
SEARCHING WEB 3.0 CONTENT
A Semantic Search Approach
Kinga Schumacher
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, IUI Group, Alt-Moabit 91c, Berlin, Germany
Michael Sintek
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, KM Group, Trippstadter Str. 122, Kaiserslautern, Germany
Keywords:
Web 3.0, Semantic web, Semantic search, Fact retrieval, Spreading activation.
Abstract:
The Web 3.0 is commonly understood as the combination of the Semantic Web and Web 2.0, where conven-
tional and social websites and data sources (e. g., DBs, XML, HTML, plain text) should be integrated and
linked as well. Thus, there is a plethora of information in various representation forms which can be mapped
to an information pool composed of a knowledge base (in RDF/S) and a text index. In doing so, structured
data (e. g., DBs) is usually mapped to the knowledge base while unstructured data (e. g., plain text) to the text
index and semi-structured (e. g., XHTML) data to both. Therefore, a search method is required which is able
to explore both the knowledge base and the text index exploiting the cross-linking of data. For this purpose,
we propose a search approach which combines fact retrieval and semantic document retrieval. It is able to
answer queries with facts and documents as well as documents together with facts, and it supports free text
and formal queries as well as queries composed of free text and formal parts.
1 MOTIVATION
Web 3.0 applications, e. g., semantic wikis, semantic
blogs, social semantic networks and social semantic
information spaces make available a huge amount of
linked content in various representation forms. To
search such content, two main tasks have to be per-
formed: First, heterogeneous data sources have to be
integrated, and, second, a search approach is required
which is able to explore linked content with various
degrees of formality. Fig. 1 shows the architecture of
such a search engine sketching the two major phases:
offline and online part. The offline part includes con-
nection of the data sources by processing the contents
in order to map/convert them to the knowledge base
(KB), which contains the ontologies and instances,
and to the text index. Depending on the formality of
data, i. e., structured, semi-structured or unstructured,
different processing steps like annotation, mapping,
natural language processing (NLP) are required to fill
the KB. Statistical analysis is typically applied to cre-
ate the text index. The information pool, composed
of the KB and the text index, integrates and enables
access to information from various data sources, po-
tentially covering the whole spectrum from simple
text documents over linked data to formally described
knowledge and, as the result, combining Semantic
Web, Web 2.0, Web 1.0 and legacy data. However,
the important benefit is that it enables to recognize
coherence between information elements from differ-
ent data sources and to reflect it in the KB by link-
ing them to each other. Therefore, this kind of data
source connection is applied in several Web 3.0 ap-
plications, e. g., in NEPOMUK (Sauermann et al.,
2007), Aletheia (Stieger and Aleksy, 2009) and In-
foSleuth (Nodine et al., 2000).
In this paper, we propose a hybrid semantic search
approach developed to explore such an information
pool (Fig. 1, online part). Our approach is not con-
stricted to simply retrieve plain facts or documents,
it deals with free-text, structured and also mixed
queries, and it is able to answer them with a combi-
nation of elements, i. e., documents and facts, specific
to the query. The rest of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: Sect. 2 introduces our approach in detail, Sect. 3
deals with the evaluation, Sect. 4 covers related work,
and Sect. 5 concludes the paper.
308
Schumacher K. and Sintek M..
SEARCHING WEB 3.0 CONTENT - A Semantic Search Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0003340703080313
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2011), pages 308-313
ISBN: 978-989-8425-51-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

OFFLINE
ONLINE
core
search
Know-
ledge
Base
formal
Semi-
structured
(XML
Structured
(DB, RDF)
Annotation
Mapping
query and res
u
Facts
Documents
Formal
(SPARQL)
OFFLINE
ONLINE
formal
and
informal
search
engine
Text-
index
informal
Un-
structured
(text,
multimedia)
(XML
,
XHTML)
Statistical
Analysis,
NLP
u
lt processing
Documents
and facts
Documents
INFORMATION
RESULT
Informal
(free
text)
informal
elements
DATA
SOURCES
PROCESSING
INFORMATION
POOL
SEARCH
ENGINE
QUER
Y
RESULT
Figure 1: Semantic Search Engine Architecture.
2 SEARCH APPROACH
Since the information pool integrates linked content
from different data sources as facts or as documents
with metadata, the search results are elements of the
KB and documents where one result can be a com-
bination of both, e. g., documents with facts. For
comprehensive search support, all kinds of queries,
i. e., free text queries, formal queries, and queries
composed of free text and also formal parts should
be allowed. This facilitates both purposeful formal
and vague free text queries and thus supports begin-
ner as well as advanced users and also users with
more and users with less knowledge about the back-
ground KB. Allowing all kinds of queries combined
with query construction assistance (e. g., by KB-based
auto-completion while the user is typing the query
terms) supports the user to create queries with as
many formal parts as possible. Given that formal parts
are precise unlike free text, they mitigate the problem
of resolving syntactic and structural ambiguity (ambi-
guity of the underlying structure of complex expres-
sions) by pre-query disambiguation. An example for a
mixed query is “which nations competed in free swim-
ming”. By typing the query terms, the system looks
for labels with the same beginning in the KB and rec-
ommends associated resources, in this case the class
Nation and the properties competesIn and hasCom-
petitor. By selection of a recommendation, the appro-
priate part of the internal query representation is re-
placed by the URI of the chosen resource. “free swim-
ming” cannot be syntactically matched to the KB, it
is interpreted as free text. A mixed result is a docu-
ment which contains the result table (person, stand-
ing) of the free swimming competition, together with
the facts that state the nationalities of the people.
For a comprehensive search on an information
pool as described above, the core search engine
should explore the KB and the text index using the
cross-linking between them. Since searching in a for-
mal KB and semantic document retrieval require dif-
ferent methods, a fact retrieval approach is needed
to find triples from the KB (incl. metadata of docu-
ments), and a semantic document retrieval approach
is needed which is able to accomplish enhanced docu-
ment retrieval embracing matched facts and their on-
tological context. The approaches have to work to-
gether in a way that the engine is able to exploit and
combine both facts and documents meaningfully con-
sidering the links and available additional (derived)
knowledge. Further requirements are the ability to re-
solve ambiguities and the feasibility to apply an ad-
equate ranking function which is suitable for mixed
result lists where a single result can be a fact or facts,
a document as well as a document with facts.
For our prototype, we selected a triple-based fact
retrieval and a graph-traversal-based semantic docu-
ment retrieval algorithm for the following reasons:
triple-based search provides the resolving of ambi-
guities (see Sect. 2.1), and the graph traversal algo-
rithm Spreading Activation enables an effective com-
bination of fact retrieval and document retrieval which
will later be shown in Sect. 2.3. In our hybrid ap-
proach, at first, the query is processed by the fact re-
trieval component which determines matching facts
and also the expanded query for document retrieval.
The matching facts together with the retrieved docu-
ments are used to set up the activation network and to
accomplish spreading. The approach is able to handle
all kind of queries, and it returns documents, facts and
also a combination of them specific to the query.
In terms of the KB, in addition to the availability
of the ontologies plus an instance base, this approach
requires either the instantiation of documents, i. e.,
each document is associated with an instance in the
KB, or the metadata of documents should explicitly
refer to instances of the KB. Furthermore, for a good
syntactic matching and improved retrieval, synonyms
of the ontological elements should be available.
2.1 Fact Retrieval
The triple-based fact retrieval approach maps query
terms to literals in the KB resulting in URIs of match-
ing and thus potentially intended properties (p
i
) and
non-properties (n
j
). These resources are used as sub-
ject, predicate or object to generate RDF queries, e. g.,
h
n
1
, p
1
,?
i
,
h
?, p
1
,n
2
i
. In (Goldschmidt and Krish-
namoorthy, 2005), the process of creating and apply-
ing queries is repeated for each new resource detected
but it is limited to only two hops in the KB in order to
avoid irrelevant inferences. We adopted and extended
this basic idea in order to enhance capabilities by pro-
viding more hops in the KB guided by the query.
In the following, G
Σ
denotes our KB as graph in-
SEARCHING WEB 3.0 CONTENT - A Semantic Search Approach
309

cluding the ontology and instances, q the query as
an ordered list of terms q = (t
1
,. ..,t
n
),n ∈ N. To
explain the syntactic matching, we define the tex-
tual content L
G
Σ
of G
Σ
as L
G
Σ
= {l| ∃
h
r, p,l
i
∈
G
Σ
, l is a Literal}. Furthermore, we define the set
of resources without literals and statements (RDFS
defines rdfs:Literal and rdf:Statement as Resources)
R
G
Σ
and divide it in the set of properties P
G
Σ
and
the set of non-properties N
G
Σ
: R
G
Σ
= {r| ∃
h
r, p,o
i
∈
G
Σ
∨ ∃
h
s,r, o
i
∈ G
Σ
∨ ∃
h
s, p, r
i
∈ G
Σ
, r /∈ L
G
Σ
},
P
G
Σ
= {p| ∃
h
p,rdf:type, rdf:Property
i
∈ G
Σ
}
and N
G
Σ
= R
G
Σ
\P
G
Σ
where
h
s, p, o
i
is an RDF triple
that consists of subject s, predicate p and object o.
Our KB supports the search engine with synonyms
of the elements (classes, properties, and instances)
which are used for the syntactic matching step. If
the user does not choose one of the recommendations
in the query construction phase (see Sect. 2) we ap-
ply the n-gram syntactic matching method to match
a query term against the KB. In the first case, the
similarity value is 1.0, in the second case it is the
computed n-gram value. Thus, the syntactic match-
ing returns for one query term t
i
∈ q a set of 3-tuples
(t
i
,r, w
t
i
r
): M(t
i
,G
Σ
) = {(t
i
,r, w
t
i
r
)| r ∈ R
G
Σ
, ∃l
j
∈
L
G
Σ
,w
t
i
r
= ngram(t
i
,l
j
)}. Only resources r were
included in the result set which are matched with a
w
t
i
r
> H where H ∈ [0,1] ⊂ R is a predefined simi-
larity threshold. To match phrases, we compare the
weights of possible phrases (processed as one term)
with the weights of their single terms. If the weight
of the phrase is higher than the average weight of its
terms then we propose that the phrase is intended. The
total result M(q, G
Σ
) is the union of the results per
query term which is the starting basis for semantic
matching: M(q,G
Σ
) = {
S
n
i=1
M(t
i
,G
Σ
)}.
For semantic matching, we do not consider the
whole KB but only the proper instances and desig-
nate this graph with G
I
. Furthermore, we define the
set of resources (again without literals and statements)
R
G
I
, properties P
G
I
and non-properties N
G
I
in G
I
anal-
ogously to the definitions for G
Σ
. We partition N
G
I
in
the pairwise disjunctive set of classes C
G
I
, the set of
things T
G
I
, i. e., resources, which are neither classes
nor literals, and the set of literals L
G
I
. When the query
is composed of only one term the semantic match-
ing step returns resources and triples of the graph
G
I
, dependent on what kind of resources the term
t
1
has matched. It returns the matched things, the
instances of matched classes, statements containing
the matched literals and statements with the matched
properties as predicate. When the query is composed
of more than one term, we iterate over every two ad-
jacent terms t
i
,t
i+1
and consider their results from the
syntactic matching (M(t
i
,G
I
),M(t
i+1
,G
I
)). We create
and apply possible SPARQL queries with the matched
resources in order to find suited triples in G
I
. In case
of two properties, the possible queries ask for either a
subject with both properties or two triples where the
object of the first triple is the subject of the second
one. If there are no results for two query terms and
one or both of the terms match against a class, we
search for triples with the instances of the matched
class. In the next iteration, we consider the resulting
triples and the query terms which produced no triples
so far. We create query templates with these terms and
the subjects/objects of the triples which were found
based on the adjacent query terms. The ordered pro-
cessing of unmatched terms enables to handle also
enumerations of instances, properties or classes. The
process is iterated and stops when either all query
terms are matched or it is not possible to include all
terms since some terms do not match existing triples
in G
I
. We also make as many hops in the KB as pos-
sible guided by the query. The result consists of a set
of instances and a set of triples. At least, we identify
triple sets in the result which build a coherent sub-
graph of G
I
. To avoid the merging of instances to a
big subgraph in order to deliver well arranged results,
each triple of a subgraph is connected to another by
the same subject or the same object but we exclude
the connection by the same class. For this, we pick
a triple
h
s
i
, p
i
,o
i
i
from the result and add all other
triples
s
j
, p
j
,o
j
to the subgraph where s
i
= s
j
or
s
i
= o
j
or s
j
= o
i
or o
i
= o
j
, o
i
/∈ C
G
i
. One subgraph
is also a set of connected triples where the connec-
tion by class is excluded or it is one triple if there
are no connected triples in the result set. The rank-
ing is based on the w
t
i
r
j
which are computed in the
syntactic matching step by exact (recommended re-
source) or n-gram match. The weight of a matched
triple is the sum of the w
t
i
r
j
of participating ontolog-
ical elements r
j
. Each expansion with new triples in-
creases the weight of the partial result by the appro-
priate w
t
i
r
j
value. Finally, the rank of a result in S
G
I
is the sum of participating elements’ weights divided
by the number of query terms. Resolving ambigui-
ties is supported by triple-based processing. Since we
do not directly transform the user query to an RDF
query, the triples found step by step lead to possible
interpretations based on the existing triples in G
I
.
2.2 Semantic Document Retrieval
The pure semantic document retrieval comprises doc-
ument retrieval and Spreading Activation and it is car-
ried out if no facts have been matched.
The idea of using SA for information retrieval is
to find more relevant information based on retrieved
WEBIST 2011 - 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
310

information elements by exploiting associations rep-
resented by semantic networks (as graphs). The on-
tological concepts are the nodes, the properties the
edges of the network, usually directed and weighted.
SA starts with the initial incoming activation of nodes
which propagate the activation along the edges acti-
vating the connected nodes. This process is iterated,
i. e., the activation spreads through the network, until
the stop condition is fulfilled. Result is the activa-
tion level of each node at termination time (Crestani,
1997). For semantic document retrieval, our network
model includes all instances, their classes and rela-
tions which connect these nodes, i. e., all properties
which link instances but not instances with literal val-
ues. To each edge a default weight w
d
is assigned. We
insert an inverse edge also if the property has no in-
verse in order to make sure that properties without an
inverse are involved if one of the connected instances
is activated. And we insert edges from classes to their
instances (but not the other way around) in order to
avoid noise in results since it stops spreading from
one instance to all other instances of a class but en-
ables to spread from a class to its instances if a class
is initially activated. We use a Lucene index for key-
word matching on the document corpus. The result is
a set of weighted documents where the associated in-
stances in the network are our initial activation points.
We apply the activation function I
j
=
∑
i
O
i
w
i j
(1 −α)
where I
i
is the incoming activation of nodes, O
i
the
outgoing activation (determined by an output func-
tion), w
i j
∈ [0,1] ⊂ R is the weight of the edge from n
i
to n
j
, and α is an attenuation factor which decreases
the activation strength with each propagation. Since
both α and the edge weights already decrease the acti-
vation level we use the simple output function O
i
= I
i
.
We apply an activation constraint which stops spread-
ing at a node when its activation level does not exceed
a defined threshold. Furthermore, a fan-out constraint
averts the danger of a too wide spreading through
nodes with high connectivity, thus to become noise
in results. It is important to assure that each directed
edge is processed only once in order to avoid endless
spreading in cycles. In each iteration, the node with
the highest activation level and pending edges is pro-
cessed. SA stops when no more nodes have an acti-
vation level above the defined threshold or the nodes
above the threshold have no pending edges. The re-
sult is the set of document instances weighted by their
activation level.
2.3 Hybrid Approach
In our hybrid search approach, at first, fact retrieval
is carried out and deliver a set of matched resources.
We use the synonyms (in KB) of matched resources
to perform query expansion before querying the text
index. The result of the document retrieval with the
expanded query is a set of weighted documents as
described in Sect. 2.2. To be able to create the ac-
tivation network, the set of matched resources of the
fact retrieval result set is to extract where we differ-
entiate between instances, properties and classes. For
the extraction of the classes and the properties only
the results of the syntactic matching are relevant. To
get the matched instances, we extract not only the re-
sources found by the syntactic matching, but also sub-
jects and objects from the triples found by the seman-
tic matching. Now, all information to set up the acti-
vation network is available. We design our semantic
network as described in Sect. 2.2 and apply the same
rules to fill the matrix. The difference is: we assign to
the properties which are matched by the fact retrieval
their computed weight instead of the low initial de-
fault weight w
d
. The set of activation nodes contains
the instances of found documents and the instances
and classes from the fact retrieval results where their
weights are applied as initial activation weight. The
spreading function, constraints and stop condition are
the same as described in Sect. 2.2. The results of the
activation process are a set of weighted nodes includ-
ing the documents. The last step of the hybrid ap-
proach is to merge the results of the spreading acti-
vation and the subgraphs. For this, we start by the
subgraphs and add the connected documents from the
results of the SA process. Note that the subgraphs
also contains the properties which are not spread since
they have a literal value. For all other found docu-
ments, the results of SA define a set of facts which de-
scribes the answer and which is also part of the result.
We only collect the high ranked resources as facts to
avoid confusing results. The rank of one object from
the result set is the average rank of the contained in-
formation elements.
3 EVALUATION
We evaluated our approach based on a manually an-
notated test bed (Grothkast et al., 2008). It contains
an ontology about Olympic Games, an instance base
which describes the Olympic Games 2004 and 122
news articles about it. The news have been manually
annotated, their metadata directly refers to the KB,
e. g., news about the 200m Swimming for Men are
annotated with the competition and people from the
instance base which are mentioned in the text. Fur-
thermore, they are associated with 8 queries, i. e., it
is known which articles are relevant for a particular
SEARCHING WEB 3.0 CONTENT - A Semantic Search Approach
311
query. The queries are: q1: standings of Australians;
q2: disciplines with gold for Australians; q3: teams
of South Korea, q4: when did Chinese win gold; q5:
places of competitions in cycling; q6: in which disci-
plines did British sportsmen compete; q7: who com-
peted in swimming; q8: which nations have a women
football team. We applied simple keyword search (1),
semantic document retrieval (2), and the hybrid ap-
proach (3) on the test set and computed the precision,
recall and F-measure per query.
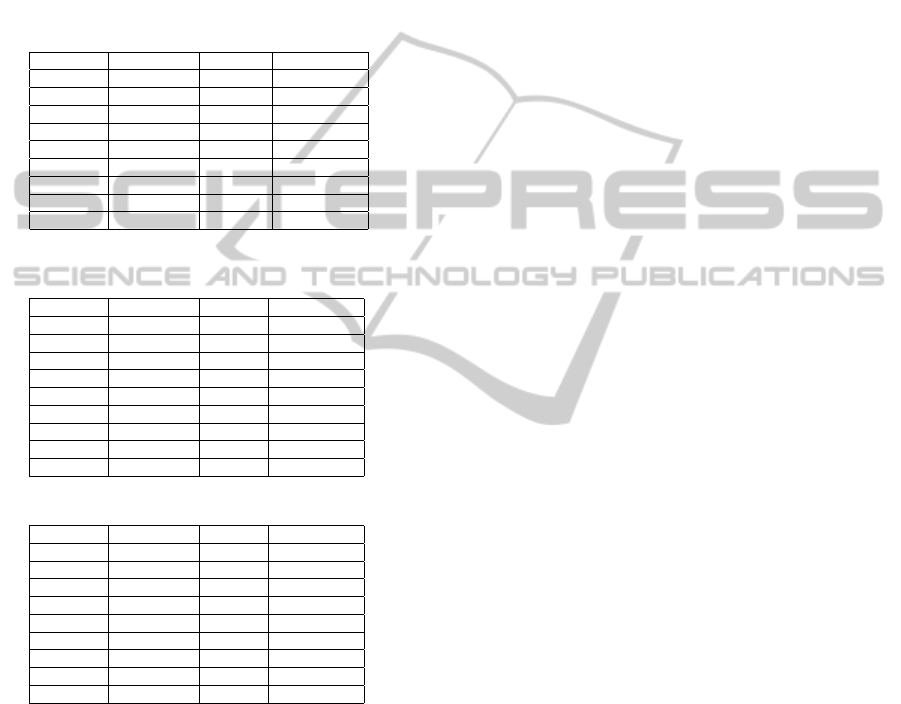
Table 1: Evaluation Results - Keyword Search.
Query Precision Recall FMeasure
q1 0.2752 1.0 0.4316
q2 0.0354 1.0 0.0683
q3 0.3421 0.8125 0.4814
q4 0.1563 1.0 0.2703
q5 0.2858 1.0 0.4444
q6 0.125 0.2857 0.1739
q7 0.0338 0.6667 0.0645
q8 0.0138 1.0 0.0274
average 0.1584 0.8456 0.2452
Table 2: Evaluation Results - Semantic Document Re-
trieval.
Query Precision Recall FMeasure
q1 0.2632 1.0 0.4167
q2 0.0345 1.0 0.0667
q3 0.2192 1.0 0.36
q4 0.0408 1.0 0.0784
q5 0.0317 1.0 0.0615
q6 0.5 1.0 0.6667
q7 0.0256 1.0 0.05
q8 0.0435 1.0 0.0833
average 0.1448 1.0 0.223
Table 3: Evaluation Results - Hybrid Approach.
Query Precision Recall FMeasure
q1 0.6042 1.0 0.7533
q2 0.069 1.0 0.129
q3 0.4688 1.0 0.6383
q4 0.2134 1.0 0.3517
q5 0.4 1.0 0.5714
q6 0.4615 1.0 0.6315
q7 0.4 1.0 0.5714
q8 0.25 1.0 0.4
average 0.3584 1.0 0.5058
The precision of the semantic document retrieval
in comparison with the keyword search decreases in
some cases but, at the same time, the recall increases.
It is caused by Spreading Activation where also news
articles are activated which are relevant for only a part
of the query, i. e., annotated with only some instances
which constitute the metadata of the documents found
by the keyword search. Recall increases for the same
reason, since documents which do not contain one of
the query terms but, e. g., a synonym of it, were acti-
vated via the shared metadata, ontological context.
The hybrid approach performs very well for both
precision and recall. It tackles the problem of too
wide spreading since it applies: 1. more precise ac-
tivation points by involving matching facts and their
ranks; 2. a query specific network setup, especially
for weights of involved properties. The best improve-
ments in comparison to keyword search and seman-
tic document retrieval can be achieved if the query
matches some properties (q2, q6 and q7), since they
guide the flooding during SA. Fewer improvements
are observable if only classes and commonly used in-
stances are matched since classes spread to all of their
instances and commonly used instances are not spe-
cific enough and cause spreading from nodes which
are far apart. E.g., in q4 where “when” matches a
class and “Chinese” is a commonly used instance, and
in q5 where both “places” and “competitions” match
classes. The fact retrieval delivers in some cases (q3,
q5, q7) the answer to the query as facts. The hy-
brid approach does not perform well if no facts are
matched because it only performs pure semantic doc-
ument retrieval in this case.
4 RELATED WORK
In (Schumacher et al., 2008), we informally presented
an early stage of our hybrid semantic search approach
that features a combination of semantic document re-
trieval and fact retrieval, but the approach described
in this paper is able to process mixed queries and the
algorithms (esp. the hybrid approach) have been dras-
tically improved with respect to efficiency.
Existing hybrid search systems address mainly the
problem of processing free text or mixed queries on
formal KBs (fact retrieval) where parts/metadata of
documents are transformed into formal knowledge
or they are considered as facts in the KB. Semplore
(Wang et al., 2009) supports faceted search and com-
plex hybrid queries on structured data by transform-
ing Web of Data into a text index. The fields represent
predefined hierarchical relations and they also hold
textual properties of an instance. (Tran et al., 2007)
describes an approach translating keyword queries
to DL conjunctive queries using background knowl-
edge and so supports semantic based declarative ques-
tion answering on formal KBs. An advanced version
of this approach first computes conjunctive formal
queries from keywords by exploration of top-k match-
ing subgraphs allowing the user to choose one (Tran
et al., 2009). This system supports free text queries in-
deed, but the users have to examine complex conjunc-
tive queries before continuing with the search. (Lad-
wig and Tran, 2010) introduces a tight integration of
the approach with query answering, i. e., graph pattern
matching. There are several further methods for graph
WEBIST 2011 - 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
312

based query processing in oder to search over graph-
structured data, e. g., BLINKS (He et al., 2007). Some
approaches apply a predefined set of query templates,
e. g., (Sacaleanu et al., 2008), where the latter real-
izes a multilingual entailment-based question answer-
ing approach. Other methods for query interpretation
are using deep NLP, e. g., Powerset (Converse et al.,
2008) or large background knowledge created with
high effort, e. g., WolframAlpha. Document search
by fact retrieval is supported by DBPedia, Semantic
Wikis and documents enriched with RDFa or micro-
formats since the document search is processed by re-
trieving the ‘included’ facts.
Our approach is essentially different to these
search methods as it provides fact and document re-
trieval, formal, free text and mixed queries, and also
mixed results, i. e., documents with facts, while all
other existing approaches support only a subset of
this.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The evaluation shows the power of our hybrid ap-
proach. It performs best if properties are involved
in the query since they alleviate the weakness of SA,
i. e., noise results caused by uncontrolled spreading.
Also in other cases, the combination performs quite
well due to the more precise fact retrieval results. If
no facts are available for a query, the search approach
performs semantic document retrieval using the meta-
data of the documents. Furthermore, our approach
delivers facts if they are available, and so the user
doesn’t need to browse the documents of the result
list. In future versions, to improve the precision if no
facts are matched, we are going to setup our seman-
tic network with edge weights which express the im-
portance of relations and we plan further evaluations
(e. g., with DBPedia). We also foresee to integrate this
approach in the digital library assistant DiLiA (Seifert
and Kruppa, 2010), by extending it to support com-
plex queries for expert users.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported in part by the THE-
SEUS Program CTC, which is funded by the BMWi
(gn 01MQ07016), and the research project DiLiA
which is co-funded by the ERDF (gn 10140159). The
responsibility for this publication lies with the au-
thors.
REFERENCES
Converse, T., Kaplan, R. M., Pell, B., Prevost, S., Thione,
L., and Walters, C. (2008). Powerset’s natural lan-
guage wikipedia search engine. Report, Powerset inc.,
California.
Crestani, F. (1997). Application of spreading activation
techniques in information retrieval. Artificial Intelli-
gence Review, 11(6):453–482.
Goldschmidt, D. E. and Krishnamoorthy, M. (2005). Archi-
tecting a search engine for the semantic web. In AAAI
Workshop on Contexts and Ontologies.
Grothkast, A., Adrian, B., Schumacher, K., and Dengel, A.
(2008). OCAS: Ontology-based corpus and annota-
tion scheme. In Proc. of the High-level Information
Extraction Workshop 2008, pages 25–35.
He, H., Wang, H., Yang, J., and Yu, P. S. (2007). BLINKS:
Ranked keyword searches on graphs. In Proc. of
the International Conference on Management of Data,
pages 305–316.
Ladwig, G. and Tran, D. T. (2010). Combining keyword
translation with structured query answering for effi-
cient keyword search. In Proc. of the 7th Extended
Semantic Web Conference.
Nodine, M., Fowler, J., Ksiezyk, T., Perry, B., Taylor, M.,
and Unruh, A. (2000). Active information gathering
in InfoSleuth. International Journal of Cooperative
Information Systems, 9(1/2):3–28.
Sacaleanu, B., Orasan, C., Spurk, C., Ou, S., Ferrandez, O.,
Kouylekov, M., and Negri, M. (2008). Entailment-
based question answering for structured data. In
Posters and Demonstrations, 22nd Int. Conference on
Computational Linguistics, pages 29–32.
Sauermann, L., van Elst, L., and Dengel, A. (2007). PIMO
– a framework for representing personal information
models. In Proc. of I-SEMANTICS 2007, pages 270–
277.
Schumacher, K., Sintek, M., and Sauermann, L. (2008).
Combining fact and document retrieval with spread-
ing activation for semantic desktop search. In Proc.
of the 5th European Semantic Web Conference, pages
569–583.
Seifert, I. and Kruppa, M. (2010). A pool of topics: In-
teractive relational topic visualization for information
discovery. In Proc. of the Conference on Visual Infor-
mation Communication, pages 195–207.
Stieger, B. and Aleksy, M. (2009). Utilization of knowl-
edge management for service business processes im-
provement. In Proc. of the Int. Multiconference on
Computer Science and Information Technology, pages
171–175.
Tran, T., Cimiano, P., Rudolph, S., and Studer, R. (2007).
Ontolgy-based interpretation of keywords for seman-
tic search. In Proc. of the 6th Int. Semantic Web Con-
ference, pages 523–536.
Tran, T., Wang, H., Rudolph, S., and Cimiano, P. (2009).
Top-k exploration of query candidates for efficient
keyword search on graph-shaped (RDF) data. In
ICDE, pages 405–416.
Wang, H., Liu, Q., Penin, T., Fu, L., Zhang, L., Tran, T.,
Yu, Y., and Pan, Y. (2009). Semplore: A scalable IR
approach to search the web of data. Journal of Web
Semantics, 7(3):177–188.
SEARCHING WEB 3.0 CONTENT - A Semantic Search Approach
313
