
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS
Vadim Vagin and Alexandr Eremeev
Moscow Power Engineering Institute (Technical University), Krasnokazarmennaya str.14, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Assumption-based Truth Maintenance System, Reasoning by Analogy, Intelligent
Diagnosis System, Knowledge Base.
Abstract: The paper is devoted to research and modeling reasoning based on Assumption-based Truth Maintenance
Systems (ATMS) and reasoning by analogy in intelligent diagnosis systems. The new heuristic approaches
of current measurement point choosing on the basis of supporting and inconsistent environments are
presented. Reasoning by analogy method is viewed. This work was supported by the Russian Fund for Basic
Research.
1 INTRODUCTION
The diagnostic systems are one of the most actively
used systems in technical areas: electronics
engineering, motor industry, robotics, space
vehicles, thermal and atomic power stations and
many others. Many diagnostics problems require
building the behaviour prognoses, the work with
contradictions and defaults, effective treatment of
new facts and assumptions. The typical problem of
diagnostics is to find a fault (faults) of a diagnosed
device on the basis of some set of observations.
At first model-based diagnostics on the basis of
Assumption-based Truth Maintenance Systems
(ATMS) and heuristic methods of choosing a
measurement point in a diagnosed device are
viewed. Modeling results of the best measurement
point choosing for the 9-bit parity checker are given.
Then we consider case-based reasoning by analogy
method for diagnostics of complex object states.
2 MODEL-BASED DIAGNOSIS
The generalized problem of diagnostics can be
formulated as follows. There is a device exhibiting
an incorrect behaviour. The device consists of
components, one or several of which are not
working properly what is the reason of incorrect
behaviour. There is a structure of connections
between components and a possibility to get
measurements on their inputs and outputs. It is
necessary to determine what of components are
faulty with minimal resource expenses.
There are several approaches to a solution of the
given problem one of which is model-based
diagnosis (Clansey, 1985; de Kleer et al., 1987;
Forbus et al., 1993). This approach is based on the
knowledge of device component functionality. The
model of a device is a description of its physical
structure, plus the models for each of its
components. A compound component is a
generalized notion including simple components,
processes and even logical inference stages.
Model-based diagnosis process is the comparison
of predicted device behavior with its observed
behaviour. It is supposed, that the model is correct,
and all differences between device behaviour and a
device model indicate availability of broken
components.
Main advantages of the model-based approach:
Diagnosing the multiple faults;
Unexpected fault recognition;
A precision of a component model
description does not depend on the
expert experience;
A possibility of new device diagnosing;
Multiple using the models;
Detailed explanations.
3 ASSUMPTION-BASED TRUTH
MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS
For building a prognosis network, a component
18
Vagin V. and Eremeev A..
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003427400180025
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 18-25
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

behaviour model, finding minimal conflicts
characterizing uncorrespondence of observations
with prognoses and minimal candidates for a faulty,
it is profitable to use possibilities given by ATMS
(de Kleer et al., 1987; Forbus,1993).
The truth maintenance systems (TMS) are the
systems dealing with the support of a coherence in
databases. They save the assertions transmitted to
them by a problem solver and are responsible for
maintaining their consistency. Each assertion has the
justification describing what kind of premises and
assumptions this justification was obtained. The
environment is a set of assumption.
The inference of an inconsistency characterizes
assumption incompatibility within the
presuppositions of which this conclusion was made.
Also there is introduced the environment set which
contains some inconsistency (de Kleer et al., 1986).
The sets of inconsistency environments E1, E2 ,…,
Em are Nogood={E1, E2 , … Em}. A consistent
ATMS environment is not Nogood.
There are the following correspondences
between ATMS and the model-based diagnosis
approach:
· ATMS premises – an observed device
behaviour;
· ATMS assumptions – components of a device;
· inferred ATMS nodes – predictions of an
diagnostic system;
· Nogood - the difference between predicted and
observed device behaviour.
4 THE CURRENT
MEASUREMENT POINT
DETERMINATION
One of the key aspects of the model-based fault
search algorithm is to determine the optimal current
measurement in a diagnosed device (de Kleer,
1987). Efficiency of the current measurement
choosing allows essentially reducing a decision
search space while the inefficiency of choice will
increase an operating time, the space of a searching
algorithm, and also require additional resource
spends to implement a measurement.
The best measurement point in a diagnosed
device is a place (point) of measuring a value giving
the largest information promoting the detection of a
set of fault components at minimal resource
spending.
One of the best procedures for reducing resource
expenses is to produce the measuring giving the
maximal information concerning predictions made
on the basis of the current information on a system.
Heuristic Methods of Choosing a Measurement
Point
The purpose of the best choosing a measurement
point is to derive the maximal component state
information. After each measuring there is a
confirmation or refutation of prediction values in a
point of measurement. So, it is possible to use the
following aspects (Vagin et al., 2006 a,b,c):
knowledge about environments that
support predicted values in the
measurement points which can be confirmed
or refuted;
knowledge about inconsistent environments;
knowledge about coincided assumptions of the
inconsistent environments.
Knowledge About Supporting Environments
The diagnostic procedure constructs predictions of
values for each device point with the list of
environments in which the given prediction is held.
The list of environments represents assumption sets
about correctness of corresponding device
components.
The mismatch between observations and
predictions speaks about a fault in a device. Based
on measured observations additional predictions of
values are formed. In general, it is obtained some
set of predictions with appropriate environments.
As we are interested with a measurement point
with the greatest information on failure the point is
selected from a quantity of assumptions.
Designate an environment set as Envs(x). Let’s
introduce the function Quan(x), by which we will
designate the information quantity obtained at
measuring values in the point x.
If the environment J represents a unique
assumption, then obviously the set cardinality will
be equal 1: |J| = 1. The information quantity
obtained from such environment is equal to 1. If the
environment consists more than one component the
information quantity obtained at confirming or
refuting a value is less because we have knowledge
not about a concrete valid / fault components but
about a component set among of which are faulty.
Therefore the information quantity obtained from a
environment consisting of more than one
assumption, we heuristically accept equal to half of
set cardinality. Thus the function Quan(x) is:
±±
!
∑∑
() ()
||1
||1
||
() ||
2
ij
i
j
j
i
J Envs x J Envs x
J
J
J
Quan x J
( 1 )
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS
19

Summing is produced on all possible values in
the point x.
Points with the greatest value of the function
Quan(x) have the greatest priority of a choice. We
will call the given method of choosing a
measurement point as SEH (Supporting
Environment Heuristics).
Knowledge about the Sets of Inconsistent
Environment
As a result of each measurement there is a
confirmation or refutation of some prediction. The
environments E
1
,E
2
,...,E
m
of refuted prediction form
the set Nogood = {E
1
, E
2
,...,E
m
}. It can be used for
directional searching for more precise definition
what kind of components from Nogood is broken.
Obviously the more of the components from
Nogood are specified by measuring a value in some
device point the more the information about which
components of Nogood are broken will be obtained.
For using this possibility, it is necessary to take the
intersection of each environment from Envs(x) with
each set from Nogood:
Envs(x) ª Nogood = {A ª B : A± Envs(x), B±
Nogood}.
For this approach the equation (1) can be
changed as follows:
±ª ±ª
!
∑∑
() ()
||1
||1
||
() ||
2
ij
i
j
j
i
J Envs x Nogood J Envs x Nogood
J
J
J
QuanN x J
Points with the greatest value of function
QuanN(x) have the greatest priority of a choice. We
will call the given method of choosing a measuring
point as SIEH (Supporting and Inconsistent
Environment Heuristics).
Knowledge about Coincided Assumptions of the
Inconsistent Environments
During diagnostics of faulty devices as a result of
confirmations and refutations of some predictions
there is a modification of a set of inconsistent
environments Nogood.
In each component set from Nogood one or more
components are broken what was a reason of
including a supporting set into the inconsistent
environments Nogood. Taking the intersection of all
sets of the inconsistent environments, we receive a
set of components which enter into each of them, so
their fault can be a reason explaining an
inconsistence of each set holding in Nogood. Thus,
we obtain the list of components a state of which is
recommended to test first of all, i.e. the most
probable candidates on faultiness.
The set intersection of inconsistent environments
is expressed by the following equation:
±
∩
i
i
E Nogood
SingleNogood E
If SingleNogood = ©, it means that there are
some disconnected faults. In this case the given
approach is inapplicable and it is necessary to define
more precisely the further information by any other
methods.
After obtaining a set SingleNogood ≠ ©, on the
basis of environments of value predictions in device
points it is necessary to select those measurement
points that allow to effectively test components to be
faulted from SingleNogood.
For this purpose we will work with the sets
obtained as a result of an intersection of each
environment from Envs(x) with SingleNogood:
Envs(x) ª SingleNogood = {J ª SingleNogood :
J ± Envs{x)}
The following versions are possible:
a) J± Envs(x): J
SingleNogood. One of
environments of the value prediction in the point x
coincides with the set SingleNogood. The given
version allows to test faulty components from the
set SingleNogood most effectively so this
measurement point x is selected with the most
priority.
b) J± Envs(x): _J ª SingleNogood_ <
_SingleNogood_. The cardinality of SingleNogood is
more than the cardinality of a set obtaining as result
of an intersection SingleNogood with a set
from Envs(x). We evaluate this version as
±
ª
()
max | |
JEnvsx
J SingleNogood
i.e. the more of
components from SingleNogood are intersected with
any environment from Envs(x), the more priority of
a choice of the given measurement point for the
observation.
c) J± Envs(x): SingleNogood ¯ J. The
SingleNogood includes in a set from Envs(x). We
evaluate this version as
±
()
min (| | | |)
JEnvsx
J SingleNogood
i.e.
the less a difference between SingleNogood and
Envs(x), the more priority of a choice of the given
measurement point for the current observation.
d) J± Envs(x): J ª SingleNogood = ©, i.e. no-
one of the most probable faulty candidates includes
in environments Envs(x) supporting predictions at
the point x. We evaluate this version as the least
priority choice, i.e. 0 in the numerical equivalent.
Also to the version (d) there are referred other
methods of definition of current measurement point
priorities which happen when SingleNogood = ©.
Thus in the estimations of a choice priority a
numerical value returned as a result of call of other
method is accepted. We call it by ResultD(x).
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
20

Figure 1: The quantity of stages required to each method for fault localization.
At appearance of the greater priority choosing
between versions (b) and (c), heuristically we accept
the version (b) as at this choice the refinement of
faulty candidates is produced better.
Note for various supporting sets of the same
Envs(x), the availability both the version (b) and the
version (c) is also possible. In this case, as a
resulting estimation for the given Envs(x) the version
(b) is also accepted.
Let's estimate the obtained results.
Designate by maxd the maximal numerical value
among versions (d) for all assessed measurement
points, and by CompCount a quantity of device
components.
Accept in reviewing the following assessments:
1.
±
ª
()
max | |
JEnvsx
JSin
g
leNo
g
ood
< CompCount.The quantity
of components which are the intersection result is
always less than the quantity of whole device
components;
2.
±
()
min ( | | | |)
JEnvsx
J SingleNogood
< CompCount. The
quantity of components in the prediction
environment is always less than the quantity of the
device components.
Taking into account these assessments, one can
introduce a numerical assessment of the obtained
results:
ResultD(x),
maxD
maxD
±
± ª ©
©
± ¯
ª
()
0, if ( ) :
if
min (| | | |),
()
if ( ) :
max| |,
if
JEnvsx
JEnvsxJSingleNogood
SingleNogood
CompCount J SingleNogood
QuanSNG x
J Envs x SingleNogood J
CompCount J SingleNogood
maxD
⎧
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎪
±ª
⎪
±
⎪
⎩
():| || |
2* , if ( ):
J Envs x J SingleNogood SingleNogood
Com
p
Count J Envs x J Sin
g
leNo
g
ood
The points with the greatest value of function
QuanSNG(x) have the greatest priority of choice.
We will call the given method as SCAIEH
(Supporting and Coinciding Assumptions of
Inconsistent Environment Heuristics).
The developed methods of heuristic choice of the
best current measurement point are recommended to
use for devices with a great quantity of components
as quality of guidelines directly depends on the
quantitative difference of environments.
5 PRACTICAL RESULTS
Let's test the developed methods of the best
measurement point choosing for the 9-bit parity
checker (Frohlich, 1998).
For each experiment one of device components
is supposed working incorrectly what is exhibited in
a value on its output opposite predicted. A
consequence of the incorrect component work is
changing of outputs of those components which
produce the results depending on values on the
output of a faulty component. These changed results
of component operations are transmitted to
appropriate inquiries of a diagnostic system.
In the beginning of each experiment to inputs of
components (Invl, Inv2, Inv3, Inv7, Inv8, Inv9,
Invl3, InvI4, Invl5) in a diagnostic complex the
vector of values (1,0,1, 0,1,0, 1,0,1) enters. Then to
the diagnostic system the value 0 retrieved from the
output of the component Nor5 that depends on the
work of a broken component and differs from
predicted is transferred. It leads to the appearance of
an inconsistency in the diagnostic system and starts
the automatic process of testing.
In fig. 1 the quantity of the stages required to
each method for fault localization is shown. A
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS
21

method stage is a measurement point choosing. The
smaller the quantity of method stages, the faster a
fault is localized.
From the obtained results one can see that the
method efficiency for different fault components is
various and hardly depends on the device structure.
Let's estimate the method efficiency. The device
is consists of 46 components. The output values of
45 components are unknown (a value on the output
of Nor5 is transmitted to the diagnostic system with
input data together). So, the maximal stage quantity
necessary for a fault definition is equal 45. Let's
accept 45 stages as 100 %. For each experiment it is
computed on how many percents each of the
developed methods is more effective than exhaustive
search of all values. Then define the average value
of results. The evaluated results are represented in
table 1.
Table 1: Results of experiments.
The method SEH SIEH SCAIEH
On how many percents the
method is more effective, %
30,79 63,17 68,65
From table 1 one can see that the greatest
efficiency of current measurement point choosing
has the heuristic method based on the knowledge
about coincided assumptions of the inconsistent
environments SCAIEH.
6 REASONING BY ANALOGY
Nowdays there are a great number of various
models, schemes, and methods that describe
mechanisms of reasoning by analogy (Haraguchi et
al., 1986; Long et al., 1994; Varshavskii et al., 2005;
Eremeev et al., 2005, 2009).
In Intelligent Systems, two types of analogies -
an analogy for solving problems and an analogy for
forecasting - are usually used:
The analogy for solving problems assumes the
application of reasoning by analogy for
increasing the efficiency of the problem
solution which, generally speaking, can be
solved without analogy as well as e.g., in
programming and proving theorems;
The analogy for prediction (forecasting) uses
reasoning by analogy for obtaining new
facts. Due to the transformation of
knowledge based on the likeness of objects,
one can make the conclusion that new facts
probably hold.
Depending on the nature of information
transferred from an object of analogy to the other
one, the analogy of properties and the analogy of
relations can be distinguished:
The analogy of properties considers two single
objects or a pair of sets (classes) of
homogeneous objects, and the transferred
attributes are the properties of these objects,
for example, analogy between illness
symptoms of two persons or analogy in the
structure of the surfaces of Earth and Mars,
etc.;
The analogy of relations considers pairs of
objects where the objects can be absolutely
different and the transferred attributes are
properties of these relations. For example,
using the analogy of relations, bionics
studies processes in nature in order to use
the obtained knowledge in a modern
technology.
We consider the methods of solution search on
the basis of structural analogy which allows to take
into account a context and based on the theory of
structural mapping. We use semantic networks as a
model of knowledge representation.
Reasoning by structural analogy taking into
account the context (Varshavskii et al., 2005).
Consider an analogy as a quadruple
A = <O, C, R, p>, where O and R are the source
object and the receiver object and C is the
intersection object, i.e., the object that structurally is
intersected with the source object and receiver
object, and has a larger cardinality of the set of
properties in the comparison with these objects. In
other words, the analogy between the source object
and receiver object is considered in the context of
the intersection C, and p is a property for the
definition of an original context.
We use semantic networks (SNs) as a model of
the knowledge representation for reasoning by
analogy. The choice of an SN for the knowledge
representation possesses an important advantage,
which distinguishes it from other models, such as
natural representation of structural information and
fairly simple updating in a relatively homogenous
environment. The latter property is very important
for real-time IDSS oriented towards open and
dynamical problem domains.
A semantic network is a graph <V, E> with
labeled nodes and arcs, where V and E are sets of
nodes and arcs, respectively. The nodes can
represent objects (concepts, events, actions, etc.) of a
problem domain, and the arcs represent relations
between them.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
22

By Pv , we denote the set of properties of an
object v ∈ V.
Objects v, v' ∈ V intersect each other on SN if
and only if Pvv' = Pv ∩ Pv‘ ≠ © , where Pvv' is a set
of common properties of objects v and v'.
By Vp , we denote a set of SN objects that have a
property p.
By Vv ,Vv ° V, we denote an object set of
objects that intersect v ∈ V.
The object C is an intersection for A if and only
if there is (C±V) & (p±PC) & (nRnC) &
»(nR<<nC) & (nRC<nR) & (
nRC >1), where nR and
nC are the numbers of properties of the receiver R
and the intersection C, respectively; nRC is the
number of their common properties, ¬(nR<<nC)
denotes that receiver R should not be much smaller
than intersection C (i.e., the possibility of absorbing
the receiver R by the intersection C, since, here, the
probability of receiving a false analogy increases).
The object O is the source for analogy A if and
only if there is (O±V) & (p±PO) & (nOnC) &
»(nO<<nC) & (nOC<nO) & (nOC >1), where nO is
the number of properties of the source O; nOC is the
number of common properties of the source O and
intersection C; and other notations are analogous to
the previous definition.
By VC, VC °Vp, we denote the set of objects
that are candidates for the role of intersection C for
analogy A.
By VO ° Vp
, we denote the set of objects that
are candidates for the role of source O for analogy A.
By VA, we denote the set of analogies A.
The set POCR = PO ª PC ª PR denotes the
context, with respect to which analogy A is
considered.
We consider the structure of the SN in detail (for
Metalevel and for Situation 1) using the example
from power engineering - operation control of the
nuclear power unit (fig. 2) (Eremeev et al., 2006a).
Let us give a semantic interpretation of the
information given in the SN for Situation 1:
It is recommended to supply the pump
TH11D01 with boric concentrate 40g/kg
caused by switching off automatic cooling
system ACS 1 due to closing the gates
TH11S24 and TH11S25;
ACS 2 is switched off due to the closed gates
TH12S24 and TH12S25;
The upper setting T517B01 is equal to 63;
The lower setting T517B01 is equal to 56;
The upper setting TH11T500 is equal to 60;
The lower setting TH11T500 is equal to 20.
Analogously, the SNs for Situations 2,3 which
are structurally close to Situation 1 are built.
Algorithm of reasoning by structural analogy
An SN with information about the problem
domain, a receiver R, and the property for defining
the original context p provide input data for this
algorithm.
The algorithm for the problem solution on the
basis of analogy taking into account the context
consists of the following steps:
Step 1. VC =©, VO =©, VA =©. Determine all
objects of the SN, except for receiver R, that have
property p (Vp' = Vp \ {R}). If there are no objects
of this kind, then the search for a solution fails
(without finding an analogy), otherwise, go to step
2.
Step 2. For the objects found in step 1, determine
all possible intersections of C with R taking into
account p (VC). If there are no intersections of C
with R (VC=©), the first search for a solution fails,
otherwise, go to step 3.
Step 3. From the objects extracted in step 1,
determine all possible sources O for analogies (VO).
In the case of success (VO ©), go to step 4,
otherwise, the search for a solution fails.
Step 4. Construct possible analogies for R using
the sets VC and VO. Add new analogy A=〈O,C,R,p〉
to VA if and only if there exists an analogy
A'=〈O',C,R,p〉, O O'. In the case of success (VA
©), go to step 5; otherwise, the search for a solution
fails.
Step 5. The analogies obtained in step 4 (VA)
(which could be previously compared with each
other taking into account the context) are given to
the decision making person (DMP), which means
successful termination of the algorithm.
Having obtained analogies, the DMP may then
make the final choice of the best ones. On the basis
of these facts, the facts (properties) that hold for the
source O are transferred to the receiver R.
Let us consider the steps of the functioning of the
algorithm using the example from power
engineering - operation control of the nuclear power
unit.
As a receiver R for the analogy, we take
Situation 4 (see fig. 3) and as the property p, we take
Close TH11S24.
In the first step, VC =©, VO =©, VA =© and Vp'
= {Situation 1, Situation 2, Situation 3}. Since Vp' ≠
©, we go to the next step.
Determine intersections of C with R taking into
account p. Add in VC only Situation 1, because the
number of common properties nRC = nR for
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS
23
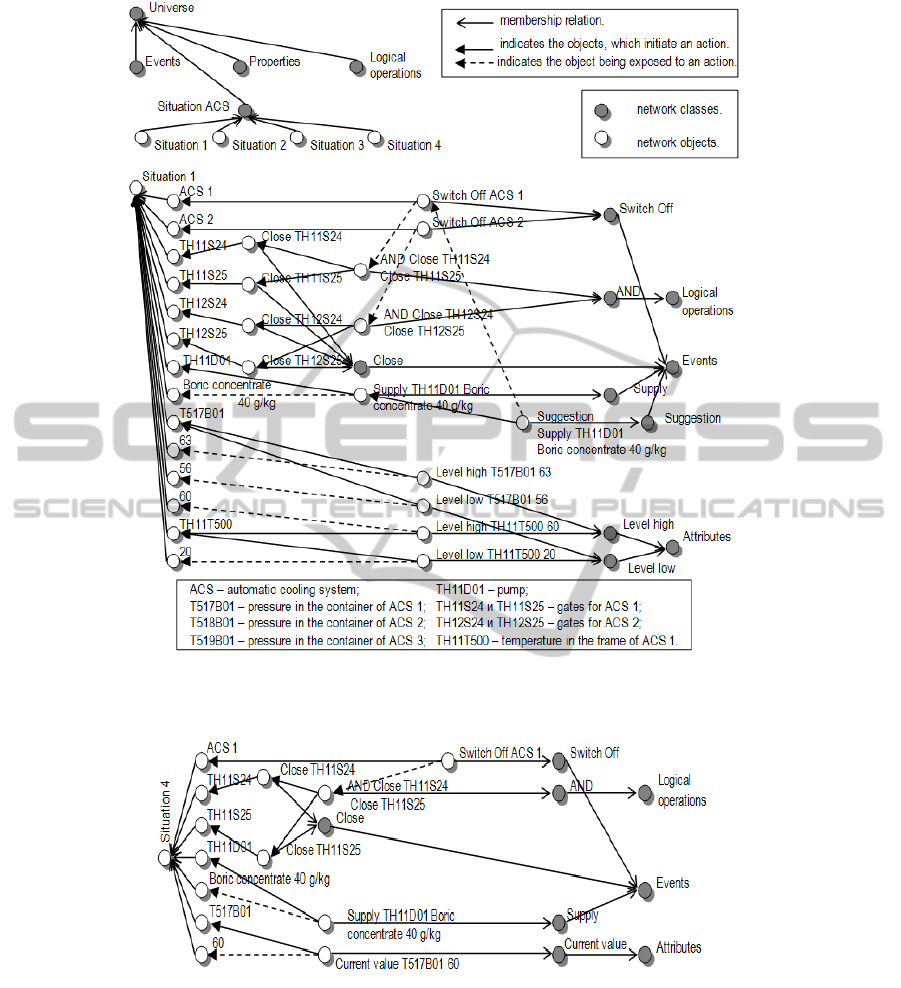
Figure 2: A fragment of the SN that represents the Metalevel and the Situation 1 that was formed in the course of ACS
functioning.
Figure 3: A fragment of the SN that represents the Situation 4.
Situation 2 and Situation 3. Since VC ≠ ©, we go to
the step 3.
Determine all possible sources O and go to step
4. In this case VO = {Situation 2, Situation 3},
because the Situation 1 is unique intersection for
analogy.
In the fourth step, we construct only two
analogies for R - Situation 4:
A1 = <Situation 2, Situation 1, Situation 4, Close
TH11S24 >;
A2 = <Situation 3, Situation 1, Situation 4, Close
TH11S24 >.
Add new analogies to VA and go to step 5.
The analogies obtained in step 4 (A1, A2) are
given to the DMP.
As a result we obtain two analogies. Choosing
one of them, the DMP can transfer facts that hold for
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
24

the source of the analogy to its receiver. In this
example, a new fact about the recommendation
“Supply the pump TH11D01 with boric
concentrate 40g/kg caused by switching off ACS 1
due to closing the gates TH11S24 and TH11S25”
arises for Situation 4.
The methods of reasoning by analogy is more
general than on the bases of cases. Analogies are
used when it is impossible to find a suitable case in a
case library. The reasoning by analogy method can
be used independently from a case- based reasoning
method as well as for correction (adaptation) of the
nearest to a problem situation case to form a new
case for completing a case library. Further we shall
consider the case-based reasoning method and its
application.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The heuristic methods of finding the best current
measurement point based on environments of device
components work predictions are presented.
Practical experiments have confirmed the
greatest efficiency of current measurement point
choosing for the heuristic method based on the
knowledge about coincided assumptions of the
inconsistent environments SCAIEH.
Advantages of heuristic methods of the best
current measurement point choosing is the simplicity
of evaluations and lack of necessity to take into
consideration the internal structure interconnections
between components of the device.
The method of reasoning by analogy on the basis
of structural analogy was considered from the aspect
of its application in modern intelligent systems, in
particular, for a solution of problems of real-time
diagnostics and forecasting . The example of the
algorithm for solution search on the basis of
analogy of properties that takes into account the
context was proposed. This algorithm uses a
modified structure of analogy that is capable of
taking into account not one property (as in the base
algorithm), but a set of properties. These properties
determine the original context of analogy and
transfer from the source to the receiver only those
facts that are relevant in the context of the
constructed analogy.
The presented methods and tools were applied at
implementation of a prototype of Intelligent
Diagnosis System on the basis of non-classical
logics for monitoring and control of complex objects
like power units and electronic circuits (Eremeev et
al., 2007, 2009).
REFERENCES
Clancey W., 1985. Heuristic Classification // Artificial
Intelligence, 25(3), pp. 289-350.
de Kleer, J. and Williams, B. C.,1987. Diagnosing multiple
faults // Artificial Intelligence, v.32, pp. 97-130.
Forbus K. D., de Kleer, J. 1993. Building Problem Solver // A
Bradford Book, The MIT Press, Cambridge,
Massachusetts, London, England.
de Kleer J. , 1986. An Assumption-based TMS // Artificial
Intelligence, v.28, p.127-162.
Vagin V. N., Golovina E. Ju., Zagoryanskaya A. A., Fomina
M. V., 2008. Exact and Plausible Inference in Intelligent
Systems / Vagin V.N., Pospelov D.A. (eds.) // M.:
Fizmatlit, - 710 p. (in Russian).
Vagin V. N., Oskin P. V., 2006a. The Heuristic Methods of
Obtaining the Effective Measurement in Diagnostic
Systems // Knowledge-based Software Engineering
Proceedings of the 7
th
Joint Conference on Knowledge-
based Software Engineering./ E. Tyugu and T.
Yamaguchi (eds). IOS Press, pp.275-284.
Vagin V. N., Os’kin P. V., 2006b. Heuristic and Probabilistic
Methods for Taking Efficient Readings in Diagnostic
Systems // Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences
International. V.l. 45, No 4,
pp. 584 -598.
Vagin V. N., Os’kin P. V., 2006c. Multiagent Simulation
Subsystem of Diagnostic Complexes Based on Device
Models // Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences
International. Vol. 45, No 6, pp. 970-982.
Frohlich P., 1998. DRUM-II Efficient Model-based
Diagnosis of Technical Systems // PhD thesis, University
of Hannover.
Haraguchi, M., Arikawa, S., 1986. A Foundation of reasoning
by Analogy. Analogical Union of Logic Programs //
Proceedings of Logic Programming Conference, Tokyo.
Long, D., Garigliano, R., 1994. Reasoning by analogy and
causality: a model and application // Ellis Horwood
Series in Artificial Intelligence.
Varshavskii, P. R., Eremeev, A. P., 2005. Analogy-Based
Search for Solutions in Intelligent Systems of Decision
Support // Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences
International, v. 44(1), p. 90–101.
Eremeev, A., Varshavsky, P., 2005. Analogous Reasoning for
Intelligent Decision Support Systems // Proceedings of the
XIth International Conference “Knowledge-Dialogue-
Solution” – Varna, v.1, p. 272-279.
Eremeev A.P., Vagin V.N., 2009. Method and tools for
modeling reasoning in diagnostic systems // ICEIS 2009.
Proc. of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise
Information Systems. Vol. AIDSS. Milan, Italy, May 6-
10,2009, INSTICC, 2009, pp. 271-276.
Eremeev, A., Varshavsky, P., 2007. Methods and Tools for
Reasoning by Analogy in Intelligent Decision Support
Systems // Proc. of the International Conference on
Dependability of Computer Systems. Szklarska Poreba,
Poland, 14-16 June, IEEE, pp.161-168.
REASONING IN INTELLIGENT DIAGNOSIS SYSTEMS
25
