FORMALLY MODELING AND ANALYZING DATA-CENTRIC
WORKFLOW USING WFCP-NET AND ASK-CTL
Zhaoxia Wang
1,2,3,4,5
, Jianmin Wang
2,4,5
, Lijie Wen
2,4,5
and Guiming Luo
2,4,5
1
Department of Computer Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
2
School of Software, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
3
Department of Logistical Information Engineering, Logistical Engineering University, Chongqing, China
4
Key Laboratory for Information System Security, Ministry of Education, Beijing, China
5
National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList), Beijing, China
Keywords: Business Entity, Data-centric Workflow, WFCP-net, ASK-CTL, Workflow Modeling, Workflow
Analyzing.
Abstract: Despite the abundance of workflow analysis techniques from control-flow perspective, there is hardly any
method for workflow verification from data processing perspective. In this paper, we restrict the WFCP-net,
a Colored Petri Net with WF-net structure, to formally describe the key business entities in a data-centric
workflow model. Then, we use ASK-CTL logic to describe the workflow requirements on business data
processing perspective. The model checking method is adopted into our verification approach, which can
explore some of the business contraventions of data perspectives in the workflow models. The effectiveness
of our works has been validated with the CPN Tools.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past decade years, abundant analysis
techniques have been developed to analyze
workflow models (Aalst et al. 2008). These analysis
techniques focus on verifying design errors
(deadlock, livelock, etc.) from control-flow
perspective. In addition to control-flow structure,
data processing semantic is also a critical factor to
guarantee the workflow correctness. Sometimes,
improperly data processing may cause workflow
structural errors. Further, misunderstanding data
processing semantic may make the workflow model
violating the business requirements of stakeholders.
Unfortunately, there is lack of methods for workflow
verification from data processing perspective. The
main reason is that the traditional process-centric
workflow modeling approach focuses on control-
flow perspective rather than data processing.
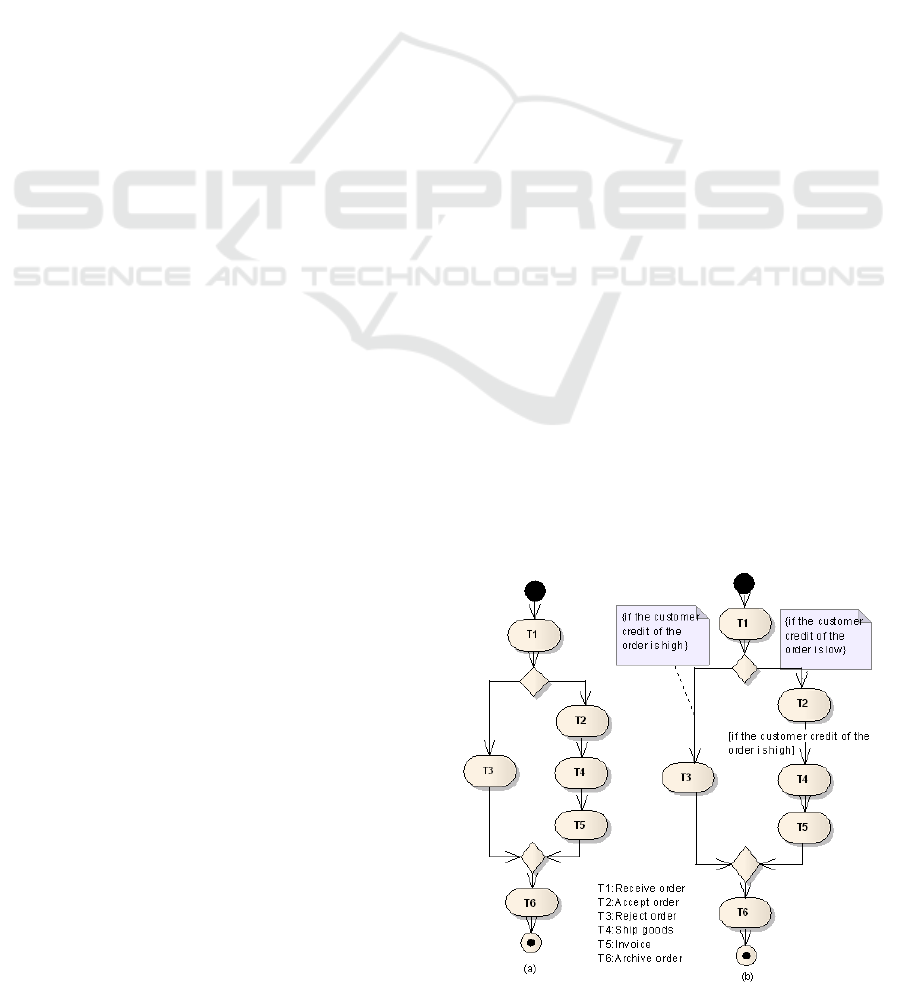
Fig. 1 shows a simple customer order process. It
is a classical example in UML textbook (Booch et al.
2005). When a customer order arrives, task T1
receives the order. Subsequently, the order is
accepted or rejected. Once the task T3 rejects the
order, the process is ended. Otherwise, the process
goes to task T2 to accept the order. After the task T2
is executed, a business entity shiplist is created. And
then, the task T4 and T5 are executed. In the end,
task T5 is executed and the order is archived. Fig.
1(a) is a conceptual model only from the control-
flow perspective and the model hasn’t any design
error from control-flow perspective.
Figure 1: A customer order process example.
139
Zhaoxia W., Wang J., Wen L. and Luo G..
FORMALLY MODELING AND ANALYZING DATA-CENTRIC WORKFLOW USING WFCP-NET AND ASK-CTL .
DOI: 10.5220/0003408601390144
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 139-144
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

However, in real business context, process must
deal with the data perspective. Fig. 1(b) shows
process model with some data processing semantic.
It is clear that improperly data processing semantic
will cause the incorrectness of process.
Data-centric approach, as an extension of the
traditional process-centric approach for workflow
modelling, has been proposed over the past several
years. The approach captures not only the control-
flow but also the evolution of the key business
entities’s lifecycle in a workflow model
(Bhattacharya et al. 2009). The data lifecycle
specification describes the possible sequences of
tasks that might occur to the business entity when it
passes through the process.
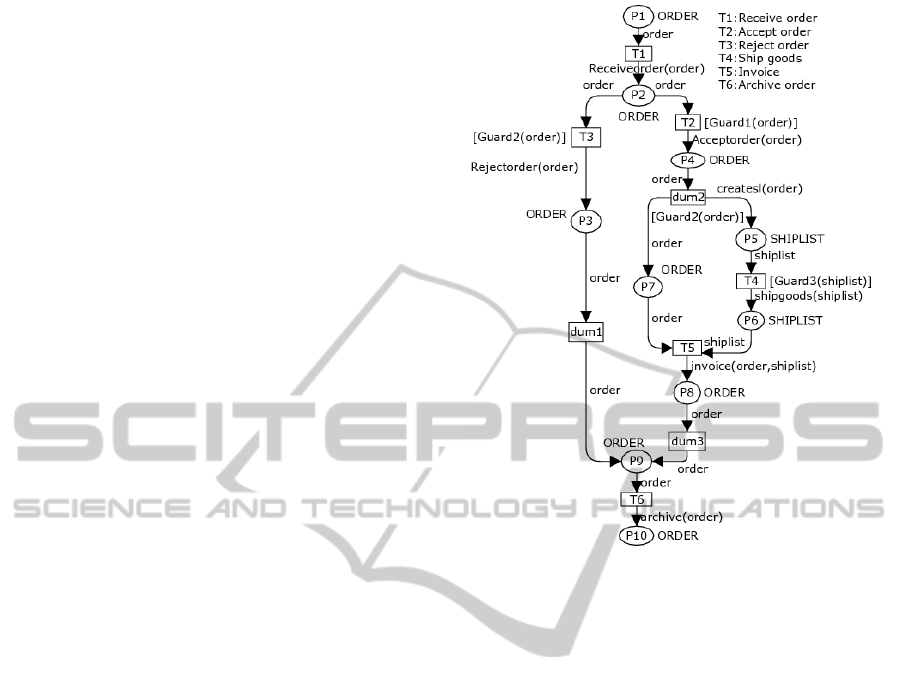
Fig. 2 shows a data-centric workflow model for
the customer order process. There are two key
business entities: order and shiplist. The lifecycles
of key business entities are described in the model.
For example, the order’s lifecycle includes six
stages: created, pending, accepted, completed,
rejected, and archived.
It provides a possibility to verify the semantic
correctness based on the data-centric workflow
model. That is, to check whether the designed model
meets some business requirements from business
stakeholders. For instance, the typical business
requirements of the customer order process are:
Requirement 1:
If the customer’s credit of the order is high, the
order is accepted.
Requirement 2:
If the customer’s credit of the order is low, the
order is rejected.
Requirement 3:
The goods shall be shipped after the order is paid.
In this paper, we restrict our previous WFCP-net,
a Colored Petri Net with WF-net structure (Liu et al.
2002), to formally describe the key business entities
in a workflow model. Then, we use ASK-CTL logic
(Cheng et al. 1996) to represent the business
requirements. Finally, the model checking method is
adopted to explore some of the business
contraventions of data perspectives.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 restricts the WFCP-net and uses
the restricted WFCP-net to model the data-centric
workflow. Section 3 focuses on analyzing the
business contravention. Section 4 introduces the
related work. Finally, conclusions and future work
are presented in Section 5.
2 MODELING DATA-CENTRIC
WORKFLOW
As a kind of workflow net, WFCP-net is proposed
by D. Liu in (Liu et al. 2002). WFCP-net is a
Colored Petri Net (CP-net) with WF-net structure.
For a detailed introduction to CP-net, WF-net and
WFCP-net, please refer to (Jensen 1997), (Aalst
1998) and (Liu et al. 2002) respectively. Here, we
restrict the original WFCP-net in two facets: data
type is described more clearly to express the
sufficient data information. Re-defining the end
place that there is only one unique end place.
Definition 1. (Restricted WFCP-net). A
−
<,,, , , ,, >
is a WFCP-net if and only if:
() < ,, > is a WF-net with source place i and
sink place o.
(ii)
: a finite set of non-empty types. =
{
,……,
}, with
∩
=∅ (we denote =
{1,…,} the ordered set of indexes);
is possibly
partitioned in static subclasses:
=
⋃
,
.
Type is called color set in CP-net. A unique color
set describes the structure of a business entity.
(iii)
is a color function. It is defined from to
.
Figure 2: Data-centric workflow model of customer order process.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
140
(iv) is a set of guard functions over .
(v)
is a set of arc expressions, which is defined
from into expressions. such that:
∀∈ :[
(
)
=(())⋀((()))⊆Σ].
maps each arc into an expression which must
be type of
(()). This means that each evaluation of
the arc expression must yield a data type over the
color set that is attached to the corresponding place.
And,
the set of variable type in arc expression is a sub-
set of
.
(vi) The initialization function:
I=
{
}
,∈(),=
∅, ≠
.
It is well known that in infinite domains (nets
with infinite colors), many verification problems
become undecidable (Aalst et al. 2008). For finite
domains (finite colors), such nets can be unfolded to
the ordinary WF-net. Then, verification problems
become decidable (Aalst et al. 2008).
Based on the above restricted WFCP-net
definition, we model the customer order process
workflow shown in Fig. 3.
Here,
=
{
,
}
is a color set which defines the data type
of the business entity order
.
ORDER=( orderid:I, customer_credit:CREDIT,
good:I, currentstate:ORDERSTATE)
is a color set which defines the data
type of the business entity shiplist.
SHIPLIST=( shiplistid:I, customer_credit:CREDIT,
good:I, currentstate:SHIPLISTSTATE)
The static subclasses of ORDER, SHIPLIST
include
I, CREDIT, ORDERSTATE, SHIPLISTSTATE:
I=int;
CREDIT=with high|low;
ORDERSTATE=with Created| Pending|Rejected|
Accepted| Completed|Archived;
SHIPLISTSTATE=with SLCreated|SLCompleted;
I
is integer type, CREDIT, ORDERSTATE and
SHIPLISTSTATE
are enumeration types.
(
)
=
1(1:),=2;
2(1:),=3;
3(1:), =4;
,ℎ.
(
)
=
(
1:
)
,∈(1,2);
(
1:
)
,∈(2,4);
(
1:
)
,∈
(
3,3
)
;
(
1:
)
,∈
(
2,5
)
;
…...
Figure 3: Data-centric model of customer order process.
3 ANALYZING DATA-CENTRIC
WORKFLOW
The aim of this section is to check the business
contravention in the workflow model with business
entities.
In this section we firstly introduce a variant of
Computation Tree Logic (CTL), ASK-CTL,
proposed by (Cheng et al. 1996). Secondly, we
formally describe the business requirements using
ASK-CTL logic and rewrite ASK-CTL formula
using SML (Standard ML) function. SML is a kind
of formal programming language, which is put
forward by (Harper 2005). Finally, the model
checking method is used to analyze whether the
workflow model matches the requirement.
3.1 ASK-CTL
In order to take into account both state (marking in
state space) information and transition (edge in state
space) information, ASK-CTL extends CTL. It has
two categories of formulas: state and transition
formulas respectively.
Definition 2. State formulas
∷=||¬|
1
∨
2
|
1
∧
2
|< >|
(
1
,
2
)
|(
1
,
2
), where:
FORMALLY MODELING AND ANALYZING DATA-CENTRIC WORKFLOW USING WFCP-NET AND ASK-CTL
141

is state formula, ℬ is transition formula.
is interpreted as the constant value true.
is a function from marking set to Boolean set,
ℳ→. can be regard as atomic proposition.
¬ , ∨ and
∧ are Boolean operators.
The <…> operator provides the possibility of
changing between state and transition formulas.
< > means that we can find an immediate
successor state from the current state and that ℬ
holds on the edge between the two states.
The standard temporal operator
(until)
combined with the path quantifiers
and (exist and
for-all respectively).
The
(
,
)
operator expresses the existence of
a path from a given marking with the property that
holds until a marking is reached at
holds.
Dually,
(
,
)
requires the property to hold
along all paths from a given marking.
Definition 3. Transition formulas
ℬ∷=||¬ℬ|ℬ
∨ℬ
|ℬ
∧ℬ
|<
>|
(
ℬ
,ℬ
)
|(ℬ
,ℬ
)
Where:
is a function from binding elements to
Boolean set
→, and is a state formula.
Table 1 illustrates a part of SML syntactic sugar of
state formulas supported by CPN tools.
Table 1: Syntactical sugar of state formulas.
ASK-CTL
syntax
SML format Syntactical sugar
¬
(), is state formula
(<>, <
>), is
used to tell ASK-CTL that the proposition
refers to node of state (eg. marking).
Argument
takes a state
space node and returns a boolean.
Argument
is used when a CTL
formula evaluates to false.
∨
(
,
)
,
are state formulas
EU (
1
,
2
)
EXIST_UNTIL (
1
,
2
), used as a state
formula, takes two arguments,
and
.
The operator is true if there exists a path,
starting from where we are now such that
is true for each state along the path
until the last state on the path where
must hold.
¬(¬)
(), as a state formula, is true if the
argument is true for all reachable state,
from the state we are at now. if,
:
→
is true. In ASK-CTL logic,
→
denoted as ¬
∨
.
Here, we emphasize the SML function
<>, <>. It is a model
checking function with two arguments: the CTL
formula to be checked and a state from where the
model checking should start.
3.2 Description of Business Entities
Related Requirements
The ASK-CTL formal description of business
requirement is the basic work for model checking.
At first, we formally describe it as ASK-CTL
formula. Subsequently, we rewrite the ASK-CTL
formula into SML format. By this way, a concrete
formalization of the business requirement is
obtained. Now we deal with the business
requirements proposed in the customer order process.
Requirement 1:
If the customer’s credit of the order is high, the
order is accepted.
Formula with ASK-CTL logic:
¬(¬(¬
1
∨
2
))
The Atomic Proposition
the customer’s credit of the order is high
is interpreted through :
Mark.example'P11 n=
1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=created}
It means to refer to the following token
1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=created}
on place P1.
The Atomic Proposition
the order is accepted
is interpreted through :
Mark.example'P4 1n=
1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=Accepted}
It means to refer to the following token
1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=Accepted}
on place P4.
Accordingly, the ASK-CTL formula can be
rewritten with the SML format:
¬(¬(∨(¬
1
,
2
))) ⟹((
(
1
)
,
2
))
The concrete SML format description is:
fun Node1 n=(Mark.example'P1 1
n=1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=Created});
fun Node2 n=(Mark.example'P4 1
n=1`{orderid=1,customer_credit=high,
good=2,currentstate=Accepted});
val A1=NF("order is created",Node1);
val A2=NF("order is accepted",Node2);
val myASKCTLformula=INV(OR(NOT(A1), A2));
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
142

eval_node myASKCTLformula InitNode;
It is noted that the term InitNode means initial
marking of the state space.
Analogously, requirement 2 and requirement 3 are
also rewritten as SML format. Please see the left
parts of Fig.4 (b) and (c) respectively.
3.3 Model Checking
Here, we adopt model checker function provided by
CPN Tools to check whether the model meet the
above business requirements.
Firstly, the occurrence graph of the CPN model
and the strongly connected components graph of the
CPN model are generated step by step.
Secondly, ASK-CTL module should be loaded in
CPN Tools. The command is shown as follows.
use (ogpath^"ASKCTL/BitArray.sml");
use (ogpath^"ASKCTL/ASKCTL.sml");
open ASKCTL;
In the end, the Evaluate ML option in the
simulation tool palette is clicked and the checking
result is shown in the right parts of Fig. 4. The
results of model checking indicate that this model
does not satisfy the requirement 1, 2 and 3. As to
requirement 1 and 2, there are errors related to
business entity order. As to requirement 3, there is
inconsistency between key business entities order
and shiplist.
4 RELATED WORK
A research area related to our work is formally
modeling of data-centric workflow. The UML
activity diagram is adopted popularly to describe the
data-centric workflow (Nigam et al. 2003).
However, the formal expression power of UML
activity diagram is weak in some sort. Ref.
Bhattacharya et.al 2007 proposes declarative
language for formal modeling of data-centric
workflow. Declarative language is good at logic
reasoning rather than expression directly. There are
well-developed formalisms for workflow modeling
based on Petri nets. A typical example is WF-net
proposed by Aalst (Aalst 1998).
However, most of them focus on control flow
perspective. Ref. Liu et.al 2007 develops a
computational model for artifact-centric operational
models based on CP-nets.
(a) the checking result of requirement 1
(b) the checking result of requirement 2
(c) the checking result of requirement 3
Figure 4: The results of model checking.
FORMALLY MODELING AND ANALYZING DATA-CENTRIC WORKFLOW USING WFCP-NET AND ASK-CTL
143

However, the computational model only summarizes
few operational patterns to some extent and does not
concern how to describe the static structure of the
artifact in the model. A WFD net is proposed to
extend WF-net with data elements in (Trcka 2009).
However, it considers isolated data element only
from local view rather than global view. Our work is
different from theirs in that we integrate the data
structure, data utility and control-flow into a unified
model. Hence, data evolvement is toughly related to
the control-flow. Accordingly, the model is suitable
for formal analysis from data processing perspective.
Another related area is formal analysis of data-
centric workflow. There are some researches
focusing on the correctness analysis of artifact-
centric system (Bhattacharya 2007 and Deutsch
2009). Above works only prove theoretically that the
decidablility of problems (e.g. reachability, complete
execution and dead end) caused by infinite domain
of data can be solved by adding some restrictions.
Our work focuses on a global data view which pays
attention to the evolvement of single business entity
and the dependencies among business entities in
business process. In addition, we highlight to verify
the business contravention between business
requirement of business stakeholder and the
designed model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a formal approach to
model and analyze data–centric workflow using
restricted WFCP-net. The approach supports
modelling data-centric workflow integrating control
flow and data flow and analyzing the correctness of
workflow model with respect to the business
requirement.
Our future works are as follows: (1) Investigate
the expressive power of data structure for business
entity in detail; (2) Consider more common solution
strategy for infinite state problem caused by the
infinite domain of data type.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the 973 Project of China
(No. 2009CB320700, 2007CB310802), the 863
High-Tech Development Program of China (No.
2008AA042301, 2007AA040607, 2007AA040602),
and the National Science Foundation (90718010,
61003099).
REFERENCES
W. M. P. van der Aalst, K.M. van Hee, A. H. M. ter
Hofstede, N.Sidorova, H. M. W. vwerbeek, M.
Voorhoeve, and M. T. Wynn, “Soundness of
Workflow Nets: Classification, Decidability, and
Analysis,” BPM Center Report BPM-08-02,
BPMcenter.org, 2008.
G. Booch, J. Rumbaugh, I. Jacobson, The unified modeling
language user guide, Addison-Wesley, 2005.
A. Nigam, N.S. Caswell, “Business artifacts: An approach
to operational specification,” IBM Systems Journal,
42(3), pp.428-445, 2003.
K. Bhattacharya, R. Hull, and J. Su, “A data-centric design
methodology for business processes,” in handbook of
research on business process management, 2009.
W. M. P. van der Aalst, “The Application of Petri Nets to
Workflow Management,” The Journal of Circuits,
Systems and Computers, 8(1), pp.21-66, 1998.
K. Jensen, Colored Petri Nets: basic concepts, analysis
methods and practical use. Basic Concepts, Vol. 1,
Berlin: Springer Verlag, 1997.
D. Liu, J. Wang, S.C.Chan, J. Sun, and L. Zhang,
“Modeling workflow processes with Colored Petri
nets,” Computers in Industry, 49(3), pp. 267-281,
2002.
A. Cheng, S. Christensen, and K.H. Mortensen, “Model
Checking Coloured Petri Nets Exploiting Strongly
Connected Components,” In Proeedings of
International Workshop on Discrete Event Systems,
1996, pages 169–177.
R. Harper, Programming in Standard ML. Carnegie
Mellon University, 2005.
R. Liu, K. Bhattacharya, F.Y. Wu, “Modeling Business
Contexture and Behavior Using Business Artifacts,” In
Proceedings of CAiSE 2007, pp.324-339.
K. Bhattacharya, C.E. Gerede, R. Hull, R. Liu, and J. Su,
“Towards formal analysis of artifact-centric business
process models,” In Proceedings of International
Conference on Business Process Management 2007,
LNCS, 2007, 288-304.
A. Deutsch, R. Hull, F. Patrizi, and V. Vianu, “Automatic
verification of data-centric business processes,” In
Proceedings of the 12th international Conference on
Database Theory, ACM, New York , 2009, pp. 252-
267.
S. Christensen and K. H. Mortensen. Design/CPN ASK-
CTL Manual (1996).[Online], Available:
http://www.daimi.au.dk/ cpntools-help/_files/
manual.pdf.
K. Jensen, S. Christensen and L. M. Kristensen. CPN
Tools State Space Manual. (2006), [Online],
Available: http://www.daimi.au.dk/cpntools-
help/_files/manual.pdf.
N. Trcka, W.M. P. van der Aalst, N. Sidorova, “Data-Flow
Anti-patterns: Discovering Data-Flow Errors in
Workflows,” In Proceedings of CAiSE 2009, pp. 425-
439, 2009.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
144
