
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
M. Sifalakis, C. Tschudin
Computer Science Department, University of Basel, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland
S. Martin
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Liege, B-4000 Liege, Belgium
L. S. Ferreira, L. M. Correia
Instituto Superior T´ecnico, Technical University of Lisbon, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords:
Cloud computing, Network services, Future internet, Service interface.
Abstract:
Two major challenges for enabling the vision of cloud computing regard (a) the generic and multi-purpose
access to (virtualised) resources, and (b) the flexible, dynamic, and on-demand composition of services verti-
cally from the physical link level, all the way “up” to the application level. Both aspects require a respective
flexibility and expressibility from the interfaces in-place, which is missing from the current static socket (and
other) interfaces below the application level. In this position paper, we propose, explain and exemplify an al-
ternative generic service interface (GSi) that borrows from object oriented design to enable properties such as
polymorphic access, generic service composition, introspection and dynamic reconfigurability, of in-network
resources; opening in this way the path for flexible creation of service clouds.
1 INTRODUCTION
For a cloud service user the ability to configure-and-
use and then pay-as-you-go a utility-like service, will
be of similar importance as will be for the cloud
provider the manageability (introspection and cus-
tomisability) of the resources comprising an offered
service. To what extend is this possible today?
An observation regarding Internet related engi-
neering is that, by antithesis to technologicalprogress,
little advancement has been made in terms of improv-
ing, standardising, and evolving our programming in-
terfaces and design patterns. One has to take a sec-
ond and ponder how much flexibility and customis-
ability can be attained below the transport level for
on-demand or dynamic allocation or federation of
flow-resources (flow-based routing schemes, proto-
col translators, network coding, assign mobility an-
chors, split/merge flows for distributing processing
and caching), expression of service requirements (e.g.
relative prioritisation of service flows, per service se-
curity level adjustment, data-flow processing), or ex-
pression of user policy (e.g. with regard to service
path selection to avoid in-transit use of an expensive
provider’s network, or an episodic path).
In several of these cases, mechanisms to attain
such objectives may be available (or might soon
emerge), but they cannot be accessed and employed
programmaticaly or on-demand, due to the lack of
sufficient expressibility in the available programming
and user interfaces. At the top-most layer (appli-
cation) of the OSI model a variety of middleware
solutions, which built on top of the socket inter-
face(Stevens et al., 2003), eased application devel-
opment by aspiring more usable interfaces than the
sockets API. Yet, they inevitably cannot offer more
expressibility and functionality beyond what sockets
provide, and at the same time they are highly pro-
prietary, essentially lacking interoperability. These
interface-levelissues contributein two of the most im-
portant obstacles for the adoption of cloud computing
as pointed in (Armbrust et al., 2009), namely service
availability and data lock-in.
To serve the needs of cloud computing, for re-
sponding to service demand that varies with time,
there will be strong demand for more dynamic, func-
tionally richer and more extensible programming and
control interfaces. Such interfaces should (a) leverage
110
Sifalakis M., Tschudin C., Martin S., S. Ferreira L. and M. Correia L..
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003449501100119
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2011), pages 110-119
ISBN: 978-989-8425-52-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

dynamic federation of resources and composition of
services (within and across cloud providers), and (b)
allow introspection of service state and on-demand
customisation of service configuration.
Starting from this tenet we explore the potential
of adopting object orientation for describing network
functions and services. We present the Generic Ser-
vice abstraction and interface (GSi) as an alternative
to the legacy socket API, that provides constructs for
describing in-network processing and transportation
services on data flows and across (heterogeneous)net-
work(s). We explain how it is possible through this
framework, to preserve service modularity, enable ab-
straction, provide access to the dynamic state in the
network (and in doing so effect cross layering), re-
use algorithms, and compose network-based services
in a structured and accountable way.
In the remaining of this article we first motivate
our work (section 2) by sketching the shortcomings
of the socket API for the purposes of cloud com-
puting. Then in section 3, we advocate the benefits
of object-orientation for the design of cloud services
and then we present and exemlify the Generic Service
framework and interface. In section 4 we provide a
use case and early proof-of-concept validation for a
service cloud that provides multi-hop Wireless Mesh
Network (WMN) paths as services. In section 5 we
provide an exploration of the literature and finally in
section 6 we conclude this paper.
2 MOTIVATION
TCP/IP was initially intended and served as a least
common denominator for heterogeneous networks al-
lowing application inter-operation across them, thus
anticipating and necessitating a global deployment
everywhere. As a result of this global adoption, the
socket interface enabling access and configurability
to the services of a TCP/IP stack, became a common
denominator and the only de-facto standard API for
building network services. However, today’s reality is
somewhat more complex. Network convergence, re-
source virtualisation and multi-tenancy in cloud com-
puting, require more than mere bridging of different
link-level transports, with a common overlay. One,
cannot factor out the additional diversity and hetero-
geneity of applications and system resources.
The socket interface appears to be rather restric-
tive in expressing the dynamism and plasticity nec-
essary for engineering custom services, integrating
new methodologies (Akyildiz and Wang, 2008; Chi-
ang et al., 2007) and diverse technologies, and embed-
ding new functions in the network stack. Regarding
the last, it is worth noting that most operating systems
today provide frameworks for enriching a systems
network functionality, but is enabled through propri-
etary interfaces not programmatically expressed at the
socket level. In this section we explore the main lim-
itations of the socket API that need to be addressed
in a “modern” API suitable for the purposes of cloud
computing and network convergence.
Static coupling of mechanism and function. The
first problem we see with the socket interface is that it
is tailored to the mechanism (TCP/IP protocol suite)
and not the functionality it serves (network commu-
nication). This is due to the protocol-centric evolu-
tion of the Internet under the domination of TCP/IP,
which led to a static interface that cannot be easily
extended to accommodate new configuration options
and parameters, beyond those that are available for
the current TCP/IP stack. This in turn has led to tech-
nological dependencies, which are difficult to get rid
of, the most probably prominent of which is the loca-
tor/identifier coupling: for example separating the lo-
cation from the endpoint of a communication has not
been feasible without re-engineering of the interface.
Lack of modularity. A second problem is the lack
of modularity since a socket expresses in a mono-
lithic way the functionality of a complete stack (and
therefore a fixed set of functions). However, today
it has become more apparent that a full-fledged pro-
tocol suite is neither necessary nor suitable every-
where: Grids of very small devices such as sensors
and RFIDs may not have the resources to operate a
complete TCP/IP stack, or they may not need it (e.g.
full mesh networks do not require routing). In other
cases the underlying network technologies may al-
ready have their own transport level and network level
functionality (Howell, ; Joel, 1993). Reinforcing TCP
and IP overthem for facilitating network-convergence
can be far from efficient and complicating for man-
agement. At the same time this means that any alter-
native composition of network functions and federa-
tion of network services cannot be expressed.
Opacity. Another important problem is that the
sole perspective expressed in the socket interface is
an end-to-end transport level view of the network.
All other functions and their parameters are indirectly
(and insufficiently as it is) represented in transport
level options and abstractions. This does not allow
deep introspection and fine grained control or con-
figurability of the individual functions in the stack,
which is why cross-layer designs rely on additional
ad-hocly defined interfaces.
Limited expressibility. As illustrated in Figure
1(b) the layered design of the TCP/IP stack considers,
and expresses in the socket interface, the interactions
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
111

user
application
inf.objects
hardware
infra.
software
netdriver
application
inf.objects
lossylossless
-1userprofile
-1classofapps
(texthandling)
-2inf.objectclasses
-1networkdriver
- infrastructuretypesN
software
netdriver
hardware
infra.
user
application
inf.
objects
- userprofiles
- classofapps
(texthandling)
- inf.objectclasses
- networkdrivers
- infrastructuretypes
N
M
L
K
P
(a) (b)
Figure 1: Old versus today’s interaction models.
between two entities as communication determinants:
(a) the user application, which is the user’s interface
and policy broker towards the network; generating in-
formation objects and selecting how they should be
delivered, and (b) the hardware infrastructure over
which communication is provided.
The challenge faced today however, is more real-
istically depicted in Figure 1(b): the number of com-
munication determinants and the possible interactions
is larger and the scope of these interactions is more
dynamic. Multimedia traffic has introduced a dy-
namic set of (often mutually interacting) information
objects with more diverse delivery requirements than
lossy/lossless, including timeliness and spatial syn-
chronisation. Moreover, these information objects of-
ten interact with the network beyond the context of
mere forwarding (e.g. caching, transcoding or other
in-network manipulation functions). The application
is not always under explicit user control and interacts
with the network in other roles than as a source or sink
of information objects (e.g. for handling of mobility).
The user (or service initiator), on the other hand, of-
ten directly interacts with the network driver (e.g. es-
tablishing vpn connections, setting routing rules, per-
forming admission and rate control, selecting inter-
faces, etc). Finally, new infrastructure technologies
permit customisability based on continuous feedback
from the network driver for better adapting to service
requirements (e.g. soft and cognitive radio, error con-
trol, security, etc). And, as a result, the network driver
in order to serve effectivelythis immense diversity ne-
cessitates dynamicity beyond routing path selection,
in the order to employ appropriate service functions
and utilise effectively a physical infrastructure, richer
and more diverse than ever before (wired, wireless,
multi-hop, ad-hoc, infrastructured, etc).
3 GENERIC SERVICE
INTERFACE (GSi)
In this section we try to bash into the aspects dis-
cussed so far by considering object orientation as an
approach and proposing a modular programming and
user interface for dynamically composing and access-
ing network services.
3.1 Object Orientation in the Design of
Network Interfaces
Object orientation provides a generic and structured
way for separating functionality from mechanism: a
(abstract) class provides the representation and spec-
ification of a type of function or service, while its in-
terface represents generic semantics for accessing a
mechanism that implements this function. Derived
typed class objects then, embody different mecha-
nisms. This distinction allows a clear separation of
incentives and roles for a user and a provider of a net-
work service. A user for example can concentrate on
the service provided as opposed to the intrinsics of the
service fabric. Encapsulation of mechanism in ser-
vice classes, in this way, also promotes the invariance
of mechanisms (e.g. different providers may offer the
same service, that a user can access invariably).
Selective information hiding, at the class inter-
face, allows controlled access to the intrinsics of a
mechanism and helps the tractability of cross de-
pendencies between different services. Combined
with Polymorphism, it allows “deep” introspection of
state, explicit invocation of service functions across
intermediating functions, and provides a consistent
methodology for representing and extending the in-
teractions among service functions. This practise en-
ables a consistent way of acquiring “cross-layer” in-
formation in an entire composite service and allevi-
ates one of the major concerns currently, against the
adoption of many proposed cross-layer optimisations;
namely the ad-hoc and intractable nature of interac-
tions that they create.
Function overloading can be used to extend the
definition and semantics of an operation or service
function, in order to group a set of semantically re-
lated services under a common usage framework (and
interface). It also enables other attractive capabilities
that empower cloud services, such as creating new
services from existing ones (to leverage composition),
encouraging algorithmic and functional reuse at dif-
ferent levels of abstraction (to assist virtualisation),
integrating and importing new functional features into
services in non-disruptive ways, etc.
Several of these features have been already ex-
ploited at and above the application level to improve
the usability of application platforms, albeit in propri-
etary ways and without much intend for standardisa-
tion. One only needs to explorethe multitude of appli-
cation level middleware platforms. On the other hand,
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
112

less intend has been seen below the socket boundary,
living the space inside the network stack rigid and un-
touchable to any customisability and optimisability.
3.2 Formalising Network Services
The Generic Service interface (GSi) opts to express in
a universal way network servicing at different levels.
In order to account for all types of services however,
we first need a network service formalisation, so that a
common interface can be applied to them. Fortunately
this does not seem to be so difficult.
From a high-level view a network service corre-
sponds to the handling of data as they flow across
a network, which typically involves processing P(·)
and/or transportation T(·) operations. For example,
an Ethernet link implements a service that applies a
transportation operation on data, while a VPN ser-
vice involves two processing operations (encryption
and decryption) in combination with a transportation
operation (e.g. PPTP (Hamzeh et al., 1999)). We can
therefore symbolically represent a network service on
data x as
S(x) = {P
i
(x) , T
j
(x)} , i = 1..n j = 1..m (1)
It draws that every P
i
and T
i
in this definition may be
regarded as another lower-level (or more basic) net-
work service, which immediately allows us to sym-
bolically express the dependency of complex (com-
posed) services in terms of simpler ones as
S
C
(x) = {S
P
i
(x) , S
T
j
(x)} , i = 1..n, j = 1..m (2)
or equivalently in a more convenient recursive sym-
bolism (not having to distinguish transportation from
processing services)
S
k
(x) = {S
k−1
(x) , S
k−2
(x), ..} (3)
Finally, to represent service composition in this for-
malisation, all we need is to specify a composition
function f
c
(·) that describes how the complex service
is provided from its dependants.
S
k
= f
c
(S
k−1
, S
k−2
, ..) (4)
Such a composition function is likely to express the
integration of the dependant services in terms of in-
terfacing, ordering, or other criteria, lending to sys-
tematic ways of expressing federation (for example in
(Sifalakis et al., 2011) f
c
is reduced to a declarative
description of data flows, while in (Cobbs, 2011) it is
expressed by a functional program).
Following this simple high-level formalisation
we are now ready to introduce the object oriented
Generic Service interface (GSi) structure.
3.3 The Generic Service Interface
Our aim is to provide programming and control prim-
itives for generic and implicit access to data manipu-
lation and transportation operations, configurable pa-
rameters and service state, such as the underlying ser-
vice mechanisms may permit. Following an object
oriented design strategy, service specific functionality
is encapsulated in subclasses of an abstract base class
that defines the generic interface. Figure 2 shows the
structure of the base GSiclass containing a list of ele-
ments (Items), which may be one of the following:
I/O Points. They represent data inputs/outputs of
the service. These may be identifiable protocol end-
points, such as a network address, a port number,
a medium access control channel, or a service han-
dler, file descriptor and other system local constructs
used to send/receive data. They provide access to
the data plane of a service and they can also be used
in “plumbing” operations between service functions
(dynamic service composition), besides data I/O.
Mediation Point. The data inputs and outputs of
generic services that compose higher order services
are plumbed together at mediation points. Exposing
this construct at the interface level provides a broker
interface for (re-)configuring on-demand the compo-
sition of a service and the federation of resources. For
example if the GSirepresents a routing service or flow
aggregation service in the network of a provider, the
mediation point would provide a control interface for
installing or modifying routing rules/filters. By anal-
ogy, if the GSirepresents a network storage service
purchased by a user, the mediation point would be an
interface to a virtual array of disk slices, where he
may release some of them to reduce the cost encoun-
tered for the service.
Composing Generic Service List. An optional list
of lower order service functions/resources (symbol-
ised as S
T
(·) and S
P
(·) earlier) on which the generic
service depends. The composition function (see f
c
(·)
earlier) that specifies how these service functions inte-
grate together to provide the higher order service may
also need to be known, in which case it can be re-
vealed in the Attribute List next.
Generic Service Attributes. A list of configurable pa-
rameters and state values related to the service pro-
vided. They may be parameters for indirectly modi-
fying or customising the service or state values corre-
sponding to information available e.g. for monitoring
the operation or quality of the service. Depending on
the type of service or function that the GSiexpresses,
they may related to a physical or virtual interface, pro-
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
113

+inspect()
+config()
+send()
BaseGSi
+virtualsetKnob()
+virtualreadDial()
+typeof()
Item
Composing
GSiList
+link()
+unlink()
+mux()
+getInfo()
MedPointList AttributeList
+setInput()
+getInput()
+setOutput()
+getOutput()
IOPointList
+setAttrib()
+getAttrib()
Figure 2: Base GSi class layout.
tocol state, service quality, and so forth.
It is worth noting that while the I/O points provide
access to the data plane of a service, the attribute list
on the other hand, exposes the control plane, and a
mediation point provides management plane access.
Therefore, one interface empowers combined opera-
tions across all three planes.
A number of interesting capabilities stem from the
object oriented design of the GSi.
First, all Items, may export a set of Knobs and Di-
als
1
, as generic configuration and introspection ca-
pabilities across the different Item types and GSi-
classes. By employing polymorphism (object oriented
design), one can set configuration information or read
attributes in a generic service class and recursively to
all its composing sub services as one operation. In
this manner, a configuration parameter expressed at a
high level has a simultaneous effect on a number of
other parameters across an entire system. Similarly,
monitoring a state value at a high level resolves in
deep introspection across the service stack, naturally
supporting cross-layer design.
Second, through the virtual function mechanism it
becomes possible to dynamically associate attributes
of a generic service class to respective attributes of
its Items and sub services without compromising the
modularity of the services. For example it is possible
to relate a user level qualitative metric of a service
(e.g. good, secure, stable, etc) to state information
from the underlying infrastructure (e.g. throughput
levels, end-to-end encryption, error-rates, etc).
Third, although interoperability and compatibility
across services is guaranteed through the unified in-
terface of the abstract generic service class, still at
the same time, a provider of a service has the flexi-
bility to decide what level of access will be allowed
for the service user (both regarding state information
and access for configuration) by offering the service
in typed subclasses with reduced attribute lists or re-
duced functionally interface primitives.
1
The metaphor of knobs and dials is inspired by (Calvert
et al., 2007).
Finally, and very importantly, once we have man-
aged to generalise the interface of services, it be-
comes possible to also generically express and im-
plement service composition as a set of operations
over a set of Generic Service classes (e.q. 1 earlier).
This can be done by means of the object-oriented
notion of generic operators, which represent algo-
rithms that implement operations on abstract elements
(operands). They can be developed agnostically to
the nature of their inputs and outputs, which makes
highly re-usable mechanisms possible for any set of
objects that respect certain interface rules. Generic
operators may provide a common framework for ex-
pressing data flow manipulations (such as network
coding, aggregation, etc), or resource federation op-
erations (e.g. clustering, mirroring, etc) for virtuali-
sation. When combined with meta descriptions that
extensively specify the interfacing potential between
different types of I/O points, they empower a dynamic
and extensible compositional capability for services.
3.4 Compartments and Clouds of
Generic Services
According to (Armbrust et al., 2009) the novelty in
cloud computing lies in (a) the illusion of an infi-
nite computing resource available on demand, (b) the
elimination of an up-front commitment by cloud users
that allows one to start small and increase resources
following their needs, and (c) the ability to pay-as-
you-go for the use of resources on a short-term ba-
sis. From these assumptions stem the feature require-
ments for a cloud: it should define and appear as one
homogeneous resource/service pool, that has specific
policy and account rules, and its own local dynamics
and resource management/pooling mechanisms (iso-
lation). These requirements do not undermine the in-
teroperability across clouds; rather they prescribe the
self-consistent and dynamic nature of a cloud, which
is therefore more than an administrative domain (it in-
cludes separation of mechanisms), or an autonomous
system (it encompasses more than routing dynamics),
or a service layer (it integrates vertically different re-
sources and network functions/services). This means
that the cloud concept requires a new contextualisa-
tion abstraction and also an interface representation at
a resource level that allows to request and access ser-
vices. Moreover, to leverage interoperability across
clouds, this interface must successfully embed the
cloud features but should not interfere with the mech-
anisms that implement them.
The Compartment construct and interface in
(Bouabene et al., 2010; Randriamasy, 2009) offers
a suitable abstraction that captures the essence of a
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
114
cloud. Compartments contextualise communication
and information services of different scales or func-
tional complexity (from a single link, a domestic net-
work, an enterprise network, to large federated struc-
tures). At the same time they reflect the presence of
policy domains for decisions (Paul et al., 2008). On
the other hand, how a specific service is implement in
a Compartment does not impact the service users, nor
does it impact decisions on policy, access control and
quality of service, in other Compartments.
In the context of Generic Services and their ob-
ject oriented design, compartments act as extended
namespaces for addressing/accessing generic services
and control elements that need to be locally identifi-
able. Moreover, a Compartment provides the cloud
interface that one may use to request a generic ser-
vice by means of two primitives: (a) one for register-
ing service points, and (b) another for accessing ser-
vices at these service points. In this way modularity is
preserved at the policy level and the functional level.
In summary, Generic Services create a premise for
functional plasticity, service composition and virtual-
isation, while Compartments provide the context for
virtualisation and the demarcation of cloud domains.
The example that follows will introduce the Compart-
ment interface as a interface for clouds, and will high-
light its use with Generic Services.
3.5 Programming with the GSi
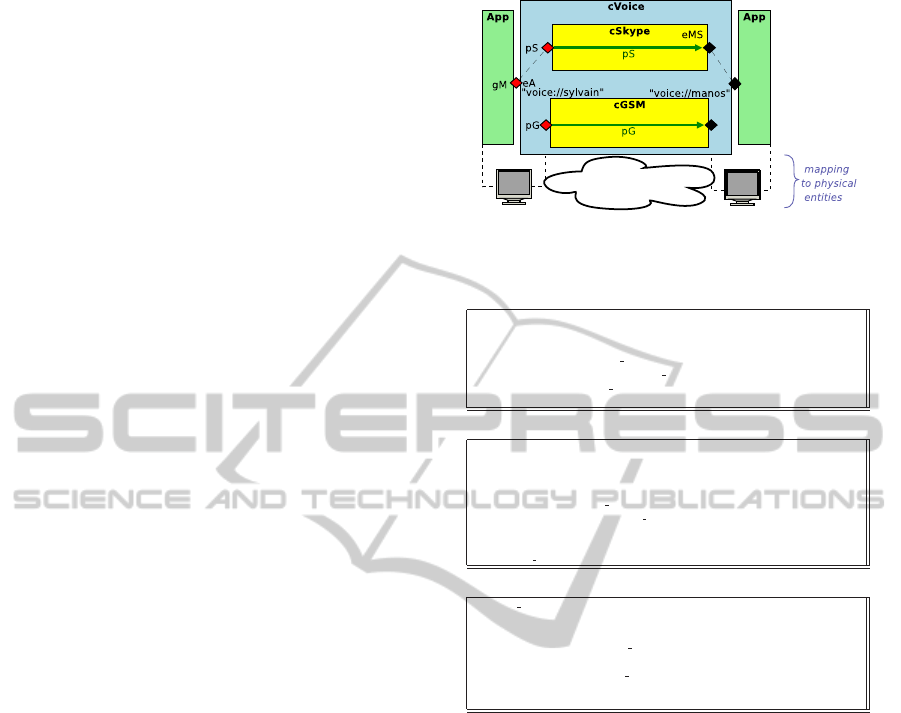
In the scenario of Figure 3, two applications establish
a voice call over a telephony service cloud (cVoice),
which integrates the underlying services of two can-
didate technologies (called Skype and GSM); in turn
provided by respective clouds providers. Initially,
the voice communication between two named enti-
ties in the cVoice cloud uses a carrier service from the
cSkype cloud. When the observed quality drops be-
low a threshold level, the carrier service transparently
switches from the cSkype cloud and to the cGSM
cloud. Access and configurability of the different ser-
vice components is effected through the GSiinterface.
A user requests for a cloud service (i.e. creation
and initial access to the service) through the Compart-
ment interface as exemplified in the code fragment
4(a). A publish call (line 2) requests association with
the cloud (registration) of the name
sylvain
, and is
used as the listening end for connection requests. The
registration of the name
manos
(Figure 3) would be
performed in a similar way. A resolve call (line 3)
is used to request a voice connection to
manos
in
cVoice. The successful activation of the service re-
turns a GSiobject gM which can be used (line 4,5) for
accessing and managing the service resources (in this
Figure 3: an abstract cVoice cloud (compartment), fed-
erating cSkype and cGSM infrastructure clouds (compart-
ments).
1: Cloud cV = System.getCloud(”cVoice”);
2: cV.publish(”sylvain”, IncomingCallHandler());
3: GSi gM = cV.resolve(”manos”);
while (gM.getAttr(CALL STATUS) == CONNECTED)
4: Sound.play(gM.getInput(AS STREAM).read(25ms));
5: gM.getOutput(AS STREAM).write(Sound.capture(25ms));
(a) Simple client voice application
1: Cloud cS = System.getCloud(”cSkype”);
2: Cloud cG = System.getCloud(”cGSM”);
3: MediationPoint m = System.getMediationPoint(LOCAL);
while (1)
4: GSi eA = resolve requests.dequeue();
5: String skypeID = lookup name(eA.getAttr(REMOTE), SKYPE);
6: GSi pS = cS.resolve(skypeID);
7: m.link(eA, pS);
8: set monitor(eA, pS);
(b) Voice compartment, call establishment
periodic monitor()
1: [GSi eA, GSi pS] = monitored.dequeue();
2: int latency = pS.getDial(LATENCY);
3: int goal = eA.getAttr(MAX LATENCY);
4: if (!acceptable(latency, goal))
5: String telno = lookup name(eA.getAttr(REMOTE), GSMNet);
6: GSi pG = cG.resolve(telno);
7: m.unlink(eA, pS); m.link(eA, pG);
(c) Voice compartment: Quality monitor and call management
Figure 4: GSi and compartment API example.
example using the I/O points to send and receive voise
samples).
At the provider end (the cVoice cloud) the code
that services the user request is shown in Figure 4(b).
Upon receiving the service request, a voice connec-
tion needs to be established over one of the infras-
tructure clouds cSkype or cGSM. In line 4, the ser-
vice request by the user (resolve call in 4(a)) results
in preparing up a GSiobject (eA) that will be passed
to the user when the service is activated. This is anal-
ogous to creating an unconnected socket for commu-
nicating with the network stack. Next, the call request
to
manos
is looked-up and recursively resolved in the
cSkype cloud (line 5-6). In other words, the cVoice
cloud is now requesting (as a user) a service from
the cSkype cloud, which results in the instantiation of
the pS GSiobject when the connection is established.
The process is completed (line 7), when the local me-
diation point is used to link the GSiobject from the
cSkype cloud to the GSiobject that will be returned to
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
115

the user by the cVoice cloud. This involves interfac-
ing the I/O points (data-plane plumbing) and linking
through any service attributes (control plane set up).
Finally, in Figure 4(c) we show the ease for au-
tomating service re-composition through the GSi, in
order to satisfy dynamically user requirements for
service quality. A call quality monitor function (ac-
tivated in line 8 of 4(b)) reads the attribute in the
GSiobject of the cSkype cloud that holds latency mea-
surements (line 2), and compares them to a quality
threshold set by the user (in an attribute of the cVoice
GSiobject). When quality drops below the set thresh-
old level, the mediation point is used to transparently
replace the cSkype service with a new one (similarly
established and accessed by means of the GSi) in the
cGSM cloud (line 5-7).
4 A USE-CASE IN WIRELESS
MESH NETWORKS
WMNs lay on the evolutionary path of wireless
networks, by extending the single-hop access wire-
less paradigm to multi-hop ad-hoc (backhaul) net-
works that combine heterogeneous radio access tech-
nologies. In this sense, WMNs intend to pro-
vide cloud-like services by federating different wire-
less link resources under a unified dynamic wire-
less multihop infrastructure. In the achievement of
this goal a number of challenges manifest the need
for cross-layer design (Akyildiz and Wang, 2008)
in order to integrate effectively the diverse wireless
network technologies (802.11 (IEEESTD.5307322,
2009), 802.16 (IEEESTD.265774, 2005), LTE (LTE-
SAE, 2008)) and radio communication solutions
(multiradio/multichannel nodes, directional antennas,
etc), in face of heterogeneous QoS constraints, multi-
hop relaying, and variability in link capacity. A sec-
ond challenge is presented as a requirement for dis-
tributed management and dynamic coordination, in
order to allow the network to self-configure (“plug-
and-play” fashion), organise and optimise its servic-
ing capacity, and incorporate self-healing capabilities
in case of failures.
A typical example regards the effective allocation
and federation of non-interfering radio channels in or-
der to improve mesh node communication and mul-
tipath capabilities in a dynamic network topology.
A promising research direction considers the use of
mesh nodes, equipped with several radio interfaces
operating simultaneously on multiple radio channels
in combination with a channel allocation strategy that
effectively assigns channels/carriers to radio inter-
faces, in order to maximise channel utilisation and
minimise interference. A fixed wireless channel as-
signment among mesh nodes results in statically en-
forced topologies, analogous to the wired ones, how-
ever, with variable quality or episodic connectivity
(due to the susceptibility of the medium to noise and
interference). Hybrid and dynamic solutions on the
other hand, where some or all radios switch dynam-
ically channels, increase inter-connectedness at the
cost of management and algorithmic complexity.
In (Ferreira et al., 2010) a novel distributed co-
operation framework is presented, which allows the
network to take advantage of the local resources and
characteristics of nodes (communication capabilities,
surrounding environment, mobility pattern, persis-
tence, energy, computation capacity) in an oppor-
tunistic fashion. Each node may assume any net-
work role in the mesh (resource management, net-
work gateway, forwarding, address assignment), con-
tributing in the collective optimisation of the network.
In (Randriamasy, 2009), a hybrid channel as-
signment strategy is proposed, where every node as-
signs channels to its interfaces following an interfer-
ence minimisation model. It enables self-organization
and provides stable interconnection by pooling the
per-technology channel frequencies (cloud resource)
into equivalence classes, and allocating them in
a way that minimises a cost function (resource
virtualisation/multi-tenancy strategy).
In the following sections we show how the use of
the Generic Service interface can ease the design of a
WMN cloud service which combines the ideas from
(Ferreira et al., 2010; Randriamasy, 2009) to provide
stable wireless paths as cloud resources.
4.1 Wireless Resource Abstractions and
Interfaces
In order to exploit multiple wireless network inter-
faces simultaneously, we eventually have to address
the heterogeneity of the different wireless technolo-
gies. Moreover, radio channel resources must be
partitioned in the physical dimensions of time, fre-
quency, space and/or code to allow multiple logically-
independent communications to take place simultane-
ously (resource pooling and distribution).
This necessitates two steps of composition, one
for the federation of different wireless link technolo-
gies and a second for the virtualisation (temporal,
spatial and frequency multiplexing) and allocation of
radio channels over them along a multi-hop wire-
less path. The modularisation and abstraction of the
WMN cloud functionality can be therefore imple-
mented in three levels: (a) at the lowest level a GSiin-
terface (GSi
wLLC
) provides access and management of
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
116

the wireless interfaces, (b) at the middle level another
GSiinterface (GSi
rMAC
) multiples the wireless inter-
faces and abstract them in virtual channel interfaces,
and (c) at the top layer a third GSiinterface (GSi
WMN
)
abstracts the federation of channel links in WMN ser-
vice paths. The last represents the interface to the ser-
vice delivered to the cloud user.
As shown in Figure 5 different GSi
wLLC
class ob-
jects (WiFi, LTE, WiMAX, etc) are interchangeably
federatable in the list of Composing Generic Services
of a GSi
rMAC
class and can be controlled by means of
software radio techniques and using internal (in the
GSi
rMAC
) multiplexing strategies. Figure 5 schemati-
cally exemplifies also common attributes in all wire-
less link technologies, which may be exposed in the
attributes of the generic GSi
rMAC
interface.
WiFi GP
+inspect()
+config()
+send()
+Knobs/Dials...
Item
+ ...
MedPointList AttributeList
+ ...
IOPointList
+inspect()
+config()
+send()
GSi
rMAC
+Knobs/Dials...
Item
Composing
GSiList
+ ...
MedPointList AttributeList
+ ...
IOPointList
+Freq
+Gainin
+Gainout
+ TxPower
+Pmcs
+Pathatten.
+Long,Lat
+ Txrate
+Mode
+SSID
+Encryption
+SNR
+FrmErr.
+ Assoc.
...
...
GSi
LTE
GSi
WIMAX
GSi
WIFI
GSi
wLLC
Composing
GSiList
Figure 5: A GSi
rMAC
object providing virtual access to mul-
tiple GSi
wLLC
objects.
4.2 Dynamic Channel Allocation and
Path Resource Management
Having localised and abstracted the various
technology-specific mechanisms (GSi
wLLC
) and
virtualised them as single-channel resources
(GSi
rMAC
), one can then develop flexible, dynamic
and technology-agnostic resource management
mechanisms for a cloud service. Although in this
case study we have concentrated on a channel
management strategy, other cloud mechanisms may
as well include routing schemes, power/rate control,
coding frameworks, QoS frameworks, etc.
The active topology is established through a set
of instantiated GSi
rMAC
service objects that hold
the dynamic interconnection state in the cloud.
Such dynamic information includes estimates of the
average channel activity and utilisation/contention,
queue associations, received power/noise estimates
from competing wireless clusters, hop-distances to
gateways and respective path attenuation, queue
occupancy, and other. Most of this information being
estimated relies heavily on information acquired,
through the same recursive API, by the active
wireless link interfaces, (i.e. GSi
wLLC
objects).
Within the WMN cloud, and for purposes of
management and control, an GSi
rMAC
object and an
encapsulated GSi
wLLC
objects provide access to the
same wireless link resource, enabling joint customi-
sation though either of two different but parallel inter-
faces, each serving a different management objective:
On one hand, the GSi
wLLC
object provides exclusive
technology-oriented management of the wireless in-
terface and through it to the link services it provides
to different flows. On the other hand, the GSi
rMAC
ob-
ject permits customisation of the wireless interface on
a per-channel basis and the temporal virtualisation a
radio channel across multiple wireless interfaces.
Regarding the user perspective of the cloud ser-
vice, all mesh nodes along an active WMN path,
can be identifiable and accessible in the context of
a WMN generic service (not in terms of its physi-
cal location, but rather through the GSi
WMN
object)
as a Mediation point. They in turn, maintain up-
to-date dynamic information, which is useful to the
cloud provider (and optionally to the cloud user) in-
cluding the distributed data structures for routing and
neighbour tables, channel usage, as well as informa-
tion about the node locality or operation environment
(e.g. geo-position, power decay and shadowing, gaus-
sian noise, and other).
4.3 Proof-of-Concept
In an early proof-of-concept validation
2
of the
aforementioned design and the channel management
mechanism from (Randriamasy, 2009) we created a
mesh topology, where 13 nodes (MAPs) form a back-
haul WMN network compartment, and each node lies
in the communication range of three others. One of
the mesh nodes provides gateway connectivity to the
Internet. Each MAP is equipped with 3 wireless inter-
faces (accessed through GSi
wLLC
classes): one IEEE
802.11b for providing connectivity to end-users, and
two IEEE 802.11a for backhaul interconnection with
other MAPs. The two IEEE 802.11a interfaces on ev-
ery node were thus available to the GSi
rMAC
classes
for channel management. The gateway establishes
WMN paths (GSi
WMN
objects) to each MAP, for
sending flows of UDP packets (servicing end users),
2
Using the OPNET Modeler simulator
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
117
of average size 1500 bytes, and constant rate 12 Mbps
for 802.11a interfaces and 11 Mbps for 802.11b.
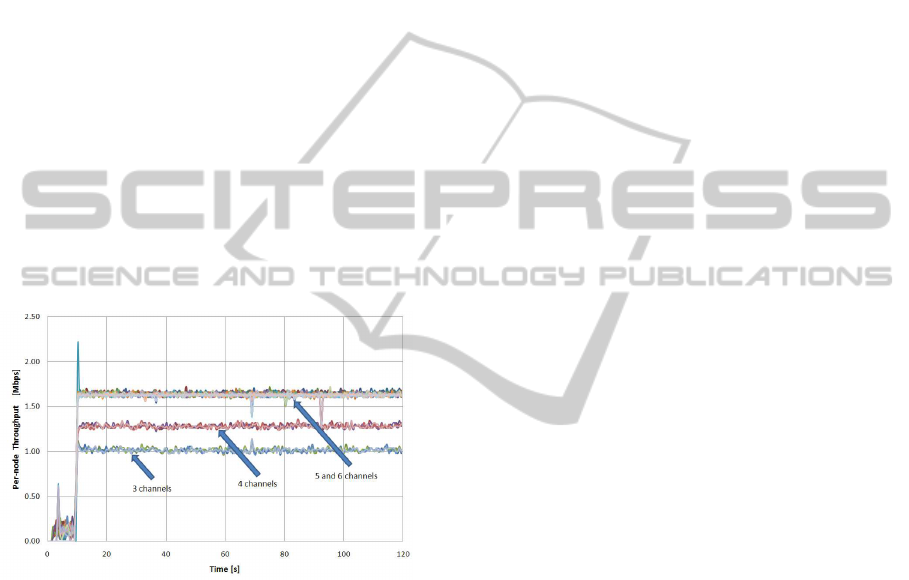
In the proposed channel assignment strategy, by
changing the GSiattribute (in the GSi
rMAC
objects) for
the number of available channels for mesh forward-
ing, from 3 to 6, improves the observed quality of the
service at the GSi
WMN
service objects. This is shown
in Figure 6 for the per-node throughput, where going
from from 3 to 5 channels, results in an increase from
1 Mbps to 1.6 Mbps. Using more than 5 channels does
not increase further the performance of the network,
because of the upper limit of the channel capacity at
the gateway.
The maximum theoretical throughput at the gate-
way node, with its two radios operating at 12 Mbps,
and considering an overhead of 15% introduced by
the MAC and PHY layers, is 20,4 Mbps. The use of
5 channels in the simulation, serves 12 multiplexed
flows of 1.6 Mbps, totaling an effective throughput
of 19,2 Mbps. This means that 96% of the theoret-
ical capacity of the WMN is exploited eliminating
almost completely channel interference problems on
the wireless medium of such a multi-hop network.
Figure 6: Per-node throughput, for increasing number of
channels.
These results, of course do not suggest that virtu-
alisation and dynamic channel management is only
possible through the Generic Service framework.
Nevertheless, they demonstrate how easy it becomes
to introduce or remove dynamic functionality without
substantial re-engineering effort for adapting the in-
terfaces, in a non-disruptive way.
5 RELATED WORK
A large number of efforts have appeared in the lit-
erature that aim to address the lack of dynamicity in
the Internet architecture. Many of them provide solu-
tions at the mechanism level within the current archi-
tecture, and several focus on interfacing and extensi-
bility within or across certain layers (e.g. cross-layer
design literature and active networking). Few other
have proposed alternative architectures and commu-
nication paradigms as a solution. As a general com-
ment our main difference to those approaches is that
we do not advocate a new Internet architecture, or the
modification of specific interfaces in order to enable
dynamicity for one mechanism or another. Rather,
we take a more distanced approach proposing an (ad-
ditional or alternative) interface for service mecha-
nisms, which is generic everywhere. It will inevitably
lead engineers to re-consider the way new services are
designed and implemented, but does not necessitate
the re-engineering of existing mechanisms.
In the role-based architecture (Braden et al.,
2002), the authors consider a component-basedmodel
founded on service roles as an alternative to the cur-
rent layer model. Although an important step is be-
ing made towards more modular, flexible and exten-
sible model, the authors do not go as far as proposing
the adoption of object orientation. A step towards the
opposite direction is taken in the NIPCA architecture
(Day, 2007), whereby a process-based modelling of
network communication is advocated, leading also to
a recursive or unified interface across different lev-
els of abstraction, however such a flat procedural-
programming style API is not less static than sockets
(Stevens et al., 2003).
In i3 (Stoica et al., 2004), the authors adopt in-
direction as a fundamental construct for on-demand
inter-stitching of network services, by means of a
publish-subscribe interface. Similarly to the i3 model
the earlier work in Plutarch (Crowcroft et al., 2003)
also promotes indirection and additionally locali-
sation of service functionality in policy domains,
whereby global inter-network services can be estab-
lished across service contexts. Both, propose inter-
faces that can be useful as an alternative to the Com-
partment interface we consider in this paper, for re-
questing and associating the end user to cloud ser-
vices (as GSi objects). The power of indirection has
been also exploited, more intuitively programmati-
cally, in the network pointers model (Tschudin and
Gold, 2002), and has been adopted in the ANA archi-
tecture (Bouabene et al., 2010). Although, this inter-
face is not object oriented and neither as expressive as
GSi, the network pointers model achieves functional
polymorphism and dynamic service composition at a
very low level.
Another aspect of object orientation, namely ab-
stract services and recursion of protocol functional-
ity is being architecturally explored in the Recursive
Network Architecture (Touch et al., 2006), whereby
layer functionality is organised and developed in pro-
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
118

tocol containers. This work goes beyond the interfac-
ing level to enforce a certain engineering practice in
order to be adopted.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have proposed the adoption of object orientation
in the design of a new generic interface (model) for
network services, alternative to sockets and all pro-
prietary solutions above the application level. Our ap-
proach builds on the generalisation of a network ser-
vice captured in a simple construct and a set of primi-
tives that promote extensibility and support (at the in-
terface level) dynamic federation/composition of ser-
vices; for creating higher order services and virtual
resources. We presented the most important aspects
of the Generic Service model and exemplified its use.
In the end we carried out an engineering exercise for
the design of a service cloud that provides wireless
multi-hop paths as services, which comprise of inter-
layer resources and rely on distributed resource man-
agement and cross-layer information exchange; ap-
proaching in this way as close as possible the cloud
reality.
Our aim in follow-up work is to experiment more
extensively with the Generic Service interface model
and declarative formalisation, in different cloud ser-
vice contexts, so as to improve its expressibility and
establish its plasticity.
REFERENCES
Akyildiz, I. and Wang, X. (2008). Cross-layer design in
wireless mesh networks. Vehicular Technology, IEEE
Transactions on, 57(2):1061 –1076.
Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A. D., Katz,
R. H., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D. A.,
Rabkin, A., Stoica, I., and Zaharia, M. (2009). Above
the clouds: A berkeley view of cloud computing.
Technical Report UCB/EECS-2009-28, EECS De-
partment, University of California, Berkeley.
Bouabene, B., Jelger, C., Tschudin, C., Schmid, S., Keller,
A., and May, M. (2010). The autonomic network ar-
chitecture (ana). IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in
Communications, 28(1):4–14.
Braden, R., Faber, T., and Handley, M. (2002). From proto-
col stack to protocol heap - role-based architecture. In
1st ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks.
Calvert, K., Griffioen, J., and Poutievski, L. (2007). Sepa-
rating routing and forwarding: A clean-slate network
layer design. In Broadnets 2007 Conference.
Chiang, M., Low, S., Calderbank, A., and Doyle, J. (2007).
Layering as optimization decomposition: A mathe-
matical theory of network architectures. Proceedings
of the IEEE, 95(1):255 –312.
Cobbs, A. (2011). All About NetGraph. accessed 30 Jan
2011: http://people.freebsd.org/ julian/netgraph.html.
Crowcroft, J., Hand, S., Mortier, R., and Roscoe, T. (2003).
A warfield, plutarch: an argument for network plural-
ism. Computer Communication Review, 33(4).
Day, J. (2007). Patterns in Network Architecture: A Return
to Fundamentals. Prentice Hall.
Ferreira, L., De Amorim, M., Iannone, L., Berlemann, L.,
and Correia, L. (2010). Opportunistic management
of spontaneous and heterogeneous wireless mesh net-
works [accepted from open call]. Wireless Communi-
cations, IEEE, 17(2):41–46.
Hamzeh, K., Pall, G., Verthein, W., Taarud, J., Little, W.,
and G., Z. (1999). Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
(PPTP). IETF RFC 2637.
Howell, A. Mobile radio interface Layer 3 specification;
Core network protocols; General Packet Radio Ser-
vice (GPRS), technical specification 24.008 edition.
IEEESTD.265774 (2005). Approved Draft IEEE Stan-
dard for Local and metropolitan area networks Cor-
rigendum to IEEE Standard for Local and Metropoli-
tan Area Networks-Part 16: Air Interface for Fixed
Broadband Wireless Access Systems (Incorporated
into IEEE Std 802.16e-2005 and IEEE Std 802.16-
2004/Cor 1-2005 E).
IEEESTD.5307322 (2009). IEEE Standard for Informa-
tion technology–Telecommunications and information
exchange between systems–Local and metropolitan
area networks–Specific requirements Part 11: Wire-
less LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical
Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 5: Enhance-
ments for Higher Throughput.
Joel, Amos E., J. (1993). Asynchronous Transfer Mode, ieee
press edition.
LTE-SAE (2008). UTRA-UTRAN Long Term Evolution
(LTE) and 3GPP System Architecture Evolution.
Paul, S., Jain, R., and Pan, J. (2008). A vision of the next
generation internet: A policy oriented view. In British
Computer Society conference on Visions of Computer
Science.
Randriamasy, S. (2009). Mechanisms for Generic Paths,
deliverable d-5.2 edition. 4WARD project, European
Commission FP7 ICT-2007.1.1 programme.
Sifalakis, M., Louca, A., Bouabene, G., Fry, M., Mauthe,
A., and Hutchison, D. (2011). Functional composition
in future networks. Computer Networks, 55(4):987–
998.
Stevens, W. R., Fenner, B., and Rudoff, A. M. (2003). UNIX
Network Programming Volume 1, Third Edition: The
Sockets Networking API. Addison Wesley, 3rd edition.
Stoica, I., Adkins, D., Zhuang, S., Shenker, S., and Surana,
S. (2004). Internet indirection infrastructure. In
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (TON).
Touch, J., Wang, Y., and Pingali, V. (2006). Recursive
network architecture. Technical Report ISI-TR-2006-
626, ISI.
Tschudin, C. and Gold, R. (2002). Network pointers. In 1st
ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks.
A GENERIC SERVICE INTERFACE FOR CLOUD NETWORKS
119
