
EFFECTIVE DATABASE MIGRATION STRATEGY - THE NEED
FOR ADDRESSING DATABASE MIGRATION CHALLENGES
OF TODAY, TOMORROW AND BEYOND
Prabin R. Sahoo
Tata Consultancy Services, Performance Engineering Research Center
Yantra Park, Thane, Maharashtra, India
Keywords: Database, Migration, Transformation, Parallel, Load, SQL, Partitions, Performance, Assessments.
Abstract: Database migration is considered to be a least priority activity in software industry. This is a wrong
perception as database migration in reality becomes a nightmare to many who have experienced it. As the
migration process starts to the new target system, migration issues crop up which pile up gradually and
become unmanageable during the migration process. That is why to eliminate the migration issues require
highly effective database migration strategies. There are several papers where migration strategies have
been mentioned, and there are a number of tools those have been developed for successful database
migration, yet database migration issues still persists and organizations find it difficult to adapt an effective
migration strategy. Organizations spend enough in purchasing tools to do the migration. By the time one
realizes that the business is suffering after the post migration, it is too late. A huge amount is spent in the
repair process. This is not because of lack of migration strategy, rather lack of effective migration strategy.
For example: Using a migration tool can be a strategy, however before that an assessment is required to find
out how much percentage of tool can do and how much percentage required to build in-house tools, how
would the database behave after migration etc? Such analysis are lacking in today’s migration strategy. This
paper proposes an effective approach towards database migration to address migration assessments, the
migration issues, also improvising reusability.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are several reasons why database migration is
required. We will discuss here the top requirements
such as: the existing technology has become
obsolete, cost of maintenance has been increased for
a vendor, there are no proper service supports
available, merger and acquisition that leads to
consolidation of business functionalities leading
towards having a single database, growth limitation,
limited database features, future bets for latest
technology adoption, mission critical needs,
conversion from batch processing application to real
time etc.
No matter how big is the organization, database
migration no doubt is a must. Though there are tools,
strategies available but those are not widely usable
because of a number of reasons such as i)
commercials tools are expensive ii) tools unable to
handle complex migrations iii) too many manual
interventions iv) improper assessments v) complex
dependencies vi) inadequate strategies vii) increased
downtime viii) reliability issues and so on.
We have done literature review in section 2, section
3 we have shown the model, section 4 describes the
strategies, and section 5 contains case study, and
section 6 is having the conclusion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In (EMC, 2007) author has mentioned steps for
database migration process. It is similar to the
methodologies followed for IT projects. There are
five phases that defines the step by step procedures.
The initial phase which is known as assessment
phase followed by planning and design, change
control, migration execution, post-migration review.
These strategies are helpful while planning for
migration. This also indicates that database
335
R. Sahoo P..
EFFECTIVE DATABASE MIGRATION STRATEGY - THE NEED FOR ADDRESSING DATABASE MIGRATION CHALLENGES OF TODAY, TOMORROW
AND BEYOND.
DOI: 10.5220/0003418103350338
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 335-338
ISBN: 978-989-8425-53-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
migration is not just a tool driven approach, it is a
project like other regular IT project. In (Joseph R.
Hudicka, 1998) the author has mentioned 7 phases
of database migrations. The author emphasizes on
having a devoted team with a clearly defined project
plan, automated tools where applicable as the
formula to success. The author has also mentioned in
this paper that database migration can be a project or
it can be an ongoing process. We will be focusing
here database migration as a project which mostly
needed migration from legacy system. In (Gints
Plivna, 1997) the author points out that though there
are several articles written about database
migrations, but most of those lack the technical
information about database migration and the author
tries to fill this gap through his paper. The author has
mentioned some of the techniques which can be
helpful for database migration from small and
middle sized database migration project. In (Premier
International Enterprises, 2004) the author has
mentioned the need of database migration and the
cause of cost overrun and demonstrates a new
approach which mitigates the risk of Code, Load and
Explode. In (Philip Howard, 2007) the author has
described the extra cost that has been expended for
database migration because of the lack of best
practices in database migration domain. In
(Christopher Burry, David Mancusi, Avanade, 2004)
the authors have discussed how to plan for database
migration. In (Todd Murihead, Dave Jaffe, Paul Rad,
2005) Dell Power Solution demonstrates the
database migration best practices involving oracle
10g
(R)
from Sun servers to Dell
TM
PowerEdge
TM
.
Though all the available approaches are relevant to
database migration it is difficult to choose which one
is best and which one is second best and so on.
Instead of finding the shortcomings in each of these,
we would like to adopt some of the best strategies
and propose on the top of it a new strategy that
would eliminate further migration issues, problems
and deficiencies.
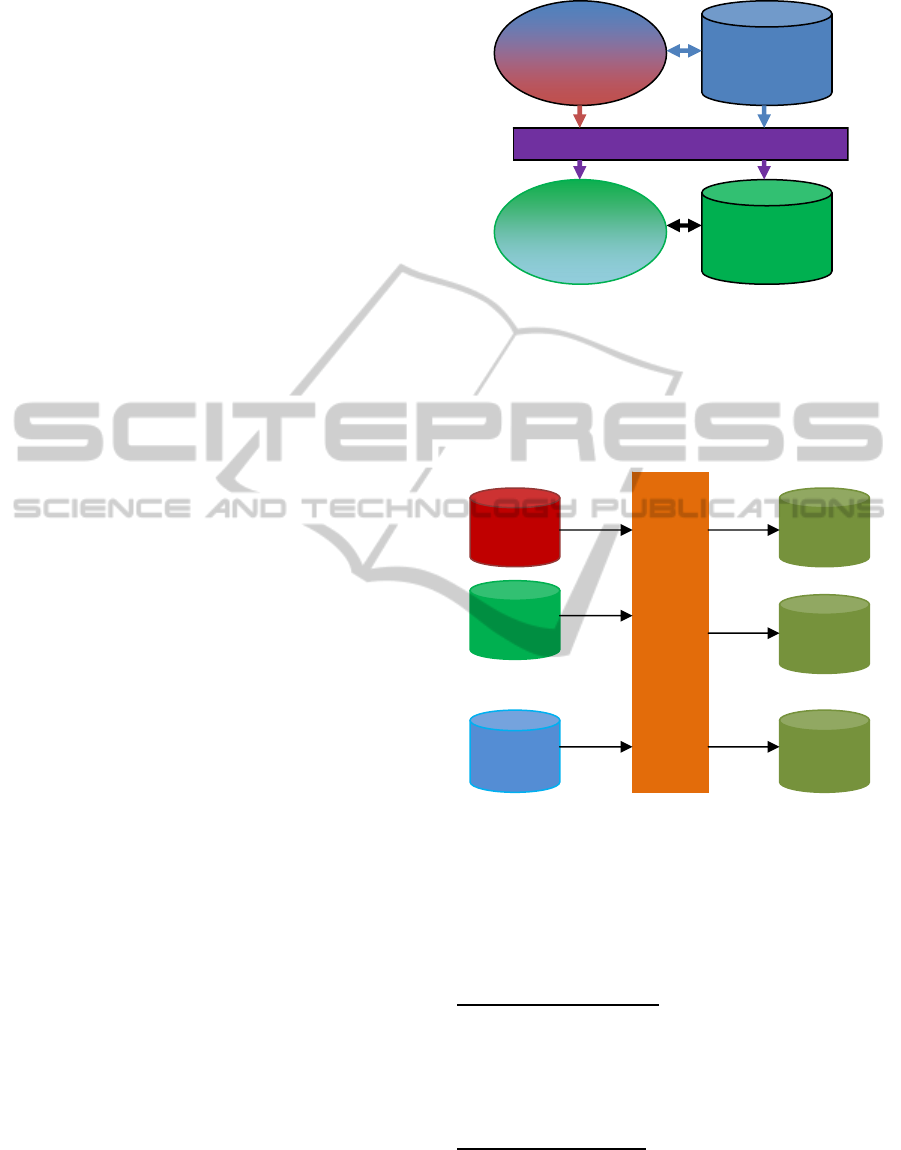
3 MODEL AND ARCHITECTURE
There are five components as shown in figure 1.0
i.e. legacy application, legacy database, new
application and new database, separated by a
transformation layer. The transformation layer plays
a major role in the migration process.
Transformation layer is the tricky part. It has 2
parts. First part deals with database transformation,
and the second part deals with application
transformation.
Figure 1: Model.
3.1 Database Transformation Layer
The database transformation layer is responsible for
transforming the legacy data layout to new data
layout.
Figure 2: Database Transformer Layer.
Figure 2.0 represents the high level view of
database transformation layer. For each source
database there is one corresponding transformer.
3.1.1 Transformers
Layout Transformations
The layout transformer takes care of the layout of
the database which includes creation of partition
group, buffer pool, tablespace, table structure
including data type conversions.
Object Transformation
Object transformation involves stored procedures,
triggers, views etc. This part is where the most of
the issues occur. It requires mostly manual
LegacyDB
NewDB
Legacy
Application
New
Application
Transformation
Source DB
Source DB
Source DB
T
R
A
N
S
F
O
R
M
E
R
Target DB
Target DB
Target DB
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
336

intervention specially the stored procedures, no tool
can completely transform without complexity and
performance compromise. Care must be taken here
to eliminate complex stored procedure, and instead
convert the stored procedure to a method in the
calling application. For example: let say a stored
procedure “ComputePayroll()” is invoked, the
procedure selects the employees and compute
payroll for each employee. Such type of stored
procedure can be offloaded from the database
system and should be handled at application level. In
general, legacy system may have stored procedure
like this one, but during migration this needs to be
converted into an object oriented framework at
application level for reusability.
Payroll.Initialize();
For(int i=0; i<SIZE;i++){
Employee eobj = Payroll[i];
eobj->process();
}
With this approach next time if another migration is
required, there is no changes required at the
processing level. The only change required at all is
at the database layer.
Data Transformation
This step helps in improving the performance during
migration. For example the SQL insertion is time
consuming process as it creates logs on insertion for
each transaction. In addition it requires DBMS for
carrying out the insertion. The import in local
database format is faster than DBMS insertions. The
source data must be converted to the target database
format for the target loader to understand. Let us
assume that we need to migrate a table Trade as in
source database to target. A script can be developed,
which can query the source database and insert it
into target database using SQL insertion command.
But this would take a lot of time if we are trying to
insert 50 millions of trade records. However, by
converting to the local formats like given below, and
loading it through load command we are able to
achieve tremendous performance.
Loader Format
0,20091120,"2009-11-20-11.06.21.000000","2009-11-20-
11.06.21.000000","XYZ",200000,0,0,100.50,300,0,"0",00
00030150.00
3.2 Application Transformation Layer
Application transformation layer is the crucial part
of the database migration. The application
transformation portion deals with how the new data
layout needs to be handled. It also deals with
connectivity for connecting to database and
retrieving the data. For example: DB2 has its own
driver programming API, Oracle, MySQL etc have
their own and so on.
4 MIGRATION STRATEGY
Database migration requires a suitable strategy.
Migration modelling helps easier migration and
improves the reusability. Migration may not be a
onetime activity. The business environment is very
dynamic, technologies changes are inevitable, and
the endless demand would make any application
system to migrate from one system to another with
respect to the change in business environment.
Scalable, reusable strategies are needed for today,
tomorrow and future. We define our strategy is this
paper is as follows.
1. Assessments
2. Build a target development environment
3. Model the target database
4. Model the target application
5. Transform legacy application/database
6. Build the application
7. Testing
8. Benchmark
9. Back out plan
10. Implementation
11. Monitoring and Control
5 CASE STUDY
In our case study we have conducted a migration
using tool vs. using our strategy and have done the
assessment on tool.
5.1 Results
Figure 3.0 shows the comparison of times using
inbuilt MySQL migration toolkit vs. using user
loader program.
EFFECTIVE DATABASE MIGRATION STRATEGY - THE NEED FOR ADDRESSING DATABASE MIGRATION
CHALLENGES OF TODAY, TOMORROW AND BEYOND
337

Figure 3: Table migration using load utility from Oracle to
MYSQL.
The loader program takes 4 hours compared to
migration toolkit which takes 7.5 hours for
migrating 50 millions of trade. So the tables with
high volume of data can be migrated using loader
utility, and tables with lesser volumes of data can be
easily migrated through MySQL migration toolkit.
Table 1: Comparison of Query Execution of source DB
and Target DB.
Query No.
Oracle
[Query Time
in Seconds]
MySQL
[Query Time in
Seconds]
1 1.83
6.86
2 0.58
8.07
3 3.70
300
4 2.07
6.98
5 1.49
155.26
6 1.50
312.72
Table 2: Calculation of Degree of complexity.
Type
No of Tables /
indexes/ stored
Procs / Time
required
No. of
entities
cannot be
migrated
Degree of
complexity
Max
Partition
10 1 10% 100
Indexes
10 0 0 100
Stored
Procs
20 5
(5/20*100)
25%
100
Data
volume
4 hrs 7.5 hrs 100% 100
6 CONCLUSIONS
We observed in our experiment that database
migration is a complex activity; not just a tool driven
activity. It is evident that before going for a database
migration, a thorough assessment is required which
would help to determine the degree of complexities.
In our case study, Table-2 shows the degree of
complexity involved in our database under
consideration. The first column shows type of
database objects, data volumes, and second column
denotes the total number of objects and total time
required for migration. Column 3 shows the number
of objects did not get migrated properly, and the
amount of time it took for migration to complete.
Column 4 denotes the degree of complexity
calculated (column-3 /column-2 * 100). Column 5
indicates the maximum percentage. Therefore
percentage of migration that cannot be done for the
above database using a standard tool in our case
MYSQL toolkit is (100+25+0+10)/400 * 100 = 33.7
~= 34%. Since we know now that 34% we cannot do
through tool, an analyst could easily find out what
percentage a tool can help and what percentage
manually or in-house tool development strategy is
required. Determination of degree of complexity is
lacking in today’s migration strategy. This paper
tries to show a simple way how to determine degree
of complexity which can be used for cost estimation
associated with the migration in terms of tools vs.
strategy. We can see in Table-1 how application
performance could be impacted without a proper
strategy. Migration is like a new system
development, and it should be handled with an
effective strategy as described in this paper, which
can address issues of today, tomorrow and beyond.
REFERENCES
EMC, 2007. Data Migration Considerations: A customer
Engineering Residency.
Joseph R. Hudicka, 1998. An overview of Data Migration
Methodology, http://www.dulcian.com/Articles/Over
view_Data_Migration_Methodology.htm.
Gints Plivna, 1997. Data Migration from old to new
application: an experience, Oracle.
Premier International Enterprises, 2004. Inc. Rapid
Application Development for Data Migration, 221
North LaSalle, Chicago.
Philip Howard, 2007. Data Migration, TOWCESTOR, UK
Christopher Burry, David Mancusi, Avanade, 2004. How
to plan for data migration, http://www.computerworld.
com/s/article/93284/How_to_plan_for_data_migration
?ta..
Todd Muirhead, Dave Jaffe, Paul Rad, 2005. Migrating
Oracle Database 10g from Sun server to Dell Servers,
Dell Power Solution.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
338
