
TILED CELLULAR AUTOMATA FOR AREA-EFFICIENT
DISTRIBUTED RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS
Bernard Girau
Universit´e Henri Poincar´e Nancy 1, LORIA Cortex Team, INRIA Nancy, Nancy, France
Nikolaos Vlassopoulos
MAIA Team, LORIA, INRIA Nancy, Nancy, France
Keywords:
Parallel pseudo-random number generators, Cellular automata, Area efficiency.
Abstract:
Generating multiple random numbers in a parallel fashion for scientific simulations is an intense task that
requires significant hardware resources. In our present work we focus on an existing Cellular Automaton and
present an efficient architecture that reuses this CA to generate pseudo random numbers in a two dimensional
context.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pseudo random number generators (PRNGs) play a
significant role in modern scientific experiments and
simulations. Modeling physical phenomenons (Abar-
banel et al., 1993; Kier et al., 2005), complex sys-
tems (Berry et al., 2006), user behaviors (Ric, 1983;
Bonnin et al., 2009), pattern recognition (Rabiner,
1989; Musti et al., 2010), performance of communi-
cating systems (Stewart, 2009), etc. intensively re-
lies on PRNGs. Therefore, the design of high-quality
PRNGs stand as a very active research subject in
itself, covering various fields such as algorithmics,
arithmetics, software engineering and hardware de-
sign.
In this paper, we focus on hardware based random
number generators that target FPGA devices. More
precisely, the purpose of this work is to study the
possibility of using cellular automata (CA) as pseudo
random number generators, when multiple distributed
sources of random bit-streams are necessary. Various
previous studies exist about CA-based PRNGs, but
the research there was focused on the generation of
a stream of pseudo random bits, from either a 1-D or
a 2-D CA. In our work, we take into account the need
for distributed PRNGs with temporal and spatial in-
dependance, with a strong constraint that is put on the
area required for their hardware implementation.
This context of area-efficient distributed PRNGs
is rather specific. The most usual use of PRNGs
corresponds to software calls to a function that se-
quentially produces random values by approximat-
ing a continuous random variable with an uniform
probability density between 0 and 1. Software pro-
grams that need to generate multiple random vari-
ables just perform successive calls to this function to
deal with the different random distributions. Hard-
ware designs also often use PRNGs, though they re-
quire to make a compromise between the implemen-
tation cost (area and speed) and the quality of the
ramdom bit-stream. In the case of FPGAs, PRNGs
based on linear feedback shift registers (LFSR) re-
main popular, especially when using Xilinx devices in
which each local lookup table of the logic resources
may be configured as 16- or 32-bits LFSRs, result-
ing in very efficient implementations (George and
Alfke, 2000). When dealing with the implementa-
tion of fine-grain distributed models where the differ-
ent computationunits work in parallel (synchronously
or not), various PRNGs are simultaneously required.
Therefore the implementation area of each PRNG of-
ten becomes one of the main bottlenecks in achiev-
ing a distributed implementation. To mention some
of these implementations, bitstream neural networks
(Salapura, 1994; van Daalen et al., 1993; Bade and
Hutchings, 1994) are well-known area-efficient neu-
ral models for which the independance of the bit-
streams throughout the network is highly problem-
atic, (Vlassopoulos et al., 2010) deals with a large
CA modelwith probabilistic rules, (Girau et al., 2010)
397
Girau B. and Vlassopoulos N. (2011).
TILED CELLULAR AUTOMATA FOR AREA-EFFICIENT DISTRIBUTED RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems, pages 397-404
DOI: 10.5220/0003371103970404
Copyright
c
SciTePress

implements a bio-inspired multi-agent model, studies
are carried out about the implementation of dynamic
neural fields for visual attention (Rougier and Vitay,
2005) with local random interactions, (Girau, 2004)
defines an asynchronous architecture of neural net-
works with random local priority handling, many dis-
tributed implementations of genetic algorithms may
be found (Graham and Nelson, 1996), etc. Most of
these implementations would take advantage of a dis-
tributed sub-process able to generate parallel high-
quality random bitstreams while using only a small
percentage of the available logic resources. In this pa-
per, we show that a flexible tiled architecture based on
heterogeneous CA provides such a sub-process with a
minimal cost.
In section 2, we rapidly describe the existing hard-
ware architectures for generating random bitstream,
as well as the methods that evaluate the quality of
these PRNGs. In section 3, we describe the tiled ar-
chitecture that we propose. Section 4 is dedicated to
the evaluation of this architecture in terms of random-
ness quality and area-efficiency.
2 DESIGN AND EVALUATION
OF PRNGs
2.1 Overview of Hardware PRNGs
In this section we present a short description of some
of the available pseudo random number generators for
hardware applications. Unquestionably, LFSRs are
among the most common ones, finding application
on a large variety of fields, ranging from bit-stream
scramblers to digital multimedia. Their basic char-
acteristics are a solid mathematical theory describing
their operation and ease of implementation, while the
major disadvantages are the low throughput, in terms
of random bits per cycle, the fact that at least a mini-
mum length is required so as for the results to be ac-
ceptable in terms of success on the standard random
number tests and finally the fact that they have a rather
high ratio of area over produced random bits.
A rather straightforward way to improve the per-
formance, in terms of quality and random bits per cy-
cle, of LFSRs, but at the cost of increased area, is to
use multiple parallel LFSRs in order to extract several
bits. This method is usually based on LFSRs having
the same length, but different characteristic polyno-
mials (i.e. the calculation of the feedback bit is done
using a different subset of bits) or are initialized using
different words. This approach, results in an increase
of the area proportional to the number of parallel bits.
A second method for generating random words
from LFSRs is by extracting multiple bits from a
rather large LFSR in a way that no immediate corre-
lations exist between two consecutive random words.
One way to achieve this is to extract bits from irreg-
ular positions of the shift register and shuffle them in
order to obtain a pseudo random word at the output.
The first disadvantage of this technique is that it re-
quires a very large LFSR so as to be able to extract
bits from intervals that are “safely” appart. As an ex-
ample, it is impossible to extract 16 bits from a 32
bit LFSR without introducing immediate dependen-
cies. Moreover, the quality of the random words is
significantly degraded with respect to the quality of
an LFSR where a single bit is extracted. On the other
hand they exhibit higher throughput and are more ef-
ficient in terms of bits per area.
Using 1 dimensional CAs as a source of random
bits has been always an attractive solution. The rea-
son for this is that CA are simple to implement and
depending on the underlying rule, they may exhibit
rather aperiodic behavior which results in very good
quality random numbers. To this end, they have been
a subject of research and several results have been
published up to now in the bibliography. As exam-
ples, (Nandi et al., 1994) and (Tomassini and Perre-
noud, 2001) present two applications of CAs as gen-
erators of sequences for cryptographic applications.
(Das and Chaudhuri, 1993) bridge one dimensional
CAs to LFSRs, while (Chowdhury et al., 1994) ex-
tend these observationsto the case of two dimensional
CAs. Finally, (Guan and Tan, 2004) present a class of
“self-programming” 1 dimensional cellular automata,
where the rule of a cell is modified during the opera-
tion of the CA (which is in a sense equivalent to using
a bigger state space).
Motivated by the complexity exhibited by the 1
dimensional CAs, the research on the posibility of
using 2 dimensional CAs as pseudo random num-
ber generators began as rather early with works like
(Hortensius et al., 1989). In the work presented there
a 2 dimensional CA is constructed by concatenating
several 1 dimensional CAs. Among the most impor-
tant remarks of this work is the fact that using non-
homogenous mixed rules, such as rule 30 and rule
150 leads to maximal cycle lengths. In our present
work we base our architecture on the works previ-
ously published by (Tomassini et al., 2000). In this
specific article, the authors use genetic algorithms to
evolve a 2 dimensional, 8 × 8 cells cellular automa-
ton for generating random numbers. The automa-
ton presented there is based on additive rules and is
non-homogenous, meaning that different cells are as-
signed a different rule. Although it is essentially a 2
dimensionalautomaton it is utilized for the generation
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
398

of a 1 dimensional bit stream.
Finally we should mention that among the solu-
tions we presented above, CAs have the best area uti-
lization with respect to the number of random bits
produced per cycle. This is because in most CA based
PRNGs a each cell is used to extract a random bit. As
we increase the dimensions of the CA (either one di-
mensional or two dimensional), this ratio remains es-
sentially constant, since for each added cell, we get
a new random bit per cycle. This ratio is the highest
among the PRNGs we presented in this section, since
in all other cases, the number of registers and logic
that is required in order to produce a random number
bit is significantly higher and increases as we move
towards configurations and lengths that produce ran-
dom numbers with higher quality.
2.2 Randomness Evaluation
Evaluating the quality of pseudo random number gen-
erators is generally achieved by testing the pseudo-
randomly generated bits through a “battery” of tests.
These tests measure some property of the bit-stream,
i.e. the distribution of sequences of consecutive ‘1’s
in the stream, and they compare these measurements
with the expected theoretical distribution of a perfect
random number generator. The evaluation is, most
of the time, performed by selecting samples from
the distribution under consideration and running the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test against the known distri-
bution. Each such test produces a result (p-value
∈ [0, 1]) that is then tested against a “confidence in-
terval” to decide whether the distribution of sam-
ples from the PRGN passes or fails the “distribution
matching” test.
The most widely used such battery of tests is
the “Diehard” test suite developed by G. Marsaglia
(Marsaglia, 1995). In our present work we use the
“Dieharder” battery of tests by R.G. Brown (Brown,
2009). This extended set of tests includes both the
original DieHard test suite, as well as a series of tests
that have been collected and developed by the au-
thor. In the “DieHarder” tests, each such test is run an
amount of times and an assesment is produced, that is
based on the percentage of the times the test passed
or failed the confidence interval. Further, a mean p-
value for the test is produced. In the following we’ll
describe how we will use these values in order to eval-
uate and compare the quality of the proposed architec-
ture with respect to known hardware PRNGs.
In order to measure how successfull is a PRNG
we have to compare it with a “benchmark” random
number generator, i.e. we have to see how it performs
with respect to the best knownPRNGs. For our exper-
iments we used as a benchmark the Mersenne-Twister
PRNG (Matsumoto and Nishimura, 1998). This
PRNG passes all except one tests in the DieHarder
battery, and the one test it fails is considered among
the “suspect” tests, i.e. one that is consistently failed
by good random number generators. For our compar-
ison we use three different empirical metrics.
The first one is the success ratio, that is based
purely on the assesment of the DieHarder tests, i.e.
the characterization of a test as “PASSED”, “WEAK”
or “FAILED”. More specifically we assign to each as-
sesment a weight, 1 for “PASSED”, 0.5 for “WEAK”
and 0 for “FAILED”, and we calculate the ratio
∑
w
i
(t)
∑
w
i
(MT)
, where index i runs over all tests and t de-
notes the currently tested PRNG, while MT denotes
the Mersenne-Twister PRNG.
Although this approach is straightforward, it fails
to take into account the difficulty of each test, i.e. the
ability of the test to identify pseudo random streams.
In order to integrate this aspect into our assessment,
we take into account the mean p-value that is pro-
duced by the battery of tests. The underlying idea
is that a test with a p-value close to the boundaries
of the confidence interval (for the Mersenne-Twister
PRNG) should be considered as a “hard” test, while
a test with a p-value in the middle of the interval
should be considered as an “easy” test. We then in-
tegrate this qualitative description by using two dif-
ferent approaches. The first considers the L
1
distance
from the middle of the interval and assigns to each
passed test the value w
i
= 1− |0.5− p
i
|, where p
i
is
the p-value for test i. Intuitively this can be described
as increasing the relative weight of “easy tests”, so
that the tested PRNG is more penalized when it fails
easy tests than when it fails difficult ones. Then we
calculate again the ratio of the sum of the weights
for the tested PRNG and for the benchmark (MT).
The second approach (third metrics) assumes that the
distribution of p-values follows a normal distribu-
tion with mean 0.5 and it calculates the weight as
w
i
= 0.5 + 0.5e
−
(0.5−p
i
)
2
0.2
2
− 0.5e
−
(0.5)
2
0.2
2
(see Figure 1).
Intuitively this further increases the relative weight of
the “easy” tests. In all above cases, weak tests are
considered as having the marginal value of 0.05.
3 ARCHITECTURE
We will now outline the proposed architecture for the
parallel PRNGs. The main motivation is that we want
to be able to generate multiple parallel streams of
random bits per cycle, by keeping the ratio nbc =
number of random bits
number of cycles
as high as possible. To take into
TILED CELLULAR AUTOMATA FOR AREA-EFFICIENT DISTRIBUTED RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS
399

0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
weight
p-value
0.5*(1+exp(-(0.5-x)*(0.5-x)*25)-exp(-0.5*0.5*25))
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
weight
p-value
0.5*(1+exp(-(0.5-x)*(0.5-x)*25)-exp(-0.5*0.5*25))
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
weight
p-value
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
weight
p-value
gaussian
L1
Figure 1: Gaussian test weighting.
account the area-efficiency of each solution, we fur-
ther use the ratio
nbc
implementation area
as suggested for
VLSI PRNGs in (Hortensius et al., 1989). As we
reviewed in section 2, CAs as random number gen-
erators have the highest such ratio, since each cell is
capable of producing 1 random bit per cycle, while
approximately occupying an area equivalent to a sin-
gle Flip-Flop and a logic gate (at least in our cases).
It is therefore desired to exploit this property as much
as possible.
Our proposed architecture is based on the work
done by (Tomassini et al., 2000). In this work,
the authors evolved an 8 × 8 heterogeneous two-
dimensional CA using genetic algorithms, so that the
pseudo random generated bits maximized certain bit
string entropies. The best candidates were then se-
lected and run against the original DieHard tests to
evaluate their performance. Although the authors
aimed at generating a single stream of pseudo random
bits from the entire CA, the main idea in the current
work is to reuse the CA developed there in order to
generate multiple parallel streams. The architectural
approach we follow is depicted in Figure 2.
BASE CA BASE CA
BASE CA BASE CA BASE CA
BASE CA
...
Figure 2: Overall Architecture.
Assume that we want to be able to generateW ×H
random words consisting of q bits per cycle in a par-
allel manner and further assume that q = q
1
q
2
. The
idea is that we create rectangular “tiles” of width q
1
and height q
2
and dividethe base CA, which is the one
described in (Tomassini et al., 2000) using these tiles.
Of course, the base CA is replicated both horizontally
and vertically, so as to always have enough cells to
fill-in the tiles, i.e. N
1
· 8 ≥ q
1
·W and N
2
· 8 ≥ q
2
· H,
where N
1
and N
2
correspond to the number of hori-
zontal and vertical copies of the base CA.
This approach introduces two issues. The first one
is that we have to ensure that the random words pro-
duced by each tile are still of high enough quality so
as to adequately pass the battery of tests. Second,
depending on the ratio of the tile size with respect
to the dimensions of the base CA that we are using
(8× 8) we may have situations where a percentage of
the underlying CA tiles is unused. Answering the first
question is the main subject of this paper, while we
will provide an answer to the second question in the
following sections, where we will review the spatial
quality characteristics with respect to tile size.
3.1 Notes on Boundary Conditions
One important thing we should mention at this point
is, that the base CA we are using has been evolved
so as to produce random bits when it operates on
free boundary conditions, i.e. the boundary cells of
the 8 × 8 array are assumed to be connected to an
all-zero environment. This property should be re-
spected while generating the tiles, since, as soon as
two neighboring base CAs are connected, there ap-
pears to be some form of “synchronization”, which
significantly reduces the quality of the generated ran-
dom bits. What we mean by synchronization is man-
ifested as very short period cycles in the generated
stream that has catastrophic results. Extending the
work of (Tomassini et al., 2000) so as to evolve base
CAs that operate under toric or periodic boundary
conditions is one of our future targets.
On the other hand having each base CA to oper-
ate on its own (disconnected from its neighbors) re-
sults in a reduced overall interconnect network. From
this point of view, free boundaries could stand for an
optimization, since they reduce the overall area of a
design. Nevertheless, evolving a CA that is based
on non-free boundary conditions should improve the
quality of the generated random numbers, which is
our primary interest, so that is one of our main future
research directions.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In this section we present the experimental results we
obtained from applying the tiled approach to the base
CA. Since the number of possible tile configurations
is very large, we will mainly focus on some examples
that we consider representative. Besides the evalu-
ation of the “tiled” architecture proposed above, we
also present a series of results on LFSRs. The main
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
400
motivation for also presenting these results is that LF-
SRs are among the main methods for generating ran-
dom bits on FPGAs and they are likely to take advan-
tage of high optimizations during synthesis. Although
they have a rather low random bits per area unit ratio,
they are still one of the main methods used.
The tile configurations we chose to study are 02×
02, 04 × 08, 01 × 03 and 03× 05 bits (or cells). Our
main motivation for choosing these is that we wanted
to investigate how a small (02×02) and a rather large
(04 × 08) tile behaves, and what happens with tiles
that are “forced” to cross the boundaries of two neigh-
boring CAs (01×03 and 03× 05). In order to present
our results graphically, we use an array that is 40×40
cells wide, so that all results appear on a same scale, in
order to be more easily comparable. Figure 3 presents
the results we obtained for the simple “ratio of suc-
cess” metric, while Figures 4 and 5 present the results
when taking into account the evaluation of the diffi-
culty of each test, with linear and Gaussian weighting
respectively.
(a) (b)
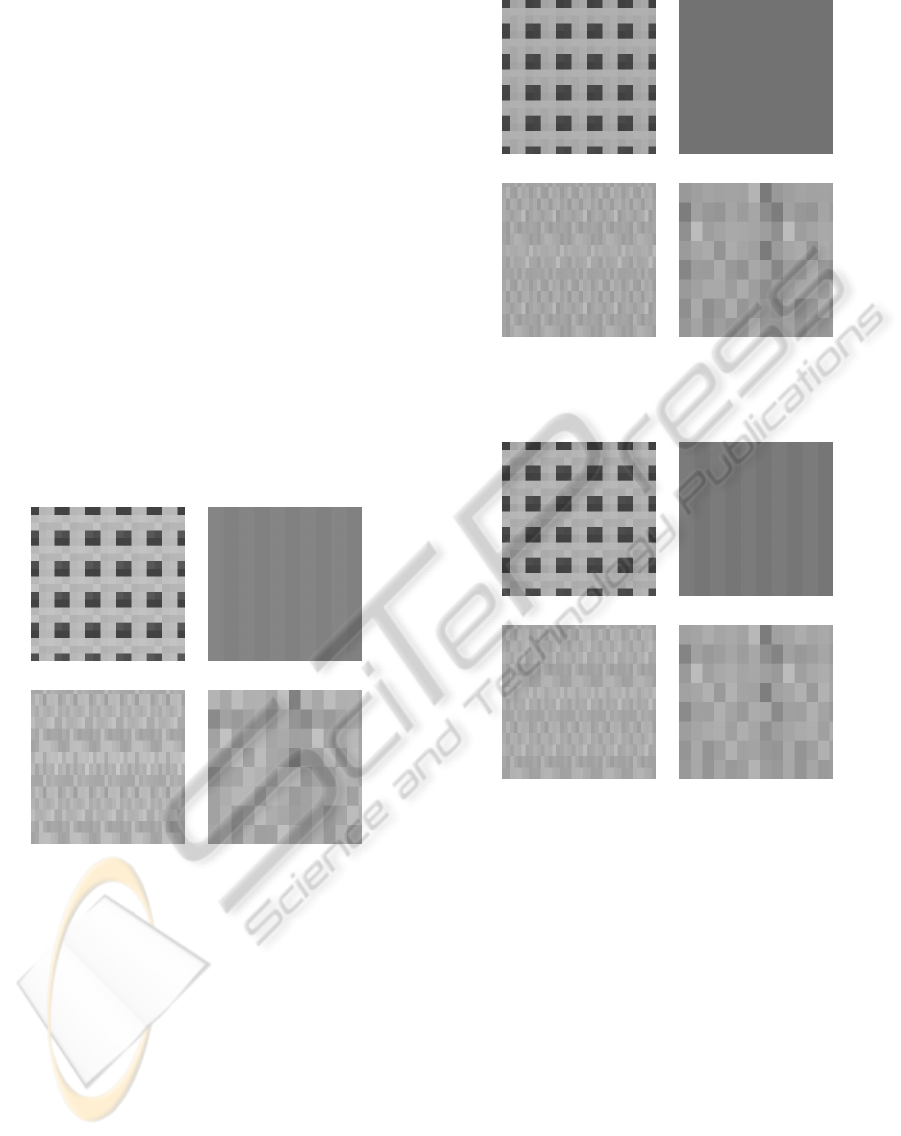
(c) (d)
Figure 3: Results for the Success Ratio Metric for (a) 02×
02, (b) 04× 08, (c) 01× 03, (d) 03× 05.
Before commenting the results we should first de-
scribe how to interpret the coloring in the Figures. In
Figure 3 the color of each cell depends on the suc-
cess ratio, i.e. the ratio of passed test of the PRNG
under test with respect to the benchmark PRNG. To
this end, lighter values (that are closer to 1.0) are con-
sidered more sucessfull than darker values (lower rel-
ative percentage of success). In Figure 4, the color
is again interpreted as the ratio of success, but in this
case the results have been weighted so as to measure
the difficulty of the tests, i.e. a test that was easier
to pass with the benchmark PRNG is weighted higher
than a difficult one, so that the tested PRNG is more
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 4: Results for the Linear Difficulty Metric for (a)
02× 02, (b) 04× 08, (c) 01× 03, (d) 03× 05.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5: Results for the Gaussian Difficulty Metric for (a)
02× 02, (b) 04× 08, (c) 01× 03, (d) 03× 05.
penalized when failing an easy test. Any difference
between Figures 3 and 4 should be interpreted with
this in mind, i.e. lighter colors in Figure 4 mean that
the PRNG under test managed to pass (at least) most
of the easiest tests. A similar interpretation holds for
Figure 5.
The first thing to notice is the very low success
rate that appears on the corner tiles of the 02 × 02
configuration. This is more or less something that can
be easily understood, since the corner boundary cells
have a higher amount of constant inputs due to the
free boundary conditions. A second thing to mention
is that regarding the 04×08tiles, we can see that there
is a slight difference in the success ratio between the
first and second tile within a CA. This difference van-
ishes when we take into account the linear difficulty
TILED CELLULAR AUTOMATA FOR AREA-EFFICIENT DISTRIBUTED RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS
401

measure of tests, and reappears when we consider the
difficulty measure to follow a Gaussian law. This is
one of the points that we would like to investigate fur-
ther, since it requires to take into account the statistics
of each individualtest and its significance on the over-
all “score” of a PRNG.
Finally, we need to note that there seems to be a
“masking” of the “badness” of a tile as we increase
its dimensions. Although at first this might seem as a
simple and efficient method to increase the quality of
the random numbers, it increases the area per random
bit, since it would require temporary buffers to store
the random bits as well as multiplexers / shift registers
and extra control so as to distribute them.
4.1 Results for the LFSR and Base CA
Implementations
In this section we present shortly the quality metric
results that we obtained for the LFSR simulations,
using the LFSR-based PRNGs designed in (George
and Alfke, 2000). These results are outlined in Ta-
ble 1. The first thing to note is that, as the length
Table 1: Quality Metric Results for LFSR PRNGs.
LFSR Length Ratio Linear Gaussian
32 0.585 0.566 0.573
48 0.632 0.604 0.619
64 0.528 0.512 0.520
168 0.637 0.620 0.630
4× 32 0.698 0.670 0.684
2× 64 0.604 0.585 0.595
168/17 bits 0.203 0.196 0.198
168/17 bits (shuffled) 0.160 0.161 0.161
of the LFSR increases, the quality increases accord-
ingly, except for 64 bits. Further, using multiple par-
allel LFSRs, initialized with different random values,
seems to yield better results, as we see for example
in the case of 4 × 32-bits LFSRs. This is also true
for 2× 64-bits LFSRs, although the corresponding re-
sults remain much lower than with 4× 32-bits LFSRs
that require the same area while generating twice the
random bit throughput. What we need to mention is
that although LFSRs provide a much lower through-
put and have a much lower factor of random bits per
area, they seem to rapidly converge to high quality
metrics (i.e. a 32 bit LFSR has a fairly good met-
ric, that is above 0.5, i.e. above 50% of success), al-
though they do not ultimately reach the quality met-
rics of the base CA (see Table 4 for a comparison).
Finally in this table we show the quality results for
two cases similar to the ones that we mentioned in the
introduction, namely using a very large LFSR and ex-
tracting several bits from it from irregular intervals.
These two methods are noted as “168/17”, meaning
that we extract 17 bits from an 168 bits long LFSR
and as “168/17 (shuffled)” where the only difference
is that the output bits are shuffled. As we mentioned,
these provide a higher throughput (17 bits per cycle in
this case) although they display a significantly lower
quality. Finally, in the specific example we present,
shuffling the bits further decreased the quality of ran-
dom numbers. This is probably an indication as to
how sensitive this method is to modifications of the
extracted bits or to the way of shuffling them.
4.2 Synthesis Results
In this section we will present some synthesis results
for both the tiled architecture and the LFSRs we men-
tioned above. As we expect, the area efficiency of the
CA based approach is much higher than that of the
LFSRs, although the LFSR implementations provide
more constant and what appears to be robust success
rates.
Table 2: Synthesis Results for the Tested LFSRs.
LFSR Length Occupied Cells
32 17
48 25
64 29
168 75
4× 32 127
2× 64 125
Keep in mind that in the case of FPGAs one slice
corresponds to possibly more that one flip flop, al-
though this is not always the case. Nevertheless, the
LFSRs we selected for our testing were among those
that are optimized for the family of Xilinx FPGAs,
(George and Alfke, 2000), which we based our syn-
thesis results on. Therefore the figures we report are
in a sense optimal. Regarding the target device, we
used a Xilinx Spartan3 FPGA (XC3S1200), which is
a rather small towards medium device, in terms of
area.
Table 3: Synthesis Results for the Tiled CA Approach.
Dimensions Occupied Cells
8× 8 78
32× 32 1229
64× 64 5048
The first thing to note is that the area increases
rapidly with the dimensions, as it is expected. Nev-
ertheless, the ratio of random bits per unit of area de-
creases only slightly, to accomodate for the extra in-
terconnect and control that is required.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
402

As we mentioned above, a second thing to note
is that, depending on the tiling scheme, we may have
cases where there is some unused area. This is un-
avoidable, since the area must increase in “steps” of
the dimensionsof the base CA, but can only be a prob-
lem in very dense designs. One way to benefit from
this problem is to rearrange the tiling scheme, leav-
ing possible unused areas among the tiles, in order to
utilize the areas that give the best quality results. Al-
though this is not a real solution to the problem of
unused (or “slack”) area, it is a fair trade-off between
area and improved random number quality.
4.3 Why not use 1 Base CA per Word?
In Table 4 we outline the metric results for the base
CA when the bits are read in raster scan order, or
when they are read in the order proposed by the au-
thors, that is by iterating the CA 4 times, so as to ac-
cumulate 4 bits per cell and then concatenate the re-
sulting 4 bit words into a 256-bits word.
Table 4: Quality Metric Results for the Base CA PRNGs.
Base CA Ratio Linear Gaussian
Raster Scan Mode 0.722 0.670 0.703
4Bits Mode 0.637 0.614 0.628
As we can see from the results of the table, the
success ratio and the other metrics are comparable
and even outperform the best LFSR results that we
presented in the previous section. Now, given these
very good properties of the base CA, it would be rea-
sonable to wonder, whether it is worth using 1 base
CA per required random word. This would seem to be
a simple and elegant solution, since the area of each
CA is comparable to a 168-bit LFSR, while the ran-
dom bit throughput and quality are much higher. The
problem with this approach is that the control circuit
and buffering that would be required in order to store
the random words and drive them to the target mod-
ules would result in a significant increase of the occu-
pied area, unless of course the required random word
length is 64 bits.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we present a method for generating dis-
tributed streams of pseudo random numbers in a two
dimensional context. Our architectural approach is
based on using a two-dimensional base CA that has
good proven properties and is capable of generating
high quality random numbers. We replicate this CA
so as to generate a “substrate” of CAs. This substrate
is then divided into tiles, so that each tile contains
a sufficient number of bits with respect to the word
length that is required for the target application. De-
pending on the selected base CA, this approach may
introduce tiles that have a significantly degraded qual-
ity with respect to the quality of the original base CA.
In order to provide a measure of comparison
in terms of the required area per random bit, we
compared our results with the most commonly used
random number generators in embedded and hard-
ware applications, namely LFSR-based PRNGs, tak-
ing into account both the required area and the quality
of the generated random streams. Now, as we men-
tioned, this comparison is rather unfair, since the ad-
vantages of CA based PRNGs, especially in terms of
the number of random bits per area unit that is nearly
constant and equal to one cell per bit, i.e. one flip-
flop plus several gates per random bit, while in the
case of LFSRs we need several flip-flops and gates
per random bit in order to achieve equivalent qual-
ity results. One point here is that, at least for FP-
GAs, there are LFSR structures that are highly op-
timized and achieve much lower than expected area
overheads. A second point is that we needed a well
established base so as to provide a way to compare
our results with other approaches, and LFSRs provide
such an established base.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that it appears that
the recent research on two dimensional CA as ran-
dom number generators has matured enough so as to
allow using them in real-world applications and sci-
entific simulations. Their complexity still does not
allow us to extract analytical formulas regarding their
behavior or to study their properties in detail, as it
is the case with LFSR-based PRNGs. This explains
why learning approaches such as genetic algorithms
are desirable. Nevertheless we can still ensure a cer-
tain level of confidence which is further strengthened
by the quality of the results we experimentally ob-
tained. Because of their regular structure and small
footprint and simple computational units involved in
their construction, they are extremely well suited for
embedded and hardware applications.
Regarding our future work, one of our first ef-
forts will be to further improve the empirical met-
rics that we used in this paper. One way to achieve
this is to take into account the independent statistics
of each one of the tests in the battery. This will al-
low us to have a more fine-grained overview of the
significance of each test, instead of using aggregated
measures. Focusing on the detailed performance we
will be able to better assess the quality of different ar-
chitectures and base CAs. Finally, as we mentioned
above, we are interested in investigating other possi-
TILED CELLULAR AUTOMATA FOR AREA-EFFICIENT DISTRIBUTED RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS
403

ble base CAs, with toric or periodic boundaries, so
as to avoid having “weak” areas where the quality of
random numbers is significantly decreased.
REFERENCES
(1983). Users are individuals: individualizing user mod-
els. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies,
18(3):199 – 214.
Abarbanel, H. D. I., Brown, R., Sidorowich, J. J., and
Tsimring, L. S. (1993). The analysis of observed
chaotic data in physical systems. Rev. Mod. Phys.,
65(4):1331–1392.
Bade, S. and Hutchings, B. (1994). Fpga-based stochastic
neural networks-implementation. In FPGAs for Cus-
tom Computing Machines, 1994. Proceedings. IEEE
Workshop on, pages 189 –198.
Berry, H., Gracia P´erez, D., and Temam, O. (2006). Chaos
in computer performance. Chaos, 16:013110.
Bonnin, G., Brun, A., and Boyer, A. (2009). A Low-Order
Markov Model integrating Long-Distance Histories
for Collaborative Recommender Systems. In Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI).
Brown, R. (2009). Dieharder prng tests.
Chowdhury, D. R., Sengupta, I., and Chaudhuri, P. P.
(1994). A class of two-dimensional cellular automata
and their applications in random pattern testing. J.
Electron. Test., 5(1):67–82.
Das, A. and Chaudhuri, P. (1993). Vector space theoretic
analysis of additive cellular automata and its appli-
cation for pseudoexhaustive test pattern generation.
IEEE Transactions on computers, 42(3):340–352.
George, M. and Alfke, P. (2000). Xapp210: Lin-
ear feedback shift registers in Virtex devices.
http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/
application notes/ xapp210.pdf.
Girau, B. (2004). FPNA: applications and implementations.
In Amos Omondi, J. R., editor, FPGA Implementa-
tions of Neural Networks, pages 43–79. Kluwer Aca-
demic Publishers.
Girau, B., Torres-Huitzil, C., Vlassopoulos, N., and Baron-
Zambrano, J. H. (2010). Reaction-diffusion and
chemotaxis for decentralized gathering on FPGAs. In-
ternational Journal of Reconfigurable Computing, ar-
ticle in press.
Graham, P. and Nelson, B. (1996). Genetic algorithms
in software and in hardware-a performance analysis
of workstation and custom computing machine im-
plementations. In FPGAs for Custom Computing
Machines, 1996. Proceedings. IEEE Symposium on,
pages 216 –225.
Guan, S.-U. and Tan, S. K. (2004). Pseudorandom Num-
ber Generation with Self-Programmable Cellular Au-
tomata. IEEE Transactions on Computer-aided De-
sign of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 23(7):1095–
1101.
Hortensius, P., McLeod, R., and Card, H. (1989). Paral-
lel random number generation for VLSI systems using
cellular automata. IEEE Transactions on Computers,
38(10):1466–1473.
Kier, L., Seybold, P., and Cheng, C.-K. (2005). Modeling
Chemical Systems Using Cellular Automata. Springer.
Marsaglia, G. (1995). Diehard prng tests.
Matsumoto, M. and Nishimura, T. (1998). Mersenne
twister: a 623-dimensionally equidistributed uni-
form pseudo-random number generator. ACM Trans.
Model. Comput. Simul., 8:3–30.
Musti, U., Toutios, A., Ouni, S., Colotte, V., Wrobel Daut-
court, B., and Berger, M.-O. (2010). HMM-based
Automatic Visual Speech Segmentation Using Facial
Data. In Interspeech 2010, pages 1401–1404.
Nandi, S., Kar, B., and Chaudhuri, P. (1994). Theory
and applications of cellular automata in cryptography.
IEEE Transactions on computers, 43(12):1346–1357.
Rabiner, L. (1989). A tutorial on hidden markov models
and selected applications in speech recognition. Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE, 77(2):257 –286.
Rougier, N. P. and Vitay, J. (2005). Emergence of Attention
within a Neural Population. Neural Networks.
Salapura, V. (1994). Neural networks using bit stream arith-
metic: a space efficient implementation. In Circuits
and Systems, 1994. ISCAS ’94., 1994 IEEE Interna-
tional Symposium on, volume 6, pages 475 –478 vol.6.
Stewart, W. J. (2009). Probability, Markov chains, queues,
and simulation: the mathematical basis of perfor-
mance modeling. Princeton University Press.
Tomassini, M. and Perrenoud, M. (2001). Cryptogra-
phy with cellular automata. Applied Soft Computing,
(1):151–160.
Tomassini, M., Sipper, M., and Perrenoud, M. (2000). On
the generation of high-quality random numbers by two
dimensional cellular automata. IEEE Transactions on
computers, 49(10):1146–1151.
van Daalen, M., Jeavons, P., and Shawe-Taylor, J. (1993).
A stochastic neural architecture that exploits dynam-
ically reconfigurable fpgas. In FPGAs for Cus-
tom Computing Machines, 1993. Proceedings. IEEE
Workshop on, pages 202 –211.
Vlassopoulos, N., Fat`es, N., Berry, H., and Girau,
B. (2010). An FPGA Design for the Stochastic
Greenberg-Hastings Cellular Automata. In Interna-
tional Conference on High Performance Computing
& Simulation - HPCS 2010, pages 565–574.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
404
