
QPF SCHEDULING SCHEME FOR PERFORMANCE
IMPROVEMENTS OF INTEGRATED MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS OVER 3.5G NETWORK
Shin-Jer Yang, Li-Chih Lin
Dept. of Comp. Science & Infor. Management, Soochow University, No. 56, Sec. 1, Kuei-Yang St., Taipei, Chinese Taiwan
Yung-Ming Hsieh
Department of Accounting, Soochow University, No. 56, Sec. 1, Kuei-Yang St., Taipei, Chinese Taiwan
Keywords: VoIP, HSDPA, HARQ, QPF (QoS-based Proportional Fairness), PF (Proportional Fairness).
Abstract: IMS can provide full IP technology platform which combines information and communications
technologies to achieve the objectives of integrated multimedia service. In IMS, SIP is introduced to
transmit session control signal. Currently, the session transmission time of SIP is affected by wireless
channel bandwidth, Frame Error Rate (FER), message exchange volume, retransmission mechanism and
other factors. In order to effectively reduce the delay time for session transmission, we did revise
conventional MAC-hs scheduling algorithm (i.e. PF) and propose QoS-based Proportional Fairness
algorithm, called QPF, to enhance the session setup on SIP with channel performance of wireless
communication. We perform simulations with comparisons on two KPIs of Delay and Throughput between
PF and QPF schemes, by using NS-2 software tool under various multimedia applications, such as VoIP,
VoD and Web. The simulation results indicate that QPF lowers 20% for VoIP delay and obtains 8.19%
more VoIP Throughput than PF. The QPF performance for VoD delay can be enhanced by 11.53%, the
Throughput is increased by 8.05%. Also, the delay for Web of QPF can be improved by 28.58%, and the
Throughput is enhanced by 25.25%. Consequently, the proposed QPF can enhance transmission
performance and obtain a higher utilization of system resources for various multimedia applications in
wireless network.
1 INTRODUCTION
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) is the system used
to control the multimedia application to be proposed
by Release 5 (R5) of 3GPP. In IMS, the session
transmission time for SIP (Session Initiation
Protocol) refers to the session setup time plus VoIP
data transfer time starting from User Agent Client
(UAC) call to the receipt of ring back tone, in which
the delay time can be divided into two parts: (1)
network transmission time which refers to time spent
for data transmission from one node to another,
including transmission and retransmission time and
(2) the delay time on network handling which is
affected by Radio Link Control (RLC) and error
detection. RLC signals will be affected by Multipath
Fading, noise interference and buildings while
transmitting over the wireless network. Also, this
will lead to worse wireless channel conditions and
high error rate in wireless link layer. In order to
reduce the impact of high error rate of wireless
channels, this paper provides a more reliable data
transmission service for the upper layer, with some
guaranteed data transmission quality mechanisms
such as Radio Link Protocol (RLP) introduced in the
wireless link layer (Fathi et al., 2004).
In order to effectively control the wireless link
layer over 3.5G network, a new sub-layer for MAC-
hs (high speed) is added on the Media Access
Control (MAC) layer of Node-B, in which the
features of Fast Scheduling and Hybrid Automatic
Repeat Request (HARQ) will effectively help reduce
the delay time for network transmission, with
different services quality that are defined by diverse
media application demands as per delay time. The
main purpose of this paper is to study and explore
5
Yang S., Lin L. and Hsieh Y..
QPF SCHEDULING SCHEME FOR PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENTS OF INTEGRATED MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS OVER 3.5G NETWORK.
DOI: 10.5220/0003428500050012
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 5-12
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the scheduling enhancement on 3.5G wireless
network transmission to achieve Quality of Service
(QoS) and performance improvement of multimedia
application service.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. In Section 2, related literature review and
discussion proceeded on the key technologies and
applications of HSDPA and on new MAC-hs
protocol. In Section 3, we will consider QoS in
terms of PF in HSDPA and propose QPF (QoS-
based Proportional Fairness) with scheduling to be
designed to improve its retransmission and
scheduling mechanism. In Section 4, we plan and set
up simulation environment and list the execution
procedure. In Section 5, we present and analyze the
simulation results. In Section 6, we make the
conclusion and indicate the future research direction.
2 PRELIMINARY AND RELATED
WORKS
2.1 Integration of IMS and 3G
Network
With the prevalence of communication system and
Internet as well as evolution of new technologies,
the integration of IP network and multimedia service
has become a new trend for future development.
IMS provides a good solution about how to attain
real-time communications and multimedia
applications over 3G networks (Kara & Planat,
2007). Hence, IMS is a technology platform upon
SIP and is irrelevant to access network. Under a
3GPP IMS structure, Call Session Control Function
(CSCF) is a primary component which is responsible
for the control of SIP-based voice and multimedia
conversation. Therefore, CSCF feature is described
as followings and its structure is shown in Figure 1
(3GPP, 2010).
a) Proxy CSCF (P-CSCF) is the entry point of IMS.
Also, it is responsible for subscriber network
searching, and providing security and authentication
functions.
b) Serving CSCF(S-CSCF) takes charge of phone
service and session control, which is the control core
of entire IMS.
c) Interrogating CSCF (I-CSCF) is used for every
calling to select corresponding S-CSCF.
In Figure 1, Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
and Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) of
GPRS pass internal IP network of 3G to provide
packet service for communication signal, in which
the message flow for communication with traditional
telecom network enters PSTN/ISDN via Media
Gateway (MG) under the control of IMS. S-CSCF
controls MG operation through Media Gateway
Control Function (MGCF), while Signal Gateway
(SG) supports Signalling System 7 (SS7) transmit
over IP network and provides signalling service
between IMS and traditional telecom network.
Figure 1: Basic infrastructure for the integration of IMS
and 3G network.
2.2 Session Transmission Time of SIP
The session transmission time of SIP refers to SIP
session setup time plus VoIP data transfer time. The
session setup time was spent on the INVITE request
sending from User Agent Client (UAC) to User
Agent Service (UAS) which is informed of receipt
of this session call from the Server (i.e. UAS
receives the request of Acknowledgement (ACK).
As a consequence, SIP time can be regarded as a
total of completion of all message processing and
delay time for VoIP data transmission between
client-side and server-side. The delay for session
setup involves many factors, in which the
transmission delay over network is the major part
including retransmission time delay and queue delay
caused by FER. The procedure of SIP session
transmission is shown in Figure 2, and the main
steps are described as follows:
a) UAC issues an INVITE request carrying with
media negotiation message at the beginning.
b) When UAS receives the invite request, it
responds the session of 183 Session Progress.
c) When UAC receives the response, it issues
PRACK temporary request as per UAS’s media
capability.
d) UAC proceeds to the verification with 200 OK.
e) UAS starts to issue 180 ringing message when
resource reservation of UAS side is done.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
6
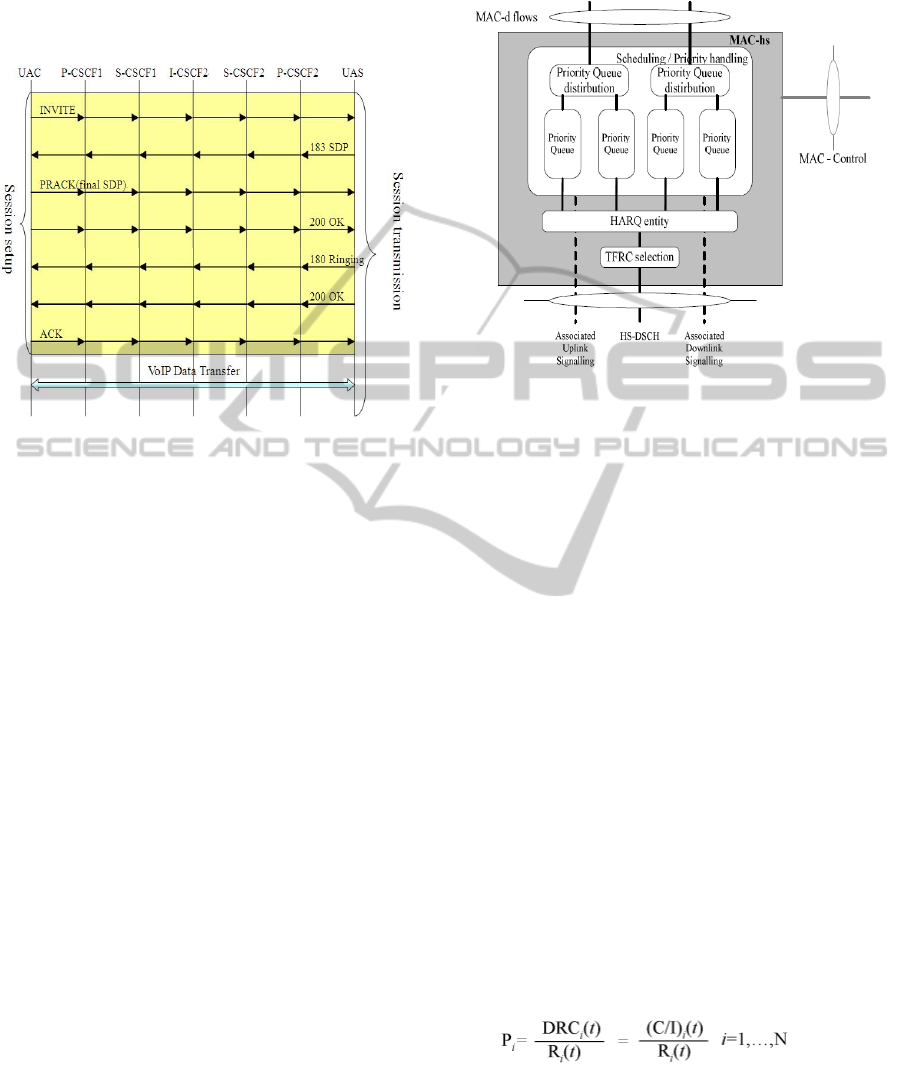
f) UAS will issue 200 OK to respond to the
primitive INVITE request.
g) UAC further confirms with ACK to be a final
response to the INVITE request and then proceeds
VoIP data transmission.
Figure 2: Delay time for SIP session setup.
2.3 Key Technologies of HSDPA
High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA),
namely the 3.5G network, is an enhanced wireless
technology of Wideband Code Division Multiple
Access (WCDMA) (Krause, 2002). The objective of
HSDPA technology is to slightly adjust or upgrade
the software without changing current 3G/WCDMA
network structure, to enhance Peak Data Rate of
Downlink transmission packet data to over 10 Mbps
and to shorten the packet latency for allowing the
system to transmit packet data more efficient.
HSDPA technology lists diverse features
including New MAC-hs and Channel, HARQ and
Fast Scheduling to be compared to WCDMA (Ghosh
et al., 2004). These features are illustrated as follows.
(a) New MAC-hs and Channel: HSDPA defines a
new MAC sub-layer as MAC-hs (3GPP, 2001) on
Node-B, where Node-B is a term used in UMTS
equivalent to the BTS (base transceiver station), with
a structure as shown in Figure 3. The MAC-hs takes
charge of directing and distributing any a requested
User Equipment (UE) for sharing channel resource of
HSDPA and provides scheduling task of High Speed
Downlink Shared Channel (HS-DSCH). The
Transmission Time Interval (TTI) of HSDPA is 2 ms.
It obtains five times growth comparing to TTI (10 ms)
of Release’99 specification and which leads to an
achievement of fast scheduling. The four functions of
MAC-hs include: (1) Flow control; (2) Scheduling
with Priority handling; (3) HARQ; and (4) Transport
Format and Resource Combination (TFRC) selection.
Figure 3: Structure diagram of MAC-hs at URTAN side.
(b) HARQ: The HARQ is an error correction
technology that is frequently used in communication.
It is a technology combining both Forward Error
Correction (FEC) and Automatic Repeat reQuest
(ARQ). Also, it can swiftly adjust the transmission
rate of channel to achieve the combinations of FEC
and retransmission according to the link conditions.
(c) Fast Scheduling: The packet scheduling of
HSDPA is directly controlled by MAC-hs of Node-
B instead of by RNC (Ameigeiras et al., 2004). The
scheduling algorithms of HSDPA were normally
divided into three types (Jalali et al., 2000): (1)
Round Robin (RR), (2) Max C/I and (3) Proportional
Fair (PF). When considering the shortest delay time
for real-time voice transmission and network
fairness of QoS, we choose to revise PF scheduling
algorithm. User who gains an improvement on
Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) will be able to
benefit from higher priority rendered by PF. PF
scheduling adopts an updating mechanism on
average speed rate to avoid starvation phenomenon
and to improve system delay time (Aniba & Aissa,
2004). In PF algorithm, each user will be given a
corresponding equation with priority level P
i
as
shown below:
(1)
In Equation (1), DRC represents Data Rate
Control while DRC
i
(t) refers to data rate supported
by scheduled user i (Total N users) at time t
according to current channel carrier to interference
QPF SCHEDULING SCHEME FOR PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENTS OF INTEGRATED MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS OVER 3.5G NETWORK
7

ratio. The updated equation of average transmission
rate R
i
(t) introduced by user i as Equation (2).
R
i
( t + 1) = (1 - 1/tc) * R
i
(t)
+ 1/tc * Current_Rate
(2)
In Equation (2), where tc represents the length of
Time slot while Current_Rate refers to the current
frame transmission rate.
3 RETRANSMITTING
AND SCHEDULING
IMPROVEMENTS IN HSDPA
Retransmitting and scheduling of HARQ in HSDPA
will be added on MAC-hs sub-layer, the major
consideration lies in swiftly and clearly controlling
usage conditions for radio resource, allowable for the
packet to quickly transmit without any delay in order
to enhance transmission efficiency. According to the
conventional 3GPP, QoS parameters of Iub (Interface
between RNC and Node-B) in HSDPA include
(Holma & Toskala, 2006): (1) Scheduling Priority
Indicator (SPI): the value range of SIP is [0, 1,…,
15], and the larger the number, the higher the priority
level; (2) Guaranteed Bit Rate (GBR); and (3)
Discard Time (DT). Also, we will categorize the
media service types into Conversational, Streaming,
Interactive and Background services by SIP priority
upon the sensitivity level of services on the delay and
diverse media service flow applications (Dixit et al.,
2002; Li & Aaron Gulliver, 2009). The fundamental
characteristics and application examples of various
service types are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Class of media service in wireless network.
3.1 Design Issues of QPF Scheduling
The QPF is proposed to revise the scheduling and
priority processor of MAC-hs based on HSDPA
scheduling, using SPI indicator to determine those
conversation types (e.g. VoIP) and higher FER
frame which requires retransmission as higher
scheduling weight than other service flows, followed
by streaming type, interactive type, and background
type. The operational flow of QPF scheduling
processing is shown in Figure 4 and its descriptions
is illustrated in the following steps.
Figure 4: Operational flow of QPF scheduling.
Step 1: Calculation and Weight Setting of
Priority Level
In Equation (3), W
i
represents weight of service type
of that subscriber, with rest of variables subject to
Equation (1). In addition, the multimedia application
type of 3G network is conformed to QoS needs, so
that the weight of service type W
i
is set as following:
4 for Conversational, 3 for Streaming, 2 for
Interactive and 1 for Background.
(3)
Step 2: Priority Value Queue
Place pri value of UE which stays synchronous with
data transmission accompanied by Dedicated
Physical Channel (DPCH) into the pri queue.
Step 3: Resource Allocation
Gather allocable real resources of Node-B.
a) Determine whether pri queue is empty and then
judge whether there are usable HS-DSCH resources.
The resource allocation process will come to an end
if there are usable non-link channel resources or
vacant pri queue.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
8

b) Calculate occupied real resources to be necessary
and send Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) for
UE according to retransmission request if HARQ
requires a resending.
c) Dispatcher will firstly transmit a retransmission
required for HARQ packet and calculate priority
(pri) value as Equation (3).
d) Choose the user who gains highest pri value to
execute dispatching, and then calculate average
service rate of each separate users as Equation (2).
3.2 QPF Algorithm Design
Based on QPF operations as depicted in Figure 4, we
design the QPF algorithm and list its pseudo codes
as follows.
Algorithm QPF( )
{
Input: #Traffic flow of HSDPA UE
#include "hsdpalink.h" //MAC-hs
implement-ation (also includes
physical layer)
#include "cqi.h" //Lookup table for CQI
to MAC-hs PDU size
#include "error_model.h" //Reads
tracefiles for CQI and transmission
power
#define FLOW_CLASS(): //Traffic flow
classification and add weight
#define FLOW_CHECK(): //Check for
activated flows
#define SORT_POWER(): //Sort by Maximum
relative CQI
#define HARQ: //HSDPA Hybrid Automatic
Repeat Request
#define CACULATE_DRC: //Calculate HSDPA
LINK Data Rate Control
#define struct queue(); //define a
priority queue structure
static vector < float > power_; //HSDPA
UE Power value
boolean retransmit_flag = true; //data
retransmit indicator
char[15] flow_type
int weight
int flow_max
OUTPUT:// Loop through the priorities
of each flow, in sort order
if ( priority is Maximum)
{ Transmission the package }
else
{ waiting in queue buffer }
---------------------------------------
------------------------
Method:
BEGIN
{
Set weight = FLOW_CLASS();
Execute FLOW_CHECK();
for (int i = 0; i < queue.size();i
++) {if ( power_.at(i) > 0.0 )
{ //channel resource enough
if ( retransmit_flag )
{ EXEC HARQ ; break; }
{power_at(i)=
power_.at(i)* weight;}
} else { power.push_back(0.0); }
}
EXEC SORT_POWER();
EXEC CACULATE_DRC;
}
End
---------------------------------------
------------------------
Procedure FLOW_CLASS()
{
if (flow_type = ”conversational”)
{set weight = 4}
else if (flow_type = ”streaming”)
{set weight = 3}
else if (flow_type = ”interactive”)
{set weight = 2}
else if (flow_type = ”background”)
{set weight = 1}
Return weight;
}End FLOW_CLASS()
---------------------------------------
------------------------
Procedure FLOW_CHECK()
{
for (int i = 0; i < flow_max; i ++) {
if ( activated_.at(i) )
{ get power for this flow
insert received power into
queue}}
Return queue()
}End FLOW_CHECK()
---------------------------------------
------------------------
Procedure SORT_POWER()
{
float pow_val;
for ( int i = 1; i < queue_.size();
i ++ ) {
pow_val = power_.at(i);
int j = i - 1;
while ( j >= 0 && power_.at(j) <
pow_val )
{power_.at (j + 1) =
power_.at(j);
j --; }
power_.at(j + 1) = pow_val;}
} End SORT_POWER()
---------------------------------------
------------------------
}
END QPF.
QPF SCHEDULING SCHEME FOR PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENTS OF INTEGRATED MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS OVER 3.5G NETWORK
9

4 ENVIRONMENT SETUP
AND PROCEDURE OF
SIMULATIONS
For the purpose of simulation experiments, this paper
utilizes network simulator of NS-2.28 software
version with insertion of EURANE-1.11 (Enhanced
UMTS Radio Access Network Extensions) module
to perform network simulations.
4.1 Setup of Simulation Environment
HSDPA network takes Dedicated Channel (DCH)
and HS-DSCH into consideration. They are
employed to signal control and data transmission,
respectively. As a result, the status of packet
transmission of these channels can be monitored to
improve transmission efficiency of network. The
network topology of simulation environment is
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Topology of simulation environment.
Table 2: Settings of Simulated Parameters.
Service Types Application Traffic Source
Peak
Sending Rate
Streaming VoD CBR 128 kbps
Conversational VoIP Expo. On/OFF 30 kbps
Interactive Web Pareto On/OFF 60 kbps
Background FTP FTP 3434 kbps
In the experiment, this paper chooses a previous
network application (Shreevastav et al.,2009) to
stand for each media service flow: (1)
conversational type: VoIP uses Exponential On/Off
to generate data flow. (2) streaming media type:
VoD uses CBR to simulate. (3) interactive type:
Web uses Pareto On/Off to generate data flow. (4)
background type: FTP application uses embedded
FTP traffic generator of NS-2 to create information
flow. The above related parameters setting is shown
in Table 2. Because Nodes of HSDPA must be
precisely configured before simulations, the
configuration parameters of these nodes including
bandwidth and delay are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Parameters Setting of Nodes.
Starting node Terminal node Bandwidth Delay
Serv. node B Serv. node A 10 Mbps 35 ms
Serv. node A GGSN 10 Mbps 15 ms
GGSN SGSN 622 Mbps 10 ms
SGSN RNC 622 Mbps 0.4 ms
RNC Node-B 622 Mbps 15 ms
4.2 Procedure of Simulation
The core network topology is composed of GGSN,
SGSN and RNC as shown in Figure 5. It will be
allocated with different application service flows (2
VoIP, 2 VoD, 2 Web) by UE side. The FTP can be
regarded as background flow. It will not only
increase the number of FTP UE to measure the
results of Delay and Throughput which pass the core
network, but also compare their differences and
analyze experimental results between PF and QPF
schemes.
5 SIMULATIONS RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
In this section, we take Transmission delay and
Throughput as KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
to measure the performance.
1. Transmission delay refers to time spent on
network transmission from UE side to the server. To
measure the results according to the transmission
delay as defined by RFC 3550, two parameters will
be derived when a voice packet (i) is received by the
receiving side. They are packet timestamp Ri and
packet RTP timestamp Si. Therefore, the
transmission delay D(i, j) between any two packet i
and packet j can be determined by Equation (4).
D(i, j) = (Rj - Ri) - (Sj - Si) (4)
The experimental results as shown in Figure 6
indicate that QPF generally gains better efficiency
than PF under light or heavy network traffic when
there is a sufficient bandwidth. Practically, the QPF
holds stable delays upon various application service
flows. Therefore, simulation results demonstrate that
the delay time can significantly decrease by taking
the advantages of QPF algorithm.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
10
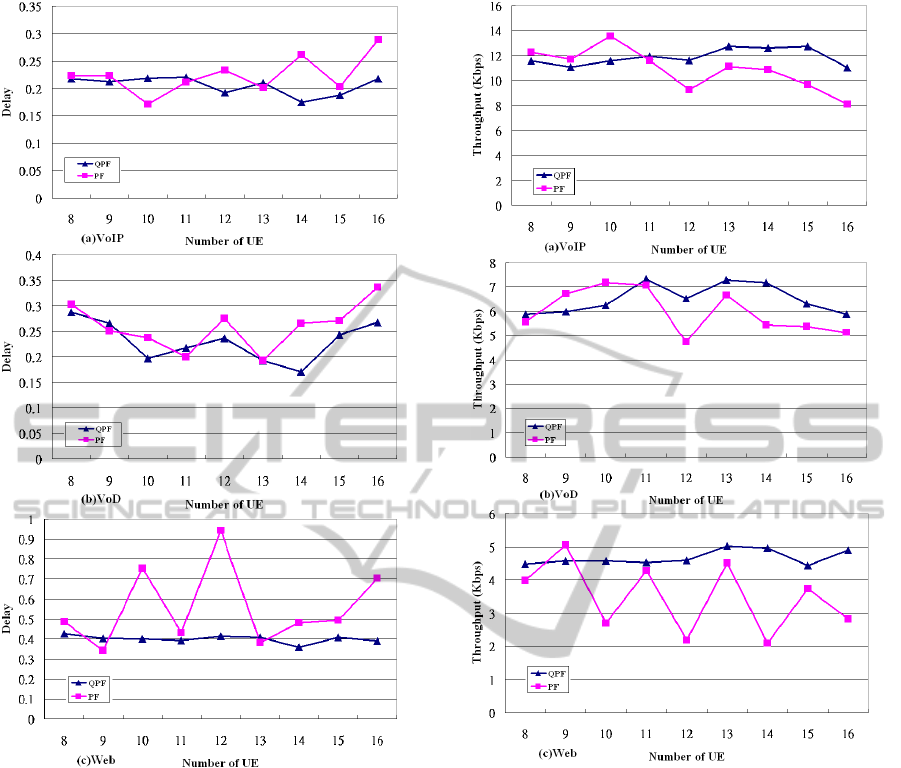
Figure 6: Simulation results in Delay.
2. Throughput is the average rate of successful
packet delivery between two nodes of network. It is
usually measured in bits per second (bit/s or bps),
which is calculated as Equation (5).
Throughput = received bits / T (5)
In Equation (5), received bits represent the
amount of bits t5o be received at all destination
nodes during a certain period of time T.
According to the experimental results as depicted
in Figure 7, the Throughputs of QPF are very close
to those of PF under light network traffic (UE =<
11), but the QPF gains higher Throughput than PF
under heavy network traffic (UE > 11). Therefore,
simulation results indicate the Throughputs of QPF
are better than PF in average.
Figure 7: Simulation results in Throughput.
The comparisons of simulation results from
Figures 6 and 7 are summarized in Table 4, which
confirm our expectation that QPF can perform better
than PF. According to Table 4, the sequence of delay
time under QPF is Web (0.4) > VoD (0.23) > VoIP
(0.2) from the weighted relationship for application
service flows. It means that the VoIP service should
be handled first because the VoIP gets the minimum
delay. Also, the delay time of VoIP-qpf (0.2) is less
than VoIP-pf (0.25) which is enhanced by 20%.
In addition, from the simulation results of
Throughput, the QPF gains better efficiency than the
PF in average. Under different application services,
the QPF produces higher average Throughput than
the PF in which VoIP service can be enhanced by
8.19%, VoD service by 8.05% and Web service by
25.25%. Hence, QPF is adoptable to multimedia
application services, because of its advantages in
QPF SCHEDULING SCHEME FOR PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENTS OF INTEGRATED MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS OVER 3.5G NETWORK
11

terms of Delay and Throughput performance over
VoIP, VoD and Web application.
Table 4: Summarized simulation results.
KPI Service
PF QPF % of diff.
Delay
VoIP
0.25S 0.2S 20
VoD
0.26S 0.23S 11.53
Web
0.56S 0.4S 28.58
Throughput
VoIP
10.9Kbps 11.9 Kbps 8.19
VoD
5.89Kbps 6.51 Kbps 8.05
Web
3.49Kbps 4.67 Kbps 25.25
6 CONCLUSIONS
IMS through full IP is a good solution to provide
cross-platform integration service between different
regions on heterogeneous wired or wireless network.
However, in real-time transmission (e.g. VoIP), the
quality of data transferring may be affected by a
delay during network transmission. Service needs in
diverse applications flows should be considered
while transmitting signals over wired or wireless
network.
This paper proposes the QPF with different levels
of priority weights given as per diverse data type of
application service flows such as VoIP, VoD and
Web etc. We perform simulations with comparisons
on two KPIs of Delay and Throughput between QPF
and PF schemes, by using NS-2 software tool under
various multimedia application services, such as
VoIP, VoD and Web. The simulation results indicate
that QPF lowers 20% for VoIP delay and gains
8.19% more VoIP Throughput than PF. The QPF
performance for VoD delay can be enhanced by
11.53%, the Throughput is increased by 8.05%. Also,
the delay for Web of QPF can be improved by
28.58% and the Throughput is enhanced by 25.25%.
Consequently, the proposed QPF can provide better
services to corresponding flow levels upon different
applications over 3.5G network, which not only
improves the effectiveness and efficiency of
multimedia application services but also enhances the
QoS of overall network.
REFERENCES
3GPP, 2001. High Speed Downlink Packet Access
(HSDPA): Overall UTRAN Description, TR 25.855,
Release 5, V5.0.0.
3GPP, 2010. IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), TS 23.228,
Stage 2, Release 10, V10.1.0.
Ameigeiras, P., Wigard, J., Mogensen, P., 2004.
Performance of Packet Scheduling Methods with
Different Degree of Fairness in HSDPA. In Proc. of
IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, 2, 860-864.
Aniba, G., Aissa, S., 2004. Adaptive Proportional Fairness
for Packet Scheduling in HSDPA. In Proc. of Global
Telecommunications Conference, 6, 4033-4037.
Dixit, S., Guo, Y., Antoniou, Z., 2002. Resource
Management and Quality of Service in Third-
generation Wireless Networks. IEEE Communications
Magazine, 39(2), 125-133.
Fathi, H., Chakraborty, S., Prasad, R., 2004. Optimization
of VoIP Session Setup Delay over Wireless Links
Using SIP, In Proc. of IEEE Communications
Conference, 6, 4092-4096.
Ghosh, A., Love, R., Ratausk, R., Xiao, W., 2004.
Performance of 3GPP High Speed Downlink Packet
Access (HSDPA). In Proc. of IEEE Vehicular
Technology Conference, 5, 3359–3363.
Holma, H., Toskala, A., 2006. HSDPA/HSUPA for
UMTS, High Speed Radio Access for Mobil
Communications. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd. 1
st
edition.
Jalali, A., Padovani, R., Pankaj, R., 2000. Data
Throughput of CDMA-HDR a High Efficiency-High
Data Rate Personal Communication Wireress System.
In Proc. of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, 3,
1854-1858.
Krause, J., 2002. ”High Speed Downlink Packet Access:
Iub/Iur Protocol”, 3GPP Specification Release 5.
Kara, N., Planat, V., 2007. Performance Analysis of IP
Multimedia Services over HSDPA Mobile Networks.
In Proc. of IP Multimedia Subsystem Architecture and
Applications, 1-5.
Li, Wei., Aaron Gulliver, T., 2009. Performance of
Enhanced Proportional Fair Scheduling in HSDPA for
Multimedia Service Streaming, In Proc. of
Communications, Computers and Signal Processing,
314-318.
Shreevastav, R., McGoldrick, C., Huggard, M., 2009.
Delivering Improved QoS and Cell Throughput in
UMTS Based HSDPA Network”, In Proc. of World of
Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks, 1-9.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
12
