
REALIZING THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF A TOP-TIER
UNIVERSITY IN TAIWAN
A Multi-criteria Evaluation and Alignment
Wei-Chien Chou and Sheng-Tun Li
Institute of Information Management, National Cheng Kung University
No.1, Ta-Hsueh Road, Tainan City 701, Taiwan, ROC
Keywords: Strategic Map, Balanced Scorecard (BSC), Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA), Top-Tier University.
Abstract: The major objective of higher education is to meet the international and local demand for top talent, the core
driving force in enhancing its international competitiveness. Since Taiwan is facing increasingly fierce
international competition as it begins to open its education market, the government’s "Plan for Developing
World-class Universities and Top-tier Research Centers." is aimed at building world-class universities to
improve the overall quality of higher education. There is therefore a great need for a set of evaluation
criteria and an alignment model to realize the strategic plan of achieving the educational objectives. This
paper presents a framework to measure the extent to which the strategic objectives of a top-tier university in
Taiwan are aligned with the results obtained through the Balanced Scorecard (BSC). To achieve this, the
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) techniques will be used to create a strategic map. With the cause-
and-effect relationship extracted from the strategy map, one can discover gaps that exist between the
strategic objectives and the present status. Our study conducted a case study on Taiwan’s higher education,
using National Cheng Kung University’s implementation of the top-tier university plan as an example.
1 INTRODUCTION
Higher education plays a key role in the
modernization of a country, as it allows for the
upgrading of national competitiveness and
prioritizes the cultivation of human talent to meet
the international and local demand. Many countries
have embarked upon a path of higher education
reform for excellent academic achievement, such as
the "Beacon Schools" program in the U.K., the
"Blue Ribbon School Program" and "Baldrige
National Quality Program" in the U.S., the “211
Project” and “985 Project” in China, and the “Brain
Korea 21 program (BK21)” in Korea. In recent years,
the Ministry of Education in Taiwan has faced rapid
social changes, including increased political freedom,
rapid economic growth, changes in the industrial
structure, and diversification of values (Ministry of
Education, Republic of China, 2011). Consequently,
it has developed a series of specific policies in an
effort to strengthen the structure and
competitiveness of higher education institutions,
among which the "Plan for Developing World-class
Universities and Top-tier Research Centers" is
aimed at improving the overall quality. Therefore,
there is a great need for a set of managerial and
strategic tools to determine appropriate courses of
action and to monitor performance for achieving the
educational objectives.
This study proposed a supportive framework
based on the BSC and used a structured manner to
realize the strategic plan. With the BSC concept as
the basis, two MCDA methods - Analytic Network
Process (ANP) and Decision Making Trial and
Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) - are used to
evaluate a series of BSC indicators, construct
strategy maps which are network structure, and
elucidate the cause-and-effect relationship and
weights between the BSC indicators. They are used
to determine key performance indicators (KPIs) and
specifically quantify the target value of KPIs as this
set of objectives. With the cause and effect
relationship extracted from the strategy map, one
can discover the gap that exists and perform a
diagnosis in terms of the strategic objectives and the
present status. Finally, our study conducted a case
study on Taiwan’s higher education using the
implementation of the top-tier university plan as an
31
Chou W. and Li S..
REALIZING THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF A TOP-TIER UNIVERSITY IN TAIWAN - A Multi-criteria Evaluation and Alignment.
DOI: 10.5220/0003448500310036
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business (ICE-B-2011), pages 31-36
ISBN: 978-989-8425-70-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

example for realizing the strategic plan of a top-tier
university, which will help managers in education-
wide alignment of strategies.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
The BSC is a performance measurement system and
a strategic management system, as well as a
management and communication tool that allows the
decision-makers, employees, and other stakeholders
to communicate results and drive performance
(Kaplan and Norton, 1992; Niven, 2002). The BSC
involves interpreting organizational vision and goals
while taking into consideration both the financial
and non-financial aspects, which correspond to the
four dimensions of "finance", "customer", "internal
process", and "learning and growth".
Because the BSC is designed to overcome the
limitations of systems that are focused primarily on
financial achievements, applications of the BSC
have been successfully implemented by public and
private non-profit organizations, such as in the
healthcare industry (Oliveira, 2001; Berler et. al.,
2005) and in government and public sector
organizations (Griffiths, 2003). The BSC has also
been used in the educational field in the past, such as
in the development of KPIs for education
(Karathanos and Karathanos, 2005; Umashankar and
Dutta, 2007), in discussions on the appropriateness
of its use as a management tool for measuring
education performance (Storey, 2002; Hamid et. al.,
2008; Yu et. al., 2009), and as an application in the
strategic management of the school to improve the
quality of education (Chen et. al., 2006; Lawrence
and Sharma, 2002; Asan and Tanyas, 2007). Many
education institutions, including the Institute of
Education, University of Southern California, Ohio
State University, University of California, Akron
University in Ohio, Edinburgh University in the UK,
and several others have adopted the BSC to measure
the effectiveness of academic programs. Literature
shows that the BSC is worth exploring and trying in
measuring performance in the field of education, but
so far most research has focused on financial results
assessment as the goal, or discussed how to develop
indicators for measuring educational performance.
2.2 Strategy Map
The strategy map proposed by Kaplan & Norton is
also called the cause-and-effect linkage of strategy
map. It describes the interaction of organizational
strategies and promotes the performance drivers in
strategy results, in order to achieve the desired
strategic goal. In terms of the role played by strategy
maps and the BSC in the field of education, they
essentially form the bridge between strategic
objectives and action plans (Chen et. al., 2006;
Umashankar and Dutta, 2007; Asan and Tanyas,
2007). Regarding the methods used in constructing
the strategy map, Solano et al. argued that a strategy
map can create value by linking tangible and
intangible assets. One can meet the financial
indicators using a strategy map built with dynamic
simulation techniques and based on the BSC and
observing the organization's system quality and the
financial situation during a five-year period (Solano
et. al., 2003). Tseng argued that past studies on the
independence of the BSC indicators do not
accurately reflect the impact they have on each
other; he therefore proposed to integrate the Fuzzy
ANP and DEMATEL methods in order to explore
the managerial implications and deal with the
interaction and dependencies within the perspectives
and guidelines, and to construct a visualized cause-
and-effect linkage using more valuable information
(Tseng, 2010).
This study considers the fact that the dynamic
simulation method of Solano et al. is unable to
ascertain the extent of influence and the weight
between various indicators, that Tseng did not
explain the concept of strategy map and KPIs, and
that other existing research of the strategy maps
focused on hierarchical structures that were based
upon financial top-level results. Therefore, using the
MCDA method can assist individuals or groups in
decision-making and generate a network structure in
strategy map rather than financial top-level results.
The DEMATEL and ANP methods can determine
the network structure among KPIs, which can in turn
work out the cause-and-effect linkage and degree of
relevance between the indicators and derive the
relative weights of each performance indicator
through the analysis of network procedures and the
assessment scales.
3 THE METHOD OF CREATING
A STRATEGY MAP PROCESS
A completed BSC not only needs to include
measurable indicators of performance evaluation,
but it also must construct cause-and-effect linkages
of four major perspectives to form a strategy map.
This study transformed the strategy map into a top-
ICE-B 2011 - International Conference on e-Business
32

to-bottom hierarchical structure, which involves the
relationships between mission, vision, and the four
major perspective of the BSC and the second-tier
relationships are those between finance, customer,
internal process, learning and growth. ANP can
represent a non-linear structure that deals with
sources and transforms into a hierarchy with the goal
at upper level and alternatives at lower level. The
DEMATEL not only can convert the relationships
between cause and effect into a structural model, but
it also can be used as a way to handle the inner
dependences within a set of criteria. Hence, we
combined the ANP and DEMATEL methods to
create a strategic map. The steps are as follows:
Step 1. Questionnaire design and fill in: The
questionnaire was developed based on performance
dimensions selected from the BSC, and each
decision maker was asked to fill in a
positive/negative sign and numbers for each
question that compared two indicators.
Step 2. Generate the direct relation matrix by
integrating views of decision makers: Deriving
direct relationship matrix A after integrated nn
×
by adding up the direction of influence and extent of
the n criterion within each decision maker's
questionnaire matrix, and
ij
a in the matrix
represents the extent of influence of criterion i on
criterion j.
Step 3. Normalize the direct relation matrix and
attain the total relation matrix: On the base of the
direct relation matrix A, the normalized direct-
relation matrix X can be obtained by using formula
(1)-(2). The total relation matrix T can be acquired
by using formula (3), in which I is denoted as the
identity matrix:
AX ×= k
(1)
nji
a
k
n
j
ij
ni
1,2,...,, ,
max
1
1
1
==
∑
=
≤≤
(2)
()
-1
- XIXT =
(3)
Step 4. Determine ANP paired comparison
module: Design the ANP questionnaire according to
the network architecture established in the previous
steps, and compare the decision makers to the
groups using paired comparison. The ANP
assessment used 1-9 scale proposed by Saaty as an
indication of level of importance, and a consistency
test was done in order to establish weight
architecture for indicators.
Step 5. Construct and solve the supermatrix:
Each assessment scale within the matrix represents
the impact that elements within a group have on
elements in other groups (external dependencies), or
the influence on elements within their own groups
(internal dependencies).
After forming the supermatrix, the weighted
supermatrix is generated by transforming and
unifying all column sums to unity. This step is used
to ensure that the sum of the probabilities of all
states equals 1. Then, we use the weighted super
matrix to generate a limiting supermatrix by using
formula (4) to calculate overall weights.
k
k
Wlim
∞→
(W : weighted matrix)
(4)
Step 6. Combine the interrelations between
criteria of DEMATEL and the weights of ANP: The
weighted supermatrix (the adjusted unweighted
supermatrix) from Step4 and Step5 can be raised to
limiting powers to calculate the overall priorities.
However, before forming the unweighted
supermatrix, the treatment of inner dependences
needs to employ the DEMATEL. The treatment of
inner dependences can theoretically use the ANP,
but DEMATEL might be a better option as it can
produce more valuable information for making
decisions. Tamura et al. proposed a composite
importance of DEMATEL to compensate for the
above-mentioned problems (Tamura et. al., 2002).
We defined the weight of performance criteria is
[
]
n
wwwWeight ,...,
21
=
The nth element of the column vector obtained
by multiplying the direct/indirect matrix T, denotes
the importance of factors resolved by resolving
factor n. Then, taking into account the importance of
factor n itself the composite importance of each
element could be evaluated as formula (5).
WeightWeightz ×
+
=
T
(5)
Step 7. Produce a causal diagram: After ANP is
applied to obtain the weights of each potential
alternative, the cause-and-effect relationships of the
perspectives and criteria involved should be
analyzed and evaluated to identify their direct,
indirect and total influences among the groups.
Following the procedure of the DEMATEL method,
we determine the intensity of the influence between
each perspective and criterion through the use of
scale and pairwise comparisons.
Once the relationships between those factors
have been measured by the decision makers, the
initial direct-relation and the normalized direct-
relation matrix can be produced. Using the values of
REALIZING THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF A TOP-TIER UNIVERSITY IN TAIWAN - A Multi-criteria Evaluation and
Alignment
33

(D-R) and (D+R) where R is the sum of columns and
D is the sum of rows in matrix Z’, the level of
influence on the others and the level of relationship
with the others are defined, as shown in formulas
(6)-(8) (Wu and Lee, 2007).
[
]
njit
nn
ij
1,2,...,, , ==
×
Z'
(6)
[]
1n
i
1n
n
1i
ij
ttD
×
×
=
=
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
∑
(7)
[]
1n
j
1n
n
1j
ij
ttR
×
×
=
=
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
∑
(8)
Criteria having positive values of (D-R) have
higher influence on one another and are assumed to
have higher priority; these called dispatchers; Those
having negative values of (D-R) and receive more
influence from another are assumed to have a lower
priority and are called receivers (Seyed-Hosseini,
2006). Meanwhile, it should be emphasized that
factors with high (D+R) values that play a central
role, and factors with high (D-R) values that mainly
dispatch influence to other factors. Thus factors with
low (D-R) values mainly receive influence from the
other factors.
4 CASE STUDY
4.1 Case Background
To apply the proposed model of Academic
Performance Measurement (APM), this study
conducted a case study of National Cheng Kung
University (NCKU)’s implementation of the top-tier
university program to describe the working of the
proposed research model and show how it helps a
top-tier university realize its strategic plans and fulfil
its objectives. The BSC of APM model integrated
decisive indicators or critical success factors, and
these reinforced each other through cause-and-effect
linkage between measurement, vision, and goals.
Our study invited the decision-makers of
NCKU to set, through open discussion, the mission
of the school's top-tier university program as
“‘Comprehensive enhancement with featured
development,’ with the aim to become one of the
world’s top 100 universities.
”Based on this vision
and the criteria set by the Ministry of Education for
the top-tier university assessment, five strategic
objectives were outlined, while decisive indicators
were designed for top-tier universities and
transformed into specific practices, including:
F
11
: Advancement on three major fronts: research,
teaching, and industry-academia collaboration.
(Finance, Customer, Internal process, Learning &
growth)
F
12
: Training future social leaders and global citizens.
(Finance, Customer, Internal process, Learning &
growth)
F
13
: Reforming undergraduate education with
emphasis on humanity, creativity, international
vision, social concerns and students with leadership.
(Customer, Internal process, Learning & growth)
F
14
: Recruitment of senior talents. (Finance, Internal
process, Learning & growth)
F
15
: Developing world-class research centers.
(Finance, Customer, Internal process, Learning &
growth)
Later, the action plans were deployed in
performance-driving indicators of the BSC’s four
perspectives (Table 1), and complex problems were
systematically presented in the form of a hierarchy,
where the upper level contains strategic objectives,
the second level contains the indicator dimensions of
financial, customers, internal processes, and learning
and growth, and the third level contains the sub-
dimension indicator items.
4.2 Evaluating the Strategy Plan
The decision-makers were asked to provide their
views on a series of paired comparisons, after which
the assessment of the decision-makers in ANP was
integrated using geometric mean, while the
assessment in DEMATEL was integrated using
arithmetic mean. The direct relationship matrix then
integrated the impact direction and impact extent of
the organization's DEMATEL, and cause-and-effect
mapping and rank calculations on direct and indirect
relationship matrix were conducted. A two-
dimensional graphic with (D+R) as the horizontal
axis and (D-R) as the vertical axis was then
produced by cause-and-effect mapping using the
rank results calculated. The purpose of using a
graphical expression is to simplify a complex cause-
and-effect relationship into a simple visual structure
so that one can clearly see the intensity of impact
between these indicators. Decision-makers can
determine whether the indicator characteristics
should be classified as “cause” or “result” based on
the location of target features, as well as how much
the KPIs affect and are affected by them.
By the very nature of education, the financial
measurements are not forward-looking and are
exclusionary to nonfinancial measures. This study
proposed a strategy map with a network structure,
ICE-B 2011 - International Conference on e-Business
34
and the cause-and-effect mapping generated through
DEMATEL was used to form the ANP structural
diagram, which produced clusters based on the
BSC’s four perspectives. After a paired comparison
between the indicators' internal relationships and the
ANP cause-and-effect linkage of the mutually
affecting clusters and elements, the weights
calculated in ANY will become the weights of the
follow-up KPIs.
Table 1: The indicators of the BSC’s four perspectives.
Indicator items
A
1
: Finance
A
11
: The amount of industry-academia collaboration or
technology transfer. (F
11
, F
13
, F
15
)
A
12
: The amount of corporate sponsorship. (F
11
, F
15
)
A
13
: The number of patents or technology licensing. (F
11
, F
15
)
A
14
: The number of signed international cooperation projects
with project funding. (F
11
, F
15
)
B
1
: Customer
B
11
: The number of collaborated with national research
institutes. (F
11
, F
12
, F
15
)
B
12
: The number Of foreign student recruitment. (F
13
)
B
13
: The number of subsidized students for international
exchange and visiting. (F
12
, F
13
)
B
14
: The number of students for the dual degree of
transnational study. (F
12
, F
13
)
B
15
: The number of students for cross-institutional course
enrollments. (F
12
, F
13
)
B
16
: The number of established cross-institutional course
programs. (F
12
, F
13
)
B
17
: Early Admission plan for senior high school students. (F
12
,
F
13
)
C
1
:Internal process
C
11
: The number of major international conferences organized.
(F
12
, F
14
)
C
12
: The number of recruiting inter/nationally-acclaimed
scholars. (F
12
, F
14
)
C
13
: The teacher-student ratio. (F
12
, F
13
, F
14
)
C
14
: The number of holding the international communication.
(F
12
, F
14
)
D
1
:Learning and growth
D
11
: The growth rate of the international journals. (F
12
, F
14
, F
15
)
D
12
: The growth rate of the international journal citations. (F
12
,
F
14
, F
15
)
D
13
: The number of editors for the international
journals/magazines. (F
12
, F
14
, F
15
)
D
14
: The number of inter/national rewards for the important
prizes. (F
12
, F
14
, F
15
)
D
15
: The number of rewarded excellent teachers. (F
12
, F
15
)
D
16
: The number of professional literatures and journals. (F
12
,
F
14
, F
15
)
D
17
: The number of promoting all sorts of courses to be
conducted in English. (F
12
, F
13
, F
14
)
D
18
: Approving the upper-intermediate GEPT. (F
12
, F
13
)
4.3 Data Analysis
In analyzing the top-tier university program using a
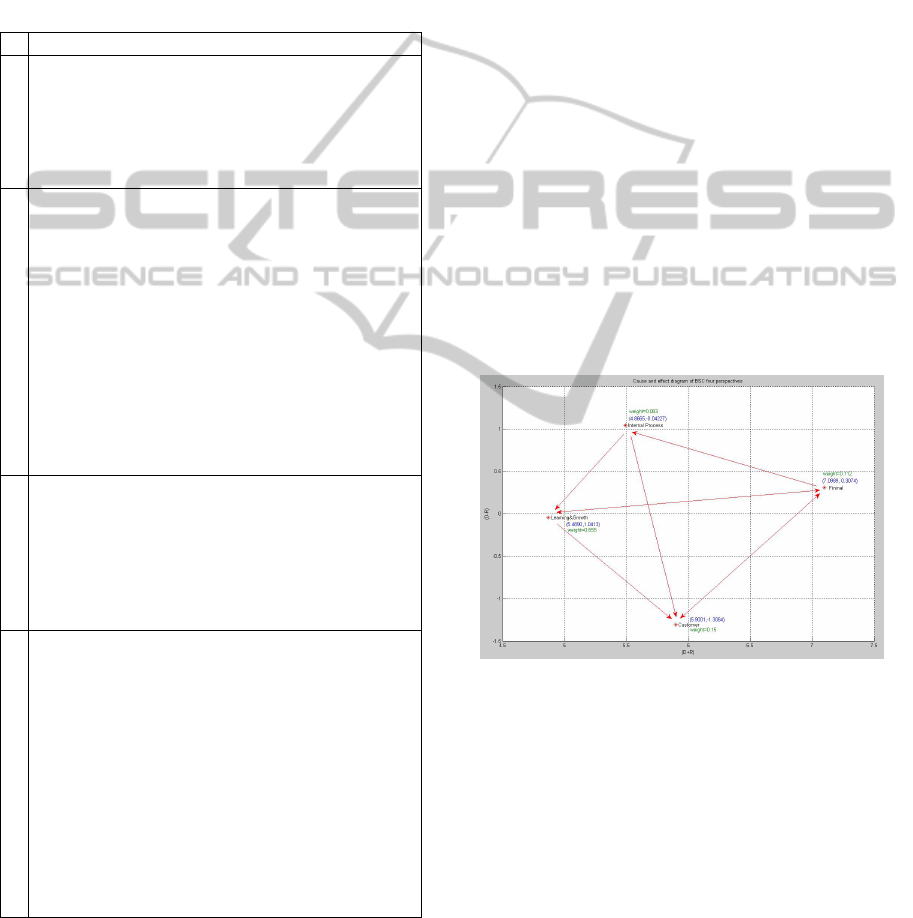
strategy map, the cause-and-effect diagram (Figure
1) formed by integrating ANP and DEMATEL with
the organization's strategy map was divided into four
quadrants according to center (D+R) and reason (D-
R) and plotted on the axis. The one with high center
and reason values was the financial dimension,
indicating the core projects that affect other
conditions, while the one with high center value and
low reason value was the customer dimension,
indicating the core projects affected by other
conditions. In analyzing the reason behind the
failure to meet the target in the "internal processes"
dimension, the perspective of the internal processes
dimension was influenced by the financial
perspective and influenced the customer and
learning and growth perspectives, in which "the
number of major international conferences
organized" was the core project in internal processes
perspective, and "the number of signed international
cooperation projects with project funding" was the
core project in the financial perspective. Based on
these findings, a review and alignment was done and
improvement measures were put forward.
Figure 1: The strategy map of BSC perspectives.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Performance management is a key issue in the
academic domain. The strategy of the top-tier
university is a mean of focusing performance
management and aligning towards the strategy plan
of an objective. This study tabled a framework based
on the BSC for strategy planning of a top-tier
university in Taiwan by using a multi-criteria
evaluation and alignment. It was then applied in the
performance management of educational
institutions, taking into consideration the following:
REALIZING THE STRATEGIC PLAN OF A TOP-TIER UNIVERSITY IN TAIWAN - A Multi-criteria Evaluation and
Alignment
35

Determine the appropriate action plans through
strategic objectives, deploy them in the BSC’s
four perspectives, and apply to the development
of top-tier university indicators;
With the use of the MCDA techniques - ANP
and DEMATEL, evaluate a series of BSC
indicators to construct the cause-and-effect
linkage of strategy map, obtain the relevant
strengths and weights between BSC indicators
and form objective functions;
Review the strategic gap between
implementation and organizational objectives
through target value of KPIs, in order to carry
out strategy alignment and possibly improve the
quality of education and international
competitiveness.
Strategic objectives are implemented to adapt to
environmental changes, one must continually review
the cause-and-effect linkage between strategy and
performance during the policy enforcement process.
As for the strategic gap, it represents the difference
between what the organization should do and what it
can do. Sometimes this means that the capacity is
greater than the demand, and sometimes it can mean
the opposite, indicating danger in organizational
operation. The greater the gap, the greater the danger
(Zack, 1999). Similar to business strategy, an
academic institution must align its strategy by
examining the achievement rate of its KPIs or target
values over time, changes in the environment, and
the status of implementation of each unit, in order to
achieve its strategic objectives.
REFERENCES
Asan, E. S., Tanyas, M., 2007. Integrating Hoshin Kanri
and the balanced scorecard for strategic management:
The case of higher education. Total Quality Mana-
gement & Business Excellence, 18(9), pp.999-1014.
Berler, A., Pavlopoulos, S., and Koutsouris, D., 2005.
Using key performance indicators as knowledge-
management tools at a regional health-care authority
level. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology
in Biomedicine, 9(2), pp.184-192.
Chen, S. H., Yang, C. C., and Shiau, J. Y., 2006. The
application of balanced scorecard in the performance
evaluation of higher education. The TQM Magazine,
18(2), pp.190-205.
Griffiths, J., 2003. Balanced scorecard use in New Zealand
government departments and crown entities. Austra-
lian Journal of Public Administration, 62(4), pp.70-80.
Hamid, S., Leen, Y. M., Pei, S. H., and Ijab, M. T., 2008.
Using e-balanced scorecard in managing the perfor-
mance and excellence of academicians. Pacific Asia
Conference on Information System (PACIS), Suzhou,
China July 3-7 2008.
Kaplan, R. S., and Norton, D. P., 1992. The balanced
scorecard: Measures that drive performance. Harvard
Business Review, 70, pp.71-79.
Kaplan, R. S., and Norton, D. P., 2004. Strategy Maps:
Converting Intangible Assets into Tangible Outcomes.
Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
Karathanos, D., and Karathanos, P., 2005. Applying the
balanced scorecard to education. Journal of Education
for Business, 80(4), p.222-230.
Lawrence, S., and Sharma, U., 2002. Commodification of
education and academic labour using the balanced
scorecard in a university setting. Critical Visions on
Accounting, 13, p.661-677.
Niven, P. R., 2002. Balanced Scorecard Step by Step. New
York: John Wiley & Sons.
Oliveira, J., 2001. The balanced scorecard: an integrative
approach to performance evaluation. Healthcare
Financial Management, 55(5), p.42-46.
Seyed-Hosseini, S. M., Safaei, N., and Asgharpour, M. J.,
2006. Reprioritization of failures in a system failure
mode and effects analysis by decision making trial and
evaluation laboratory technique. Reliability Enginee-
ring and System Safety, 91(8), p.872-881.
Solano, J., De Ovalles, M. P., Rojas, T., Padua, A. G.,
Morales, L.M., 2003. Integration of systemic quality
and the balanced scorecard, privacy and security in e-
business. Information Systems Management, Winter
Issue, pp.66-81.
Storey, 2002. Performance management in schools: Could
the balanced scorecard help?. School Leadership &
Management, 22(3), p.321-338.
Tamura, M., Nagata, H., and Akazawa, K., 2002.
Extraction and systems analysis of factors that prevent
safety and security by structural models. Osaka, Japan.
Proceedings of the 41st SICE Annual Conference
Tseng, M. L., 2010. Implementation and performance
evaluation using the fuzzy network balanced scorecard.
Computers & Education, 55(1), p.188-201.
Umashankar, V., and Dutta, K., 2007. Balanced scorecards
in managing higher education institutions: an Indian
perspective. International Journal of Educational
Management, 21(7), p.54-67.
Wu, W. W., and Lee, Y. T, 2007. Developing global
managers' competencies using the fuzzy DEMATEL
method. Expert Systems with Applications, 32(2),
p.499-507.
Yu, M. L., Hamid, S., Ijab, M. T., and Soo, H. P., 2009.
The e-balanced scorecard (e-BSC) for measuring
academic staff performance excellence. Higher
Education: The International Journal of Higher Edu-
cation and Educational Planning, 57(6), p.813-828.
Zack, M. H., 1999. Developing a knowledge strategy.
California Management Review, 41(3), p.125-145.
Ministry of Education, Republic of China (Taiwan), 2011.
The Excellent Development of University Education.
[online] (Updated 29 June 2006) Avaiable at: <http://
english.moe.gov.tw/ct.asp?xItem=1209&ctNode=363
&mp=1> [Accessed 30 Jan 2011]
ICE-B 2011 - International Conference on e-Business
36
