
TEMPORAL META-DATA MANAGEMENT FOR MODEL
DRIVEN APPLICATIONS
Provides Full Temporal Execution Capabilities throughout the Meta-data EIS
Application Lifecycle
Jon Davis and Elizabeth Chang
Curtin University of Technology, Curtin Business School, Bentley, 6102, Australia
Keywords: Meta-data, Meta-model, Temporal execution, EIS, Lifecycle, Version control, Version management.
Abstract: In this paper we discuss how the application of temporal data management techniques to the atomic
elements of a meta-data application model can provide for a complete temporal execution capability for
meta-data Enterprise Information Systems (EIS) applications by maintaining a perfect synchronisation of
historical data and historical application states. Temporal data management is a well understood field as it
applies to the common database and its application to the meta-data EIS application lifecycle in such a
solution would minimise the reduction of historical information accessibility currently experienced in most
applications as the logical application functionality and data formats are regularly changed due to often
irreversible version upgrades.
1 INTRODUCTION
Software applications are released by developers as
discrete versions, which often create platform or
data structure incompatibilities with previous
versions. Data structure incompatibilities are
typically resolved via the developer’s specific
upgrade process however there can be instances
where the update results in issues such as reduced
data granularity or access, especially for historical
data, or where some previous desired functionality is
lost and replaced with different functions.
Throughout the application’s lifecycle there will
be great variance in functionality and data access
that can usually only be accessed as a functional
snapshot at any instance.
As a result of ongoing research into the
modelling of meta-data Enterprise Information
Systems (EIS) applications, we have merged
temporal data management techniques with the
atomic modelling level of the meta-data EIS models
to form our temporal meta-model framework for EIS
applications.
This merging of techniques can be supported by
a single runtime execution engine for the modelled
meta-data EIS applications that provides full
temporal independence for the application and data.
As the executed application is based on the meta-
data definition for a designated time, and the data is
similarly and simultaneously managed temporally,
then the true state of an application in terms of its
version, functionality and data is immediately
accessible, at any required historical time, regardless
of the patch or update history and its effects.
This paper reviews related works, including
temporal data management, examines the
application to a meta-data based application model,
and provides examples where the hybrid application
can be used effectively in real enterprises.
2 RELATED WORKS
The following related issues have guided this
research.
2.1 Temporal Data Management
Temporal data management techniques have long
been a well developed and understood field
(Gregersen, 1999). With varying levels of
complexity solutions available they tend to adhere to
the same basic rules.
376
Davis J. and Chang E..
TEMPORAL META-DATA MANAGEMENT FOR MODEL DRIVEN APPLICATIONS - Provides Full Temporal Execution Capabilities throughout the
Meta-data EIS Application Lifecycle.
DOI: 10.5220/0003467203760379
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 376-379
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(Wrembel, 2007) describe their multiversion data
warehouse which internally manages discrete sets of
each schema version (the data structure) and the
instance version (the actual data).
When temporal data management is applied to
application logic it is analogous to dynamic source
code version management.
2.2 Source Code Version Control
The management of source code has followed
software development trends through multiple
programs and variants (De Alwis, 2009), across
multiple and distributed teams tracking the
development of the components and managing the
baseline of software developments (Ren, 2010)
throughout the multiple phases of projects (Kaur,
2009).
To support a temporal execution environment
requires a level of control over the atomic meta-data
definitions within the meta-data EIS application
model and is also fundamentally tied to direct
dynamic execution.
2.3 Model Driven Engineering
Model Driven Engineering (MDE) is a generic term
for software development that involves the creation
of an abstract model and how it is transformed to a
working implementation (Schmidt, 2006).
With potentially frequent and rapid changes to
the application’s meta-data model definition, by
users, a more dynamic versioning capability as
provided by applying temporal data management to
the meta-data is a complementary solution.
2.4 Dynamic Meta-data Model
Framework for EIS Applications
Our ongoing research project is based on our
assertion that performance of the analysis and
efficient collection of this information can also
perform the bulk of the design phase for an EIS
application, largely as a simultaneous activity. With
the collective design requirements stored and
available in a meta-model structure, EIS applications
can be executed automatically from the model with
the availability of the runtime components (Davis,
2004).
It is the application of temporal data
management to this meta-model structure that can
extend the temporal scope of the application logic to
any historical state, regardless of any subsequent
levels of fixes, patches or upgrades performed to the
underlying meta-model of the modelled application.
3 TEMPORAL META-DATA
MANAGEMENT
The benefits of a solution providing temporal
application logic include:
• Historical execution of applications regardless
of the deployment history of application fixes,
patches or upgrades that may have:
o Altered the underlying data including
deleting or transforming existing data,
o Removed or modified logical
application functionality.
• Access to historic or previous business rules,
• Access to the exact state of historical data, prior
to any subsequent rollup or additional
processing.
3.1 Definitions
We provide the following definitions:
• Temporal Data Window: is the period of time
over which the application data in the database
is guaranteed to be known and available for any
point of time within that period.
• Temporal Application Window: is the period
of time for which the current application version
maintains full compatibility with the data
schema and provides full application
functionality over the complete database.
• Temporal Application Effectiveness: is the
multiplication of the Temporal Data Window
and Temporal Application Window to provide
an indication of the maximum temporal
accessibility of the system architecture as a
whole.
3.2 Measuring Temporal Application
Effectiveness
We review the practical Temporal Application
Effectiveness of various application and database
architectures using these criteria as follows:
3.2.1 Common Application
A Common Application is defined as any
application executed from a static non-temporally
varying codebase, and accessing a database schema
TEMPORAL META-DATA MANAGEMENT FOR MODEL DRIVEN APPLICATIONS - Provides Full Temporal
Execution Capabilities throughout the Meta-data EIS Application Lifecycle
377
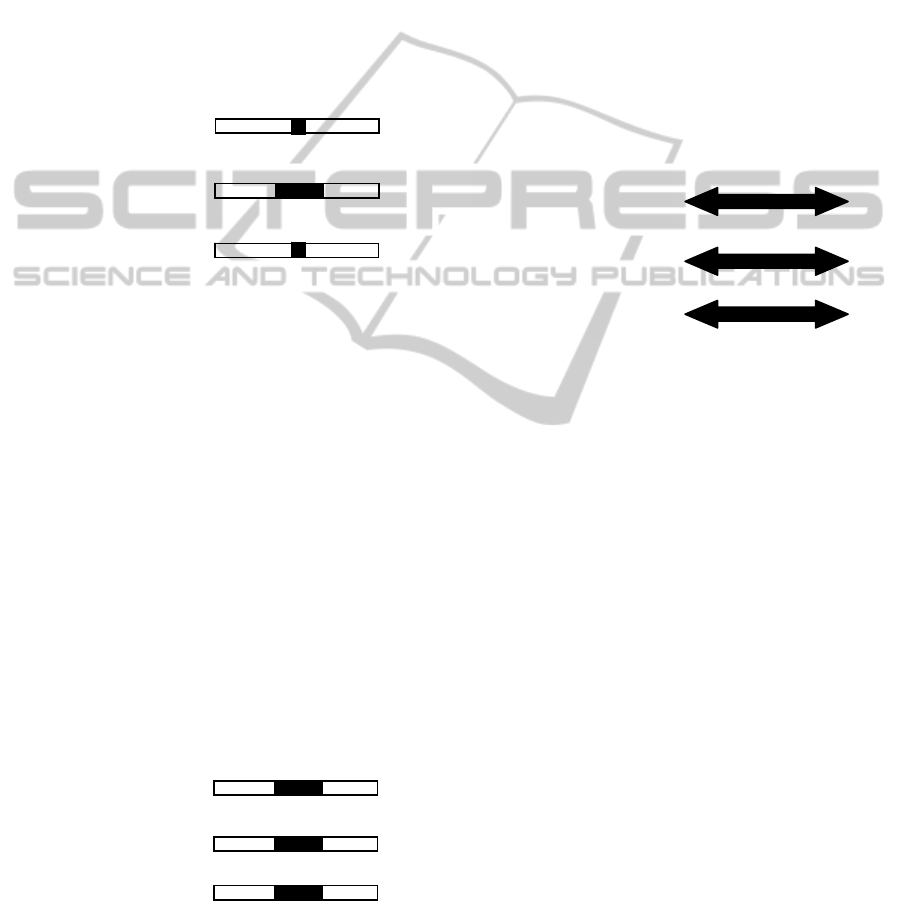
without temporal data management features - the
most common style of applications.
As data is not temporally managed, data is only
current and representative as of the current moment
in time, hence the Temporal Data Window of this
system can only ever be equal to the period since the
most recent data transaction.
The Temporal Application Window of the
system is the absolute period of the current version
of the application.
The Temporal Application Effectiveness (see
Figure 1) is thus at a minimum due to the low
Temporal Data Window, where only the current data
state can ever be known with certainty.
Figure 1: Temporal analysis of the Common Application.
3.2.2 Temporal Data Application
A Temporal Data Application is an application
which is similar to the Common Application but
accesses a database schema which provides effective
temporal data management features.
The Temporal Application Window of the
system is identical to that of the Common
Application.
The Temporal Data Window of this system could
become continuous but as the application is changed
then it is limited to only increase to match the time
period of the Temporal Application Window for the
Common Application.
The Temporal Application Effectiveness
achieved is now much higher than the Common
Application, as all historical data states within a
static application version are available.
Figure 2: Temporal analysis of the Temporal Data
Application.
3.2.3 Full Temporal Meta-Data Application
A Full Temporal Meta-Data Application is defined
as an application executed from a dynamic and
temporally varying codebase, and accessing a
database schema which also provides effective
temporal data management features.
The Temporal Data Window of this system is
continuous.
The Temporal Application Window of the
system is now increased to include the full periods
of all various or discrete system lifecycles or
generations.
The Temporal Application Effectiveness
achieved is also at a maximum, as the true data state
can be obtained at any time and with full application
functionality support.
Figure 3: Temporal analysis of the Full Temporal Meta-
Data Application.
3.3 Practical Examples of Using Full
Temporal Meta-Data Applications
To illustrate some of the operational benefits that
Full Temporal Meta-Data Applications (FTMDA)
can bring, the following example scenarios are
provided:
• Data Rollover: Financial systems in particular
aim to concentrate on the current financial year
encouraging closing off and rolling over from
the previous year The FTMDA can remove the
need for any unnecessary archival or pruning of
the data by allowing users to access full
historical data on demand, and more
importantly, accessing the historical data using
the previously current business rules rather than
any since updated or revised business rules.
• Reporting: The re-production of statistical or
analytical reports can also be difficult as source
data or reporting and processing formats are
changed. The FTMDA allows a rollback to
access both the historical data and the original
reporting and analysis tools (themselves also
instances of potentially changed meta-data
logic).
TemporalApplication
Effectiveness
Temporal
ApplicationWindow
TemporalData
Window
TemporalApplication
Effectiveness
Temporal
ApplicationWindow
TemporalData
Window
TemporalApplication
Effectiveness
TemporalApplication
Window
TemporalData
Window
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
378

• Auditing: Audit records are not always
maintained throughout the lifecycle of a system.
However, it is inherent in the FTMDA that a
complete audit history of the data is maintained
in order to facilitate the temporal data
management aspects.
• Aged Data: an alternative to data rollover is
other selective data pruning based on aspects
such as the age of data or in terms of its
relevancy based on how often it is accessed.
The FTMDA can rollback to access the full and
complete availability of data.
• Upgrade Reversion: not all aspects of
application fixes, patches or upgrades are
desirable in terms of features or even
application stability. A temporary session
rollback to when the desired functionality was
available can be provided by the FTMDA for
that user.
4 CONCLUSIONS
With the higher Temporal Application Effectiveness
of the Full Temporal Meta-Data Application, there is
a greater ongoing continuity of system access and
usage, and thus a greater potential for minimising
the cost of maintaining that application due to the
greater operational stability and seemingly static
nature of an operating application within that period.
The ready availability of historical data and
access, reduces information turnaround times, and
minimises maintenance costs of separate historical
environments. High costs that are typically incurred
due to major (and even some minor) upgrades or
generational changes, both in real financial terms as
well as potential accessibility disruption until the
revision system has been bedded down and is
operating effectively, can be greatly reduced due to
the automated update capability of the meta-data EIS
application as well as the full temporal rollback
capability for data and application logic, if required.
The very nature of the meta-data EIS application
further acts to greatly reduce these upgrade costs as
the update of meta-data and any upgrade of the
runtime engine is relatively seamless and incur only
minor migration downtimes (if any).
Adding the temporal meta-data management to
temporal data management provides a key benefit to
the implementation of meta-data EIS applications
over traditional code based EIS applications.
Combined with the additional benefits of meta-data
EIS applications they provide a significant
opportunity for lifecycle savings as well as
previously unexperienced end user flexibility and
interaction that cannot otherwise be readily
provided.
REFERENCES
Gregersen, H., Jensen, C., 1999. Temporal Entity-
Relationship Models – A Survey. In IEEE
Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.
May/June 1999, Vol 11, No.3.
Wrembel, R., Bartosz, B., 2007. Metadata Management in
a Multiversion Data Warehouse. In Journal on Data
Semantics VIII, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
De Alwis, B., Sillito, J., 2009. Why are software projects
moving from centralized to decentralized version
control systems ? In CHASE ’09 Proceedings of the
2009 ICSE Workshop on Cooperative and Human
Aspects on Software Engineering. 2009.
Ren, Y., Xing, T., Quan, Q., Zhao, Y., 2010. Software
Configuration Management of Version Control Study
Based on Baseline. In Proceedings of 3
rd
International
Conference on Information Management, Innovation
Management and Industrial Engineering. Nov 2010.
Vol 4. Pp118-.
Kaur, P., Singh, H., 2009. Version Management and
Composition of Software Components in Different
Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle. In
ACM Sigsoft Software Engineering Notes, Jul 2009.
Vol 34. Iss 4. Pp493-.
Schmidt, D., 2006. Introduction Model-Driven
Engineering. In IEEE Computer Science, Feb 2006,
Vol 39, No.2, pp25-31.
Davis, J., Tierney, A., Chang, E., 2004. Meta-data
framework for EIS specification, In 6th International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, Porto,
Portugal, April 2004.
Chang, E., Davis, J., Chalup, S., 2003. A new look at EIS
life cycle – introducing the concept of generational
change. In Proceedings of the 5th International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems,
France, May 2003.
Zarras, A., 2008. Applying Model-Driven Architecture to
Achieve Distribution Transparencies. In Information
and Software Technology, July 2006, Vol 48, Issue 7,
pp498-516.
Davis, J., Tierney, A., Chang, E., 2005. A User Adaptable
User Interface Model to Support Ubiquitous User
Access to EIS Style Applications. In Proceedings of
the 28th International Conference on Computer
Software and Applications, Edinburgh, Scotland, July
2005.
Davis, J., Tierney, A., Chang, E., 2005. Merging
Application Models in a MDA Based Runtime
Environment for Enterprise Information Systems. In
Proceedings of the 3rd International IEEE Conference
on Industrial Infomatics, Perth, Australia, August
2005.
TEMPORAL META-DATA MANAGEMENT FOR MODEL DRIVEN APPLICATIONS - Provides Full Temporal
Execution Capabilities throughout the Meta-data EIS Application Lifecycle
379
