ease of Usage.
To ascertain why some users had a more positive
experience overall as when compared to others, we
asked them which feature of the VLEM they liked
or disliked. The results for the “best features” and
“worst features” of the VLEM are shown in Figures
12 and 13 respectively. As can be seen from the fig-
ures, the best feature of the VLEM was considered to
be the forums. Users stated that forums were essential
because they enabled communication and collabora-
tion. As for the worst features, 25% of the people se-
lected the user profile. One of the reasons for this very
high number is the fact that the current system lacks
the functionality that allows a user to update his/her
profile on the iPhone. The button size was consid-
ered as the next worst feature. This suggestion was
taken into consideration and has since been incorpo-
rated into the application.
Finally, we asked the users their opinion as to
what was missing in the current implementation of
the VLEM. From Figure 14, we can see that most of
the users wished for additional functionality, such as
a library. This is a very interesting suggestion, which
will be investigated further in the future. Many others
wished for quizzes and pictures. The functionality to
support quizzes already exists (in terms of communi-
cation). As for the ability to have pictures, it may not
be feasible because of an increase in traffic. An inter-
Figure 12: Best features of VLEM.
!"#$
%&#$
'#$
'#$
%(#$
(%#$
What%do%you%believe%is%the%worst%
feature%of%the%applica5on?%
)*+,-.$
/01+2$345.$
6+*073$
-.33+23$
8)).8*829.$
2+:;42<$
Figure 13: Worst features of VLEM.
esting addition that was also suggested was having a
help menu for the buttons. As we see in Figure 4(b),
this suggestion was incorporated into the application.
Figure 14: Missing Features of VLEM.
We believe this survey was helpful in providing
a direction towards improving specific aspects of the
application. It provided us with valuable experience
concerning usability aspects and it also gave us fresh
ideas concerning implementation issues.
5.2 VBF
Nine fellow-students evaluated our Voice-Based
Framework and completed a a survey on the appli-
cation. The application was explained to the volun-
teers and each one chose to use the system as they
saw fit (a few of them adopted a passive approach
by just downloading and listening to existing infor-
mation, while others were active in posting and an-
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING
167

swering questions). This survey was structured so that
opinions could be harvested on the topics deemed im-
portant for the target audience in an attempt to coun-
teract some of the differences between the test au-
dience and the target audience. Much like the Hu-
man Access Points (HAPs) discussed in (Gary Mars-
den, Andrew Maunder and Munier Parker, 2008), the
test users have knowledge of what is possible with
technology, they just lack the cultural and contextual
knowledge that is desired from a HAP. For this rea-
son, they were given a survey to answer, after they
had used the application for a period of time, rather
than just asking for open-ended feedback. The aim of
this was to encourage them to think about the applica-
tion in terms of what has been deemed important for
the target audience based upon existing literature.
First of all the simplicity of the User Interface (UI)
was looked into and users were asked questions about
how intuitive the interface and structure of the appli-
cation was. Although most users were able to get to
the desired task without much trouble, several users
did point out that it was not always obvious what a
button would do before they pressed it. This feedback
was taken on board, and although all the buttons re-
main as they are, the layout files have been simplified
for ease of editing at a later date and plenty of screen
space has been left on most pages to allow some in-
structional text to be placed.
The next questions concerned the quality of the
audio. As might be expected, all responses to the lat-
ter question were positive, since the bitrate and qual-
ity are higher than that of a telephone call.
The users were next asked about the speed and re-
sponsiveness of the application. Although they were
using different handsets, with varying components,
they all reported that the application was very respon-
sive upon button presses. This is due to the sim-
ple interface that has been implemented and the fact
that all expensive operations are handed off to a sepa-
rate thread which will not impede the UI. Users were
specifically asked about the time taken for new posts
downloaded from the server to appear on screen after
the browser was started and what kind of network they
were connected to at the time. The results showed that
even on the slower 2G network, updates did not take
a long time (usually under 3 seconds).
Overall the test was very useful; the interface
has been made more flexible to accommodate users’
suggestions and some potential extensions have been
identified. As stated at the beginning of this evalua-
tion, the test was limited in its scope, but provides a
basis for moving forward to test the framework with
the intended audience in the future.
6 FUTURE WORK
We aim to integrate the text and voiced based systems
on one platform containing both features of VLEM
and VBF. This would be based on the use of Moodle
as we think its focus on educational content manage-
ment would prove very useful for teachers. We will
also focus on the use of Android phones as, although
the user interface development support is not as so-
phisticated as the iPhone, it is cheaper and so is more
likely to be available as a smartphone platform in the
future in developing countries
One problem with both applications occurs when
a user loses connectivity during an upload or a down-
load. In order to combat this problem, the aim would
be to break up the data being transferred into smaller
chunks that are monitored so that if the network con-
nection did fail then the transfer would only need to
be restarted from the most recent chunk of data.
One of the possible extensions of VBF is a voice
recognition system. There are a couple of ways that
voice recognition could be used to improve the func-
tionality of the framework; the first involves imple-
menting a voice-based menu system, where a user is
prompted to enter the number on the keypad. Another
area where voice recognition could really add func-
tionality to the application is in using it to create text
transcriptions of the audio posts that have been made.
With these text-based questions a decent search func-
tionality becomes a real possibility. It would also give
users the option to read the posts themselves rather
than listening or use speech synthesis to listen if they
are on a particularly slow connection and do not want
to download the audio file.
7 RELATED WORK
Mobile phones have been used for implementing ru-
ral computing applications e.g. (Derenzi et al., 2008)
presents a system for providing the IMCI (Integrated
Management of Childhood Illness) protocol using a
PDA, and (Maunder et al., 2008) provide a cost-
effective way of accessing relevant public information
by sharing it using a Bluetooth enabled camera phone.
A mechanism to interact with paper documents and
automate paper-intensive information processing for
micro-finance groups using an interface toolkit is pro-
vided in (Parikh, 2005; Parikh et al., 2006). De-
sign principles that address the challenges in design-
ing rural computing applications are outlined in (Gary
Marsden, Andrew Maunder and Munier Parker, 2008;
Parikh and Lazowska, 2006). All of the above work,
while focusing on support for people in rural areas,
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
168

does not address educational applications. Most of
the information flow is one-way and the interface used
is passive where the local community do not interact
with the system on an everyday basis.
There has been some work on using technology
for education in rural areas in Africa through a World
Bank survey (Farrell, Glen and Shafika Isaacs, 2007)
as well as the SchoolNet project (SchoolNet Africa,
2008). These differ from our approach in that they
aim to establish high quality education through the
use of Information Technology in existing schools. In
(Kam et al., 2008; Kam et al., 2009b) games (based on
traditional village games) on cell phones are used to
improve the English language skills of the children.
In (Jones and Marsden, 2004), the authors use mo-
bile phones and PDAs to allow pupils to communicate
with the lecturer during classes. This project though is
only helpful in the scenario when pupil attend classes.
The BBC Janala project (BBC Janala, 2009) uses mo-
bile phones, TV and radio to improve the English lan-
guage skills of people in Bangladesh, however there
is no feedback from users and the emphasis is on lis-
tening to spoken English over the phone. The Mo-
bilED (Ford and Leinonen, 2006) project provides a
learning and teaching environment that is enhanced
with the use of mobile technology and services. The
framework consists of an audio wikipedia that can be
accessed by pupils by sending an SMS with a key-
word and in return they get to hear the article relevant
to the keyword. Though this idea has its merits, it is
very restrictive since it assumes an advanced level of
knowledge. Although the above works uses technol-
ogy for education in rural areas, none of the projects
provide for a complete environment wherein pupils in
rural areas can learn at their own time without forsak-
ing their livelihood. Also, these projects do not allow
for collaborative learning, which is a very important
learning tool.
There has been quite a lot of work on developing
voice-based interfaces for rural areas. This is primar-
ily due to the fact that rural communities have sig-
nificantly different communication needs and patterns
as compared to urban communities (Seshagiri et al.,
2007; Kolko et al., 2007). Given the fact that people
are comfortable using telephones, a voice-based in-
terface would work very well with such communities.
(Cervantes and Sambasivan, 2008) is an audio-based
classified advert service, where users call in to post,
listen or delete an advertisement. An Audio Wiki
that acts as a repository of spoken content that can
be accessed and modified through the use of any tele-
phone is presented in (Kotkar et al., 2008). The World
Wide Telecom Web (Kumar et al., 2007) is a project
that allows people to create their own “spoken” web-
pages. Users navigate using a simple speech-based
interface and the “pages” are organised by user (akin
to a web-page). VoiKiosk(Agarwal et al., 2009) is a
voice based kiosk that provides access to information
in rural areas. This was extended in (Patel et al., 2010)
to provide a message board (coupled with some radio
broadcast) that serves small farmers and is used pri-
marily as a forum for exchanging agricultural advice.
Most of the related work mentioned above use
voice-based solutions to cater to and solve certain
problems. None of them, however cater for educa-
tion. Given the level of technology penetration in ru-
ral areas, voice-based systems offer a promising solu-
tion due to the fact that people are used to using tele-
phones. However, most of the related work tackles the
problem with respect to a particular topic and hence
both the complexity of the system and the amount of
data managed, is less. Also, having a pupil phoning
in and having to scroll to multiple questions belong-
ing to multiple topics will only add to their cost.
8 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have prototyped smartphone sys-
tems to enable e-Learning in rural areas in developing
countries such as in Africa and in India. One system
focused on text-based access to a sophisticated educa-
tional content management system, while the voice-
based system focused on supporting interactions with
teachers and other pupils. These frameworks serve a
dual purpose, with the former acting as an educational
portal that allows a pupil to be able to keep up with
their lessons at their own time, without necessarily
forsaking their livelihood, while the latter provides a
forum for interactive communication that is achieved
through voice messages (since users are more used to
using their mobile phones as a tool for calling). The
proposed systems were implemented as a proof-of-
concept and evaluated. Although the systems have
not been tested with the target audience, the frame-
work has been set up as much as possible to allow
flexibility in the interfaces. The results were very en-
couraging and some of the suggestions have been im-
plemented. We also identified areas for future work.
We are hoping to be able to deploy these systems and
test them out in the field.
The implementations were based on smartphones,
which could be criticised as being currently too ex-
pensive for developing countries. One reason for our
use of smartphones was that their development envi-
ronments are much easier to use for proof-of-concept
systems. Simpler phones do not have the ability to
display suitable learning material although they might
SMARTPHONE BASED E-LEARNING
169

be adequate for voice based-interactions. It is also
likely that the Android open platform smartphones
will drop sufficiently in cost to be affordable in de-
veloping countries within a couple of years. Though
the motivation for this work was for e-Learning in ru-
ral areas in developing countries, the ideas suggested
can also be used to enhance learning experiences in
developed countries.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, S., Kumar, A., Nanavati, A., and Rajput, N.
(2009). Content Creation and Dissemination by-and-
for Users in Rural Areas. In Proc. 3rd IEEE/ACM Int.
Conference on Information and Communication Tech-
nologies and Development (ICTD2009), pages 17–19.
Azim Premji Foundation (2004). The Social Context of El-
ementary Education in Rural India.
BBC Janala (2009). http://www.bbcjanala.com/.
Cervantes, R. and Sambasivan, N. (2008). VoiceList: user-
driven telephone-based audio content. In Proceedings
of the 10th international conference on Human com-
puter interaction with mobile devices and services,
pages 499–500. ACM.
CNN. Weapon against epidemics: Cell phones (2009).
http://www.cnn.com/2009/TECH/science/06/16/
cellphones.health.disease/index.html.
Derenzi, B., Lesh, N., Parikh, T., Sims, C., Maokla, W.,
Chemba, M., Hamisi, Y., Hellenberg, D. S., Mitchell,
M., and Borriello, G. (2008). e-IMCI: Improving Pe-
diatric Health Care in Low-Income Countries. In CHI
2008, ACM Press, pages 753–762.
Farrell, Glen and Shafika Isaacs (2007). Survey of ICT and
Education in Africa: A Summary Report, Based on 53
Country Surveys. Washington, DC: infoDev / World
Bank.
Ford, M. and Leinonen, T. (2006). Mobiled: A mobile tools
and services platform for formal and informal learn-
ing. In mLearn 2006, the 5th International Conference
on Mobile Learning.
Gary Marsden, Andrew Maunder and Munier Parker
(2008). People are People, but Technology is not
Technology. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
Society, October 2008, pp 1-10.
Jean Dr
`
eze and Geeta Gandhi Kingdon (2001). School Par-
ticipation in Rural India. Review of Development Eco-
nomics, 8(2):198–222.
Jones, M. and Marsden, G. (2004). “Please Turn ON Your
Mobile Phone” - First Impressions of Text-Messaging
in Lectures. In Mobile HCI, pages 436–440.
Kam, M., Agarwal, A., Kumar, A., Lal, S., Mathur, A.,
Tewari, A., and Canny, J. (2008). Designing e-
learning games for rural children in india: a format for
balancing learning with fun. In DIS ’08: Proceedings
of the 7th ACM conference on Designing interactive
systems, pages 58–67. ACM.
Kam, M., Kumar, A., Jain, S., Mathur, A., and Canny, J.
(2009a). Improving Literacy in Rural India: Cell-
phone Games in an After-School Program. In pro-
ceedings of 3rd IEEE/ACM International Conference
on Information and Communication Technologies and
Development (ICTD2009).
Kam, M., Mathur, A., Kumar, A., and Canny, J. (2009b).
Designing digital games for rural children: a study of
traditional village games in india. In CHI ’09: Proc.
27th Int. Conference on Human factors in computing
systems, pages 31–40. ACM.
Kolko, B. E., Rose, E. J., and Johnson, E. J. (2007). Com-
munication as information-seeking: the case for mo-
bile social software for developing regions. In WWW
’07: Proceedings of the 16th international conference
on World Wide Web, pages 863–872. ACM.
Kotkar, P., Thies, W., and Amarasinghe, S. (2008). An Au-
dio Wiki for Publishing User-Generated Content in the
Developing World. In HCI for Community and Inter-
national Development (Workshop at CHI 2008).
Kumar, A., Rajput, N., Chakraborty, D., Agarwal, S., and
Nanavati, A. (2007). WWTW: the world wide telecom
web. In Proceedings of the 2007 workshop on Net-
worked systems for developing regions, page 7. ACM.
Marsden, G. (2003). Using hci to leverage communication
technology. Interactions, 10(2):48–55.
Maunder, A. J., Marsden, G., and Harper, R. (2008). Sna-
pandgrab: accessing and sharing contextual multi-
media content using bluetooth enabled camera phones
and large situated displays. In CHI ’08: extended ab-
stracts on Human factors in computing systems, pages
2319–2324. ACM.
Moodle (2010). http://moodle.org/.
Open Handset Alliance (2010). http://www.openhandset
alliance.com.
Parikh, T. (2010). Voice as Data: Learning from What Peo-
ple Say. In Proceedings of AAAI Artificial Intelligence
for Development (AI-D’10).
Parikh, T. S. (2005). Using mobile phones for secure, dis-
tributed document processing in the developing world.
IEEE Pervasive Computing, 4(2):74–81.
Parikh, T. S., Javid, P., Sasikumar, K., Ghosh, K., and
Toyama, K. (2006). Mobile phones and paper doc-
uments: evaluating a new approach for capturing mi-
crofinance data in rural india. In CHI ’06: Proceed-
ings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in
computing systems, pages 551–560. ACM Press.
Parikh, T. S. and Lazowska, E. D. (2006). Designing an ar-
chitecture for delivering mobile information services
to the rural developing world. In WWW ’06: Proceed-
ings of the 15th international conference on World
Wide Web, pages 791–800. ACM.
Patel, N., Chittamuru, D., Jain, A., Paresh, D., and Parikh,
T. S. (2010). Avaaj otalo - a field study of an interac-
tive voice forum for small farmers in rural india. In
CHI ’10: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on
Human Factors in computing systems.
SchoolNet Africa (2008). http://www.schoolnetafrica.org/.
Seshagiri, S., Aman, S., and Joshi, D. (2007). Connect-
ing the ”bottom of the pyramid”: an exploratory case
study of india’s rural communication environment. In
WWW ’07: Proc. 16th int. conference on World Wide
Web, pages 855–862. ACM.
World Bank (2009). http://blogs.worldbank.org/edutech/
surveying-the-use-of-mobile-phones-in-education-
worldwide.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
170
