
BIOPEN: A PROPOSED WEB APPLICATION FOR
IMPLEMENTING THE BIOLOGICAL ELECTRONIC PROTOCOL
SYSTEM OF ENTEROPATHOGENS CHARACTERIZATION
Personalized Web Sites and Services
Terumi Paula Bonfim Kamada, Danielle Forbeci Suzuki, Maicon Silva Costa
Leonardo Magalhes Cruz and Luiz Ant
ˆ
onio Pereira Neves
Bioinformatics Master Program, Federal University of Paran
´
a - UFPR, Curitiba, Brazil
Keywords:
Protocol electronic, Enteropathogens, Health care system, Information technology, Biological database.
Abstract:
In the present work, we have developed a Biological Electronic Protocol System for Enteropathogens Char-
acterization (BIOPEN) with a Web Application interface that allows users to query data for characterization
and analysis of pathogens through an integrated management of accurate collection, storage and retrieval of
data, which aids decisions in health actions to combat diseases caused by these microorganisms. The proposed
tool is an electronic protocol that aims to facilitate data sharing in health care, using a structured database to
store information concerning about clinical assays and molecular characterizations of pathogenic strains and
clinical isolates. BIOPEN was developed using open source facilities and is freely distributed, allowing a par-
ticular laboratory create a customized, reliable, and low cost database. Thus, the principal contribution of this
work is to provide a tool that store and integrate results of physiological, biochemical, and molecular clinical
tests that can help researchers in taxonomic identification of clinical isolates and prospective epidemiological
studies.
1 INTRODUCTION
The objective of this research is the development
of a web application called BIOPEN which stand
for Biological Electronic Protocol System of En-
teropathogens Characterization as a research tool.
This project presents an integrated uniform interface
for sharing biological data among researchers in the
Internet about characterization of Enteropathgens or-
ganisms for medical evaluation. The development of
this system has been done through a shared electronic
protocol, by implementing a web platform for integra-
tion of researchers and professionals in various areas,
such as medicine, biology, technology and informa-
tion systems, biochemistry and bioinformatics. The
web resources allow the connection to multiple re-
mote locations and advanced research centers (Gorga
et al., 2002). And so, the use of technology is relevant
for providing the information to improve care for dis-
eases that have high priority in health systems.
And so, the use of technology is relevant for pro-
viding the information to improve care for diseases
that have high priority in health systems.
(Young et al., 2007) suggests the use of the soft-
ware for storage, communication, treatment and avail-
able of biological and medical information. The
strategies should be developed, for example, creating
electronic information or records of electronic proto-
col. The use of web technologies, integrating medical
information clinical and laboratory treatment allow a
fast distribution. Then, using information technology
is the key to success of health organizations.
Currently, the health sector is experiencing an
accelerated growth of implementations of computa-
tional systems, including software development, net-
work design and communication tools and so creating
the need for new strategies of information manage-
ment in health centers (Young et al., 2007). More-
over, (Doebbeling et al., 2006) comment that the tra-
ditional forms of information storage, retrieval and
analysis tools are inadequate in the health’s area be-
cause the majority of investments in information tech-
nology also have focused only on the administrative
part.
However, (Uslu and Stausberg, 2008) failed to
define the economic benefits of cost-effectiveness of
438
Paula Bonfim Kamada T., Forbeci Suzuki D., Silva Costa M., Magalhaes Cruz L. and Antônio Pereira Neves L..
BIOPEN: A PROPOSED WEB APPLICATION FOR IMPLEMENTING THE BIOLOGICAL ELECTRONIC PROTOCOL SYSTEM OF ENTEROPATHO-
GENS CHARACTERIZATION - Personalized Web Sites and Services.
DOI: 10.5220/0003403404380441
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2011), pages 438-441
ISBN: 978-989-8425-51-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

electronic protocol. The authors based on two basic
factors proposed by (Berg et al., 1998): First, proto-
cols should not be overly structured or have a degree
of complexity to not generate problems of usability
and second, the system must ensure immediate bene-
fits for primary users. As these factors were insuffi-
cient for research, (Bean and Martin, 2001) proposed
a system whose data generated by health electronic
protocol provides a mechanism of action in the pub-
lic health system that can quickly identify problems
and take necessary measures to prevent the spread of
disease. Therefore, (Druszcz, 2006) declared that the
use of electronic protocols can provide greater credi-
bility to clinical data and, consequently, improve the
methods of scientific research.
(Aranha Junior et al., 2009) and (Pinto, 2006) and
(Doebbeling et al., 2006) define the protocol as an ap-
propriate resource of information technology used in
the medical field for capturing, storing and searching
data effectively and becoming a high relevant tool for
clinical studies.
On the other hand, (Bean and Martin, 2001) alerts
that the implementation of health electronic protocols
can be effective if planned previously. The biggest
challenge for implementing these protocols is to im-
prove the electronic interface to facilitate communica-
tion among users of the practice of infectious diseases
in public health (Wurtz and Cameron, 2005).
The pathogens used in this project are the enter-
obacteria. These organisms have their importance in
disease infectious, especially in diarrhea which is a
major cause of death in developing countries as re-
ported by (UNICEF/WHO, 2009). Considering the
difficulty in identifying these pathogens and their im-
portance as a cause of diseases in humans, this re-
search aims to assist the map-reading of data, after
characterization of these species, sharing the contents
of these data to researchers and professionals through
the creation of an efficient electronic protocol. This
project has been built based on the integration project
electronic protocols called SINPE (Integrated System
Protocols Electronics) proposed by (Aranha Junior
et al., 2009).
Such analysis will generate various types of
data for identification and characterization of these
pathogens. Several biochemical and molecular tests
are used, such as tests of resistance to antibiotics and
characterization exams of species, for example RFLP
(Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) among
others (Aguilera-Arreola et al., 2007). Hence storing
in a systematic, objective and secure way, allowing
the user to recover the data and further analysis is im-
portant.
Therefore, the present research proposes the
BIOPEN. This project is a data management with
electronic protocol using data coming from laboratory
analysis and the characterization of pathogens by the
molecular tests for prospective epidemiological stud-
ies. For this reason, the protocol resources and inte-
gration of electronic databases are our main contribu-
tion of this research.
2 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
Four steps were followed to achieve the objectives.
The first step involved the architecture and definition
of data modeling; in the second step an interface for
the electronic protocol was designed; in the third step,
it illustrates the implementation of planned applica-
tion and in the fourth step tests were performed to
validate the proposed system.
2.1 Results of Step 1:
Architecture and Data Modeling
This step is the definition of the data modeling, us-
ing a tool to describe the input and output and rela-
tional modeling to identify all the system’s informa-
tion based on literature.
This data modeling is relational and has been built
using twenty-seven tables as illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1 shows the visualization and sequencing
of the tables used in the database. The sequencia table
and organism table are the main reference. The first is
related to the taxonomies of bacteria (domain, king-
dom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species, be-
sides the classification of a more specific using the ni-
trogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine
and uracil) as gene, isolated, read and sequence of a
gene. In the second table, which makes the base of the
database, will be stored tests and results of laboratory
analysis in addition to the registration administration.
The used tool for creating this data modeling is the
DBDesigner. This tool is freeware and has resources
for implementing of SQL codes.
For architecture modeling of electronic protocol,
we are used the (JUDE, 2010). This modeling tool
supports the software planning and specification by
UML (Unified Modeling Language). This diagram
represents a use case that describes the feature set of
electronic protocol. The proposal of the electronic
protocol structure is based on user interactions with
the system, such as consultations accomplishment,
maintenance of records, information generation and
generation of statistical graphics.
The proposed system offers user registration, or-
ganism registration, records the test results, generates
BIOPEN: A PROPOSED WEB APPLICATION FOR IMPLEMENTING THE BIOLOGICAL ELECTRONIC
PROTOCOL SYSTEM OF ENTEROPATHOGENS CHARACTERIZATION - Personalized Web Sites and Services
439
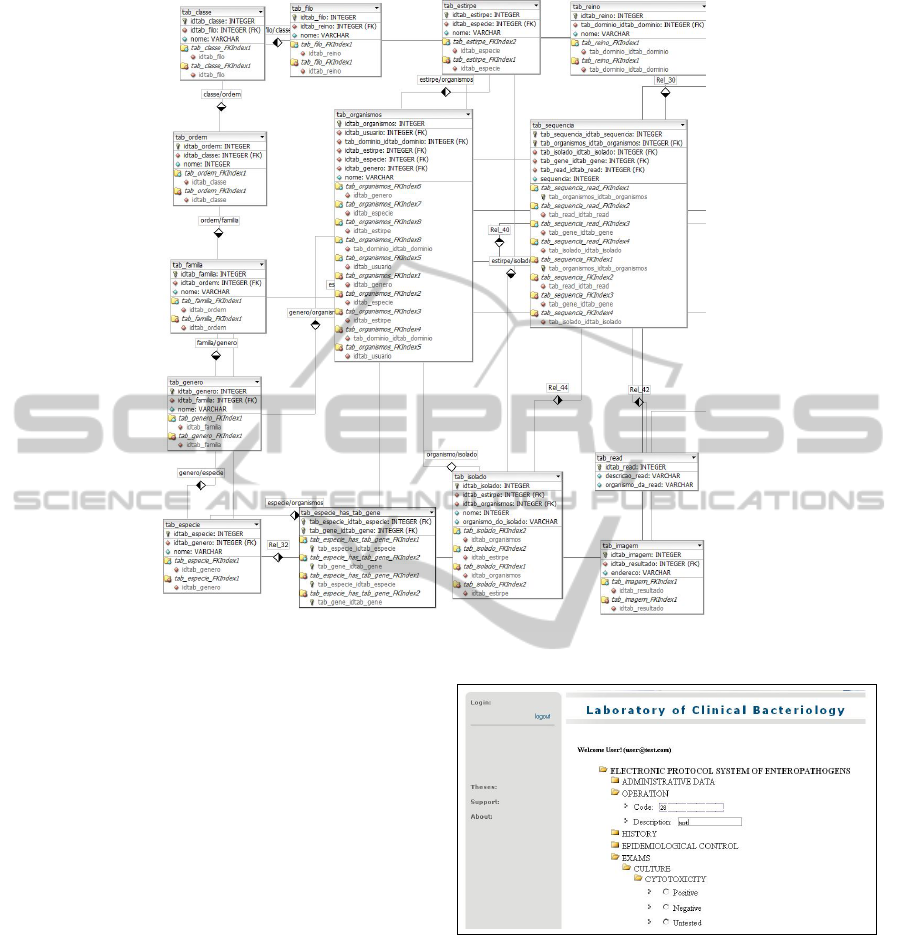
Figure 1: Data modeling of BIOPEN Project.
graphics based on these results and information re-
trieval according to the requirements of researchers.
Analyzing the protocol modeling, we have divided
the information in six main groups that are: admin-
istrative data, operation control, history reports, and
epidemiological control and test results. Each one has
a detailed description in step 2.2 with its features. We
have created sub-items like a division of the principal
groups as illustrated in Figure 2.
Relating to its architecture, Figure 2 shows the
concept of the screens and its links. This way, the
user can easily navigate through several pages inter-
actively. For example, the Figure 2 shows that the
screens contain fields with selection logic and this be-
comes the user interface more friendly.
2.2 Results of Step 2:
Conception of Interface Design
During stage 2.2, an user friendly interface has been
implemented, similar to other reported web appli-
cations ((Aranha Junior et al., 2009) and (Porcides
et al., 2010). (Porcides et al., 2010) propose a web
application called SBIM (Shared Biological Image
Figure 2: Main Screen of BIOPEN Project.
Manager). This project presents an integrated uni-
form interface for sharing biological images among
researchers in the Internet.
(Aranha Junior et al., 2009) propose the use of sta-
tistical graphs in SINPE project, showing data objec-
tively and organized. This functionality is been im-
plemented in this project.
WEBIST 2011 - 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
440

2.3 Results of Step 3: Implementation
The third step consists in the computational imple-
mentation of the proposed system using the pro-
gramming language PHP and the DBMS (Data Base
Management System) PostgreSQL. Both are freeware
tools. Currently, this phase is being implemented
based on the proposed modeling in the previous steps.
2.4 Results of Step 4: Validation Tests
In the fourth step, tests were made to validate the pro-
posed system. In this phase, the validation protocol is
based on methods proposed by (Pressman, 1995), the
use of a checklist to evaluate the user perception of the
system and initial tests of database. As initial results
of validation, tests were used to evaluate the database
using the command truncate table and retrieval of re-
sults by the name of the exams, besides the positive
and negative conditioning. The recovery of examina-
tions and the names, and the names with the condi-
tioning of positive and negative shows the average of
7503.2 ms and 5222.75 ms.
3 CONCLUSIONS
This project is in implementation stage. The rele-
vance of BIOPEN project is to facilitate the availabil-
ity of data about diseases caused by enteropathogens
among laboratories of Bacteriology in web environ-
ment, becoming a public database of any research, re-
liable and secure information that could be used in
prospective epidemiological studies. This is the prin-
cipal contribution of this research. In future studies
we will implement some other functionalities, as al-
gorithms for data mining with pattern features for im-
proved researches.
REFERENCES
Aguilera-Arreola, M. G., Hern
´
andez-Rodr
´
ıguez, C.,
Z
´
u
˜
niga, G., Figueras, M. J., Gardu
˜
no, R., and Castro-
Escarpulli, G. (2007). Virulence potential and ge-
netic diversity of Aeromonas caviae, Aeromonas
veronii, and Aeromonas hydrophila clinical isolates
from Mexico and Spain: a comparative study. Cana-
dian Journal of Microbiology, 53(7):877887.
Aranha Junior, A. A., Campos, A. C. L., Pinto, J. S. a. d. P.,
Agulham, M. A., Scheferbecker, M. E., and Branco,
A. B. (2009). Electronic protocol for structurated data
collection of pediatric patients in nutritional therapy
using SINPE
c
(Integrated System of Electronic Pro-
tocols). Rev. Col. Bras. Cir., 36:73 – 77.
Bean, N. and Martin, S. (2001). Implementing a network for
electronic surveillance reporting from public health
reference laboratories: an international perspective.
Pubmed. Emerg Infect Dis., 07:773–779.
Berg, M., Langenbergb, C., Bergc, I., and Kwakkernaatc, J.
(1998). Considerations for Sociotechnical Design: ex-
periences with an electronic patient record in a clinical
context. International Journal of Medical Informatics,
52:243–251.
Doebbeling, B. N., Chou, A. F., and Tierney, W. M. (2006).
Priorities and Strategies for the Implementation of In-
tegrated Informatics and Communications Technol-
ogy to Improve Evidence-Based Practice. Journal of
General Internal Medicine, 21:50–57.
Druszcz, C. C. (2006). Aplicac¸
˜
ao Multic
ˆ
entrica Informa-
tizada da Coleta de dados Cl
´
ınicos na Apendicite
Aguda. Master’s thesis, Programa de P
´
os-Graduac¸
˜
ao
em Cl
´
ınica Cir
´
urgica do Setor de Ci
ˆ
encias da Sa
´
ude
da Universidade Federal do Paran
´
a, Curitiba, UFPR,
Brasil.
Gorga, C., Marchaukoski, J., Silva, L., Cat, M., Sunye, M.,
and Bellon, O. (2002). A health care information sys-
tem for neonatology support. In Proceedings of 15th
IEEE International Conference on Computer Based
Medical Systems(CBMS’2002), Maribor, Slovenia.
JUDE (2010). Jude website [online] avaliable at
http://jude.change-vision.com. accessed on january
1th, 2011.
Pinto, J. S. P. (2006). Interface de Visibilizac¸
˜
ao de
Informac¸
˜
oes para o Sisema Integrado de Protoco-
los Eletr
ˆ
onico. Master’s thesis, Programa de P
´
os-
Graduac¸
˜
ao em Cl
´
ınica Cir
´
urgica do Setor de Ci
ˆ
encias
da Sa
´
ude da Universidade Federal do Paran
´
a, Curitiba,
UFPR, Brasil.
Porcides, G. M., Stein, L. H., Kamada, T., Giraldi, G. A.,
and Neves, L. A. P. (2010). An on-line medical imag-
ing management for shared research in the web using
pattern features. In Proceedings of VI Workshop de
Viso Computacional - WVC2010, pages 36–41, Presi-
dente Prudente, SP, Brazil.
Pressman, R. S. (1995). Engenharia de Software. Pearson
Makron Books, S
˜
ao Paulo.
UNICEF/WHO (2009). Diarrhoea: Why children are
still dying and what can be done [online] avaliable
at http://www.unicef.org/health/index 51412.html.
Unicef, New York.
Uslu, A. and Stausberg, J. (2008). Value of the Electronic
Patient Record: an analysis of the literature. Journal
of Biomedical Informatics, 41:675–682.
Wurtz, R. and Cameron, B. (2005). Electronic labo-
ratory reporting for the infectious diseases physi-
cian and clinical microbiologist. Clin. Infect. Dis.,
40(11):1638–1643.
Young, A. S., Chaney, E., Shoai, R., Bonner, L., Cohen,
A. N., Doebbeling, B., Dorr, D., Goldstein, M. K.,
Kerr, E., and Nichol, P. (2007). Information Tech-
nology to Support Improved Care For Chronic Illness.
Journal of General Internal Medicine, 22:425–430.
BIOPEN: A PROPOSED WEB APPLICATION FOR IMPLEMENTING THE BIOLOGICAL ELECTRONIC
PROTOCOL SYSTEM OF ENTEROPATHOGENS CHARACTERIZATION - Personalized Web Sites and Services
441
