
LEARNING STYLES THEORY FOR INTELLIGENT LEARNING
ENVIRONMENTS
Adapting the Instruction
Yasmín Hernández and Guillermo Rodríguez
Gerencia de Tecnologías de la Información, Instituto de Investigaciones Eléctricas, Reforma 113,Cuernavaca, Mexico
Keywords: Learning styles, LMS, Intelligent learning environments, Learning objects.
Abstract: It is well known that personalized tutoring helps to improve the learning process and to obtain better results.
With this aim we are developing a model including the learning styles of the students. We based our model
on the Felder-Silverman Learning Styles Model. According to the student learning style, the instruction is
established by a proposed set of rules. To prove our model we propose to use an LMS in compliance with
SCORM. In this paper we present our general proposal.
1 INTRODUCTION
Up to the present time most of the intelligent
learning environments personalize learning basically
by following what the student knows and selecting
the next learning object or tutorial action according
to the student’s current knowledge. This is usually
implemented with a student model where student’s
knowledge state is a subset of the knowledge of an
expert in the subject matter (overlay model).
However, to adapt the instruction to students is not
only concerned with students’ current knowledge;
therefore many other proposals have appeared to try
to adapt the instruction to other aspects of students.
In (Ferguson et al, 2006) the authors propose to
model students in terms of skills mastery to select
the next problem or hint to be presented to students.
There are proposals which emphasize the
importance of the motivational and affective state.
For example, self-efficacy has been proposed as a
highly accurate predictor of students’ motivational
state and their learning effectiveness (McQuiggan
and Lester, 2006). Other proposals of
personalization are based on the use of affective
models, for instance, a model of a affective tutor is
presented in (Hernandez, Sucar and Conati, 2008);
however few proposals are reported in the literature;
and the same happens with personalization using
learning styles (Graf and Kinshuk, 2007). A general
framework to include learning styles in educational
systems is presented in (Parvez and Blank, 2008). In
this paper we present a proposal to adapt the
instruction base on the Felder-Silverman Learning
Styles Model; the instruction is presented according
a rules set taking into account student learning style
which is identified by an assessment instrument gave
to students. The rest of the paper is organized as
follows: in the next section, the learning styles
model is presented; in section 3, an introduction to
the LMS Moodle is provided; in section 4 we
present our proposal, we justify why to use Moodle
to implement intelligent tutors at Instituto de
Investigaciones Eléctricas (Electrical Research
Institute) in México. Finally, conclusions, future
work and references are provided.
2 LEARNING STYLES MODEL
Learning theories describe proposals about how the
people learn new concepts and abilities; several
learning theories have been proposed, all of them
states different, and some times, contrasting points
of view; for example the dispute between proposals
focused in the student and proposals focused in the
teachers. The learning styles theory relies on the
hypothesis where each individual has a particular
way to learn including strategies and preferences,
emphasizing that individuals perceive and process
information in different ways. Consequently,
learning styles theory states individuals’ learning has
more to do with a process focusing the learning style
456
Hernández Y. and Rodríguez G..
LEARNING STYLES THEORY FOR INTELLIGENT LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS - Adapting the Instruction.
DOI: 10.5220/0003403604560459
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2011), pages 456-459
ISBN: 978-989-8425-49-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

than with the individuals’ intelligence
(Funderstanding, 2008). Several learning styles
models have been proposed, our proposal is based
on the Felder-Silverman learning Styles Model (Graf
and Kinshuk, 2007; Blouin, 2010; Felder and
Silverman, 1988), which is a well-known and
broadly used learning styles model. In this section,
firstly, the model is presented and then the rule-
based proposal to incorporate learning styles in
intelligent tutors is presented.
The Felder-Silverman categorizations of learning
styles are: sensing-intuitive, visual-verbal, active-
reflective, and sequential-global.
Active and reflective learners. The active style
learner understands information best by doing
something with it and likes group work. The
Reflective style learner understand
information best by thinking about it quietly
first and prefers to work alone.
Sensing and intuitive learners. The sensing
learner likes learning facts and solves
problems by well-established methods and
dislike complications. The intuitive learner
prefers discovering possibilities and
relationships and likes innovation and dislikes
repetition.
Visual and verbal learners. The visual
remembers best what they see: pictures,
diagrams, flow charts, time lines, films, and
demonstrations. The verbal gets more out of
words, written and spoken explanations
Sequential and global learners. The sequential
gains understanding in linear steps and
follows logical stepwise paths in finding
solutions. The global learns in large jumps and
solves complex problems quickly once they
have grasped the big picture.
To identify the learning style of a person, the
Felder-Silverman assessment instrument is used; this
instrument is a Soloman and Felder questionnaire,
consisting of 44 questions (Felder and Soloman,
1993).
To implement the Felder-Silverman Learning
Styles Model we use a collection of rules where each
rule proposes a set of teaching instructions for one
learning style (Savic and Konjovic, 2009). Table 1
shows the rules.
Rules are conceptually easy to implement in
tutoring systems. However, to apply these rules,
every lesson of a course has to be converted into 8
different lessons according to the teaching
instructions. This effort is justified if there are many
potential students classified in each of the learning
styles so that they can benefit of the personalized
learning objects. Given the learning styles remains
over the complete session, the learning style of a
person is assessed once at the beginning of the
course.
Table 1: Rules of teaching instructions for each learning style in the Felder-Silverman model.
Learning style Teaching instructions
Active Show exercises at the beginning of the chapter because they like challenges and problem solving
Show less examples. They are not interested in the way others have done something, because they
want to solve a problem by themselves
Reflective Show exercises at the end of a chapter
Show examples after explanation content, but before exercises
Show less exercises, because they learn better by thinking about a topic instead of solving problems
actively.
Sensing Show examples at the beginning of a chapter (before explanation content) because they like
concrete content.
Show exercises after explanation content, because they solve problems by already learned
approaches
Intuitive Show less examples, because they like to discover topic application by themselves
Show examples after explanation content, because they like abstract content more than concrete
Show exercises before explanation content, because they like challenges
Show less exercises with a similar teaching goal because they don’t like repetition
Visual If possible, show resources as a picture or a video
Verbal Show resources as a text or an audio
Sequential Show learning content in a standard sequence – explanation content, examples, exercises and
summary, because they like linear approach
Global They are less interested in details, because they need to create a global picture of the topic.
Therefore, add an overview of each chapter at the beginning of the lesson
Show summary before examples and exercises, because summary helps you to create a global
picture
LEARNING STYLES THEORY FOR INTELLIGENT LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS - Adapting the Instruction
457
3 LEARNING MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM
The use of programs to manage the activities around
training and education is rapidly growing;
universities and other institutions are widely using
them to support the education/training programs.
The simplest definition of learning management
system (LMS) is a software application for the
administration, documentation, tracking, and
reporting of training/education programs for e-
learning and b-learning; however, an LMS is also
concerned with centralize and automate
administration, provide self-service and self-guided
services, assemble and deliver learning content
rapidly, consolidate training initiatives on a scalable
web-based platform, support portability and
standards and personalize content and enable
knowledge reuse (Ellis, 2009). The functions of an
LMS vary from systems for managing training and
educational records, to software for distributing
courses over the WWW with features for online
collaboration.
An LMS should provide the following elements:
The syllabus for the course, administrative
information, a notice board for up-to-date course
information, student registration and tracking
facilities, basic teaching materials (These may be the
complete content of the course, or copies of visual
aids used in lectures), additional resources
(including reading materials, and links to outside
resources in libraries and on the Internet), self-
assessment quizzes which can be scored
automatically, formal assessment procedures,
electronic communication support including e-mail,
threaded discussions and a chat room, with or
without a moderator, differential access rights for
instructors and students, production of
documentation and statistics on the course, easy
authoring tools for creating the necessary documents
including the insertion of hyperlinks. In addition, the
LMS should be capable of supporting numerous
courses, so that students and instructors in a given
institution experience a consistent interface when
moving from one course to another (Wikipedia,
2010). An important feature of LMS is the
adherence to standards, such as SCORM (Ellis,
2009); it means that the LMS can share content
complying with standards regardless of the
authoring system that produced it.
There are many commercial and open source
LMS. Some of popular commercial LMS are:
Blackboard (Blackboard, 2010), WebCT (WebCT,
2010) and the leading open source LMS is Moodle
(Moodle, 2010). For our proposal we decided to use
Moodle.
Moodle is a software package for producing
Internet-based courses and web sites. It is a global
development project designed to support a social
constructionist framework of education. The word
Moodle was originally an acronym for Modular
Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment.
Moodle allows providing documents, graded
assignments, quizzes, discussion forums, etc. to
students with an easy to learn and use interface.
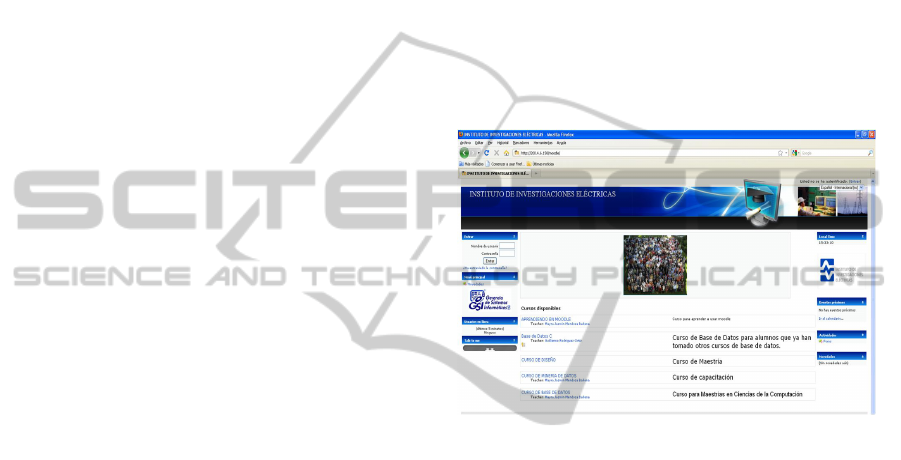
Figure 1 shows a screenshot of the Moodle site we
are assembling to develop our proposal for the
Instituto de Investigaciones Eléctricas (Electrical
Research Institute) at México.
Figure 1: Moodle site for the Instituto de Investigaciones
Eléctricas (Electrical Research Institute) at México.
Figure 1 shows the elements from a Moodle site
we are developing for the proposal; it is composed
by a log-in section, a calendar, a news section and a
list of the available courses. The availability of a
course depends on the student profile.
As we mentioned, an important feature of LMS
is the adherence to standards, such as SCORM,
therefore, we develop the instructional material as
lessons, tests, and exams in compliance with
SCORM (ADL, 2009). SCORM is a specification
for e-learning system.
To develop courses to be presented by Moodle
and SCORM compliant we base our proposal on an
algorithm rooted in artificial intelligent planning
techniques proposed by (Brusilovsky and Vassileva,
2003). This method obtains a SCORM activity tree
from a AND/OR graph or a tree that represents a
tutor plan. In this way, an individual course is
generated for each student base on her individuals
needs and on a learning goal. This will allow
running SCORM compliant intelligent tutors in
Moodle.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
458

4 INTEGRATION APPROACH
As previous work, we developed a student model
that considers the affect and knowledge to decide the
next tutorial action. The tutor monitors the affective
state of students and reacts in consequence. The
affective state is established with base on students’
personality traits and their performance in the
tutorial session (Hernández, Sucar and Conati, 2009;
Hernández, Sucar and Conati, 2008). Now, we want
to have more adaptive instruction identifying the
learning style of students and to provide students
with an instruction according with their learning
style. In this way, our integration approach allows
building intelligent tutors that are adaptive in
response to the knowledge state, the affective state
and the learning style of the students. To incorporate
learning styles in the adaptation of tutoring systems
allows identifying the best tutorial action given the
students’ preferences, strategies, experience, and so
on.
The learning style assessment instrument
(Felder-Silverman) is applied to the student to
indentify the student learning style just once, when
the student visit for the first time the educational
environment or maybe at the beginning of a course.
Once, the learning style is identified we base in the
AND/OR graph and in the rules from Table 1, we
generate a course individualized for each student. In
this way, the learning style determines the type of
explanations to be presented to the student when
taking the course. Additionally, during the course,
the tutor monitors and reacts to the knowledge and
affective states of the student; therefore, the course
is re-planned considering the new students
conditions and with base on the learning style rules.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we presented an approach that will
allow us to integrate affective behavior and learning
styles of the students into intelligent environments to
complement the current approach in intelligent
tutors that follow what the student knows using a
model that tracks the knowledge state of the student.
The affective behavior and learning styles models
increase the degree of personalization of the
intelligent environments.
In the future we plan to implement and test our
approach using a training course for the IIE
postgraduate center and we plan to include the new
SCORM features that support intelligent tutors.
REFERENCES
ADL, Advanced Distributed Learning, 2009.
ADL-Overview: SCORM 2004 4th Edition Overview
Ver.1.0. http://www.adlnet.gov/Pages/Default.aspx
Blackboard, 2010. Blackboard, http://
www.blackboard.com/
Blouin,T., 2010. Felder-Silverman Learning Styles Model,
http://chat.carleton.ca/~tblouin/Felder/felder.html
Brusilovsky, P. Vassileva J., 2003. Course Sequencing
Techniques for Large Scale Web-based Education, In
International Journal of Continuing Engineering
Education and Life-long Learning, 13, (1/2), 75-94.
Ellis,R. K., 2009. A Field Guide to Learning Management
System, Learning Circuits, ASTD.
Felder, R. M, Silverman, L. K., 1988. Learning and
teaching styles in engineering education, Eng. Educ.
78(7), pp. 674-681.
Felder, R. M., Soloman, B. A., 1993. Learning styles and
strategies, NCSU.
Ferguson, K., Arroyo, I., Mahadevan, S., Woolf, B., Barto
A., 2006. Improving Intelligent Tutoring Systems:
Using Expectation Maximization to Learn Student
Skill Levels, In: Ikeda, M., Ashley K., Chan T.W.
(eds), ITS 2006, LNCS 4053, pp 565-574, Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2006.
Funderstanding, 2008. Engaging kids, learning theories,
http://www.funderstanding.com/about_learning.cfm
Graf, S., Kinshuk, 2007. Providing Adaptive Courses in
Learning Management Systems with Respect to
Learning Styles, In: Proceedings of World Conference
on E-Learning in Corporate, Government, Healthcare,
and Higher Education 2007, pp. 2576—2583.
Hernández, Y., Sucar, L.E., Conati, C., 2009.
Incorporating an Affective Behavior Model into an
Educational Game. In: Lane, H. Ch., Guesgen H. W.
(eds.), FLAIRS 2009, pp. 448--453. AAAI Press,
Florida
Hernández, Y., Sucar, L. E., Conati, C., 2008. An affective
Behavior Model for Intelligent Tutors, In: Woolf, B. et
al (eds.), ITS 2008, LNCS 5091, pp.819-821, 2008.
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2008.
McQuiggan, S., Lester, J., 2006. Diagnosing Self-Efficacy
in Intelligent Tutoring Systems: An Empirical Study,
In: Ikeda, M., Ashley K., Chan T.W. (eds), ITS 2006,
LNCS 4053, pp 453-462, Springer-Verlag Berlin
Heidelberg 2006.
Moodle, 2010. Moodle, http://moodle.org/
Parvez, S. M., Blank G. D., 2008. Individualizing Tutoring
with Learning Style Based Feedback. In: Woolf, B. et
al (eds.), ITS 2008, LNCS 5091, pp.291-301, 2008.
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2008.
Savic, G., Konjovic, Z. 2009, “Learning style based
personalization of SCORM e-learning courses”
7th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems
and Informatics (SISY 2009), p 349-53, 2009 IEEE
WebCT,2010.WebCT,http://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/WebCT
Wikipedia, 2010, Virtual Learning Environment,
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_learning_environ
ment.
LEARNING STYLES THEORY FOR INTELLIGENT LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS - Adapting the Instruction
459
