
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER
CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN ENGINEERING
Chris Thompson, Douglas Schmidt
Dept. of Computer Science, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
Hamilton Turner, Jules White
Dept. of Elec & Computer Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Mobile computing, Low-power, Model driven engineering.
Abstract:
Smartphones are mobile devices that travel with their owners and provide increasingly powerful services.
The software implementing these services must conserve battery power since smartphones may operate for
days without being recharged. It is hard, however, to design smartphone software that minimizes power
consumption. For example, multiple layers of abstractions and middleware sit between an application and the
hardware, which make it hard to predict the power consumption of a potential application design accurately.
Application developers must therefore wait until after implementation (when changes are more expensive) to
determine the power consumption characteristics of a design.
This paper provides three contributions to the study of applying model-driven engineering to analyze power
consumption early in the lifecycle of smartphone applications. First, it presents a model-driven methodology
for accurately emulating the power consumption of smartphone application architectures. Second, it describes
the System Power Optimization Tool (SPOT), which is a model-driven tool that automates power consumption
emulation code generation and simplifies analysis. Third, it empirically demonstrates how SPOT can estimate
power consumption to within ∼3-4% of actual power consumption for representative smartphone applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Emerging Trends and Challenges. Recent advances
in mobile device and smartphone technologies have
greatly increased the capabilities of these devices. For
instance, the Google Nexus One has a 1Ghz proces-
sor and the Motorola Droid has a 550 Mhz processor,
compared to the older Palm Treo’s 315 Mhz proces-
sor. Despite these performance increases, these de-
vices still possess limited battery capacities that ap-
plication developers must manage carefully.
To optimize power consumption effectively, de-
velopers must understand the trade-offs between per-
formance and battery life, as well as the implications
of their software architecture on power consumption.
Functional requirements, such as minimum applica-
tion response time, can conflict with power consump-
tion optimization needs. For example, a traffic acci-
dent detection application (White et al., 2010) must
be able to detect sudden accelerations indicative of a
car accident. To detect acceleration eventsthat indica-
te accidents, the application must sample device sen-
sors and perform numerous calculations at a high rate.
Conflicts occur between the functional requirements
e.g. the minimum sensor sampling rate needed to ac-
curately detect accidents, and the non-functional re-
quirements e.g. sustaining operations on the mobile
device without frequent battery recharging.
Due to complex middleware, OS, and network-
ing layers, it is hard to predict the effects of ap-
plication software architecture decisions on power
consumption without actually implementing a design,
which makes it hard to analyze the power consump-
tion of design until late in the development cycle,
when changes are more expensive (Kang et al., 2008).
For example, a developer may elect to use HTTPS in-
stead of HTTP to satisfy a security requirement by
making communication between the application and
server more confidential. It is currently hard, how-
ever, to predict how much additional power is con-
sumed by the added encryption and decryption of data
without actually implementing the system.
101
Thompson C., Schmidt D., Turner H. and White J. (2011).
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN ENGINEERING.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems, pages 101-113
DOI: 10.5220/0003372801010113
Copyright
c
SciTePress

It is also hard to quantify the trade-off between
power consumption and security, as well as many
other design decisions. Moreover, certain design
decisions, such as data transmission policies (e.g.,
should an application transmit immediately or wait
for a specific medium like a Wi-Fi or 3G cellular con-
nection) are especially hard to analyze early in the de-
sign cycle, due to their variability. For instance, if
an application only sends data intermittently, it may
be beneficial to transmit small amounts of data over
cellular connections due to the decreased power con-
sumption of 3G cellular connection compared to Wi-
Fi (Agarwal et al., 2007). However, if a large amount
of data must be sent, the total time required to trans-
mit it over 3G may negate the benefit of using the less
power consumptive connection. The cellular connec-
tion will take longer to transmit the data, therefore,
which may in turn consume more total power than the
Wi-Fi radio that can transmit the data faster.
Solution Approach → Power Consumption
Emulation of Mobile Software Architectures
with Model-driven Testing and Auto-generated
Code. By using Model-driven Engineering
(MDE) (Schmidt, 2006), we allow develop-
ers to specify a domain-specific modeling lan-
guage(DSML) (L´edeczi et al., 2001) to capture
key software architecture elements related to power
consumption. Developers can then use automated
code generators to produce emulation code from
this model. Developers can also execute the gen-
erated emulation code on target hardware, collect
power consumption information, and analyze the
application’s power consumption.
This emulation code allows developers to ana-
lyze a proposed software architecture prior to invest-
ing significant time and effort in a complete imple-
mentation of the design. The auto-generation of em-
ulation code also enables developers to compare a
range of different designs quantitatively during initial
phases of a development process, which allows devel-
opers to select designs that satisfy both functional and
non-functional requirements while minimizing power
consumption. This analysis can also occur early in
the software lifecycle (e.g., at design time), thereby
avoiding costly changes being required later in order
to optimize power consumption.
This paper describes the System Power Optimiza-
tion Tool (SPOT), which uses MDE techniques to an-
alyze the power consumption of mobile software ar-
chitectures. SPOT allows developers to create high-
level models of candidate software architectures using
the System Power Optimization Modeling Language
(SPOML) that capture key software components re-
lated to power consumption. SPOT generates emu-
lation code from the model that can be executed on
target devices. As this emulation code is executed,
it is also instrumented to collect power consumption
data; the power data can later be downloaded and
analyzed offline. This emulation and analysis cy-
cle allows developers to understand the power con-
sumption implications of their designs without expen-
sive and time consuming manual programming using
third-generation languages, such as C#, C/C++, and
Java.
SPOT’s generated emulation code mimics key
power-consuming aspects of a proposed software
architecture. Key power consumptive components
of mobile application software architectures include
GPS, acceleration, orientation, sensor data con-
sumers, and network bandwidth consumers (Pering
et al., 2006). Focusing SPOT on these components al-
lows developers to model the most significant power
expenditures of their applications. Moreover, as ap-
plications are constructed, the generated emulation
code can be replaced incrementally with actual appli-
cation components, allowing developers to refine the
accuracy of the analysis continuously throughout the
software lifecycle.
Paper Organization. The remainder of this paper
is organized as follows: Section 2 outlines a mo-
tivating example we use to showcase and evaluate
SPOT’s functionality throughout the paper; Section 3
summarizes the challenges associated with predict-
ing power consumption of mobile application soft-
ware architectures; Section 4 describes the structure
and functionality of SPOT and SPOML; Section 5
empirically evaluates SPOT’s power prediction capa-
bilities and shows how its modeling primitives and
emulation infrastructure can accurately predict power
consumption for representative mobile applications
on the Android smartphone platform; Section 6 com-
pares SPOT with related work; and Section 7 presents
concluding remarks.
2 MOTIVATING EXAMPLE:
THE WRECKWATCH CASE
STUDY
This section describes WreckWatch (White et al.,
2010), which is an open-source
1
mobile application
we built on the Android smartphone platform to de-
tect automobile accidents. We use WreckWatch as a
1
WreckWatch is available from vuphone.googlecode.
com.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
102

case study throughout this paper to demonstrate key
complexities of predicting the power consumption
of mobile software architectures. As shown in Fig-
Figure 1: WreckWatch Operation.
ure 1, WreckWatch operates by (1) monitoring smart-
phone sensors (such as GPS receivers and accelerom-
eters) for sudden acceleration/deceleration events that
are indicative of an accident. Data about the event
are then (2) uploaded to a remote server over HTTP
where first-responders and/or other motorists can ac-
cess the information via a web browser or Android
client. WreckWatch allows bystanders (3) to upload
images of the accident to the same web server, thereby
increasing the information first-responders possess
before arriving at the scene.
To detect traffic accidents accurately, Wreck-
Watch runs continuously as a background service and
continuously consumes a great deal of accelerometer
and GPS data. The application must therefore be con-
servative in its power consumption. If not designed
properly, WreckWatch can decrease smartphone bat-
tery life significantly.
3 CHALLENGES OF DESIGNING
POWER CONSCIOUS MOBILE
APPLICATIONS
This section describes the challenges associated with
developing power-aware mobile software, such as
the WreckWatch application described in Section 2.
High-level mobile application development SDKs,
such as Google Android or Apple iPhone, simplify
mobile application development, but do not simplify
power consumption prediction during application de-
sign. In fact, the abstractions present in these SDKs
make it hard for developers to understand the power
implications of software architecture decisions until
their designs have been implemented (Parikh et al.,
2002), as described in Section 3.1. Interaction with
sensors, such as accelerometers or GPS receivers and
network interaction, can also result in a significant
amount of power consumption, as described in Sec-
tions 3.2 and 3.3.
3.1 Challenge 1:
Accurately Predicting Power
Consumption of Framework API
Calls
Each line of code executed results in a specific
amount of power consumed by the hardware. In the
simplest case, this power consumption results from a
small series of CPU operations, such as reading from
memory or adding numbers. In some cases, however,
a single line of code can result in a chain of hardware
interactions, such as activation of the GPS receiver
and increasing the rate at which the screen is redrawn.
Moreover, although the higher levels of abstraction
provided by modern smartphone SDKs make it easier
for developers to implement mobile application soft-
ware, they also complicate predictions of the effects
on the hardware.
For example, WreckWatch heavily utilizes the
Google Maps API and the “MyLocation” map over-
lay, which provides end users with a marker indicat-
ing their current GPS location. The use of the “My-
Location” is typically accomplished with fewer than
10 lines of code, but results in substantial power con-
sumption. This is because the overlay is redrawn at a
high rate to achieve a “flashing” effect, and because
the overlay enables and heavily utilizes the GPS re-
ceiver on the device, which further increases power
expenditure. It is hard to predict how using arbitrary
API calls, such as this overlay, will affect application
power consumption without implementing a particu-
lar design and testing it on a particular target device.
This abstraction in code makes power-
consumption analysis on arbitrary segments of
code hard. Predicting power usage from high-level
design abstractions, such as a UML diagram, is even
harder. Section 4 describes the MDE and emulation
approach we use to address this challenge.
3.2 Challenge 2:
Accurately Predicting Power
Consumption of Sensor Usage
Architectures
In applications utilizing sensor data, the most accu-
rate sensor data is obtained by sampling as often as
possible. Sampling at high rates, however, incurs
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
103

high power consumption (Krause et al., 2005) by not
allowing sensors to enter low power modes and by
increasing the amount of data processed by applica-
tions. Reducing the sample rate can decrease appli-
cation power consumption considerably, but also re-
duces accuracy. The trade-offs between power con-
sumption and accuracy at a given sampling rate are
hard to determine without empirical tests on a target
device due to the high-degree of layering in modern
smartphone APIs and system architectures.
For example, WreckWatch was originally de-
signed to collect GPS data every 500 milliseconds
and consume accelerometer data at Android’s pre-
defined NORMAL rate setting. During the devel-
opment of WreckWatch, it was clear that reducing
WreckWatch’s GPS sampling rate would reduce over-
all power consumption, but it was unclear to what de-
gree. Moreover, it was hard to predict what sample
rate would provide sufficient accuracy and still allow
the phone to operate for days between charges. Sec-
tion 4 describes how we use automatic code gener-
ation to create emulated applications that accurately
analyze the power consumption of a candidate sensor
utilization architecture without incurring the substan-
tial time and effort to manually implement the archi-
tecture.
3.3 Challenge 3:
Accurately Assessing the Effects of
Different Communication Protocols
on Power Consumption Prior to
Implementation
Each application and network communication proto-
col has a specific overhead associated with it and can
result in significant power consumption (Heinzelman
et al., 2000). Certain protocols require more devel-
opment overhead to implement, but have low runtime
overhead (e.g. bandwidth consumption, message pro-
cessing time, etc.). It is hard to determine early (e.g.,
at design time) in an applications lifecycle, however,
how this overhead will affect power consumption and
whether the number of messages transmitted will be
substantial enough to impact power consumption sig-
nificantly. This challenge is exacerbated if certain
network operations consume more power than others,
e.g., receiving data often consumes more power than
transmitting data (Wang et al., 2006).
For example, to provide the most accurate situa-
tional awareness to first responders—and provide the
most accurate congestion information to motorists—
the WreckWatch application must periodically re-
quest wreck information from the central web server.
These updates must be done periodically and were
originally intended to run over HTTP. Using HTTP
results in a significantly less developer effort but
results in a considerable amount of communication
overhead from the underlying TCP and HTTP proto-
cols, which ultimately transmits substantial amounts
of data that have no relevance to the application. It is
hard to determine at design time if/how this additional
data transmission will significantly impact powercon-
sumption. Section 4 shows how we used MDE code
generation to implement and analyze potential com-
munication protocols rapidly.
4 THE SYSTEM POWER
OPTIMIZATION TOOL (SPOT)
This section describes the structure and functional-
ity of the System Power Optimization Tool (SPOT),
which is an MDE tool that allows developers to model
potential mobile application software architectures to
predict their power consumption, generate code to
emulate that architecture, and then systematically an-
alyze its power consumption properties. SPOT ad-
dresses the challenges described in Section 3 by al-
lowing developers to understand the implications of
their software architecture decisions at design time.
SPOT’s development process enables develop-
ers to generate visual, high-level models rapidly, as
shown in Figure 2. These models can then be used to
analyze the power consumption of mobile application
software architectures (step 1 of Figure 2). SPOT thus
helps overcome key challenges of predicting power
consumption by generating device logic that can be
used to gather power consumption information on
physical hardware during early phases of an applica-
tion’s software lifecycle, which helps minimize ex-
pensive redesign/refactoring costs in later phases.
SPOT uses models shown in Figure 2 to generate
instrumented emulation code for the given platform
or device (step 2 of Figure 2). When executed on
actual hardware (step 3 of Figure 2), this generated
code collects power consumption and system state in-
formation. This power consumption data can then be
downloaded and analyzed offline to provide develop-
ers with application power utilization at key points
throughout the lifecycle and execution path (step 4 of
Figure 2).
SPOT also supports the use of custom code mod-
ules. These models allow developers to replace auto-
matically generated code with actual application logic
while still providing the same analytical capabilities
available when using generated code. SPOT therefore
not only allows developers to perform analysis early
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
104

(Optional)
Developer replaces
model elements
with specific code
Figure 2: SPOT Modeling and Analysis Process.
in the development cycle, but also to perform contin-
uous integration testing throughout development.
SPOT is implemented as a plugin for the Eclipse
IDE. Its runtime power consumption emulation and
capture infrastructure is built using predefined, user-
configurable classes that emulate specific power con-
suming components, such as GPS data consumers.
This infrastructure captures power consumption in-
formation during executing by using the device’s
power API. For example, power data collection on
the Android platform is performed by interfacing
with the OS application power API, i.e., the Android
power consumption API as implemented by the “Fu-
elGauge” application.
The remainder of this section describes how
SPOT’s DSML, emulation code generation, and per-
formance measurement infrastructure help applica-
tion developers address the challenges presented in
Section 3. Section 4.1 describes SPOT’s modeling
language, SPOML, Section 4.2 describes how SPOT
generates emulation code, and Section 4.3 describes
how SPOT analyzes and evaluates emulation code
during execution.
4.1 Mobile Application Architecture
Modeling and Power Consumption
Estimation
SPOT describes key power-consuming aspects of a
mobile application via a DSML with specific lan-
guage elements. This DSML allows developers to
specify their software architecture visually with re-
spect to power consuming components, as shown in
Figure 2. Prior work (Thompson et al., 2009; White
et al., 2010; Turner et al., 2009) showed how the fol-
lowing components are often significant power con-
sumers in mobile applications:
• CPU Consumers are used to represent CPU-
intensive code segments such as calculations on sen-
sor data. Developers can specify the amount of CPU
time that should be consumed by specifying the num-
ber of loop iterations of a square root calculation that
should be run. For example, WreckWatch developers
can model the mathematical calculation time to deter-
mine the current G-forces on the phone.
• Memory Consumers generate dynamically al-
located memory. These consumers allow developers
to analyze not only the power consumed by actual op-
erations, but also their impact (such as the frequency
and duration of garbage collector sweeps) on garbage
collection. Developers can specify the amount of
memory to consume as bytes. For example, Wreck-
Watch developers can model the effects of caching ac-
cident images of varying sizes.
• Accelerometer Consumers, which interact
with system accelerometers and consume accelerom-
eter data. These consumers can be configured to uti-
lize the full range of system-supported sample rates.
For example, WreckWatch developers can model the
sensor interaction needed to accurately detect car ac-
cidents.
• GPS Consumers interact with the device’s GPS
receiver. These consumers can be configured with
custom sample rates as well as a minimum distance
between points, i.e., the sensor will only return a data
point if the distance between the current point and
the last point is greater than a specified value. GPS
consumers allow developers to analyze the impact of
using a location service configuration on power con-
sumption. For example, WreckWatch developers use
this capability to model how polling for a vehicle’s lo-
cation at different rates impacts power consumption.
• Network Consumers emulate application net-
work interaction by periodically transmitting and re-
ceiving data. Network consumers allow users to sup-
ply SPOT with sample data that is then transmitted
at the interval specified. For example, WreckWatch
developers can provide a URI along with server and
port information to configure SPOT to make a specific
request. These consumers can also be configured to
execute at varying times to emulate periodic updates.
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
105

• Screen Drawing Agents utilize graphics li-
braries, such as OpenGL, to emulate a graphics-
intensive application, such as a game or streaming
video to a first responder’s WreckWatch client. Users
can configure these consumers by specifying the types
and size of objects to draw on the screen, along with
any transformations that should be performed on the
object. For example, WreckWatch developers can use
the drawing agents to show how the use of images and
video for situational awareness impacts battery life.
• Custom Code Modules allow developers to
specify their own code to run against the profiling
package. This capability allows developers to extend
SPOT’s functionality to meet their needs, as well as
incrementally replace the emulation code with actual
application logic as it becomes available. Replacing
the emulation logic allows developers to perform test-
ing as development progresses and increase the ac-
curacy of the evaluation and analysis. For example,
WreckWatch developers can use these consumers to
include a service for uploading multimedia content
about an accident to a central web server.
The metamodel for SPOT’s DSML, called the
System Power Optimization Modeling Language
(SPOML), allows application developers to build
software architectural specifications that determine
power consumption from key power consuming com-
ponents. SPOML was created using the metamod-
eling features of the Generic Eclipse Modeling Sys-
tem (GEMS) (White et al., 2009), which is a tool
for rapidly generating visual modeling tools atop the
Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF). GEMS is built
atop Ecore, which provides metamodeling and mod-
eling facilities for Eclipse (Budinsky et al., 2003).
The primary application serves as the root element
of the model. Power consumption modules can ex-
ist within either activities (which are basic building
block components for Android applications and rep-
resent a “screen” or “view” that provides a single, fo-
cused thing a user can do) or services (which are back-
ground processes that run without user intervention
and do not terminate when an application is closed).
Each activity or service can contain one or more
power consumer modeling elements described above.
Developers can therefore emulate potential decisions
that they make when designing a mobile device ap-
plication, which allows them to emulate a wide range
of application software architectures. For example,
Figure 3 shows a SPOML model of the WreckWatch
application’s sensor usage design.
Acceleration and GPS consumers run in indepen-
dent services, while the network consumer runs in the
application’s activity. This model results in an appli-
cation that monitors GPS and accelerometer values at
Figure 3: WreckWatch Model
all times regardless of what the user is doing. It only
utilizes the network connection, however, when the
user has the WreckWatch application open and run-
ning.
4.2 Generating Software Architecture
Emulation Code
Predicting the power consumption of an arbitrary de-
sign decision is hard, as described in Section 3.1.
SPOT addresses this challenge by generating appli-
cation emulation code automatically to execute on the
underlying device hardware. SPOT’s automatic gen-
eration of emulation code allows application develop-
ers to reduce the time required to write enough code to
analyze system power consumption accurately. This
emulation code is instrumented so the architecture’s
power expenditures can be examined after a test run.
In addition to instrumenting the code, SPOT has
the potential to apply the same model for multiple
target platforms, such as Android and iPhone, as
long as configurable code is available for the power-
consuming elements. This emulation and analysis
cycle allows developers to observe the power con-
sumption of their design very early in the develop-
ment cycle, as well as evaluate their software designs
across multiple hardware configurations to assess how
changes in hardware affect application power con-
sumption. For example, even though the Motorola
Droid and Google Nexus One both run the Android
platform, each possesses key hardware differences,
such as the type and size of the display, that impact
power consumption.
The generated emulation code allows developers
to address the remaining challenges of selecting an
optimal communication protocol and optimizing sen-
sor polling rates, as described in Section 3. Gen-
erated emulation code allows developers to evaluate
the power consumption of a potential design empiri-
cally, rather than simply guessing its power consump-
tion or waiting until an application implementation is
complete before running tests. Moreover, develop-
ers can quantitatively compare the power consump-
tion effects of choosing different networking proto-
cols and can evaluate the power consumption of dif-
ferent sensor sampling rates.
To accomplish this mobile software architectural
emulation, SPOT uses a set of predefined code blocks
that can be configured at runtime to perform power
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
106

consuming operations. SPOT uses an XML config-
uration file to perform any necessary configuration
and create an application that emulates the powercon-
sumption of the desired software architecture. To gen-
erate this XML configuration file, SPOT interprets the
model outlined in Section 4.1. Users of SPOT de-
fine the model and tweak configuration parameters,
and SPOT can then compile the model and parame-
ters into an intermediate XML format which is uti-
lized to configure prebuilt implementations of each
power consuming element described in Section 4.1.
Figure 4 shows a sample of the XML configura-
tion file generated for the WreckWatch model shown
in Figure 3. The XML shown in Figure 4 represents
Figure 4: Sample WreckWatch Emulation XML.
a configuration with two backgroundservices running
an accelerometer consumer and a GPS consumer. The
GPS consumer samples every 500 milliseconds, with
a minimum radius between sample points set to 0.
The accelerometer consumer is set to sample at the
NORMAL rate, which is a constant defined by An-
droid. There is also a network consumer transmitting
sample data every 30 seconds and repeating infinitely.
The network consumer is configured to connect to a
specific host on a specific port and utilize the HTTP
protocol.
The predefined power consumers have config-
urable options (such as the sample rate of the GPS
and data to transmit over the network) provided by the
XML configuration file. These power consumption
elements are generic and applicable to a wide range
of platforms, such as Android, iPhone, or BlackBerry.
The predefined power consumers are implemented on
the Android platform as follows:
• CPU Consumers are implemented as a set of
nested loops that perform basic mathematical opera-
tions, such as square root calculations, on randomly
generated data. This module utilizes the CPU while
minimizing utilization of other system resources,
such as memory that could skew power consumption
information. For example, this consumer uses primi-
tive types to avoid allocating dynamic memory. Users
can adjust the length of the loops via a configurable
parameter. Various end device processors result in
same-length loops performing differently on divfer-
ent devices, in a manner similar to CPU-intensive al-
gorithmic performance on end-user devices.
• Memory Consumers are implemented by dy-
namically allocating custom objects that wrap byte
arrays. To analyze the frequency of garbage collec-
tion, a Java
WeakReference
object is used to inform
the garbage collector that they can be reclaimed, de-
spite having active references within running code.
The object’s
finalize()
method (which is called im-
mediately before the object is reclaimed by the An-
droid Dalvik virtual machine) is overridden to record
the time of garbage collection, thereby allowing de-
velopers to analyze the frequency of garbage collec-
tion runs. The
WeakReference
object will thus be
reclaimed during every garbage collection run.
Due to the limitations of the Android instrumen-
tation API, garbage collection and memory usage
must be inferred through analysis of the frequency
and duration of garbage collection runs, rather than
through direct power consumption measurement. Al-
though this limitation prevents developers from in-
cluding memory statistics in the data along with CPU,
sensor, and network utilization, they can still exam-
ine how their design uses memory. Users can also
configure the amount of memory and frequency of al-
location, as well as supply custom objects (such as
WreckWatch’s image caches) to use rather than the
byte arrays used by default.
• GPS Consumers are implemented by code that
registers to receive location updates from the GPS re-
ceiver at specific intervals.
• Accelerometer Consumers are implemented
using the configuration specified in the XML file,
along with generic setup code to establish a connec-
tion to the appropriate hardware.
• Network Consumers are implemented as em-
ulation code containing a timer that executes a given
networking operation, such as an HTTP operation at
a user defined interval.
• Screen Drawing Agents allow users to specify
3D and 2D graphics to draw on the screen. Develop-
ers will specify object contents along with any poten-
tial motion or actions.
• Custom Code Modules allow developers to
supply their own code blocks to extend the function-
ality of SPOT and enhance emulation accuracy as the
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
107

development cycle progresses by substituting the faux
emulation code with actual application logic. SPOT
allows developers to supply class files to load into the
emulation application dynamically, as well as method
“hooks” to allow the emulation code to interact with
the custom code properly.
4.3 Power Consumption
Instrumentation
SPOT uses an instrumentation system to capture
power consumption statistics as the emulation code
is executed, as shown in Figure 5. Components in
Figure 5: SPOT Instrumentation System.
the instrumentation system are either
Collectors
,
Recorders
, or
Event Handlers
.
Collectors
inter-
face directly with the specific power API on the sys-
tem and pass collected data to
Recorders
, which per-
sist the data collected by
Collectors
by writing it to
a file or other storage medium.
Event Handlers
re-
spond to the events fired by entering or leaving emu-
lation code blocks.
These components are dynamically loaded via
Java reflection to ensure extensibility and flexibil-
ity. For instance, developers can implement a cus-
tom
Collector
to monitor which components are in
memory at any given time. Alternatively, developers
could define
Recorders
to log power consumption
information to another data storage medium, such as
a local or network database rather than a flat file.
To analyze an architecture effectively, SPOT
records battery state information over time to al-
low developers to pinpoint specific locations in their
application’s execution path that demand the most
power. To collect power consumption information
accurately, SPOT uses an event-driven architecture
that precisely identifies the occurrence of each major
application-state change, such as registering or unreg-
istering a GPS listener and SPOT takes a “snapshot”
of the power consumption when the application per-
forms these operations. This event-drivenarchitecture
allows developers to understand the power consump-
tion of the application before, during, and after key
power-intensive components.
In addition to event-triggered power snapshots,
SPOT also periodically collects power consumption
information. This information allows developers to
trace overall power consumption or power consump-
tion within a given block. The power information
Collector
that collects snapshots and periodic sam-
ples can be configured to run in a separate process to
prevent contamination of the data.
To accomplish event-driven power profiling,
SPOT fires events immediately before an application
enters a component that was defined in the model and
immediately after it leaves a model-defined compo-
nent. These events work in conjunction with the peri-
odic power consumption updates to provide develop-
ers with a complete description of how their software
architecture elements consume power. SPOT’s event-
driven model of collecting power consumption data
also allows developers to identify precisely what the
application was doing when key power consumption
spikes occur, further helping them optimize their de-
signs.
SPOT’s emulation infrastructure currently runs on
the Android mobile platform and uses the power con-
sumption API utilized by the “FuelGauge” applica-
tion in the core Android installation. The power con-
sumption API provides application developers with
access to the amount of time the application utilizes
the CPU, sensors, wake-locks, and other system re-
sources, in addition to the overall power consumption.
Android’s power consumption API provides
power-consumption information on a per-package ba-
sis. By implementing SPOT in a different package,
developers can analyze power consumption without
influencing it. Collecting power consumption infor-
mation in this manner increases accuracy. Moreover,
SPOT can be implemented simply as a collector to
analyze existing applications without modifying their
source code.
5 RESULTS
This section analyzes the results of experiments that
empirically evaluate SPOT’s MDE-based capabilities
presented in Section 4. These experiments measure
SPOT’s ability to collect power consumption infor-
mation on a given model, as well as accurately model
the power consumption of a proposed application
software architecture. These results show how SPOT
can assess and analyze power consumption informa-
tion gathered through the Android’s power consump-
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
108
tion API and evaluate SPOT’s accuracy in predicting
power consumption information about a software ar-
chitecture at design time.
5.1 Hardware/Software Testbed
All tests were performed on a Google Nexus One with
a 1Ghz CPU, 512MB of RAM, 512MB of ROM and
a 4 GB SD card running the default installation of
Android 2.1 (Eclair). The SPOT application was the
only third-party application running at the time of ex-
perimentation. The same power consumption infor-
mation gathering logic was used to collect informa-
tion on emulation code, as well as the sample appli-
cations. The information was analyzed in Excel based
on power consumption data written to the device’s SD
card in the form of a CSV file.
To assess the consumption characteristics of dif-
ferent designs, the current SPOT version generates
an Android application package. It then periodically
samples the battery usage statistics from the OS writ-
ing these values to a CSV file on the SD card. SPOT
also fires events when the application’s state changes,
e.g., when the GPS is started or a sensor is discon-
nected. These events allow SPOT users to examine
the power consumption of active hardware, in addi-
tion to the overall consumption of the application.
SPOT uses an XML-based configuration file that
is generated from the SPOML model described in
Section 4.1. This XML file is loaded on to the de-
vice’s SD card and parsed at startup. Due to the way
that the power consumption API collects information,
the data gathered reflects only power consumed by
the SPOT application and does not include any power
consumed by system processes, such as the GUI dis-
play or garbage collector.
5.2 Experiment 1:
Empirical Evaluation of SPOT’s
Emulation Code Accuracy
Overview. This experiment quantitatively com-
pares the power consumption of two Android appli-
cations and the power consumption of the emulation
code derived from their respective SPOT models. En-
suring SPOT’s accuracy is important since it allows
developers to compare the power consumption of key
power consuming components in their mobile archi-
tecture.
The applications used in this experiment
are the WreckWatch application presented
in Section 2 and OpenGPSTracker (open-
gpstracker.googlecode.com),which is an open-source
Figure 6: Comparison of WreckWatch Application Logic
and Emulation Code.
Android application that uses GPS to track the coor-
dinates of the phone and display it on a Google Map
on the device. The GPS points, and other information
about the route, are stored on the device to allow the
user to replay the route later. OpenGPSTracker also
determines device speed as GPS points are collected.
Hypothesis. SPOT is intended to provide develop-
ers with an estimate of how a proposed application
software architecture will consume power. We there-
fore hypothesized that SPOT could provide power
consumption information to within 25% of the ac-
tual power consumption of WreckWatch and OpenG-
PSTracker. Based on prior work (Thompson et al.,
2009; White et al., 2010; Turner et al., 2009), we
also hypothesized that the components we chose rep-
resented the key factors in mobile application power
consumption and would be adequate to provide this
level of accuracy.
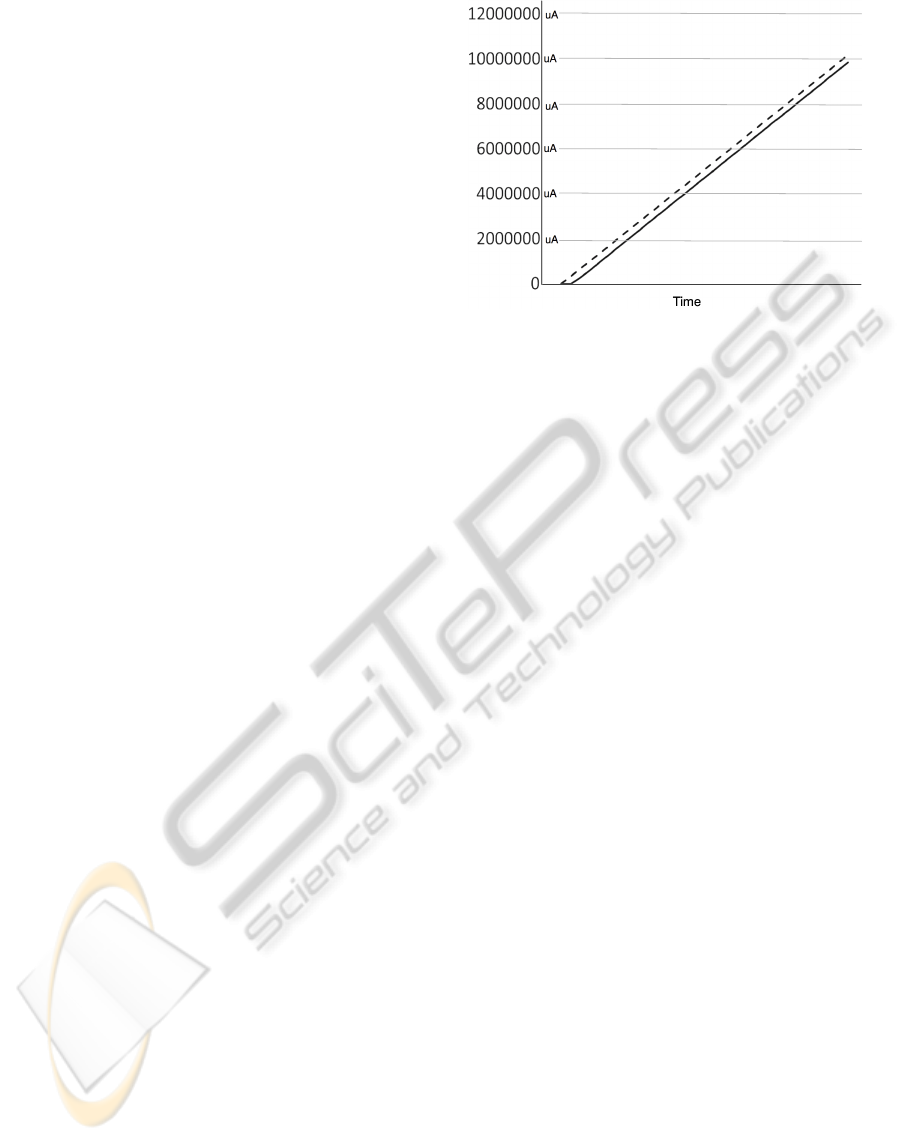
WreckWatch Results. Figure 6 shows the graph of
the actual power consumption of the WreckWatch ap-
plication compared with the power consumption of
the WreckWatch emulation code generated by SPOT.
The emulation code’s power consumption follows the
same trend as that of the application and provided a
final power consumption value that was within 3%
of the actual power consumed by WreckWatch. The
SPOT model consisted solely of GPS and accelerom-
eter consumers and did not attempt to model any ad-
ditional aspects of the WreckWatch application. The
model was accurate due to the substantial amount
of power required by the GPS receiver. This result
confirms that the GPS, sensor, and network modules
that SPOT provides are key determinants of mobile
powerconsumption. Although WreckWatch performs
a number of CPU-intensive calculations on sensor
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
109

Figure 7: Comparison of OpenGPSTracker Application
Logic and Emulation Code.
data to determine if an accident occurred, these calcu-
lations are minor power consumers compared to sen-
sor users.
OpenGPSTracker Results. Figure 7 shows the
graph of the actual power consumption of the OpenG-
PSTracker application compared with the power con-
sumption of the emulation code generated by SPOT.
As with the WreckWatch emulation code, the OpenG-
PSTracker emulation code consumes power at a rate
similar to the actual application. Over the same time
period, the emulation code for the OpenGPSTracker
application was accurate at predicting power con-
sumption to within 4%. The SPOT model for the
OpenGPSTracker application only used a GPS con-
sumer and did not attempt to model any Google Maps
functionality (or requisite network functionality) or
any processing required to determine speed or store
the location information. In this instance, the GPS
power consumption was sufficient to model the power
consumption of the entire application.
With both applications, SPOT modeled and pre-
dicted the power consumption of the actual applica-
tion to within 4% of the actual power consumption.
This result confirms our hypothesis that SPOT can
provide an accurate prediction of power consumption
by modeling key components of a mobile application.
5.3 Experiment 2:
Qualitative Comparison of Sensor
Sample Rates
Overview. This experiment evaluates the effects of
sensor sample rates on an application’s overall power
consumption. The rate at which sensor data is con-
sumed can have a significant impact on application
power consumption, as described in Section 3.2. For
example, Android’s accelerometer provides four enu-
merations for sample rate: NORMAL, UI, GAME, and
FASTEST. Although these sample rates provide vary-
ing levels of QoS, the trade-off between a given level
of QoS and power consumption is not readily ap-
parent at design time. The enumeration names give
developers a clue to potential uses, as well as rank
these sample rates according to rate and consequently
power consumption. Alternatively, the GPS receiver
allows developers to specify a value as the delay, in
milliseconds, between samples.
SPOT allows developers to evaluate the power
consumption of potential sensor sample rates. For
experiment 2, we compared the power consumption
of the GPS receiver while sampling at once every 2
seconds, once every 30 seconds, and once every 500
milliseconds.
Hypothesis. We hypothesized that SPOT could
capture the power consumption effects of sensor
sampling rate changes. In particular, we believed
sampling rate changes of a few hundred millisec-
onds would produce power consumption changes that
SPOT could detect.
Results. Figure 8 show SPOT’s output for three dif-
ferent sample rates for the GPS sensor. The dashed
Time
uA
uA
uA
uA
uA
uA
5 Minutes
Time
30s Sample Rate
2s Sample Rate
500ms Sample Rate
Figure 8: GPS Sample Rate Comparison.
line represents the power consumption of the applica-
tion when the sensor was sampled every 500 millisec-
onds, the solid line represents a sample taken every
2 seconds, and the dotted line represents the power
consumption of the application sampling the sensor
twice per minute. The samples in this graph were col-
lected over 5 minutes and support the following ob-
servations:
• Power Consumption During the First Several
Seconds is Uniform Regardless of Sample Rate.
Each graph is approximately equivalent for the first
several seconds of data gathered during the GPS sam-
pling, which implies that if developers need access to
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
110

GPS for a short period of time, the greatest benefit
would come from using a higher sample rate.
• The Greatest Improvement in Power Con-
sumption Due to a Lower Sample Rate will Oc-
cur Over Time. Although the graphs demonstrate a
noticeable difference in power consumption over the
5-minute sample period, the improvement in battery
life from a change in sample rate will only be real-
ized when sampling occurs over an extended period
of time.
Ultimately, the amount of power consumed by the
GPS receiver is directly proportional to the sampling
rate of the application. Reducing the sampling rate
of the GPS receiver is an effective means to reduce
the overall power consumption of an application if the
receiver is active for longer than ∼2 minutes.
5.4 Summary and Analysis of Results
The results of the two experiments presented above
show how SPOT can accurately analyze and predict
an application’s power consumption based on a model
of the application software architecture. This capabil-
ity allows developers to understand the implications
of their design decisions early in the software lifecy-
cle, i.e., without implementing the complete applica-
tion. The emulation code SPOT generates is accurate,
e.g., for our WreckWatch application it could predict
power consumption within 3% of the actual applica-
tion’s power consumption. SPOT’s accuracy stems in
part from the significant power consumption of hard-
ware components, such as the GPS receiver, that con-
sume significantly more power than other hardware
components on the device, such as the CPU or even
accelerometers.
6 RELATED WORK
This section describes previous work in five cate-
gories: (1) system execution modeling tools, (2)
hardware-based power consumption optimization, (3)
network protocol and interface optimization, (4) post-
implementation power consumption analysis, and (5)
our previouswork on design-time power consumption
analysis.
System Execution Modeling Tools. The Compo-
nent Utilization Test Suite (CUTS) (Hill et al., 2008)
is a system execution modeling tool (Smith and
Williams, 2001) that allows developers to model key
architectural elements of distributed systems that de-
termine performance. CUTS allows developers to
model a distributed software architecture and then
generate emulation code to predict performance. Al-
though CUTS and SPOT share common domain-
specific modeling patterns, CUTS’s modeling ab-
stractions focus on performance-related aspects of
distributed systems, whereas SPOT’s modeling ab-
stractions focus on important power consumers in
mobile applications, such as GPS usage. Moreover,
it is not possible to capture power consumption in-
formation from CUTS emulation code or to generate
mobile emulation applications for Android or iPhone.
Hardware-based Power Optimizations. Conven-
tional techniques for reducing mobile device power
consumption have focused on hardware- or firmware-
level modifications to achieve the target consump-
tion (Pering et al., 2006). These techniques are highly
effective, but are limited to environments in which the
hardware can be modified by the end user or devel-
oper. Further, these modifications tend to result in a
tightly coupled architecture which makes them diffi-
cult to use outside of the context in which they were
developed. In other words, a solution might reduce
power consumption for one application or in one en-
vironment, but may not have the same effect if any of
those assumptions change. Moreover, such modifica-
tions are typically beyond the scope of software engi-
neering projects and require substantial understanding
of low-level systems. In some instances, hardware-
level modifications can actually hurt power consump-
tion by increasing overhead. These techniques are
also useful for reducing overall power consumption
but do not help in power consumption analysis that is
necessary when developing power-conscious applica-
tions. SPOT is complimentary to these approaches in
that developers can use SPOT to identify the most ef-
fective method to minimize power consumption with-
out requiring extensive hardware knowledge or re-
stricting the optimizations a single hardware platform.
Network Protocol and Interface Optimization.
Due to the limited battery power available to mo-
bile and embedded systems, a great deal of work
has been done on the notion of optimizing system
power consumption. Network interfaces consume a
large portion of overall device power (Krashinsky
and Balakrishnan, 2005) and consequently, a great
deal of work has focused on reducing the power con-
sumption of networking components. Ultimately, the
amount of power consumed is directly proportional
to the amount of data transmitted (Feeney and Nils-
son, 2001) and in some instances require 100 times
the power consumed by one CPU instruction to trans-
mit one byte of data (Liu et al., 2004). Therefore,
the power consumption of the network interface can
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
111

be reduced by reducing the amount of data transmit-
ted. Moreover, utilizing MAC protocols that reduce
contention can significantly reduce power consump-
tion (Chen et al., 1998). While MAC-layer modifi-
cation is effective, it is typically beyond the scope of
software-engineering projects, which is common with
mobile application development.
SPOT seeks to accomplish similar goals by mod-
ifying the data transmitted by the application layer,
rather than attempting to modify the underlying net-
work stack. SPOT helps developers analyze the data
they transmit to maximize throughput of relevant data
(e.g. actual data versus markup or framing overhead)
thereby reducing power consumption. In addition,
SPOT can function in a complimentary role allowing
developers to analyze the power consumption of net-
work protocol optimizations to identify the most ef-
fective configuration.
Post-implementation Power Consumption Analy-
sis. Previous work (Creus and Kuulusa, 2007) not
only identified software as a key player in mobile
device power consumption, specifically Symbian de-
vices, but also sought to allow developers to analyze
the power consumption of applications during execu-
tion. Moreover, other work (Landsiedel et al., 2005)
utilized a similar approach to analyze the power con-
sumption of sensor nodes in a wireless sensor net-
work. This power consumption analysis provided
highly accurate results but suffers from the pitfalls of
post-implementation testing, including increased cost
of refactoring if problems are discovered. To pre-
vent costly post-implementation surprises, SPOT al-
lows developers to analyze designs before any code is
written and allows them to perform continuous inte-
gration testing through the use of custom code com-
ponents to further refine the accuracy of the model as
development progresses.
This paper also extends our earlier work on MDE
power consumption described in (Thompson et al.,
2009) by providing the following new significant con-
tributions: (1) it quantitatively examines SPOT’s ac-
curacy in evaluating power consumption of software
architectures, (2) it examines the impact of different
software architecture components, such as GPS uti-
lization, on overall application power consumption,
(3) it empirically evaluates the effects of software ar-
chitecture design decisions, such as sensor sample
rate, on overall application power consumption, and
(4) it describes how data produced by SPOT can be
utilized to refine and optimize the power consumption
of a sample application.
7 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The System Power Optimization Tool (SPOT) is an
MDE tool that allows developers to evaluate the
power consumption of potential mobile application
architectures early in the software lifecycle, e.g., at
design time. Our experiments indicate that SPOT
provides a high degree of accuracy, e.g., it pre-
dicted the power consumption of the WreckWatch and
OpenGPSTracker applications to within ∼3-4%. We
learned the following lessons developing and evaluat-
ing SPOT:
• Sensor Sample Rates Play an Important Role
in Long-term Power Consumption. The power con-
sumed by the device sensors is largely uniform over
the first several minutes of activation regardless of
sample rate. It is only when these sensors are used for
an extended period that the benefit of lower sample
rates is realized. Developers must therefore consider
the amount of time to activate the sensor in addition
to the overall sample rate.
• Certain Hardware Components Draw Signif-
icantly More Power than Others. In the case of
utilizing the GPS receiver, the power consumed by
the location (GPS) service is so substantial that it be-
comes difficult to identify the effects of enabling or
disabling other hardware components. Due to this
“masking” effect, developers may overlook a signifi-
cant consumer of power in an application. In general,
small changes in GPS sample rate can have significant
impacts on overall application power consumption.
• Certain System-related Operations such as
Garbage Collection are not Reflected in Data
Gathered by SPOT. Through the current method of
data collection SPOT is only able to gather power
consumption information about operations that it per-
forms such as CPU, memory or sensor operations that
it specifically requests. Our future work will therefore
develop mechanisms for capturing the impact of these
services on power consumption.
• Power Consumption of Networking Hard-
ware is Dependent on data Transmitted which is
often Dependent on User Interaction. The power
consumption of hardware, such as the Bluetooth or
Wi-Fi interfaces, is dependent on the data transmitted
and received on the device. This data is often gen-
erated at run-time by user interaction with the pro-
gram. While it is effective for the developer to gener-
ate some sample data and provide it to SPOT, it would
be more effective if developers could simply describe
the data, e.g., via a schema file. Our future work is
extending SPOT so it can process a data schema file
and generate data that is random, yet still valid to the
application.
PECCS 2011 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
112

• Although GPS is a Major Consumer of Power,
not all Applications Rely on GPS. Although GPS
is a major consumer of power on today’s smartphone
devices, it is still important to understand the power
consumption of applications that do not use the GPS,
even if their power consumption is less drastic. Our
future work is therefore analyzing SPOT’s accuracy
with mobile applications (such as 3D games with
acceleration-based controls, streaming video players,
and audio recording/processing applications) that do
not use GPS, such as 3D games, feed readers, and
multimedia applications.
SPOT is available in open-source form at
syspower.googlecode.com.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, Y., Chandra, R., Wolman, A., Bahl, P., Chin, K.,
and Gupta, R. (2007). Wireless wakeups revisited: en-
ergy management for voip over wi-fi smartphones. In
ACM MobiSys, volume 7.
Budinsky, F., Steinberg, D., Merks, E., Ellersick, R., and
Grose, T. J. (2003). Eclipse Modeling Framework.
Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
Chen, J., Sivalingam, K., Agrawal, P., and Kishore, S.
(1998). A comparison of MAC protocols for wireless
local networks based on battery power consumption.
In IEEE INFOCOM, volume 1, pages 150–157. Cite-
seer.
Creus, G. and Kuulusa, M. (2007). Optimizing Mobile Soft-
ware with Built-in Power Profiling. Mobile Phone
Programming and its Application to Wireless Net-
working, F. Fitzek and F. Reichert, Eds. Springer.
Feeney, L. and Nilsson, M. (2001). Investigating the energy
consumption of a wireless network interface in an ad
hoc networking environment. In IEEE INFOCOM,
volume 3, pages 1548–1557. Citeseer.
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., and Balakrishnan, H.
(2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for
wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the
33rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sci-
ences, volume 8, page 8020. Citeseer.
Hill, J., Schmidt, D. C., Slaby, J., and Porter, A. (2008). Ci-
CUTS: Combining System Execution Modeling Tools
with Continuous Integration Environments. In Pro-
ceeedings of 15th Annual IEEE International Confer-
ence and Workshops on the Engineering of Computer
Based Systems (ECBS), Belfast, Northern Ireland.
Kang, J., Park, C., Seo, S., Choi, M., and Hong, J. (2008).
User-centric prediction for battery lifetime of mo-
bile devices. In Proceedings of the 11th Asia-Pacific
Symposium on Network Operations and Management:
Challenges for Next Generation Network Operations
and Service Management, pages 531–534. Springer.
Krashinsky, R. and Balakrishnan, H. (2005). Minimizing
energy for wireless web access with bounded slow-
down. Wireless Networks, 11(1):135–148.
Krause, A., Ihmig, M., Rankin, E., Leong, D., Gupta, S.,
Siewiorek, D., Smailagic, A., Deisher, M., and Sen-
gupta, U. (2005). Trading off prediction accuracy and
power consumption for context-aware wearable com-
puting. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE Interna-
tional Symposium on Wearable Computers, pages 20–
26. IEEE Computer Society.
Landsiedel, O., Wehrle, K., and Gotz, S. (2005). Accurate
prediction of power consumption in sensor networks.
In Proceedings of The Second IEEE Workshop on Em-
bedded Networked Sensors (EmNetS-II). Citeseer.
L´edeczi,
´
A., Bakay, A., Maroti, M., V
”olgyesi, P., Nordstrom, G., Sprinkle, J., and Karsai,
G. (2001). Composing domain-specific design envi-
ronments. Computer, pages 44–51.
Liu, T., Sadler, C., Zhang, P., and Martonosi, M. (2004).
Implementing software on resource-constrained mo-
bile sensors: experiences with impala and zebranet.
In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference
on Mobile systems, applications, and services, pages
256–269. ACM New York, NY, USA.
Parikh, D., Skadron, K., Zhang, Y., Barcella, M., and Stan,
M. (2002). Power issues related to branch prediction.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium
on High-Performance Computer Architecture, pages
233–44. Citeseer.
Pering, T., Agarwal, Y., Gupta, R., and Want, R. (2006).
Coolspots: Reducing the power consumption of wire-
less mobile devices with multiple radio interfaces. In
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Mobile systems, Applications and Services, page 232.
ACM.
Schmidt, D. C. (2006). Model-Driven Engineering. IEEE
Computer, 39(2):25–31.
Smith, C. and Williams, L. (2001). Performance Solutions:
A Practical Guide to Creating Responsive, Scalable
Software. Addison-Wesley Professional, Boston, MA,
USA.
Thompson, C., White, J., Dougherty, B., and Schmidt, D.
(2009). Optimizing Mobile Application Performance
with Model-Driven Engineering. In Proceedings of
the 7th IFIP Workshop on Software Technologies for
Future Embedded and Ubiquitous Systems.
Turner, H., White, J., Thompson, C., Zienkiewicz, K.,
Campbell, S., and Schmidt, D. (2009). Handbook
of Research on Mobility and Computing: Evolving
Technologies and Ubiquitous Impacts, chapter Build-
ing Mobile Sensor Networks Using Smartphones and
Web Services: Ramifications and Development Chal-
lenges. IGI Global.
Wang, Q., Hempstead, M., and Yang, W. (2006). A re-
alistic power consumption model for wireless sensor
network devices. In Proceedings of the Third Annual
IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sen-
sor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks
(SECON).
White, J., Clarke, S., Dougherty, B., Thompson, C., and
Schmidt, D. (2010). R&D Challenges and Solutions
for Mobile Cyber-Physical Applications and Support-
ing Internet Services. Springer Journal of Internet
Services and Applications (to appear).
White, J., Hill, J., Tambe, S., Gray, J., Gokhale, A., and
Schmidt, D. C. (2009). Improving Domain-specific
Language Reuse through Software Product-line Con-
figuration Techniques. IEEE Software Special Issue:
Domain-Specific Languages and Modeling.
ANALYZING MOBILE APPLICATION SOFTWARE POWER CONSUMPTION VIA MODEL-DRIVEN
ENGINEERING
113
