
PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY
OF LEARNING OBJECTS IN COLLABORATIVE
E-LEARNING SYSTEMS
Ali Alharbi, Frans Henskens and Michael Hannaford
School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, The University of Newcastle, Newcastle, Australia
Keywords:
Collaborative e-learning systems, Learning objects, Self-regulated learning, Learning style.
Abstract:
Learning objects are the building blocks of the learning resources in any e-learning system. In collaborative
e-learning systems, the learning objects are produced and consumed by different learners. Finding high-
quality learning objects that are related to a learner’s profile is one of the major problems that may cause
e-learning systems to fail. This is especially true as the number of learning objects in the learning environment
increases. This paper presents a pedagogical framework to improve learners’ interactions with learning objects
in collaborative e-learning systems. The proposed framework is based on the theory of learning styles and the
cyclical model of self-regulated learning. By incorporating the experiences and contributions of different
learners with the available learning objects, the quality of the learning objects in the system can be increased.
Learners’ awareness of their preferred learning style can help them to find appropriate learning objects. This
can be achieved by the help of the e-learning system that can generate a recommendation list of appropriate
learning objects based on the learner’s learning style.
1 INTRODUCTION
A collaborative e-learning system provides an envi-
ronment where people who share common interests
collaborate together by creating and sharing knowl-
edge to provide the opportunities for everybody to
learn (Wang et al., 2005).
The dominant education paradigm has shifted
from the traditional teacher-centred to one where the
student plays a more central role. This approach
is based on the constructivism theory of education
where the emphasis is placed on the learner to dis-
cover and construct knowledge through active par-
ticipation (Glasersfeld, 2009). Social Constructivism
(Pritchard and Woollard, 2010) is an extension of con-
structivism theory where the focus is placed on the
role the environment plays in helping the learner con-
struct knowledge. According to this theory, learn-
ing is a social process and, rather than only being
passively received or constructed by each individual
learner, knowledge is also the result of engaging in so-
cial activities. This view of learning is also related to
some contemporary theories of education such as So-
cial Cognitive Theory (SCT) (Bandura, 2001). SCT
views human behaviour as being influenced continu-
ously by the social and physical environment.
Learner-centred education paradigm places more
responsibilities on learners to control and regulate
their personal learning process in a collaborative so-
cial environment. In this new education paradigm, our
vision of the learning resources should be changed,
so that more emphasis is placed on learner-generated
resources, and in this case the learner is no longer a
passive consumer of knowledge but active as a con-
sumer and producer of knowledge and learning re-
sources (McLoughlin and Lee, 2010).
In e-learning systems, the building blocks of
learning resources are referred to as learning objects.
A learning object can be defined as any digital re-
source that has a pedagogical objective and is in-
tended to be used and reused in different learning con-
texts (Sosteric and Hesemeier, 2002). Images, anima-
tions and simulations are all examples of learning ob-
jects. However, a learning object can also be an entire
web page that combines text, images, and other re-
sources to deliver a complete unit of learning.
In collaborative e-learning systems, learning ob-
jects are created to be shared and reused in different
contexts (Koohang, 2004). Having low-quality learn-
ing objects is one of the major problems that cause
353
Alharbi A., Henskens F. and Hannaford M..
PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LEARNING OBJECTS IN COLLABORATIVE E-LEARNING SYSTEMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003475803530358
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CeLS-2011), pages 353-358
ISBN: 978-989-8425-50-8
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

e-learning systems to fail (Han et al., 2003). Another
problem is that it can be difficult to find learning ob-
jects related to a learner’s profile (Shishehchi et al.,
2010). This is especially true as the number of learn-
ing objects in the learning environment increases.
This paper presents a pedagogical framework to
improve learners’ interactions with learning objects
in collaborative e-learning systems. The proposed
framework is based on the theory of learning styles
and the cyclical model of self-regulated learning. By
incorporating the experiences and contributions of
different learners with the available learning objects,
the quality of the learning objects in the system can
be increased. Learners’ awareness of their preferred
learning style can help them to find appropriate learn-
ing objects. This can be achieved by the help of the
e-learning system that can generate a recommenda-
tion list of appropriate learning objects based on the
learner’s learning style.
A learner can then use different learning strategies
which can contribute to increase the quality of learn-
ing objects by providing different notes, comments,
summaries, examples, ratings or reflections associ-
ated with the same learning object.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents the theoretical background of this paper by
defining and discussing the concepts of self-regulated
learning and learning styles. Section 3 presents the
proposed pedagogical framework for improving the
learning process in the collaborative e-learning sys-
tems based on the self-regulated learning and the
learning styles. Section 4 discusses some implications
of the proposed pedagogical framework on searching
and recommending of learning objects that are related
to different learning styles. Finally, section 5 presents
conclusions and proposals for future work.
2 THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
2.1 Self-Regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning (SRL), an educational ap-
proach influenced by the constructivism and social
views of learning, is an important area of research
in education and psychology. Self-regulated learning
can be defined as “ self-generated thoughts, feelings
and actions that are planned and cyclically adapted
to the attainment of personal goals” (Zimmerman,
2000).
Basically, self-regulated learning refers to the
ability of the learners to understand and control
their learning process and environment. To achieve
this, learners have to specify their goals, select and
use appropriate strategies, and monitor their learn-
ing progress towards achieving their goals (Schunk,
1996). Students with the ability to self-regulate their
learning can have high academic achievement with
less effort (Pintrich, 2000).
Despite the fact that there are a variety of
self-regulated learning models, these models are
all similar to Zimmerman’s Cyclical Model of
Self-Regulated Learning. Zimmerman (Zimmer-
man, 2000) developed a model that represents self-
regulated learning as a process of three cyclical
phases (Figure 1): (1) forethought, (2) performance,
and (3) self-reflection.
Figure 1: SRL Cyclical Model.
Forethought phase involves processes that oc-
cur before learning including goal settings, previous
knowledge activation and strategic planning. Goal
setting is the process of determining the outcomes of
the learning task. Strategic planning involves the se-
lection of strategies and resources required for per-
forming the task and time planning.
Performance phase involves processes that oc-
cur during learning. This includes cognitive learn-
ing strategies students use to deal with the learning
material. Rehearsal, elaboration, organizational and
critical thinking strategies are examples of cognitive
strategies that have been reported to have positive im-
pact on the academic performance of students (Pin-
trich and De Groot, 1990). Rehearsal strategies are
the basic methods used by the learner to keep the in-
formation in the working memory, and involve strate-
gies such as note taking and repeating the learning
material. Elaboration strategies are methods used by
the learner to keep the information in the long-term
memory, and involve methods such as summarizing,
paraphrasing, relating new information to the exist-
ing knowledge of the learner and using examples and
analogies. Organizational strategies are methods used
by learners to link the important ideas of the learn-
ing materials such as creating concept maps. Re-
hearsal strategies are example of surface level pro-
cessing strategies which focus on memorizing of facts
and information retrieval, while elaboration and orga-
nizational strategies are deep level processing strate-
gies which focus on understanding the relationship
between learning material (Zusho et al., 2003).
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
354

The performance phase involves also metacogni-
tive strategies the learners may use to monitor their
progress such as self-recording and self-questioning.
Self-recording is a technique used by learners to
record each learning activity and its results. Self-
questioning or testing is a strategy used by the learn-
ers to assess their understanding of the learning ma-
terial by performing a test to evaluate performance
against a predefined goal or standard. During this
phase, the learner can use resource management
strategies such as searching for suitable learning re-
sources and seek help from other learners in the learn-
ing environment.
The phase of self-reflection involves processes
that follow the learning task including the learners’
perceptions of their performance and experience with
the learning material.
The self-regulated learning phases are cyclical;
feedback from previous phase is used to adjust the
next phase (Zimmerman, 2000).
2.2 Learning Style
Learning is a process whereby individuals acquire
new knowledge. Research indicated that students tend
to gather and process information in different ways.
These differences are known as learning styles. Many
definitions can be found in the literature for the term
learning style. The learning style can be defined
as “a particular way in which an individual learns”
(Pritchard, 2009). Shaw and Marlow (Shaw and Mar-
low, 1999) describe the learning style as “a distinctive
and habitual manner of acquiring knowledge, skills
or attitudes through study or experience”. One of the
most comprehensive definition of the learning style is
the one provided by Keefe (Keefe, 1988) who defined
learning style as “ the characteristic cognitive, affec-
tive and psychological behaviors that serve as relativ-
ity stable indicators of how learners perceive, interact
with and respond to the learning environment”.
Learning styles can be identified using different
learning style models. Felder and Silverman (Felder
and Silverman, 1988; Felder and Spurlin, 2005) de-
veloped a model to identify students’ learning styles
especially in science and engineering education. This
model consists of four dimensions:
2.2.1 Sensing/Intuitive
This dimension describes the type of information an
individual preferentially perceives. Sensing learners
prefer concrete contents and facts and oriented toward
the details whereas intuitive learners prefer abstract
concept, theories and mathematical formulas and dis-
like details. Sensing learners tend to solve problems
using well-established methods and dislike complica-
tions. Intuitive learners like innovations, new ideas of
solving problems and dislike repetition.
2.2.2 Visual/Verbal
This dimension describes the channel through which
the learner most effectively perceives information.
Visual learners prefer learning through visual medium
such as pictures, charts and diagrams whereas verbal
learners prefer spoken or written materials and expla-
nations.
2.2.3 Active/Reflective
This dimension describes how the learner processes
information. Active learners prefer learning in groups
and they tend to try things out whereas reflective
learners prefer working alone and think about how
things work before try them.
2.2.4 Sequential/Global
This dimension describes how the learner progresses
towards understanding the information. Sequential
learners prefer following a logical, step by step linear
approach whereas global learners prefer absorbing the
learning materials randomly in big jumps without fol-
lowing step by step approach until grasping the full
picture.
3 PROPOSED PEDAGOGICAL
FRAMEWORK FOR
COLLABORATIVE
E-LEARNING SYSTEMS
The framework proposed in this paper is to en-
hance the educational effectiveness of the collabora-
tive learning environment based on the cyclical model
of self-regulated learning and learning style that are
well-grounded in the educational theories. The self-
regulated learning cyclical model (section 2.1) is ap-
plied to provide an alternative and effective design for
collaborative learning environment. The new peda-
gogical framework takes into consideration the learn-
ing styles of learners before involving in any learning
activity within the learning environment. The pro-
posed framework consists of the following compo-
nents (Figure 2):
PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LEARNING OBJECTS IN COLLABORATIVE
E-LEARNING SYSTEMS
355

Figure 2: Pedagogical Framework for Collaborative e-
Learning Systems.
3.1 Learning Styles Identification
This component is responsible for identifying learn-
ers’ learning styles based on Felder-Silverman learn-
ing style model. An instrument known as Index of
Learning Style (ILS) (Felder and Spurlin, 2005) can
be used to achieve that. Felder-Silverman model de-
scribes the learner’s preferences based on four di-
mensions: Sensing-Intuitive, Visual-Verbal, Active-
Reflective and Sequential-Global. Based on the re-
sult, a learner’s profile will be created to contain in-
formation about his/her learning styles. This module
is responsible for increasing learners’ awareness of
their learning styles by providing guidelines to help
them to better utilize the strengths of their learning
styles. Also, this can help the collaborative e-learning
system to recommend suitable learning objects for the
learners based on their learning styles. The following
are sample of the guidelines that can be given to the
learners based on their learning styles:
1. Sensing Learners:
• Find real world examples to link the content of
the learning object with the real word.
• Focus on the learning objects that contain facts
and procedures.
• Find learning objects that contain experiments
results.
2. Intuitive Learners:
• Read the summaries written by other learners.
• Find learning objects that contain innovative
ideas of applying the concepts.
• Find learning objects that use theories and
mathematical formulas.
3. Visual Learners:
• Focus on learning objects that use visualization
(e.g., pictures, diagrams, animations, etc.).
• Draw concept maps to link key points in the
learning objects.
4. Verbal Learners:
• Find descriptions for diagrams and other visual
learning material.
• Focus on learning objects that contains audio
learning resources.
• Write summary for the learning object in your
own words.
5. Active Learners:
• Find learning objects that contain simulations.
• Discuss the content of the leaning object with
other learners.
6. Reflective Learners:
• Read the comments and reflections written by
other learners about their experience using the
learning object.
• Think of possible questions or applications of
the content of the learning object.
7. Sequential Learners:
• Look at the outline of the content of the learn-
ing object.
• Use concept map to see how the key points in
the learning object linked to each others.
8. Global Learners:
• Take overview of the learning object before go-
ing into the details.
• Link the content of the learning object with
something you already know.
3.2 Collaborative Learning Cyclical
Process
This is the main component of the pedagogical frame-
work in which the learners participate in the learn-
ing process by interacting with learning objects. To
increase the educational effectiveness of the learn-
ing process, this paper applies the cyclical model of
self-regulated learning. The model consists of three
phases: forethought, performance and self-reflection
as described in section 2.1.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
356
3.2.1 Forethought (Planning and Activation)
Before engaging in learning activity, learner has to set
goals and plan for their time using tools that should
be provided by the e-learning environment. Choosing
suitable learning objects is very important task that
need to be done in this phase. This can be achieved by
the help of the information gathered from the interac-
tion of other learners with learning objects. Also, the
e-learning system can recommend suitable learning
objects based on the result of the learning style iden-
tification in the previous phase. After that, the learner
should assess their previous knowledge required to
understand the content of the learning object. To
achieve that, learning objects have to be associated
with extra information on the prerequisite knowledge
required before using the learning objects.
3.2.2 Performance (Action)
In this phase, the learner starts the learning task by
using different cognitive and metacognitive learning
strategies as discussed in section 2.1. The learner can
perform a number of actions on the learning object:
• Note taking and commenting.
• Paraphrasing and summarizing.
• Providing real world examples of applying the
concept.
• Outlining and creating concepts maps for the con-
tent of the learning object.
• Rating and tagging the learning object.
In this phase, learners also use metacognitive strate-
gies such as self-testing to check their understanding
of the concepts covered by the learning object. This
can be achieved by providing assessment questions
associated with the learning object.
3.2.3 Reflection Phase
This phase involves the processes that occur after
completing the learning task. In the proposed frame-
work, the e-learning system should allow learners
to write reflections on their experience in using the
learning objects and whether the learning goals have
been achieved or not. Learners’ reflections on their
experience of using the learning object will be associ-
ated with the learning object and can help other learn-
ers to choose suitable learning objects and plan for
their learning process.
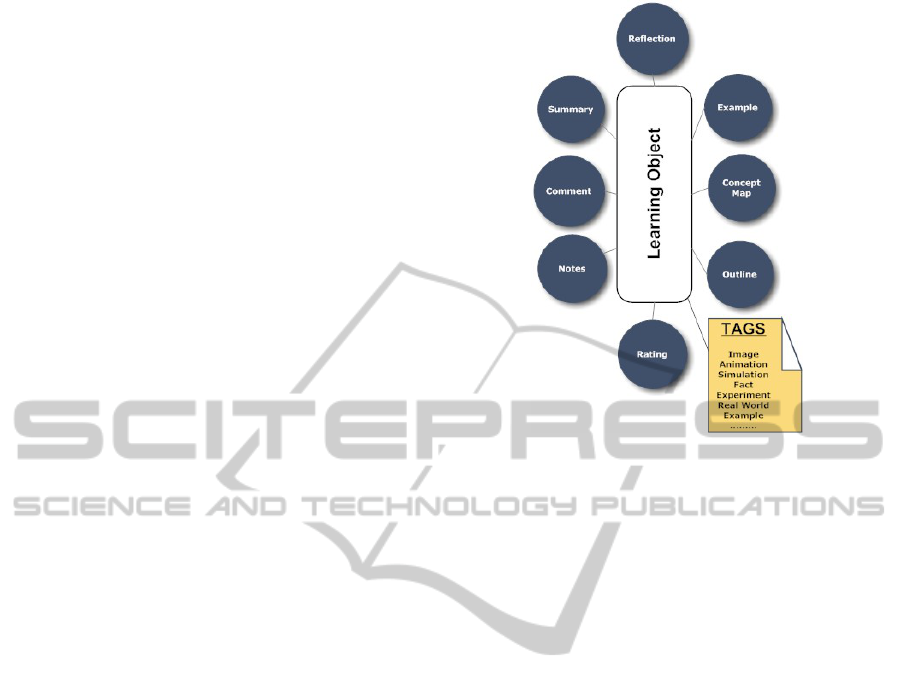
Figure 3: Extension of the Learning Object.
4 IMPLICATIONS OF THE
PROPOSED FRAMEWORK:
SEARCHING AND
RECOMMENDING OF
SUITABLE LEARNING
OBJECTS
In the proposed framework, learners follow cyclical
model to consume the knowledge provided by the
learning objects in the collaborative e-learning sys-
tem. According to this, learners with different learn-
ing styles interact with the learning objects by follow-
ing a number of strategies which will result in pro-
viding different notes, comments, summaries, exam-
ples, ratings and reflections associated with the same
learning object and generated by learners with differ-
ent learning styles (Figure 3). In this case, the learner
is not only a consumer of the knowledge but also a
producer. This can increase the quality of the learn-
ing objects to be compatible with different learning
styles.
Searching and recommending of learning objects
can be improved as a result of applying the proposed
framework. The experience of a learner in using spe-
cific learning objects can help other learners to find
suitable learning objects for them based on the collab-
orative comments, ratings and reflections provided by
learners with different learning styles. Also, appro-
priate tags can be used to index the learning objects
to match different learning styles. For examples, for
PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LEARNING OBJECTS IN COLLABORATIVE
E-LEARNING SYSTEMS
357

sensing learners, appropriate tags can be fact, experi-
ment, real world example, while for intuitive learners,
the tags can be innovative idea, mathematical formula
and theory. For Visual learners, the appropriate tags
can be image, diagram, and simulation while for ver-
bal learners, explanation and audio. For sequential
learners, appropriate tags such as outline can be used
while for global learner, overview is one of the sug-
gested tags that can be used. Recommendation sys-
tems can be integrated to the collaborative e-learning
environment to provide learners with suitable learning
objects based on their learning styles and the interac-
tion of other learners with learning objects.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presented a pedagogical framework based
on the learning styles and the self-regulated learn-
ing to improve the quality of the learning objects in
collaborative e-learning systems.The proposed frame-
work can also help learners to find suitable learning
objects compatible with their learning styles. This
work will continue by conducting empirical studies
involving students using a collaborative e-learning
system based on the proposed pedagogical frame-
work. These empirical studies will help to evaluate
the educational effectiveness of the proposed frame-
work.
REFERENCES
Bandura, A. (2001). Social cognitive theory: an agentic
perspective. Annual review of psychology, 52:1.
Felder, R. and Silverman, L. (1988). Learning and teaching
styles in engineering education. Engineering educa-
tion, 78(7):674–681.
Felder, R. and Spurlin, J. (2005). Applications, reliability
and validity of the index of learning styles. Interna-
tional Journal of Engineering Education, 21(1):103–
112.
Glasersfeld, E. (2009). Amplification of a Constructivist
Perspective. Issues in Education, 3(2):203–209.
Han, K., Kumar, V., and Nesbit, J. (2003). Rating learning
object quality with bayesian belief networks. In World
Conference on E-Learning in Corp., Govt., Health., &
Higher, volume 1, pages 1598–1601.
Keefe, J. (1988). Profiling and Utilizing Learning Style.
NASSP Learning Style Series. Publication Sales, Na-
tional Association of Secondary School Principals,
1904 Association Drive, Reston, VA.
Koohang, A. (2004). Creating learning objects in collabora-
tive e-learning settings. Issues in Information Systems,
4(2):584–590.
McLoughlin, C. and Lee, M. (2010). Personalised and self
regulated learning in the Web 2.0 era: International
exemplars of innovative pedagogy using social soft-
ware. Australasian Journal of Educational Technol-
ogy, 26(1):28–43.
Pintrich, P. (2000). Multiple goals, multiple pathways: The
role of goal orientation in learning and achievement.
Journal of Educational Psychology, 92(3):544.
Pintrich, P. and De Groot, E. (1990). Motivational and
self-regulated learning components of classroom aca-
demic performance. Journal of educational psychol-
ogy, 82(1):33–40.
Pritchard, A. (2009). Ways of learning: learning theories
and learning styles in the classroom. David Fulton
Publish.
Pritchard, A. and Woollard, J. (2010). Psychology for the
classroom: Constructivism and social learning. Psy-
chology for the Classroom.
Schunk, D. (1996). Goal and self-evaluative influences dur-
ing children’s cognitive skill learning. American Edu-
cational Research Journal, pages 359–382.
Shaw, G. and Marlow, N. (1999). The role of student learn-
ing styles, gender, attitudes and perceptions on infor-
mation and communication technology assisted learn-
ing. Computers & Education, 33(4):223–234.
Shishehchi, S., Banihashem, S., and Zin, N. (2010). A
proposed semantic recommendation system for e-
learning: A rule and ontology based e-learning rec-
ommendation system. In Information Technology (IT-
Sim), 2010 International Symposium in, volume 1,
pages 1–5. IEEE.
Sosteric, M. and Hesemeier, S. (2002). When is a Learn-
ing Object not an Object: A first step towards a theory
of learning objects. The International Review of Re-
search in Open and Distance Learning, 3(2).
Wang, J., Sun, Y., Fan, Z., and Liu, Y. (2005). A collabora-
tive E-learning system based on multi-agent. Internet
and Network Economics, pages 455–463.
Zimmerman, B. (2000). Attaining self-regulation: A social
cognitive perspective. Handbook of self-regulation,
13:39.
Zusho, A., Pintrich, P., and Coppola, B. (2003). Skill and
will: the role of motivation and cognition in the learn-
ing of college chemistry. International Journal of Sci-
ence Education, 25(9):1081–1094.
CSEDU 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
358
