
METERING THE CLOUD PROVIDERS
Fahad Abdel Kader
Technical University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany
Keywords: Cloud metering, Cloud computing, Verification of cloud bill, Architecture of cloud meter, Functioning of
automated metering, Metering algorithm.
Abstract: Cloud computing has recently emerged as a modified computing platform, which offers a variety of services
for different level of users. At the moment, such services are offered at very low prices, but as the concept
of cloud computing will find more adopters, a real market will emerge. At that point in time it will be
critical for the customers to verify the bills that they receive from their cloud provider. Therefore, there is a
need to not only verify the correctness of the bill but also that the whole process should be real time and
automated. An automated cloud metering solution is presented in this paper. The idea is to design a meter
which monitors the respective activities as defined in the terms of SLA and generates a bill accordingly.
This generated bill will then be automatically compared with the cloud provider’s bill for any errors. This
position paper describes the architectural design of the cloud meter and functioning of the automated meter,
and then concludes with the information about the future work.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional grids and data centers have recently
evolved into cloud computing with an economical
pricing model, based on the utilization of resources.
With the introduction of friendly user interface,
cloud computing allows the users to deploy their
application on a highly scalable, available and fault
tolerant platform, hosted by the cloud providers
(Cloud Providers, 2010). Cloud computing major
reason of success is the economic model associated
with it, i.e. “Pay as You Go (
Cloud economic model,
2010)”. The users are only billed for the amount of
the service used, rather than paying for the whole
package. An SLA is an electronically (sometimes
paper based) signed agreement between the user and
the cloud provider for the service the user is
interested in and thus billing is done accordingly
(EC2, 2011) (Azure, 2011). But there is no method
till writing of this paper, which allows the user to
independently verify the bill being sent by cloud
provider for services usage.
Metering is a widely applied concept for
measuring the volume used of any utility. Meters are
being constantly used in our daily life such as
electric, water and gas meters. These utility meters
not only help to measure the usage of utility but also
helps the consumer to have the confidence that the
amount he has been billed is correct. It is a human
nature that when money involves in any sort of
activity, the trust line becomes thin. He wants to
make sure that he is not being cheated or fooled.
The development of the Internet has bridged the
path to the new information era and with the advent
of cloud computing, we are now moving one step
forward towards making computing as a utility.
Cloud computing offers different services (Lizhe,
Gregor, et.al., 2008) to users, among which some of
the famous ones are: Infrastructure as a Service
(IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as
a Service (SaaS). These services are offered at very
attractive prices and allow the organizations/users to
reduce their cost on purchasing computing hardware,
software and then later maintaining them. The cloud
computing also leverages the users from worrying
about investing in the up-gradation of their systems
at some regular time intervals.
To enjoy any of the service offered by the cloud
provider, the customer formally e-signs the contract
defined in terms of the SLAs with the service
provider. The SLA basically specifies contractual
commitments of the provider on which services will
be offered to the customer. The committed quality
level of a service is specified in a set of Service
Level Objectives (SLOs) in the form of service
metrics, threshold values, and tolerances
(Telemanagement Forum, 2011). Billing by the
525
Abdel Kader F..
METERING THE CLOUD PROVIDERS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003449605250528
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2011), pages 525-528
ISBN: 978-989-8425-52-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
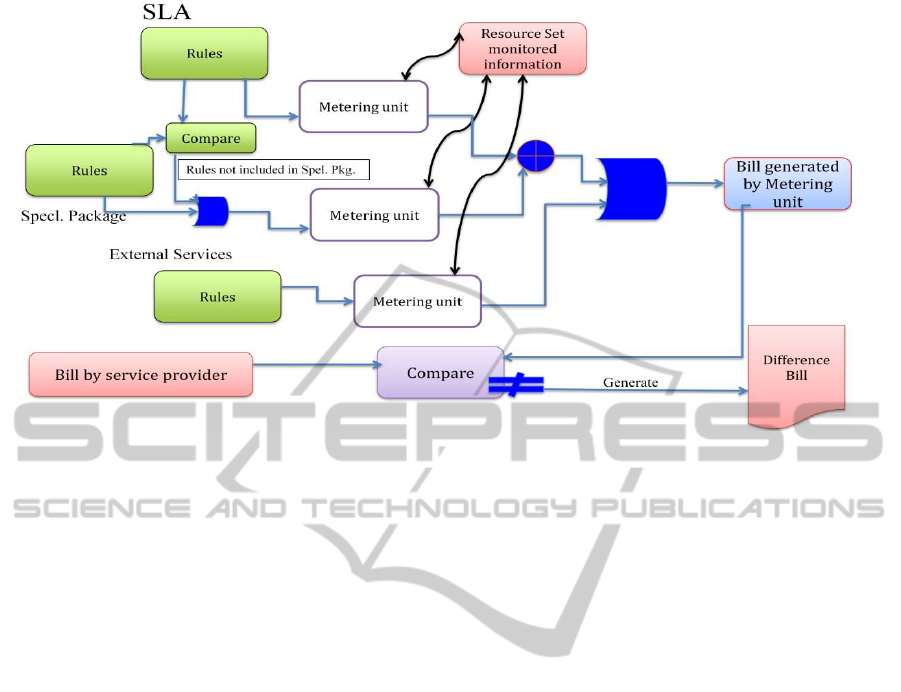
Figure 1: Cloud Meter Architecture.
cloud providers for the usage of services are done on
the terms finalized in the SLA.
This paper talks about the design of a cloud
meter that can be used by the user to independently
and automatically very the bill being sent by the
provider. By using this cloud meter the user will
then have the confidence that they are being billed
only for the resources they have used. In case the
cloud provider fails to meet any terms mentioned in
the contract, the penalties could also be identified
and then verified automatically.
2 RELATED WORK
Industry as well as academia have done research or
developed some products for monitoring SLA
compliance. However, most of these approaches are
narrowed to some specific services, e.g., web
services, or a certain set of SLA parameters, e.g.,
availability, round-trip time, and response time
(Daidalos, 2004), (Hasan, Stiller, B., 2007), (Keller,
A., Ludwig, H., 2003) (SSSC). The IBM’s Web
Service Level Agreement (WSLA) Framework gives
a general concept for the SLA management and
mainly focuses on web services (Keller, A., Ludwig,
H., 2003). The SLA management lifecycle by IBM
comprises of five stages: negotiation and
establishment, deployment, measurement and
monitoring, corrective management action, and
termination (Keller, A., Ludwig, H., 2003). The
functionality needed for these various stages is
implemented as WSLA services, which interact
across different domains.
However, these monitoring approaches and tools
cannot be applied to the cloud computing because
cloud computing doesn’t give access to underlying
hardware. Only a virtual OS is the interface, which
is hosted on a hypervisor. And thus this
virtualization layer hides all underlying information
of the hardware from the interacting user. Although
some companies (Monitoring), have launched
commercial monitoring service for cloud computing
but these monitoring software are mostly restricted
to monitor certain features of cloud providers.
However need of a general 3rd party automated
metering tool to monitor cloud providers in an
independent manner are still missing.
3 ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN OF
CLOUD METER
Fig.1 depicts the cloud metering architecture having
the Metering Unit as a major component, which
consists of sets of automated meters. The automated
meters may or may not interact with each other for
conducting a particular metering. The Metering Unit
implements the Meter Algorithm for a particular
metering application. A meter algorithm is a
technical description of rules signed in the SLA.
A metering process requires at least two types of
input: SLAs (the regular SLA signed at the
beginning of a contract. Additionally if some special
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
526
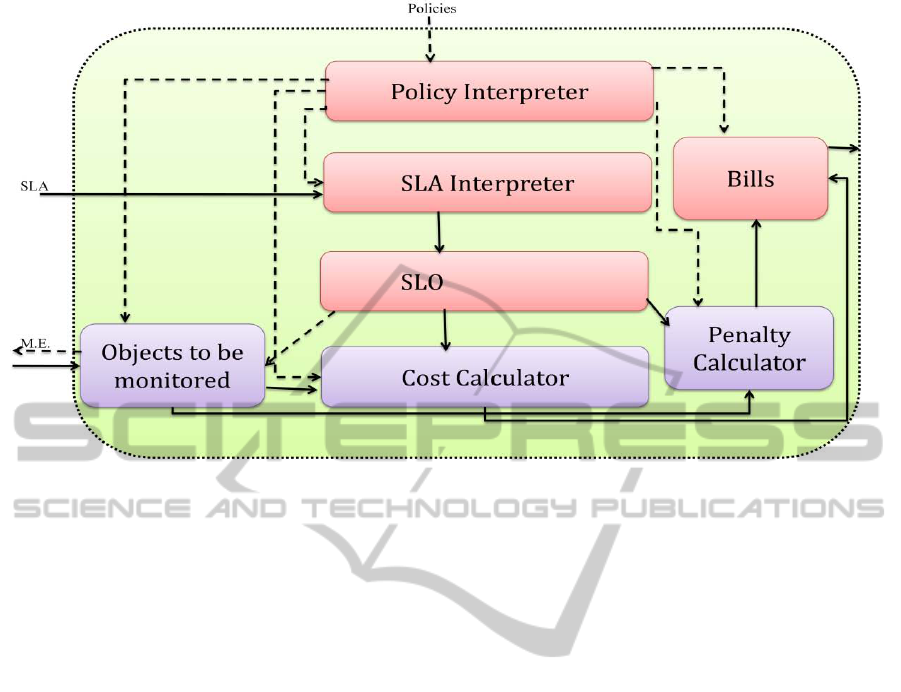
Figure 2: Automated Meter’s Internal Architecture.
package is offered by the provider during the age of
contract for some special service then this SLA also
becomes the part of an input. It is not necessary that
this special package covers all the areas of the
signed regular SLA, therefore this is considered as
an additional input only at the time it is offered.
Beside the above two mentioned SLAs, if some
other external service(s) being used then it’s SLA is
also considered as an input for the metering unit)
and secondly the monitored information (provided
by the Resource Set monitored information).
Monitored information describes what actually
happens, whereas SLA describes expected
situations. The metering unit then evaluates these
data using the automated meters.
The result of this metering process is the bill
generated by combing all the metering units. This
generated bill is then automatically compared with
the cloud provider’s bill and is checked for any
difference in the two bills. In case of any difference,
a bill containing the areas of differences is
generated. For transparent metering of the cloud
providers, none of the components has to be
installed on the cloud provider’s servers. But for
different service layers of cloud computing, the
cloud meter component placements and monitoring
methods vary. But these placement techniques and
monitoring methods are not discussed in this paper.
4 INTERNAL ARCHITECTURE
OF AN AUTOMATED METER
As described, a metering unit contains a set of
automated meters and it implements the meter
algorithm for a particular application. This means
that automated meters have the task to execute the
metering algorithm. In order to reduce
implementation complexity and to achieve
modularity, the following assumptions are made in
designing the architecture of an automated meter:
• A metering Unit deals with a set of SLAs.
Without the loss of generality each automated meter
is assumed to be responsible for a particular SLA.
• Each SLA contains a set of conditions linked by
a logical expression. Hence, the result of the
evaluation of each condition as well as the
evaluation of the logical expression linking all the
conditions determine the compliance of relevant
monitored data with a SLA.
The approach developed here proposes the following
common metering algorithm:
1. Interpret and apply valid monitoring policies
during the metering.
2. Interpret the assigned SLA Specification, for
which the automated meter is responsible.
3. Retrieve relevant monitored resource usage data.
4. Evaluate monitored data whether they meet SLA
conditions. Evaluate the logical expression linking
METERING THE CLOUD PROVIDERS
527

all SLA conditions and accordingly calculate the
cost.
5. Generate a bill as a result of the evaluation.
Fig.2 shows the architecture of the automated meter
to execute the proposed meter algorithm. The
Policies Interpreter (PI) takes policy decisions and
configures other components based on metering
policies. The SLA Interpreter retrieves the SLA
assigned to the meter based on the configuration
information from PI. The SLA interpreter; then
generates the SLOs and cost calculator. Cost
calculator takes the relevant monitored resource
usage data and then generates the relevant usage bill
from it. The SLO determines whether there is a
violation of the SLA based on the result of
monitored data. In case of any violation, the
respective penalty cost is calculated by the penalty
cost calculator and the cost is then added to the bill.
The final bill is then sent to the bill generator.
5 CONCLUSIONS
An architectural design step for metering the service
usage on cloud providers has been completed. Since
different layers of services offered by cloud
computing have different user interfaces, therefore
different monitoring techniques are being currently
studied and are in final stages of designing the
monitoring block. Implementation of the metering
unit will then be started immediately and as a first
step the SLA interpreter will be made. The ultimate
goal is to have a framework for automated metering
of different service layers offered by cloud
computing giving users the confidence that they are
not being overbilled.
REFERENCES
Cloud Providers, 2010. https://groups.google.com/
group/cloud-computing/web/list-of-cloud-platforms-
providers-and-enablers?hl=en&pli=1
Cloud economic model, 2010. http://technology.inc.
com/hardware/articles/200805/cloud.html
Telemanagement Forum, 2011. SLA Management
Handbook, Release 3. GB917
Daidalos, 2004. A4C Framework Design Specification.
Deliverable D341
Hasan, Stiller, B., 2007. Auditing Architecture for SLA
Violation Detection in QoS-Supporting Mobile
Internet. IST Mobile and Wireless Comm. Summit,
Vol. 1. Aveiro, Portugal
Keller, A., Ludwig, H., 2003. The WSLA Framework:
Specifying and Monitoring Service Level Agreements
for Web Services. Journal of Network and Systems
Management, Vol. 11, Issue 1
Monitoring, http://www.monitortools.com/cloud/
SSSC (Softek Storage Solutions Corporation). SOFTEK
EnView: Datasheet.
EC2, 2011. http://aws.amazon.com/ec2/#pricing
Azure, 2011. http://www.microsoft.com/windowsazure/
pricing/default.aspx
Lizhe, Gregor et al., 2008. Cloud Computing: a
Perspective Study. Proceedings of the Grid Computing
Environments (GCE) workshop. Held at the Austin
Civic Center: Austin, Texas.
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
528
